Blood Physiology Lecture 1 (Blood & RBCs)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is a liquid connective tissue composed of different cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets) dissolved in plasma. Also contains gases, waste products, nutrients, and hormones?
Blood
Blood is found in:
The circulatory system, in the blood vessels
Blood is heavier or more viscous than:
Water
What are the functions of blood?
Transport of substances in blood, regulation of ion and pH balance, defense and immune protection, homeostasis or the prevention of blood loss
Whole blood may be separated by:
Centrifugation
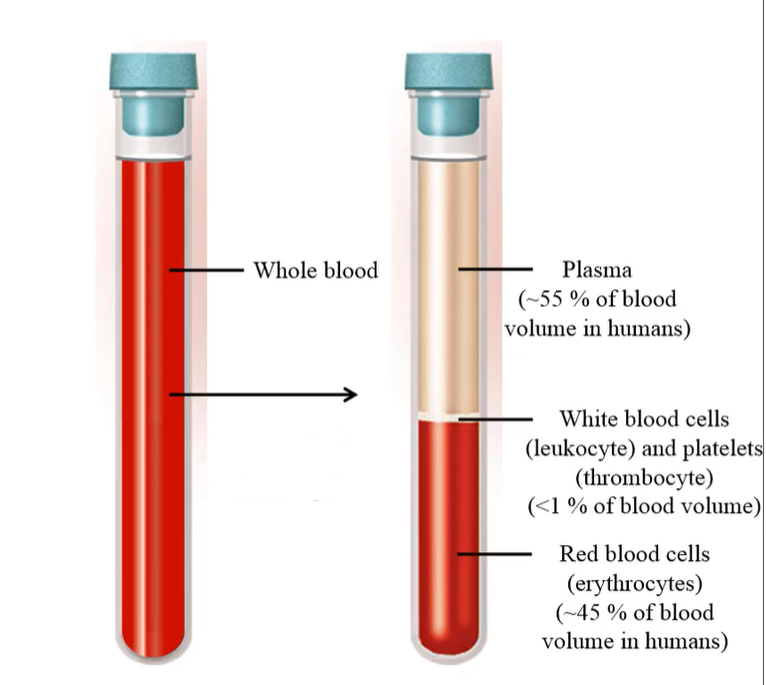

The upper layer in the centrifuged test tube is:
plasma
How much does plasma make up in blood volume?
~55%

The middle layer of centrifuged blood is called:
buffy coat; contains white blood cells and platelets
How much of the buffy coat (WBC and platelets) make up the blood volume?
<1%

The bottom layer of the centrifuged blood is:
red blood cells
How much of total blood volume does red blood cells make up?
~45%
% of total blood volume occupied by packed red blood cells is called: (calculated by volume of RBC / total volume)
Hematocrit
Hematocrit for a healthy female is:
42% (+ or - 5%)
Hematocrit for a healthy male is:
47% (+ or - 5%)
Low % hematocrit indicates:
Anemia (low oxygen due to low RBC)
High % hematocrit indicates:
polycythemia
Intracellular fluid is:
Fluid inside cells
Extracellular fluid is:
Fluid outside cells
What components does extracellular fluid include?
Plasma and interstitial fluid
Plasma is the:
liquid portion of blood containing water, electrolytes, organic molecules, trace elements, gases
Substances transported by blood include:
gases: oxygen and carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste products and hormones
What are the classes of plasma protein?
4: Albumins, globulins, fibrinogen, transferrin
What is the function of albumins?
contribute to colloid osmotic pressure of plasma, carry/transport substances in plasma
What function as clotting factors, enzymes, antibodies, carriers for various substances in plasma?
Globulins
What forms fibrinogen threads for blood clotting?
Fibrinogen
What functions to transport iron?
Transferrin
What is Serum?
Fraction of plasma where fibrinogen & all other clotting factors are removed
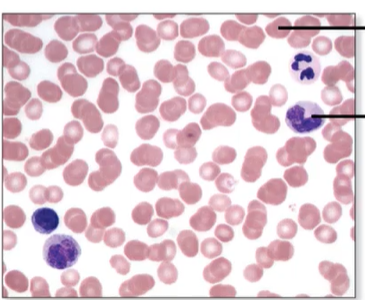
What are the types of blood cells?
Red (erythrocytes), White (leukocytes), platelets (thrombocytes)
Numbers of blood cells are measured in
microliters of blood (1 μl = 10-6 L)
What is the function of red blood cells?
transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide
What is the normal blood cell count of RBC/erythrocytes for females?
4.2 to 5.4×106μl
What is the normal blood cell count of RBC/erythrocytes for males?
4.7 to 6.1×106μl
What is the normal blood cell count of WBC/leukocytes?
