Genetic Mutations
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
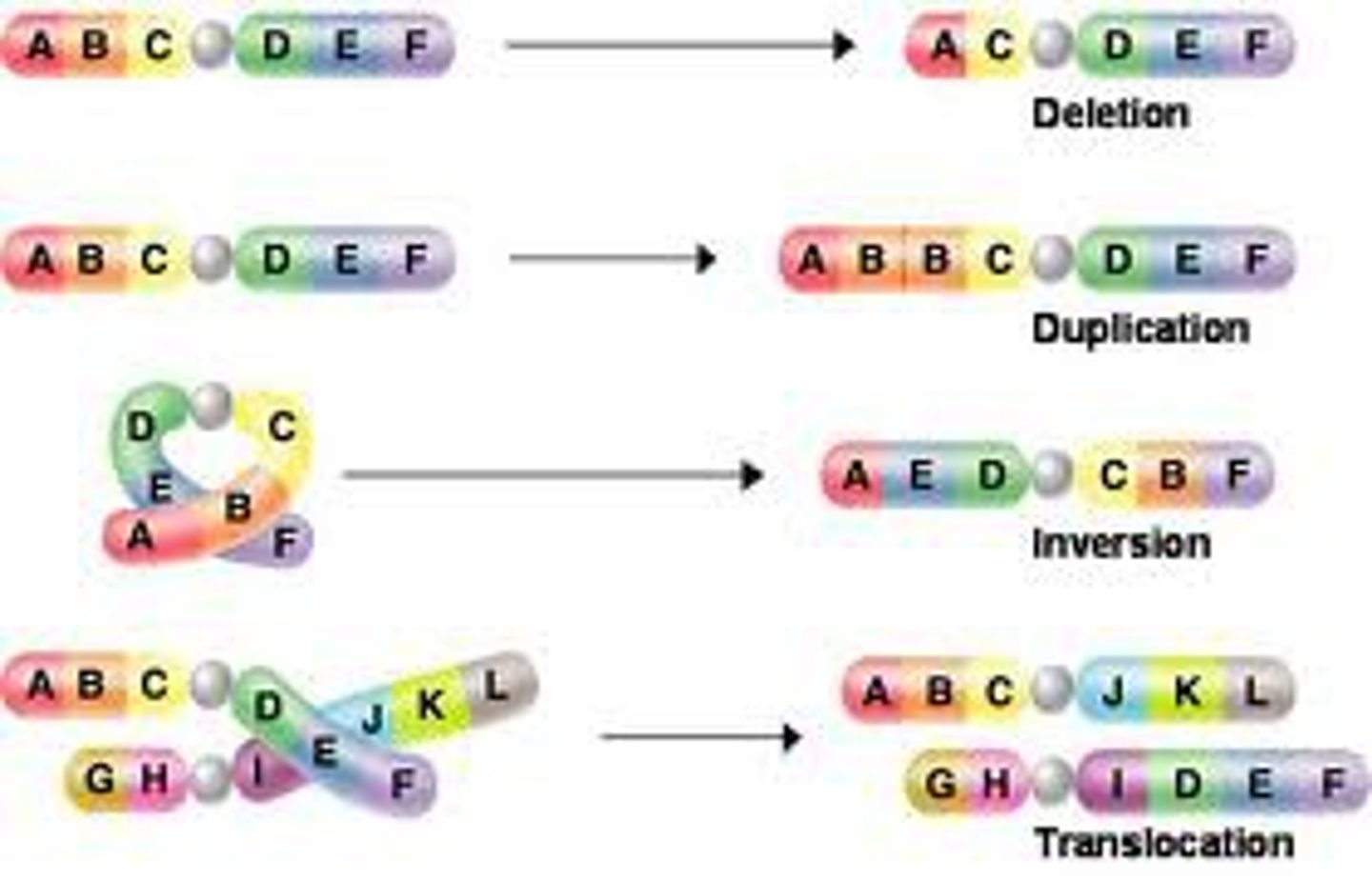
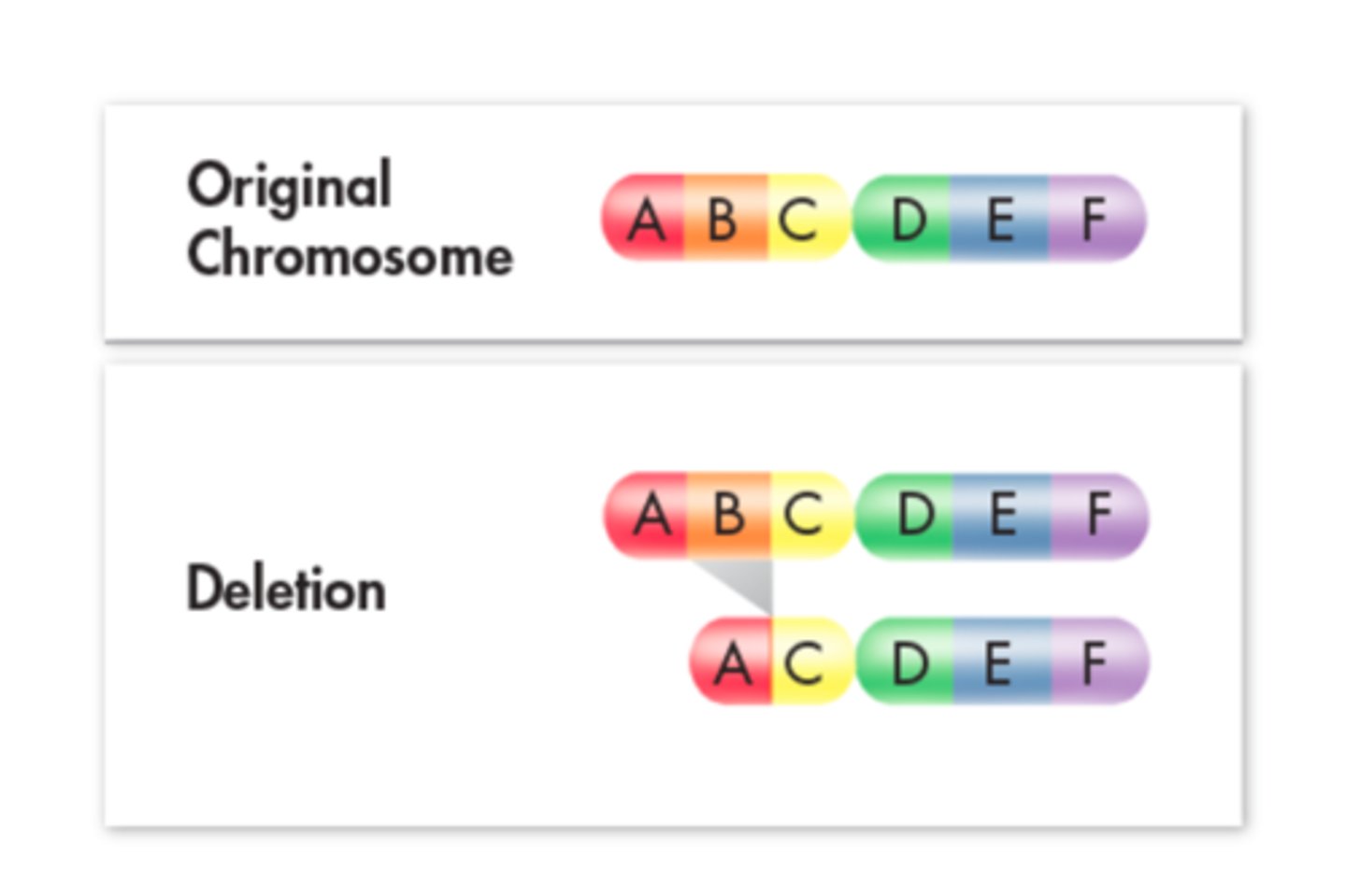
Point mutation deletion
A genetic mutation in which one base is omitted or left out; A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.

