MGMT 3 SG
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
the process of screening, selecting, and interpreting stimuli so that they have meaning to the individual.
What is perception?
confirmation bias
escalation of commitment
anchoring effect
framing bias
stereotyping
projection
availability of information
fundamental attribution error
What are the decision making traps (i.e., cognitive biases) that we must avoid to make good decisions?
ethics are broadly applied social standards for what is right or wrong in a particular situation, or a process for setting those standards.
——————————————————————-
morals are individual and personal beliefs about what is right or wrong.
What are ethics? How are morals and ethics the same or different?
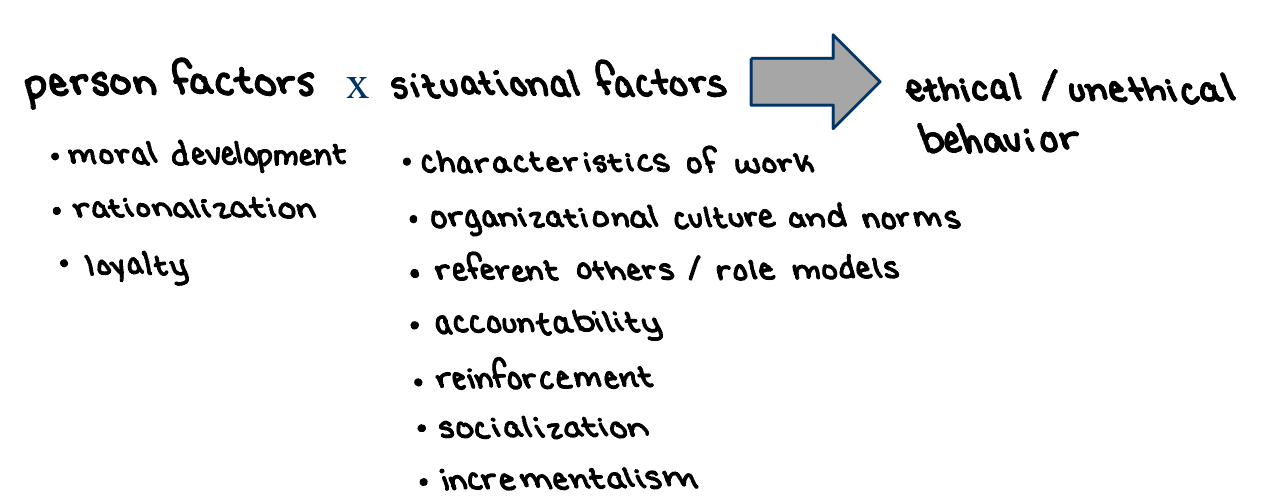
person factors x situational factors → ethical / unethical behavior
How is it that good people can do bad things?
utilitarianism (end-results ethics) → the rightness of an action is determined by evaluating its project / expected consequences.
EX] “the ends justify the means”
——————————————————————-
universalism (process / duty ethics) → determine rightness or wrongness before outcomes (motivates, or reasons for acting, are important).
EX] human conduct should be guided by primary moral principles, “we must be held accountable for the WAY we make decisions.”
Understand Utilitarianism and Universalism
define the problem
generate alternative solutions
evaluate and select an alternative
implement and follow up on situation
What are the steps in the standard model of problem solving?
determine the facts and state the problem
who will be affected by the decision?
identify relevant factors
develop a list of 3-5 options
test options
make a tentative choice
review choice
What are the steps in NIU’s Ethical Decision Making Guide?
the shared assumptions of team or organizational members and the shared history that created the assumptions that guide behavior in organizations.
——————————————————————-
provides a sense of identity and encourages commitment
helps individuals make sense of team / organizational events
reinforces team / organizational values
guides and shapes individual behavior (type of social control system)
What is organizational culture and how does it influence individual and group behavior?
physical structures
language
rituals and ceremonies
stories and legends
shared values
shared assumptions
What are the levels of culture?
innovation and risk-taking
attention to detail
outcome orientation
people orientation
team orientation
aggressiveness
What are the characteristics of organizational culture?
corporate egoist culture
instrumentalist culture
moralist culture
What are the ethical components of organizational culture?
ethical leadership
supervisor reinforcement of ethics
peer commitment to ethics
embedded ethical values
What are the four components of an ethical culture?
respect others
serve others
are fair
are honest
act as ethical role models
What are the characteristics of ethical leaders?
there are mini-cultures within a large organization, typically defined by department and geographical separation
Why do larger organizations sometimes have sub-cultures?
what leaders pay attention to, measure, and control on a regular basis…
how leaders react to critical incidents
how leaders allocate scarce resources, rewards, and status / recognition…
how leaders recruit, select, promote, retire, and remove organizational members
How do leaders shape organizational (or team) culture?
leadership that inspires followers to transcend their own self-interests for the good of others.
charisma
inspirational motivation
intellectual stimulation
individual consideration
What are the components of transformational leadership?
