Simple Epithelium and their Pathologies (histology)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
simple squamous
apical surface is smooth
width greater than height
flattened nucleus
rest on the basement membrane
ex: cornea and blood vessels (endothelium), air sacs of lungs
simple cuboidal
apical surfaces may have brush borders
width is equal to height is equal to depth
central and spherical nucleus
rest on the basement membrane
ex: kidneys
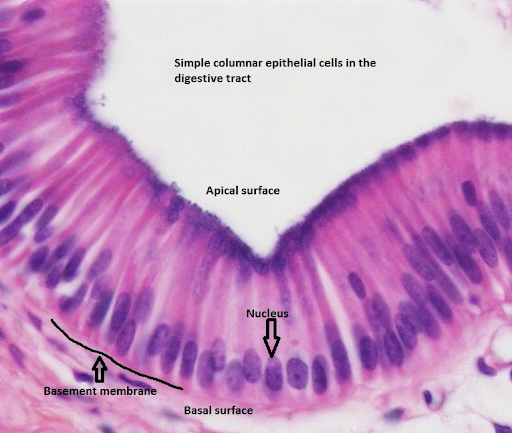
simple columnar
apical surface may have brush border
height is greater than width
elongated ovoid nucleus on the basal region of the cell
rest on the basement membrane
ex: digestive tract and fallopian tubes
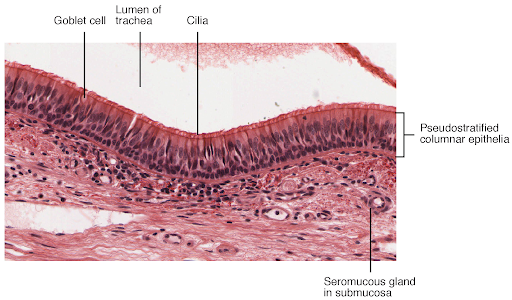
pseudostratified columnar
appears layered but is actually only one layer on the basement membrane
nonuniform cells
columnar and basal cells
usually ciliated
ex: respiratory tract
keratin
dead cells on the epithelium with no nucleus (not always on top of alive cells)
junctions
epithelial cells rest on the basement membrane to which they are anchored via __________ called hemidesmosomes
cilia
elongated, motile structures that transport material
microvilli
smaller than cilia, composed of actin filaments, help with absorption
sterocilia
long microcilia, also made of actin filaments
functions of the epithelium
-protects the body from injury
-absorption of material
-transportation of material along a surface
-secretion of mucus, hormones, and proteins
-gas exchange (in lungs)
-lubrication between surfaces
classify epithelial tissue by
-their number of layers
-their shape (the name of the superficial layer/transitional)
epithelium
type of body tissue that covers all internal an external surfaces of the body, lines the body cavities and hollow organs and is the major tissue in glands
-continuously removed by mitosis
avascu
apical domain
free surface that is exposed to the luminal fluid
may have projections
lateral domain
orients perpendicularly to the apical and basal membranes and is frequently referred to
types of junctions
tight
adherens
desmosomes
gap
hemidesmosomes
basal domain
attached to an extracellular matrix that supports the epithelial tissue mesothelium
mesothelium
epithelial layer of serous membranes that lines the body cavities and covers the organs that project into the cavities
simple squamous epithelial tissue
2 layers- parietal and visceral (cover different things)
parietal layer of mesothelium
face the cavities of the body
serosal/visceral layer of mesothelium
covers the organs
function of mesothelium
lubrication- prevents organs from touching, protects organs
mesothelial cells
-flattened
-pentagonal shape
-form irregular borders with one another
-basically simple squamous
effusion
excessive fluid in a mesothelial lined cavity
in lungs- pleural ______
in perricardium (heart)- pericardisis
in the peritoneum (digestive tract)- peritonitis
mesothelioma
cancer of the mesothelium (like a tumor)
ex: in lungs, testes, heart, abdomen linings
characteristics of cancer cells
long, slender, and curved microvilli
may invade nearby tissues and organs
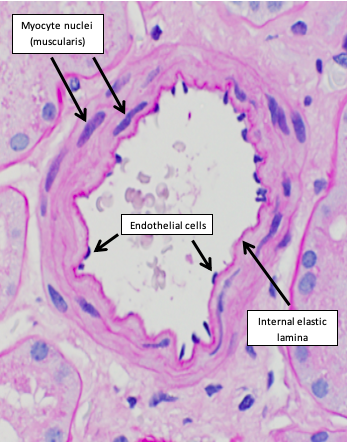
endothelium
simple squamous epithelium lining the lumen surface of all types of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels (also called vascular __________)
plays a role in the circulatory system
endothelial cells
flattened and elongated
face parallel to the direction of blood flow
rest on the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes
circulatory system- endothelium
knows when there are changes in blood pressure, oxygen tension, and blood flow (responds by secreting substances that effect the tone of vascular smooth muscle)
controls blood coagulation by producing ron Willebrand factor (controls platelet adhesion to collagen in connective tissue at injury site and prevents bleeding)