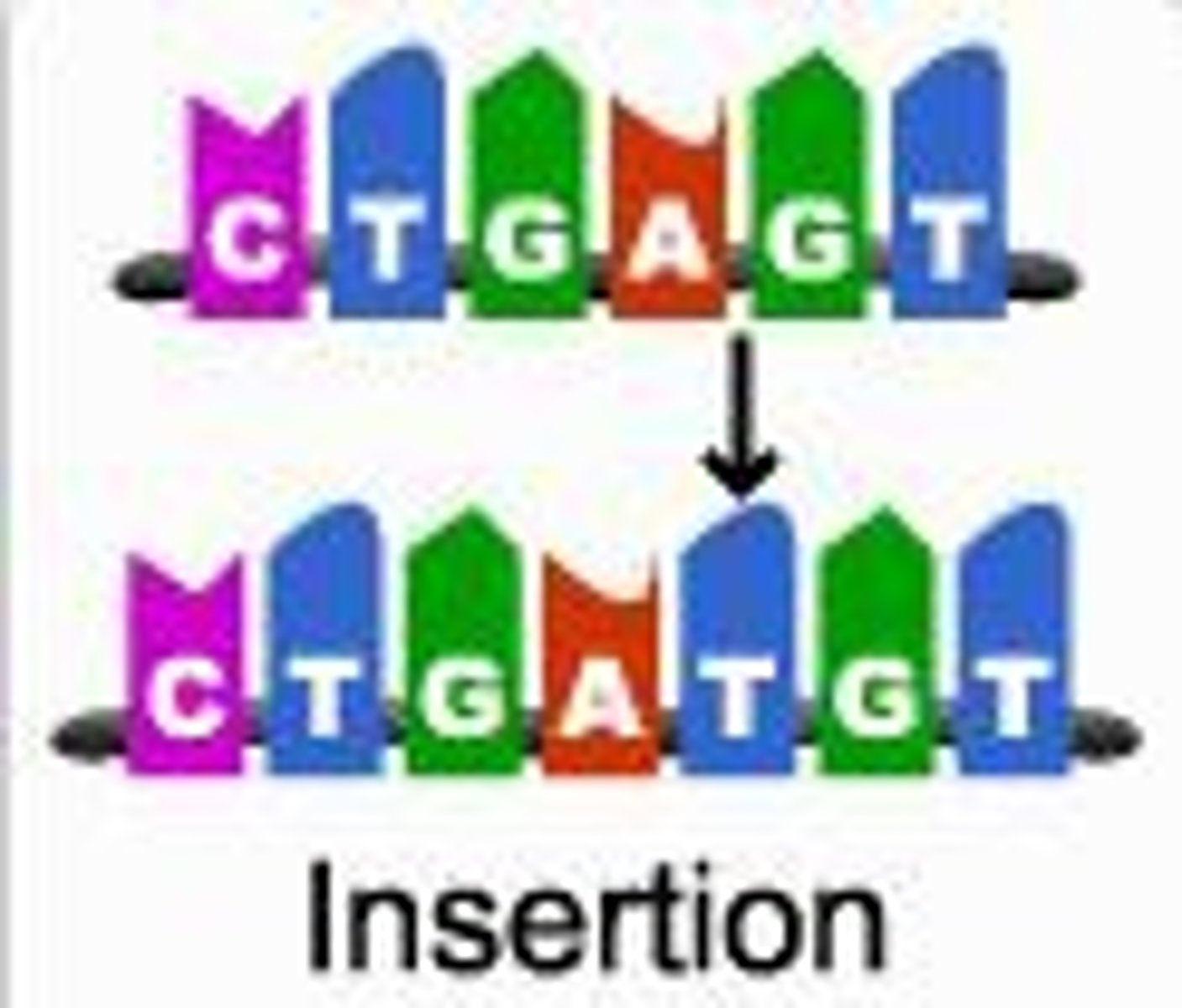
insertion
A type of point mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene; one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. The bases are still read in groups of three, but now those groupings shift in every codon that follows the mutation.
