Peds 27&28
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Kids born with heart problems, we will often see…
small (FTT)
developmental delays
sweaty (harder working heart)
activity intolerance
developmental delays
tachypnea
tachycardia
pale/cyanotic
fluid retention (legs)
cold hands/feet
Kid with heart issues comes into clinic we will do all ____ ____
vital signs (full minute APICAL)
temp (infection)
pulses (weaker pulses in feet as from from heart)
Always look at difference between ____ and _____ ______ in these kids
upper and lower extremities (color, temp, pulses)
Diagnostic testing for heart issues
Chest x-ray (size of heart)
ECG (rhythm)
Echocardiogram (EF, blood flow)
Cardiac catheterization (Dx or treatment)
Need to be ____ before cardiac cath.
NPO as they will have sedation
When any child comes back from cardiac cath procedure what is the most important thing we do?
Monitor Airway
then vitals (full set)
Apical pulse (one minute) (lung sounds as well)
Insertion site (there will be a pressure dressing)
Pain scale!!
I&O
With an arterial cath they have to keep extremity straight for _______. If it is venous it is _____.
6-8 hours
4-6 hours
How to get kid to keep extremity straight?
Pressure bags
Have parent’s hold it or swaddle
First sign of bleeding on dressing
Shadow (put a circle around it) (do the same thing for pulse site)
If site is bleeding where do we hold pressure?
1 inch above site
call provider
Sometimes the affected leg (the one that had the incision) will have…
a weaker pulse initially (cooler/pale extremity)
It is not normal for them both to be strong/equal initially and then weaken later.
For infants after cardiac cath we check…
blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
they haven’t eaten for a long time and they are little (NPO)
#1 complications from cardiac cath
bleeding
clot
Important to educate parent’s of cardiac cath kids on…
s/s of infection
Most common congenital heart disease
ventricular septal defect (VSD)
two types of cardiac defects
Congenital (5-8/1,000 births)
Acquired (infection, autoimmune)
Causes of CHD
Multifactorial-85%
Genetic-10/12%
Maternal (drugs/illness) or environmental-1-2%
28% of kids with CHD have another issue like down syndrome
CHD associated with down syndrome
VSD
CHD causes 1 of 2 things
HF
Hypoxemia
Heart failure is
Heart not effectively pumping
Decreased contractility and volume overload
HF s/s
Tachycardia; fatigue; weakness; restlessness; pale, cool extremities; decreased BP; decreased urine output
Hypoxemia/pulmonary congestion s/s
Tachypnea, dyspnea, respiratory distress, exercise intolerance, cyanosis, fatigue, pale
Systemic venous congestion (more HF but also hypoxemia) s/s
Peripheral and periorbital edema, weight gain, ascites, hepatomegaly, neck vein distention
Hypoxic kids position and medication
Knee to chest position (blood gets to legs faster)
Oxygen

Medications to improve cardiac function
Digoxin (will lower HR as it creates stronger better contractions)
ace inhibitors (vasodilator and decrease heart workload, PRIL)
Decrease preload with what medication?