4.5 to 10×103μl
What is the normal blood cell count for platelets/thrombocytes?
1.5 to 4×105μl
Polymorphonuclear granulocyte white blood cells are classified according to:
staining characteristics of cytoplasmic granules and structure of the nuclear lobes
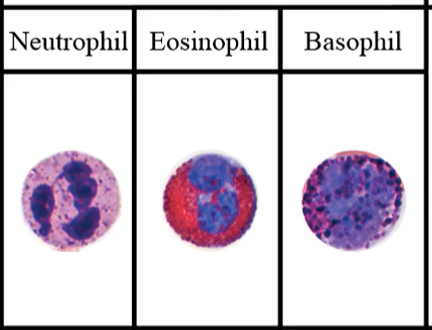
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are:
Polymorphonuclear granulocyte white blood cells
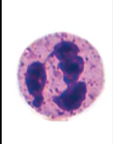
What is the function of neutrophils?
phagocytes (cell eating)
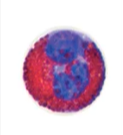
What is the function of Eosinophils?
Defense against parasites

What is the function of Basophils?
inflammation response
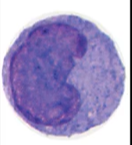
What are the function(s) of monocytes?
phagocytes and immune defense; leave the blood stream and are transformed into tissue macrophages
What are the types of lymphocytes?
B-cell, T-cell
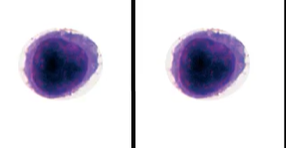
What do B-cells function as?
antibody production and humoral (body fluid) immunity
What is humoral immunity?
Immunity mediated by macromolecules found in extracellular fluids, such as antibodies, complement proteins, antimicrobial peptides. Involves substances found in the humors/body fluids.
What is the function of T-cell?
cellular immunity
What is cellular immunity?
Immune process that involves the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and release of various cytokines in response to an antigen.
What are cytokines?
small chemical messenger proteins in the immune system
What is the process of blood cell formation?
Hematopoiesis
Where does hematopoiesis occur before birth?
Yolk sac, liver, spleen
Where does hematopoiesis occur after birth?
Bone marrow
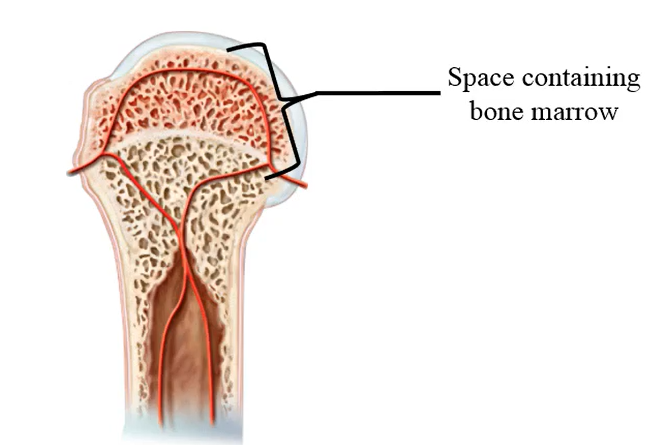
In hematopoiesis all blood sells originate from a:
pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell
What is a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell?
an undifferentiated cell capable of giving rise to any type of blood cell
What regulates hematopoiesis?
Cytokines
Cytokines are like what?
Hormones, as they are released into blood and act on receptors on target cells
Cytokines are also called:
Hematopoietins, or growth factors that influence development of blood cells
What regulates production of RBCs?
Erythropoietin
What regulates production of platelets?
Thrombopoietin
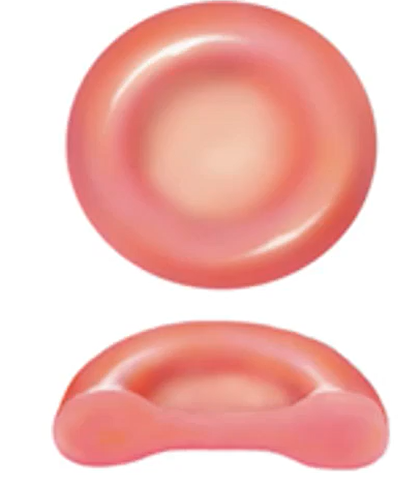

What shape is RBCs?
Biconcave
What is the function of RBCs?
transport of oxygen (and carbon dioxide)
RBCs lose what during development?
nucleus and other organelles
RBCs contain many:
hemoglobin molecules
What is the lifespan of RBCs?
120 days
Heme is:
The non protein portion of hemoglobin (Hb)
Globin is:
The protein portion of hemoglobin (Hb)
What is hemoglobin A?
HbA/adult hemoglobin, hemoglobin in healthy adult
WHat is a single Hemoglobin A made of?