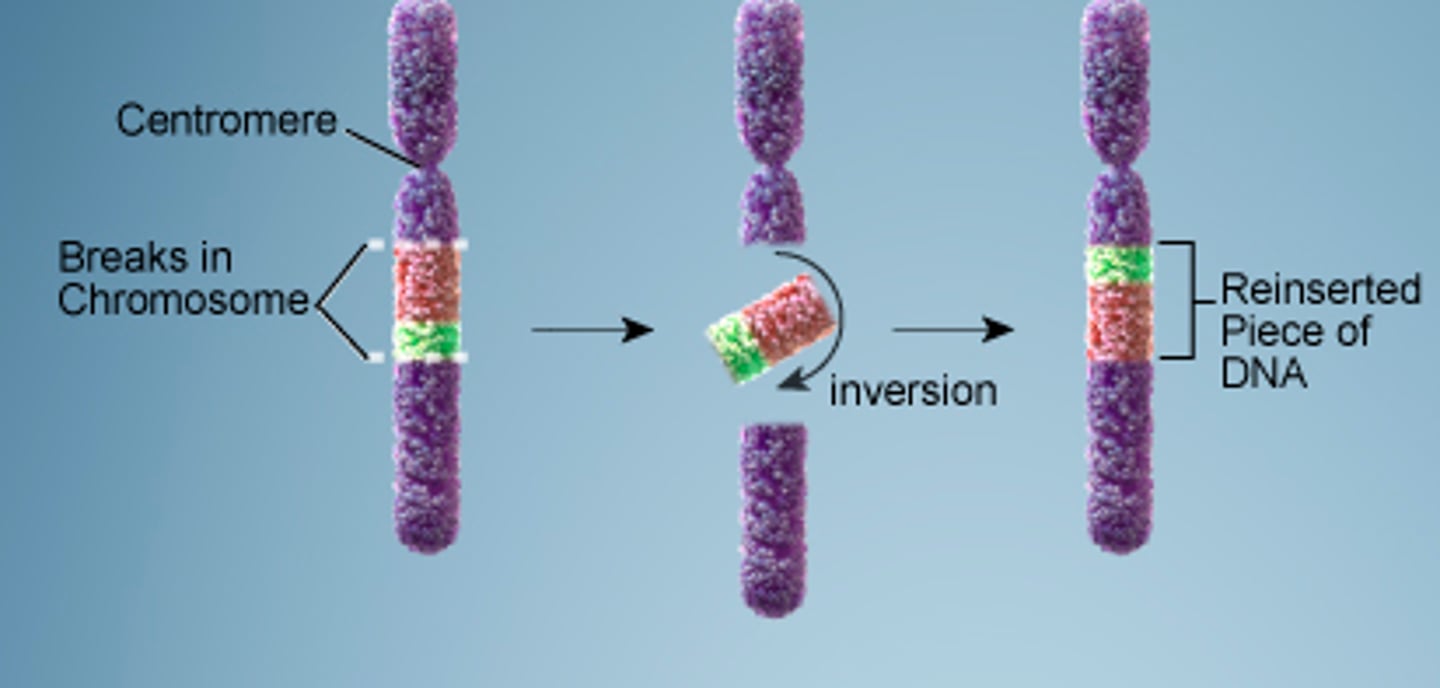
inversion
A mutation in which the order of the genes in a section of a chromosome is reversed; reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome.
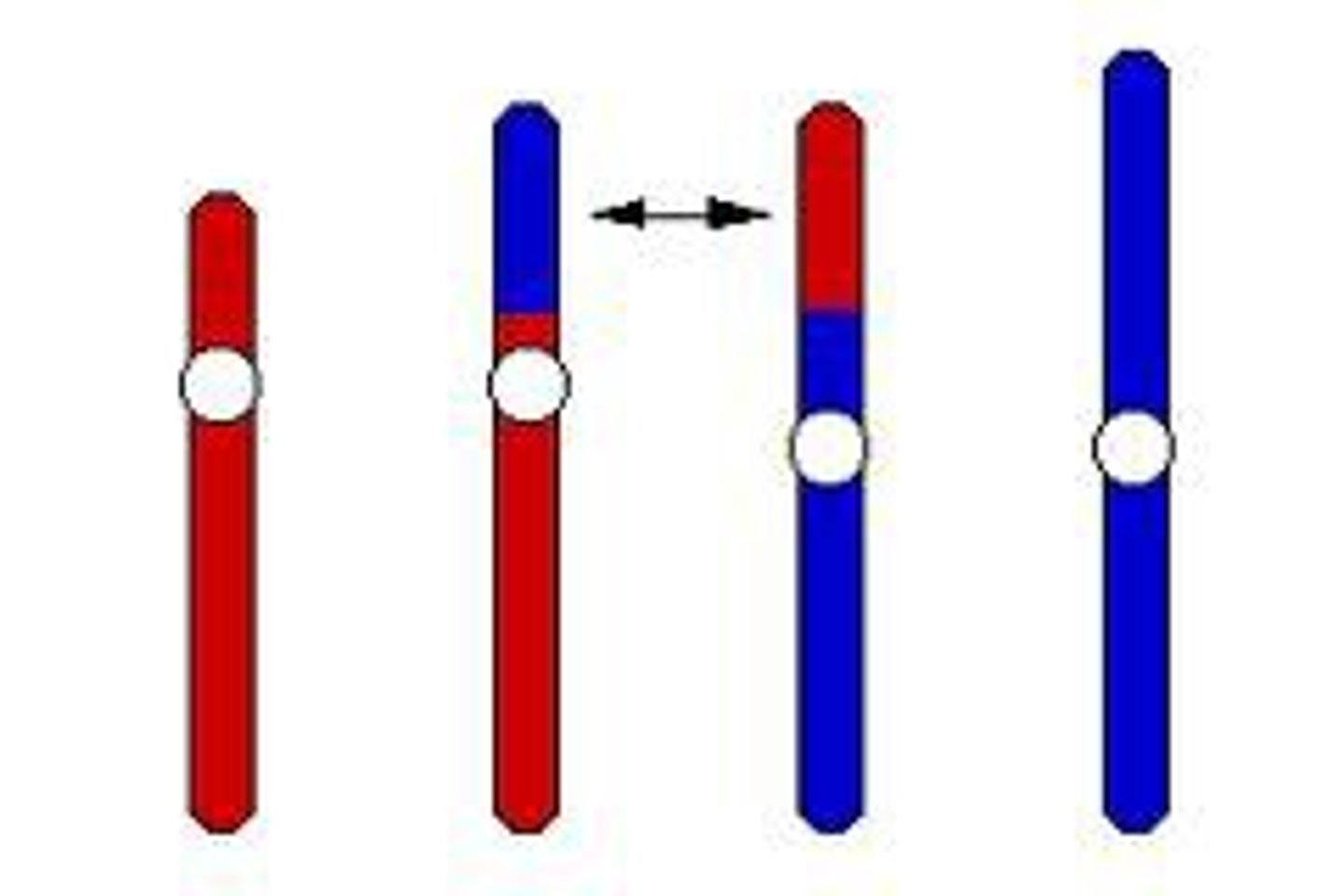
translocation
The process in which a segment of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome; occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another.
