1.4: Proteins
1/10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
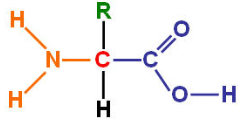
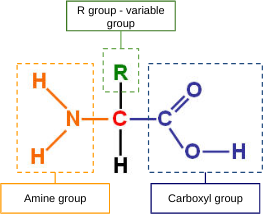
Label the orange, green, and blue parts of this diagram
Write the wird equation for the formation of a dipeptide.
Peptide 1 + peptide 2 → dipeptide + water
Describe the process of dipeptide formation (4 marks)
A condensation reaction (1 mark) between two amino acids (1 mark)
Forms a peptide bond (1 mark) between amino acids
Water is formed as a byproduct (1 mark)
Describe the opposite reaction (4 marks)
Hydrolysing (1 mark) a dipeptide would involve the addition of water (1 mark)
The peptide bond would be broken (1 mark)
Two amino acids would be produced (1 mark)
What kind of reaction form a polypeptide?
Condensation polymerisation
What are proteins?
Proteins are polypeptide chains that have folded up into a specific 3D shape
What are the two shapes a protein can be?
Globular (metabolic finctions, e.g enzymes, receptor molecules, and transport proteins in plasma membranes)
Fibrous (structural, e.g keratin in our hair and collagen in connective tissue)
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (different for each protein)
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
Either alpha helix of beta pleated sheet (only alpha helix on AQA spec)
Maintained by hydrogen bonds (between N-H and C=O groups on different amino acids in a polypeptide chain)
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
A specific 3D shape (different for each protein)
Maintained by bonds between R groups - including:
Hydrogen bonds (weak)
Ionic bonds
Disulphide bridges/bonds (covalent bonds)
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
Several polypeptides
Maintained by bonds between polypeptides
Lots of hydrogen bonds (weak)
Ionic bonds
Disulphide bridges
May be non-protein (prosthetic) groups. E.g haem groups in haemoglobin