FRST 210 lecture 14- SExual reproduction II
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Where does the megasporangia and microsporangia arise in the flower?
Megasporangia=ovary
Microsporangia=Anther
Meiosis and pollen development in angiosperms
Inside each microsporangium (pollen sac) within an anther, there are many microspore mother cells
Tapetum
Nutritive tissue that nourishes the developing microgametophytes
How many microspores does one microspore mother create?
Microspore via mitosis
Each microspore develops into a microgametophyte (pollen grain)
Mitosis creates a generative cell and tube cell (vegetative cell) within the pollen grain
How many celled pollen grains are in a mature microgametophyte?
2
What does the pistil include?
Stigma, style, and ovary
The ovary bears ovules (whichcontain a megasporangium and eventually the megagametophyte)
How many ovules does a single megaspore mother cell within an megasporangium (embryo sac) have?
One, this cell undergoes meiosis!
How does megagametophyte development in angiosperms work?
A megaspore mother produces forur megaspores via meiosis
→ Only one megaspore develops into a megagametophyte
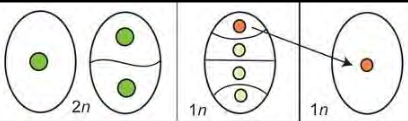
Second step of megagametophyte development in angiosperms:
The functional megaspore divides (three times) via mitosis creating 8 nuclei
Each nucleus is moved to a particular position to form the cells of the megagametophyte
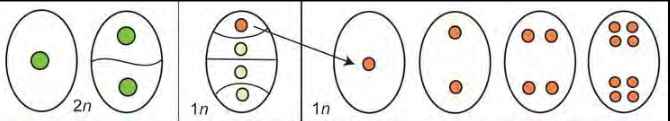
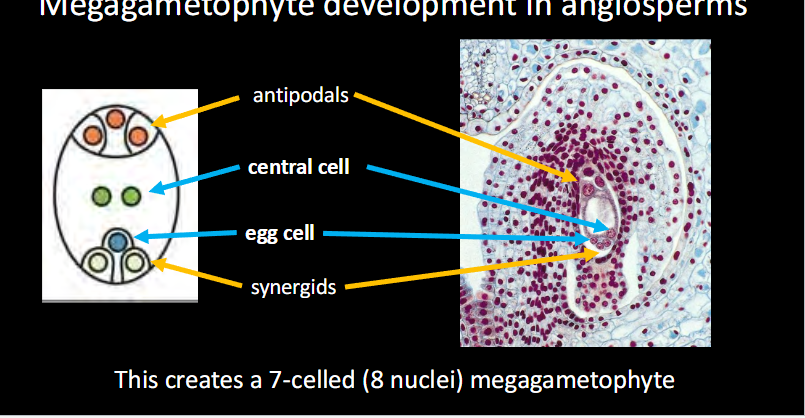
Third step of megagametophyte development in angiosperms:
Near the micropyle, one nucleus becomes the egg( and two become synergids)
The opposite end forms three antipodal cells
The central cell has two “polar nuclei” (→ Cell is diploid)
These processes create a 7-celled (8n nuclei) megagametophyte
Advantages of animal pollination
Will happen frequently if species are healthy, animals often come back to flowers and carry and disperse pollen around them
Animals can dleiver pollen more directly to the stigma of a flower
Animal pollination can facilitate cross-pollination between differen t plants, allowing better genetic diversity
Disadvantages of animal pollination
In times where animal species may be endangered less flowers are likely to be pollinated, so dependence on pollinators is not perfect
Changes in resource availability, habitat, and climate can disrupt pollinator-plant interactions, leading to reduced pollination success
How does the microgametophyte fertilize the macrogametophyte?
Generative cell divides to create two sperm in microgametophyte→: only one sperm will fertilize the egg to create a zygote (2n)
The other sperm fuses with polar nuclei to create a triploid cell (3n)
This process is called double fertilization, creating a zygote
Endosperm
Triploid, nutritive tissue created from double fertilization as the other sperm fused with polar nuclei
Fruits
Seeds develop inside ovaries, and ovaries ripen into fruit (protection to seeds)
What are the ploidy for developing seeds? For endosperm?
Developing seeds have a diploid embryo, with triploid endosperm as nutritive tissue
T/F species develop either pollen or ovules in each flower
T
T/F Do many species produce both micro and megagametophytes (pollen and ovules) within the same flower?
True, this is called homospory.