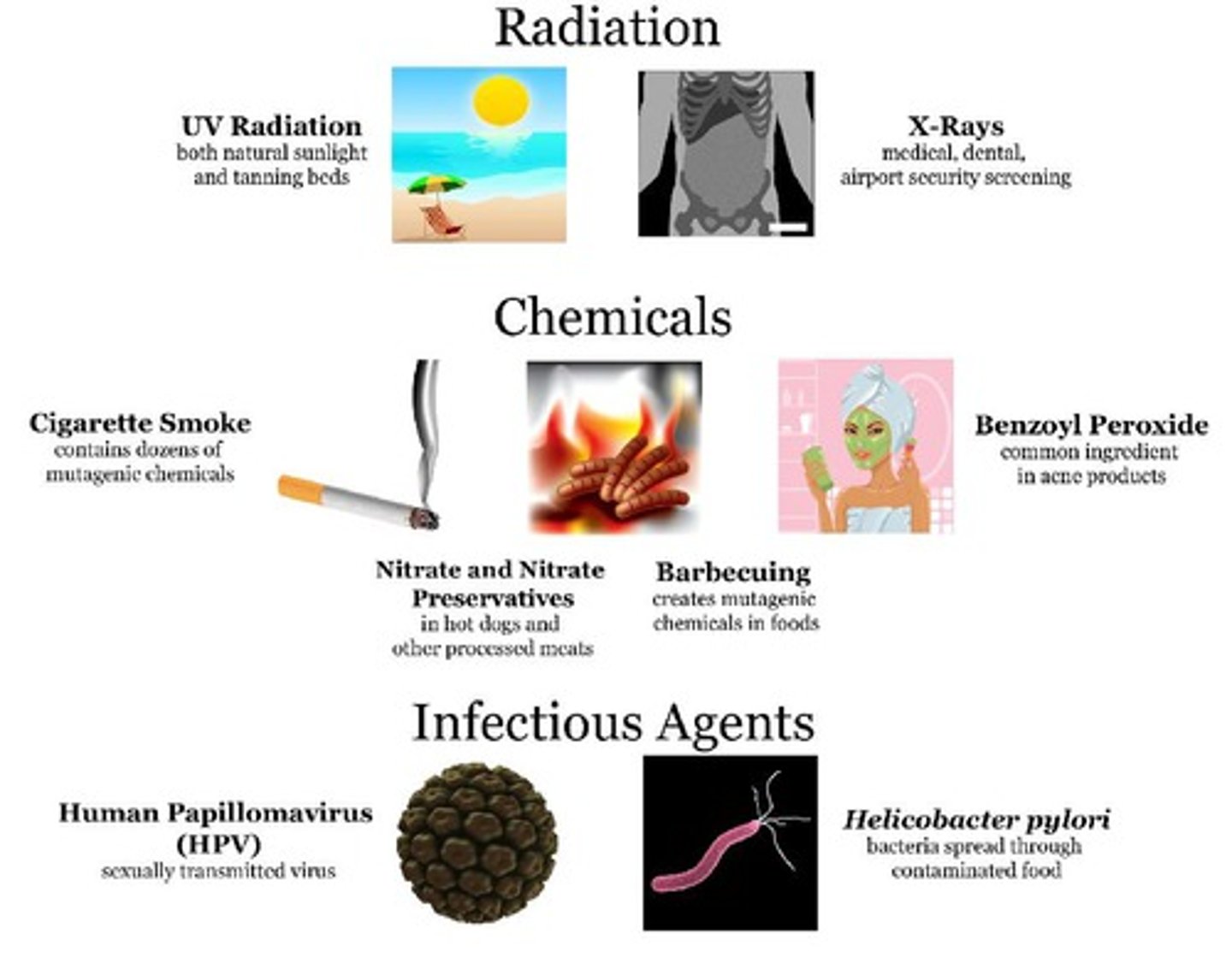
mutagen
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
mutation
An alteration in DNA structure or sequence of a gene; heritable changes in genetic information.
frameshift mutation
A mutation caused by an insertion or deletion of base pairs in a gene sequence in