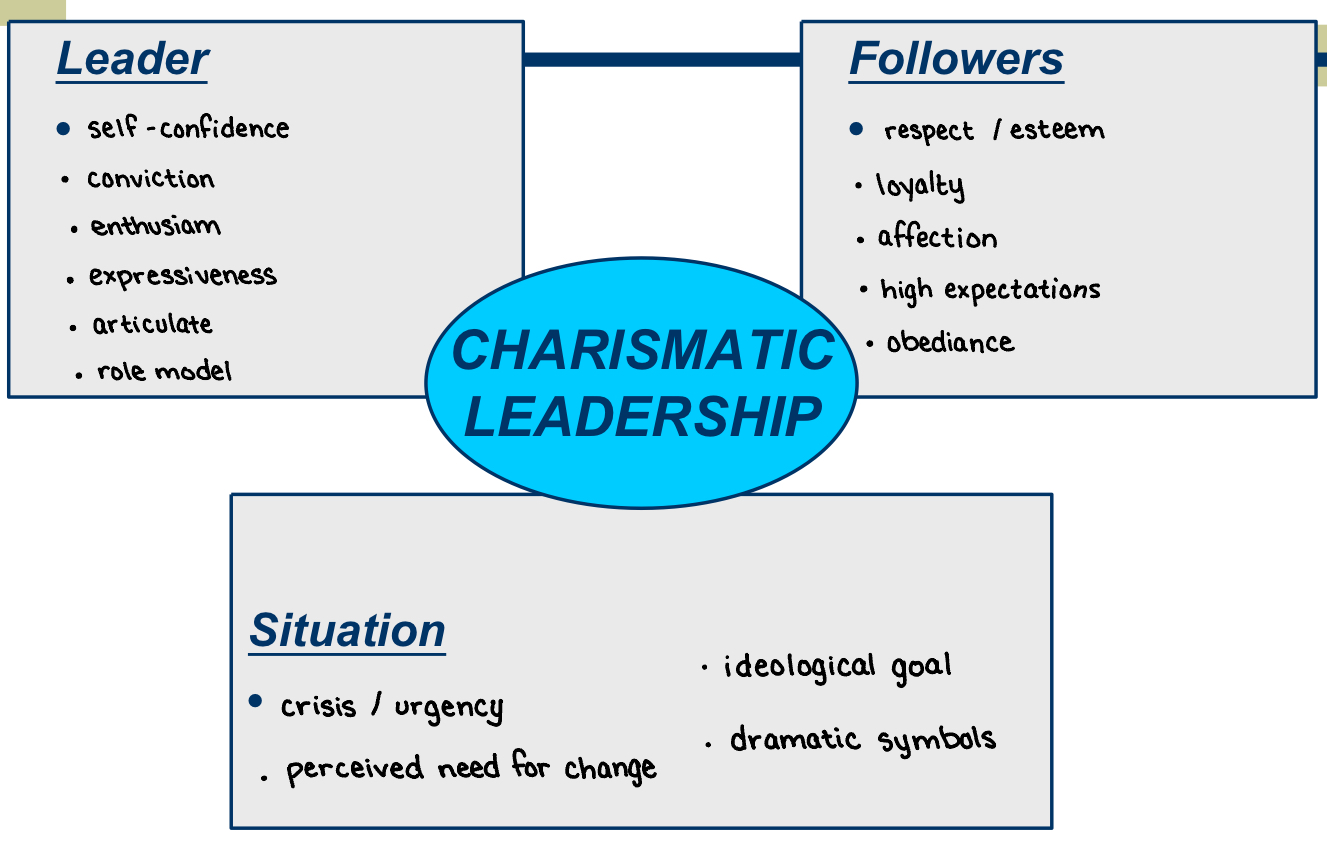
—
What are the typical leader, follower, and situational characteristics of charismatic
leadership?
start presentation with introduction that catches audience’s attention (how is it relevant to them!)
plan for how to finish presentation
project a powerful, confident, and dynamic presence
communication style (eye contact, facial expressiveness, gestures)
DON’T rely on note cards, instead practice!