4 globin chains (2 alpha and 2 beta chains), 4 heme groups and 4 divalent iron atoms (divalent; 2+)
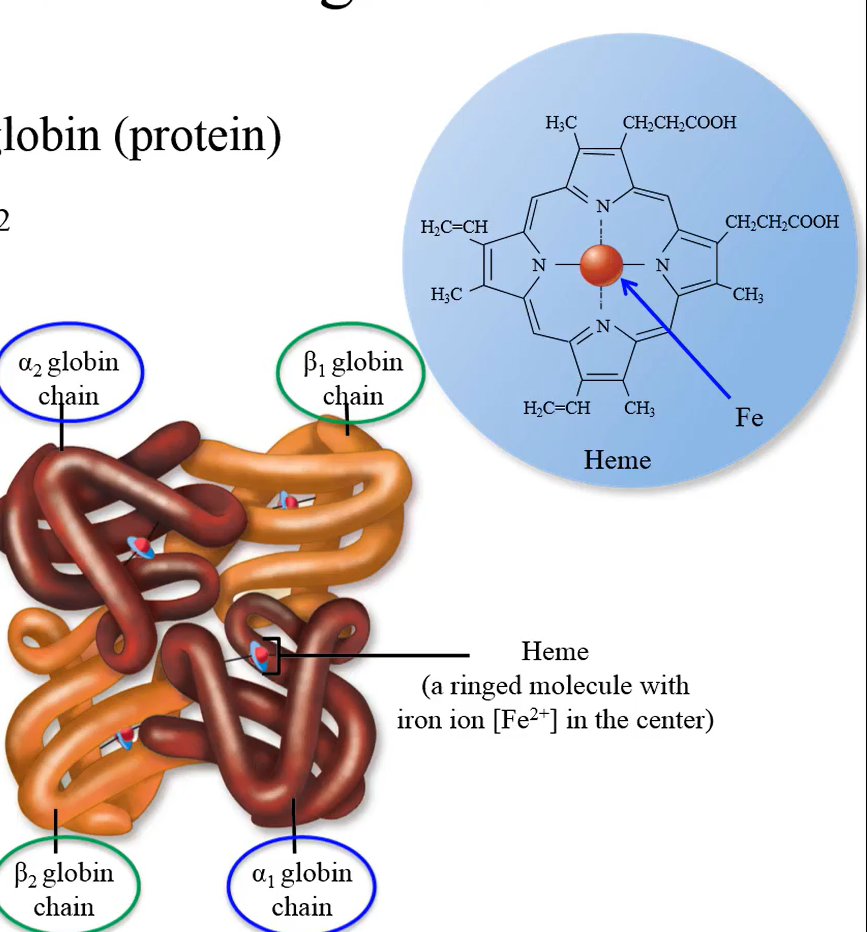
Each iron in hemoglobin A can bind to:
a single oxygen; each hemoglobin can therefore bind 4 oxygen
Majority of oxygen in the body is transported in:
red blood cells bound to hemoglobin
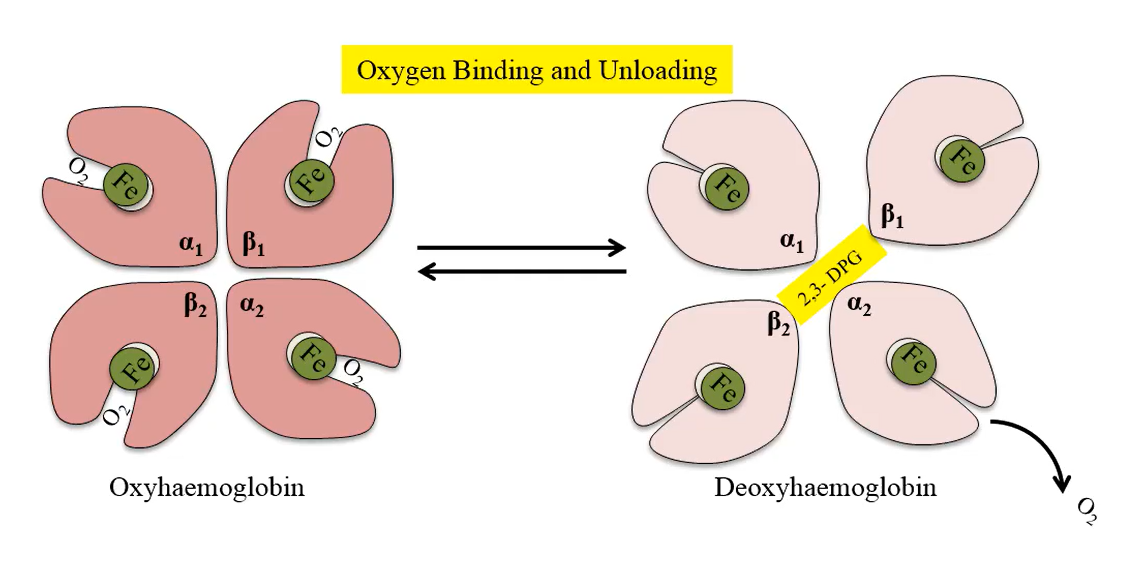
Hemoglobin binds oxygen in a:
loose and reversible manner
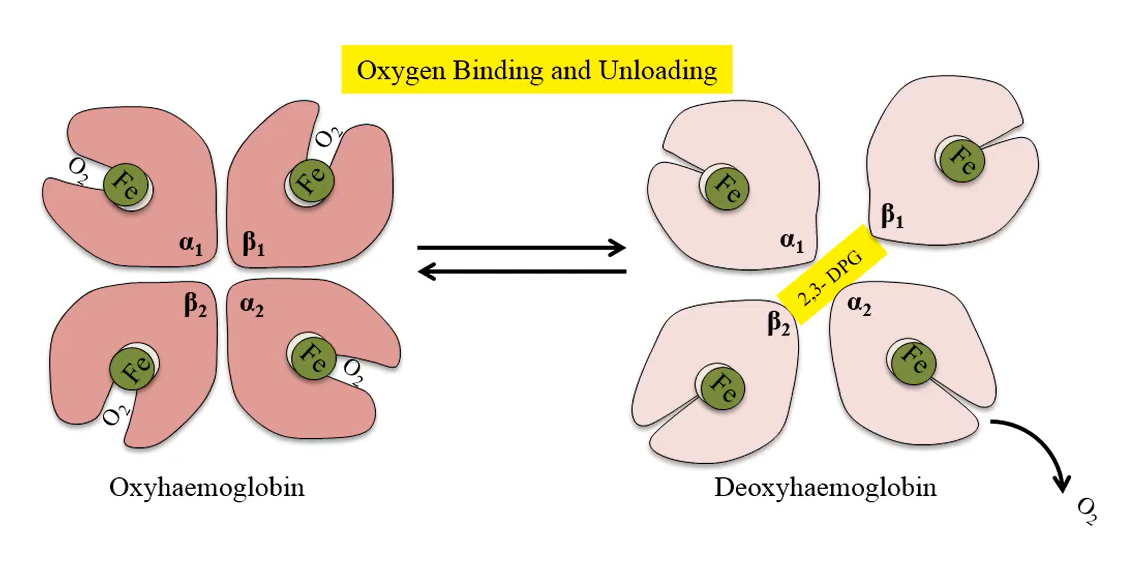
Relaxed binding structure of hemoglobin allows oxygen to bind in a:
cooperative manner; the binding of successive oxygen molecules facilitates or helps the binding of the next oxygen
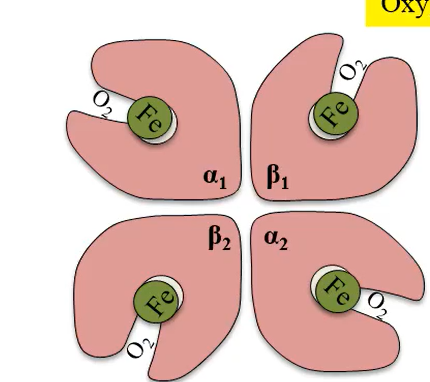