produces anticoagulant substances that stop blood clotting and allows blood to freely flow in normal conditions
tunica intima
1st layer- endothelial cells
2nd layer- basement membrane
3rd layer-subendothelial connective tissue
4th layer- internal elastic lamina (wavy)
artherosclerosis
formation of deposits of yellowish plaques that contain cholesterol, lipoid material, and lipophages (macrophages)
forms the innermost layers of large and medium sized arteries
common causes: endothelial dysfunction, dyslipidemia, inflammatory and immunological factors, hypertension
cholesterol, fatty, walls, clots, stroke
deposits of _________ and __________ material accumulate in the inner layers of a blood vessel resulting in damage to the vessel ____ (disruption of the endothelium)
when cholesterol hardens, it may occlude blood flow to distant tissues and blood _____ may form
clot formation/dislodged pieces of plaque may result in vascular occlusion and __________
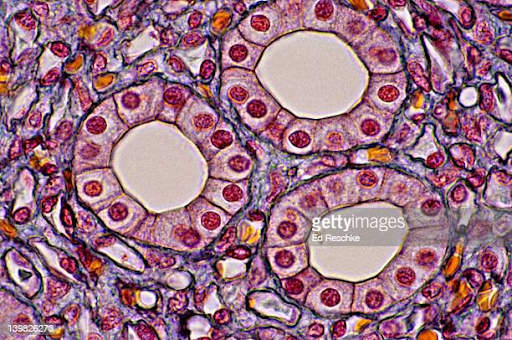
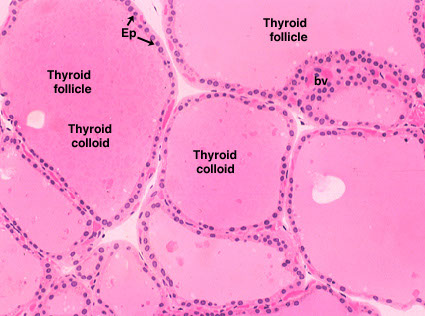
follicular cells
simple cuboidal cells that line the thyroid follicles of the thyroid gland
-adjacent follicles are separated by a thin layer of connective tissue
-colloids
colloid
fluid that contains hormones
hyperthyroidism
excessively high levels of thyroid hormone secretion
-lifelong
-goiter may appear (large bump on throat)
-the follicular cuboidal cells may become columnar cells when stimulated or in a state of hyperfunction
hypothyroidism
excessively low levels of thyroid hormone secretion
-the follicular squamous cells may become flattened and cells when stimulated or in a state of hyperfunction
kidneys
bowman’s capsule
glomerulus
distal convoluted tubule
prox
simple cuboidal epithelium
the appearance of this epithelium varies in different segment of the unniferous tubules
proximal tubules
the cuboidal cells have pink-stained cytoplasm and display numerous long microvilli on the apical surface
-microvilli generally fill the lumen
-pink stain due to acidophillia from numerous mitochondira that provide ATP—> necessary to power the ion pumps in the basolateral membranes of the cells
distal tubules
the cuboidal cells have short and scanty microvilli
-display less acidophillia than the proximal tubules
absorption, secretion
microvilli indicate _______ and _________ functions
substances reabsorbed in the proximal tubules
-water
-sodium
-chloride
-proteins
-glucose in the glomer
renal faconi syndrome
an impariment of proximal tubular function in the kidney resulting from an abnormality in the epithelial lining
causes: genetic defects (mostly in children) and by certain environmental factors
-rickets in children or osteromalacia in adults
some substances that should be reabsorbed into the bloodstream are instead excreted into the urine (may lead to failure to thrive in children and decreased bone mineralization)
histological features of renal faconi syndrome
-epithelial cells become squamous rather than cuboidal
-nuclei are distorted
-the basement membrane becomes wrinkled and thickened
-microvilli are reduced in number and length
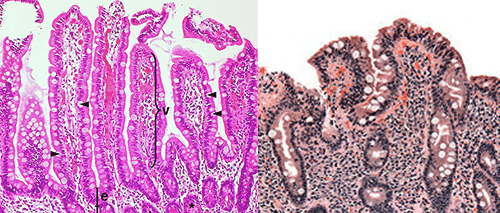
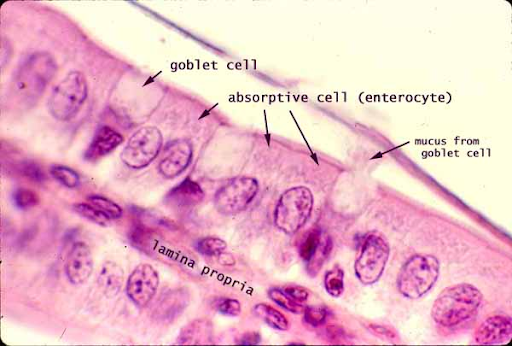
simple columnar epithelium
typical of the lining of the digestive tract
apical surface has a brush border (microvilli)
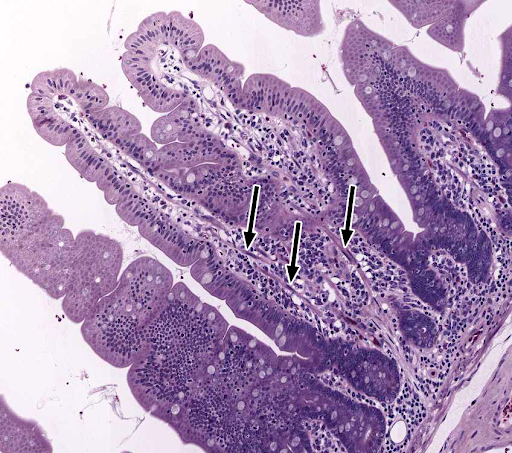
goblet cells
cells with seemingly empty cytoplasm
-mucus secreting cells interspersed among the simple columnar absorptive cells (enterocytes)
celiac disease
villi flattened, damaged, or not present
disorder of the small intestine
gluten reacts with the lining of the small intestine, leading to an attack by the immune system and damage to the microvilli and villi
-if left untreated, can lead to malabsorption, anemia, bone disease, and rarely, cancer
treatment: avoid eating food with gluten
histological features: villous atrophy, inflammatory cells