DNA such that the reading frame of the gene, and thus the amino acid sequence of the protein is altered.
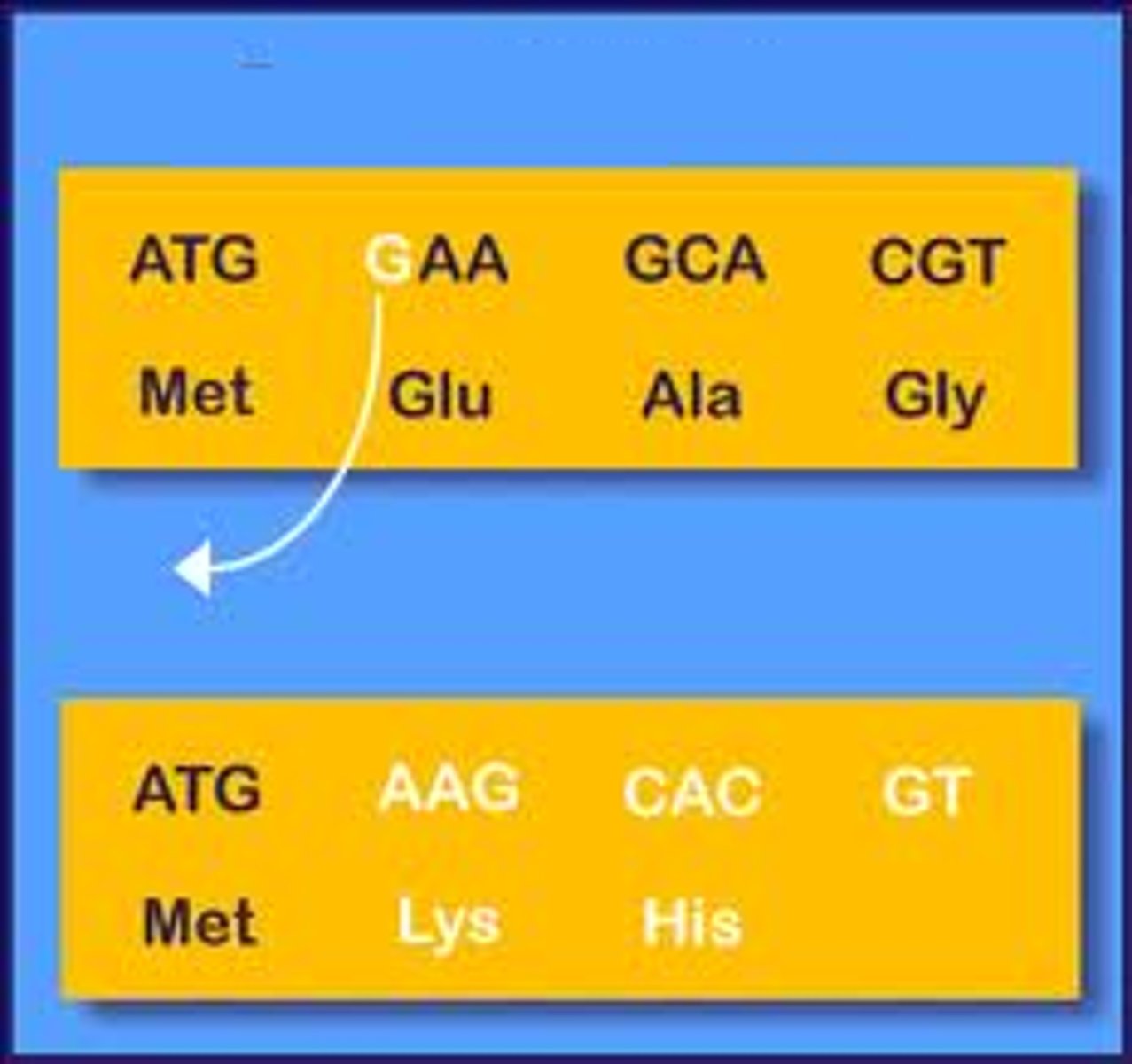
point mutation
A mutation in which only one or a few nucleotides or nitrogenous bases in a gene are changed; they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence and generally occur during replication.