Oxyhaemoglobin is hemoglobin to which:
oxygen is bound; it has a relaxed binding structure
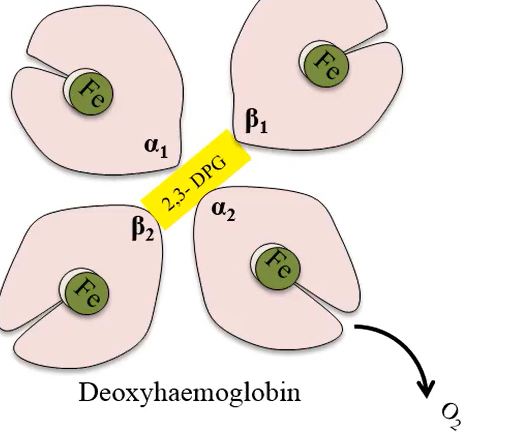
Deoxyhemoglobin is hemoglobin that has:
A tight binding structure and has given up oxygen
The process by which a ferrous iron combines with one molecule of oxygen is called:
Oxygenation
Hb can bind:
oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitric oxide and carbon monoxide
Hb has a higher affinity for:
carbon monoxide (200 x higher) than for oxygen (prefers to bind to carbon monoxide tightly)
Carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless and has high affinity for Hb, making it:
fatal as Hb cannot bind oxygen and deliver it to the body