How can you make a more effective and charismatic presentation?
unrealistic expectations
dependency and counter-dependency
reluctance to voice disagreement with leader
need for continuing “magic”
communication manipulation
poor management practices (hands-on, controlling, lack of attention to detail)
——————————————————————-
unethical charisma
uses power for personal gain
promotes own vision
closed to criticism
top-down communciation
insensitive to followers
VS.
ethical charisma
uses power to serve others
match vision to follower needs
open to feedback
develops followers
encourages thinking
What are the dark sides to charismatic leadership? What is the difference between ethical and unethical charisma
active resistance
passive resistance
compliance
enthusiastic support
What is the typical reaction process to organizational change?
keep everyone informed (education)
use two-way communication and listen to your employees
enhance management credibility and trust
How can you minimize cynicism about change?
establish a sense of urgency
build a powerful coalition
develop a vision and strategy
communicate the vision
enable employees to act
create and reward short-term wins
consolidate gains
institutionalize the changes
Understand Kotter’s eight steps to organizational change.
partnering with clients in a thought=provoking and creative process that inspires them to maximize their personal and professional potential
——————————————————————-
the employee (client) is ultimately responsible for their own growth
What is coaching and how is it different from mentoring, consulting, and therapy?
situation → outcome → alternatives → rollout
Understand the steps of the SOAR model
power dimensions → the degree to which less powerful members of a society accept unequal power distribution.
high power distance culture = hierarchies are respected; leaders are authoritative
low power distance culture = power is decentralized; leaders are more democratic
individualism → emphasis on personal goals and individual rights
collectivism → focus on group harmony and collective goals
Understand the different cultural dimensions and how that might impact leadership effectiveness and group interactions
refer to the unconscious beliefs and assumptions people have about what makes someone a "good leader." these beliefs are shaped by culture, society, and personal experiences
What is implicit leadership and how might culture influence this according to the GLOBE project?
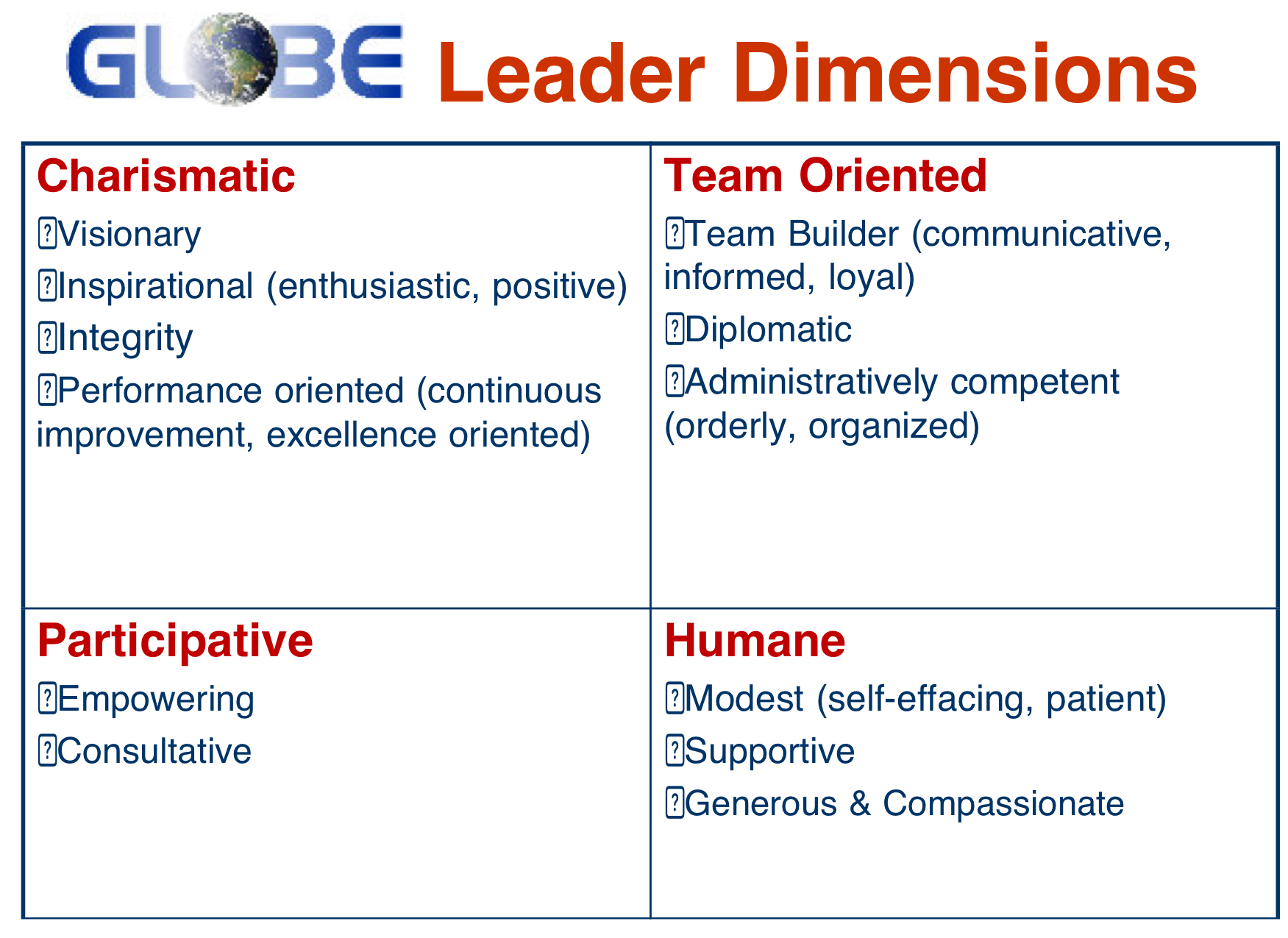
charismatic
team oriented
participative
humane
What GLOBE leadership dimensions are universally endorsed around the world?