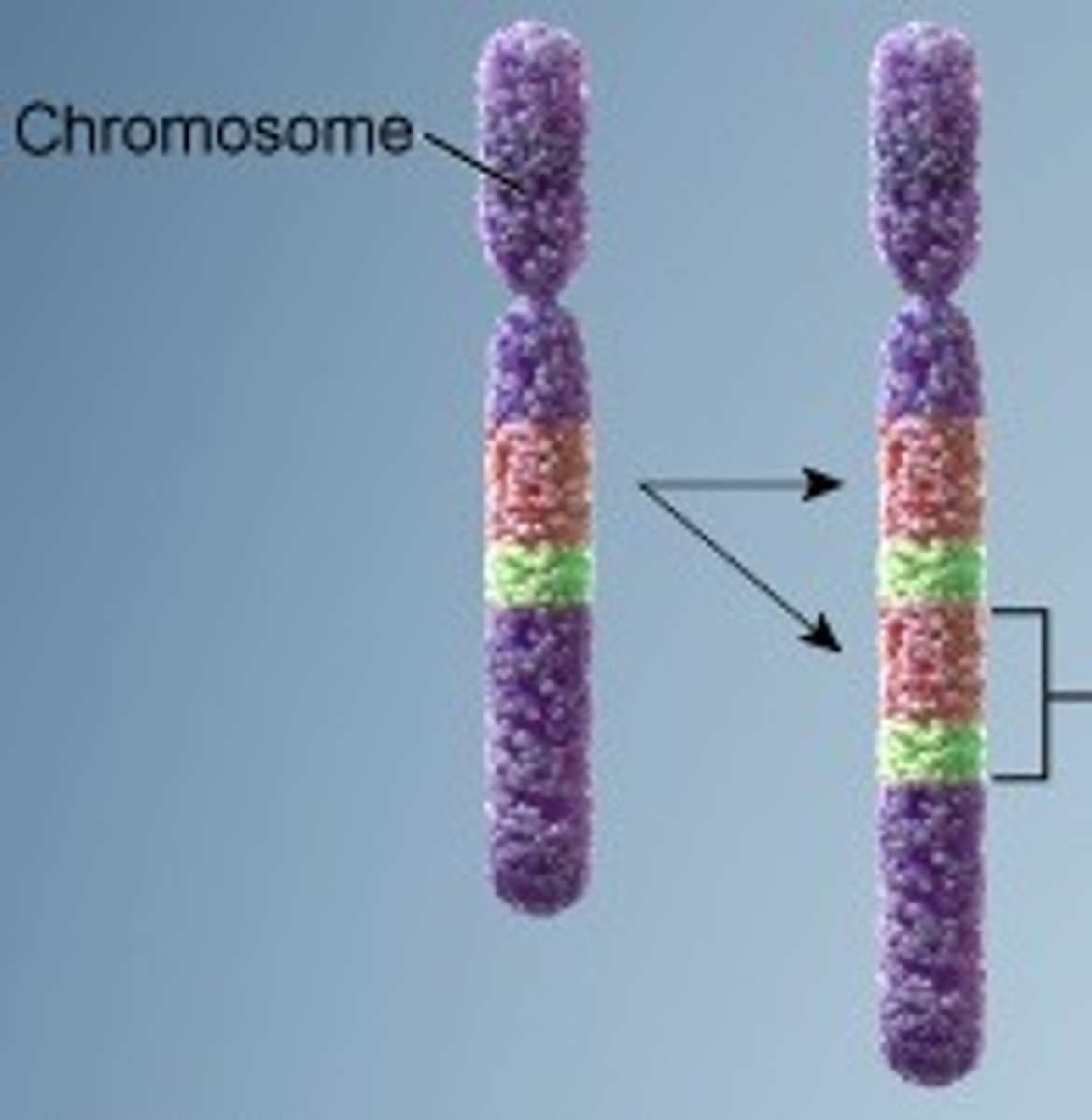
duplication
Type of chromosomal mutation that produces an extra copy of all or part of a chromosome.