Diuretics (rid fluids)
How can we decrease cardiac demand/O2 consumption in these kids
rest and conserve energy for feeding and breathing
Defect is a ____ and stenosis is a ____
hole
narrowing
Kids with heart defects will often have a ____
murmur
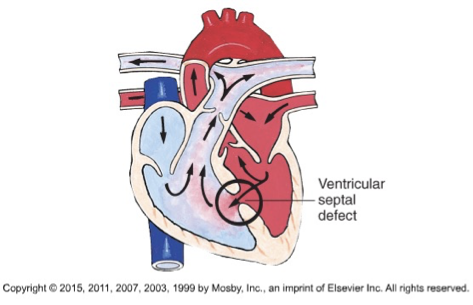
VSD is
a hole in ventricular septum and heart is tipped slightly to right
Blood will flow from left to right due to gravity
right atrium will get way bigger than it should—> HF
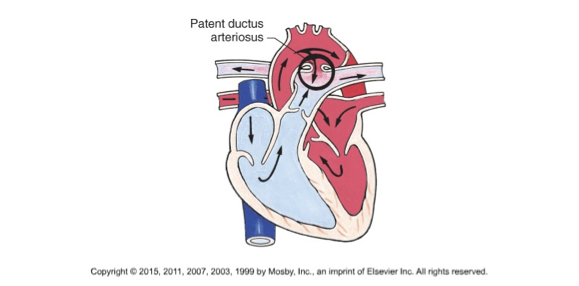
PDA is
a normal fetal artery connecting the main body artery (aorta) and the main lung artery (pulmonary artery) to direct blood away from lungs
should close by 15 hours after birth
VSD s/s
Murmur and symptoms of HF
VSD treatment
Cardiac that repair (patch)
Open heart surgery if hole is big
PDA s/s
Machinery murmur/ HF s/s
PDA treatment
Cardiac cath (coil insertion)
Aortic stenosis (HF)
Aortic valve narrowing
blood black flow will be before the stenosis (left ventricle will be weaker)
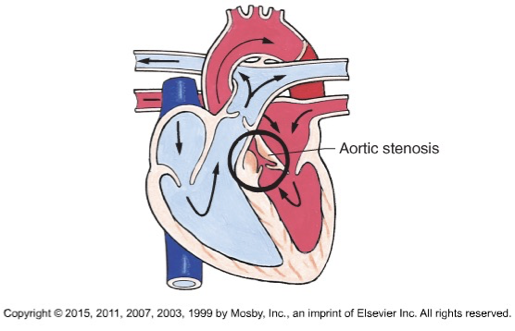
Aortic stenosis treatmemt
cardiac cath (balloon angioplasty)
Tetralogy of Fallot (hypoxemia) drug and position
O2
Knees to chest
Tetralogy of Fallot (hypoxemia) treatment
staged repair
treat one and then give them time to heal
what is a tet spell
not enough oxygen and they will turn BLUE
Open heart surgery
heart is stopped and pt. is on echmo
Closed heart procedure
heart is still beating
Post op open heart surgery things
Airway
full vital signs
Heart/lung sounds
Incision
Pain
I&O!!!!
Activity progression
abnormal chest tube output
more than 3ml/kg/hr for 3 hours or more than 5-10ml/kg in one hour
I&O is super important for heart surgery espically on kids. this includes
flushes, IV, oral, NG
Drawing blood, urine, stool, NG
with UOP we need at least
1mg/kg/hr
complications post op heart surgery
CHF (fluid overload)
dysrthmia
electrolyte imbalance
bleeding
atelectasis
Neuro changes (poor blood flow to brain)
Infection
Post op open heart surgery we monitor
pulses
cap refil
color
warmth
Teach parent’s to give _____ at same time every day
digoxin
do not give if we miss dose or throwup
Digoxin checks before we give it? Levels?
HR
infants-90
children-70
adults-60
Digoxin toxicity s/s
vomiting, neuro signs, visual disturbances, bradycardia, anorexia
Why give aspirin in a kid that just had heart surgery
platelet aggregator/blood thinner
All open heart surgeries get
prophylactic abx
Endocarditis is
infection of valves and endocardium
Endocarditis s/s
temp
ekg changes
new murmur
super tired
large spleen
osler nodes
janeway lesions
Endocarditis needs what for treatment and dx?
IV abx for 2-8 weeks
Blood culture and echocardiogram for dx
If abx doesn’t work with Endocarditis they have to…
replace valves
People with open heart surgery will always get….
prophylactic abx before or after dental procedures or surgeries
RF is…. and is caused by….