negotiations are fixed sum
you need to be either tough or nice
good negotiators are born
experience is a great teacher
good negotiators rely on intuition
What are some common negotiation myths and why are they incorrect?
intrapersonal conflict
interpersonal conflict
intragroup conflict
intergroup conflict
What are the different levels of conflict?
competitive
misperception and bias
emotionally decreased competition
blurred issues (generalizations)
magnified differences / minimized similarities
——————————————————————-
creates incentive to solve underlying problem
promotes awareness of self and others
can stimulate new ideas, etc
Why/how can conflict be dysfunctional or beneficial?
contending (competing)
yielding (accommodating)
inaction (avoidance)
problem solving (collaborate)
compromising
What are the five major strategies for managing conflict?
what do i want?
what is my B.A.T.N.A?
——————————————————————-
who are the other parties?
what are the other party’s issues (and priorities)
what is their B.A.T.N.A?
When planning for negotiations, what things should you consider for yourself and the other side?
goals of one party are in fundamental and direct conflict with goals of other party
resources are fixed and limited
each party wants to maximize their share of resources
typically has a negative, macho, offensive connotation
What is distributive bargaining?
aim to create value and find mutually beneficial solutions that satisfy the needs and interests of both parties
emphasize the commonalities between the parties and minimize the differences
What is integrative bargaining?
good guy / bad guy
highball / lowball
bogey
intimidation / aggressive behavior
——————————————————————-
ignore them
discuss them — negotiate the negotiation process
respond in kind (i.e., do the same thing to them)
co-opt (i.e., befriend) the other party
What are some typical “hard ball” distributive bargaining tactics and how do you deal with these?
the history of the relationship between the parties
a belief that an issue can only be resolved distributivity
the mixed-motive nature of most negotiating situations
Why are integrative negotiations hard to achieve?
be enthusiastic and gracious
always assume salary is negotiable
what other things are negotiable?
know your priorities
develop rapport
cultivate alternatives
live up to your commitments
get offer in writing before you negotiate any terms
be willing to walk away
What are some tips for negotiating your job offer?
recognizing and seizing opportunity
creating value
assuming risk (but not recklessly so)
— learning from mistakes
overcome attention
What is an entrepreneur?
an inborn trait
the sole domain of “inventors”
limited to “outsiders”
something that requires piles of money
an individual sport
What is entrepreneurship not?
curious
tolerant of ambiguity
risk acceptance
action orientation
passion
need to achieve
future focus
idea generation
execution
self-confidence
optimism
persistence
interpersonal sensitivity
What are the individual personality traits and skills of someone with an entrepreneurial mindset?
scalable start-up
small business
established organization
social enterprise
What are the four contexts of entrepreneurial behavior?
autonomy
competitive aggressiveness
innovativeness
pro-activeness
risk taking
What are the characteristics of entrepreneurial orientation?
the state or quality of being creative. the ability transcend traditional ideas and to create meaningful new ideas
What is creativity?
keep track of ideas
step away and do something else
listen to or watch something that stimulates
break down the problem into smaller parts
don’t get discouraged
create in teams: collective creativity
How can we improve our creativity
preparation
incubation
illumination
implementation
What is the creative process?
ability to generate new ideas
systematic process of creating value out of creative ideas
How are creativity and innovation similar or different?