When mutations produce an extra part or copies of chromosomes.
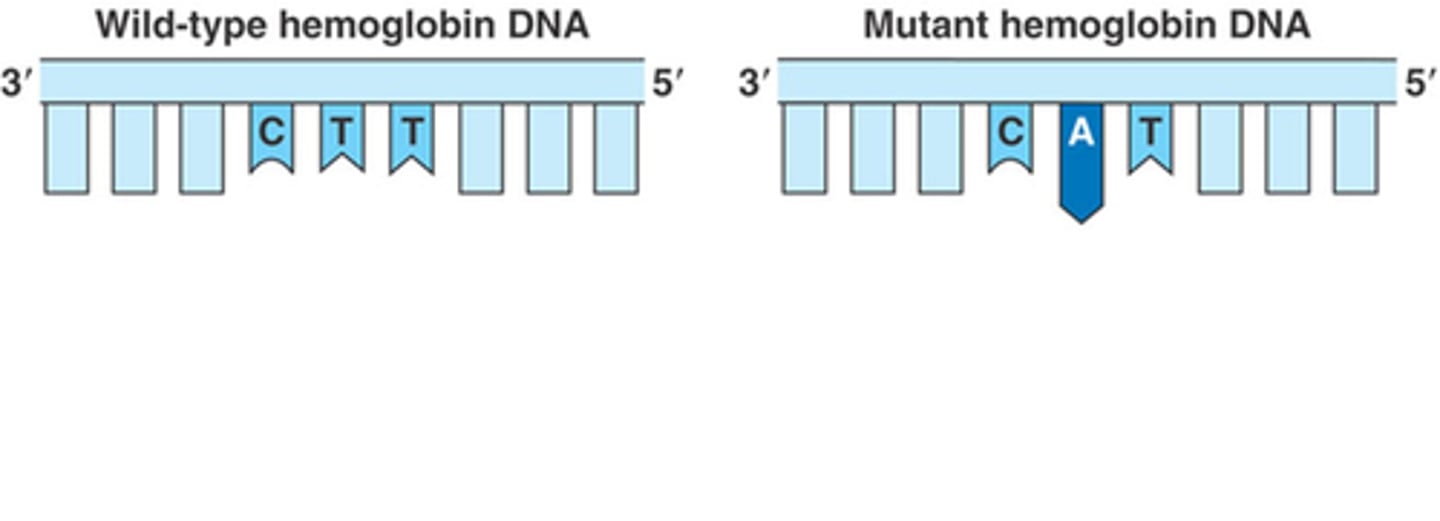
substitution
A mutation in which a nucleotide or a codon in DNA is replaced with a different nucleotide; one nitrogenous base is changed to another and may only affect one amino acid, if any.

gene mutations
produces changes in a single gene.
chromosomal mutations
produces changes in whole chromosomes; involve changes in the number or structure of chromosomes; these can change the location of genes on chromosomes and can even change the number of copies of some genes.
Types of point mutations
deletion, insertion, & substitution
Types of chromosomal mutations
deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation.
Chromosomal Deletion
Chromosomal mutation that involves the loss of all or part of a chromosome.
Effects of Genetic Mutations
~little or no effect
~produce beneficial variations
~negatively disrupt gene function
~produce proteins with new or altered functions that can be useful to organisms in different or changing environments
Causes of Genetic Mutations
~Genetic material is altered by natural events or by artificial means.
~Many mutations are produced by errors in genetic processes.
~Point mutations are caused by errors during replication.
~The cellular machinery that replicates DNA inserts an incorrect base roughly once in every 10 million bases.
~Small changes in genes can gradually accumulate over time.