inflammatory disease that affects heart valves (immune response 2-6 weeks after infection)
Strep
RF s/s
polyarthritis
Erythema marginatum (Rash on trunk and extremities, not itchy)
Chorea (jerky movements)
Nodules on hands
Worse with anxiety
Testing for RF
throat culture
ASLO titer
CRP/ESR
RF treatment
penicillin IMx1 or oral x10 days
Most common hematologic disorder in childhood
Anemia
What is anemia
decrease in RBC and/or HGB below normal levels or decreased o2 carrying capacity of blood
2 causes of anemia
rbc and/or hgb depletion
or something in the body is changing RBC size, shape, and/or color
When anemia develops slowly the child can ____
adapt
s/s of anemia
dizzy
light-headed
slowed-thought process
poor concentration/memory
headache
no energy
muscle weakness
growth retardation
pale
Diagnostics for anemia
CBC (RBC, HGB, HCT)
Iron (TIBC)
Bone marrow aspiration
Physical exam
HGB below 10-11 shows anemia in kids
Management of anemia
treat underlying cause (bleeding)
blood transfusion (if hemorrhage)
diet
IV fluids
Oxygen
Bed rest
Kids with anemia are more at risk for ____ _____ and _____
Cardiac decompensation
Infection (wear mask, keep them away from sick people)
With blood transfusion blood must be started within ____ minutes
30 minutes (increases energy)
Infuse blood over maximum of ____ hours
4
Always monitor pt. with blood transfusion as ____ ____ is the most common cause of death from blood transfusion
ABO incompatibility
also allergic reaction, febrile reaction
We transfuse blood very slowly the first ______
15-20 minutes
Nurses role in blood transfusions
monitor patient
take vitals
stay with patient for first 20 minutes
s/s of transfusion reaction and what to do
tachycardia, fever, back pain, chills
stop infusion, notify provider
Iron deficiency anemia
caused by inadequate dietary supply of iron
Most common nutritional deficiency worldwide
Iron deficiency anemia risks factors
prematurity
excessive intake of milk (poor source of iron)
Mom had this so baby has it
Malabsorption issue
rapid growth
poor diet
Iron deficiency anemia treatment
Iron fortified foods
breastfeeding mom takes supplements
Iron supplement (liquid for kids but can stain teeth, give through straw) 1 hour before or 2 hours after milk (best on empty stomach)
Give with vitamin c
kids with iron deficiency can be
underweight or overweight
Iron deficiency anemia diagnosis
CBC
TIBC (total iron binding capacity)
Patient education on iron
green tarry stools
gi upset (diarrhea, nausea, constipation)
Improve diet (green leafy vegetables, red meats)
Sickle cell anemia is _____
genetic, almost exclusively in African Americans
Sickle cell crisis is caused by an _____. Severity is determined by
obstruction
location (brain, heart, lungs)—> stroke, heart issues.
There is no cure for sickle cell but we can try to prevent sickling episodes through ____ ____
supportive care
Sickle cell diagnosis
genetic testing at birth (Stained blood smear)
Sickle cell crisis causes
demands leading to more oxygen need
car accident
sick
infection
stress
airplanes
dehydration
s/s if sickle crisis is in elbow
engorgment at elbow
weak distal pulse
cool extremity
pale extremity
poor cap refill
S/S of sickle cell crisis
Fever
extreme pain
tissue engorement
In general what do we need to watch for/do in kids with sickle cell anemia
FTT
growth rates
minimize things that can cause stress and sickness
get all immunizations (live, yearly)
keep them hydrated
top interventions for sickle cell crisis
fluids (IV/Oral)
O2
treat pain (NSAIDs or narcotics)
rest
monitor I&O
blood transfusion
Shock s/s
Can treat sickle cell crisis with _____.
warmth, no cold
ROM
gentle massage
Sickle cell supportive care can be a medication called
hydroxyurea (keeps RBC round)
Usually kids get HIV/AIDS from
infected mother
older kids: high risk behaviors (unprotected sex, sharing dirty needles)
HIV is…
immune system disorder
affects t-cells
s/s of HIV in kids
large lymph nodes
large spleen
sick looking
FTT
developmental delays
reoccurring mouth infections
HIV diagnosis
Blood test
AIDS defining conditions in kids
pneumonia
bacterial infection
wasting syndrome
Candidal esophagitis
Goal of HIV
prevent growth of virus and prevent infections
Diet and protection for HIV kids
high protein, high calorie
wear mask in public
avoid sick people