Geology 1100 - Unit 4
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Driving Force
Components of gravity acting parallel to the slope
increases as the slope gets steeper
Resisting Force
Friction between object and sliding surface
Decreases as the slope gets steeper
Angle of Repose
Maximum angle at which loose material is stable (~30 degrees for many materials)
Variables that impact mass movement
Slope
Water
Vibration
Material (weathering, planes of weakness)
Vegetation
Combination of Factors
Mass Movement Variable - Slope
Erosion of undercutting at the base of slopes or cliffs increases likelihood of failure
Mass Movement Variable - Water
Adds weight and decrease resisting forces
Mass Movement Variable - Planes of Weakness
Provides surfaces along which resisting forces are weaker
Mass Movement Variable - Vibration
Seperates surfaces between grains allowing downslope movement to begin
Mass Movement Variable - Vegetation
Roots provide cohesion
Plants hold and remove water
Trees add weight
Mass Movement Variable - Fire
Loss of vegetation which alters water budget, roots decay and cohesion decreases
Drainage Basin
Area of land for chich all of the precipitation is collected and ultimately flows out of the same outlet
Area is “drained” by a particular stream and its tributaries
Drainage Divide
Local high point that separates drainage basins
Headwater
Where a river or stream starts
Trunk Stream
The main river channel
Tributary
Smaller streams and rivers that flow into the trunk stream
Distributaries
Breaking up trunk stream into smaller channels
Mouth
Where a river ends (typically only used at ocean or large lake)
Longitudinal Profile
Changing elevation from headwaters to mouth
Base Level
Lowest level to which stream can erode its channel
1st Order Streams
Permanent Streams with no Tributaries
2nd Order Streams
Streams with 2 (or more) 1st order tributaries
3rd Order Streams
Streams with 2 (or more) 2nd order tributaries
4th Order Streams
Streams with 2 (or more) 3rd order tributaries
Sediment Load
Material a river transports.
3 types
Dissolved
Bed
Suspended
Dissolved Load
Material in a solution.
Bed Load
Solid Particles that slide, roll and/or skip along riverbed
Suspended Load
Solid particles swept along by the water that rarely touch the bottom
Capacity
Ability of the water flowing in a stream to move sediment
Competence
Largest particle a stream can transport
Aggradation
If capacity & competence are less than the load that the stream is carrying deposition will occur
Degradation
If capacity & competence are greater than the load that the stream is carrying, erosion/scour will occur
Graded Stream
A stream whose capacity & competence matches its load
Narrow V-Shaped Valley or Canyon
Relatively steep slopes
Downcutting (erosion of the stream bed) dominates over lateral migration
often include rapids waterfall
Wide Valleys
Relatively shallow slope
Lateral migration of channel
Well developed floodplain
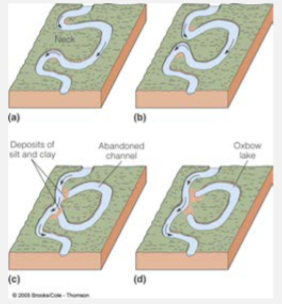
River Meandering
Erode in some places and deposit in others causing channel to move around over time

Cut Bank
Highest velocity on the outside curve causes erosion
Point Bar
Lower velocity on the inside curve leads to deposition
Oxbow Lake
Meander bends cut off by erosion of the narrow neck results in crescent shaped lakes
Straight Channels
Steep gradients, narrow channels, eroding into bedrock
Often have distinct “pool and riffle” morphology
Braided River
Typical of settings with high sediment input. The water can only move a position of it at any time. Deposition within the broad channel causes the flow to break into multiple intertwining flows (“braided”) that migrate rapidly over time
Recurrence Interval
Average time between events of a certain size
Floods - Zoning
Floodplain regulation to uses flood prone areas in a manner that reduces risks and costs
Floods - Prevention
Build Structures to control and/or contain floods
Artificial levees
Channelization
Dams
Damage Control
Sandbagging, pumping, evacuation, rescue
Channelization
Straightening of existing stream channels
Stabilization of banks
Dams
Once pitched as the ultimate solution to flooding
Pros of Dams
Regulation of water flow
Generation of hydroelectric power
Provides recreation opportunities
Cons of Dams
Loss of property for reservoir
Sedimentation in the reservoir (limited lifetime)
Ecological consequences
Possibility of catastrophic failure
Ways for water to reach streams and rivers
Melting snow or glaciers
Precipitation falling directly on surface of stream or surrounding area then flowing into stream
Soaking into ground then flowing as groundwater
Groundwater
Any water occurring in the ground, i.e. below the earths surface
Pore space
Space between sediment grains, in open cracks, fractures, or voids
Porosity
amount of pore space in a unit of soil, sediment or bedrock (expressed as a percentage).
unaffected by grain size.
Unsaturated Zone/Zone of aeration
Pore space partially filled with water
Zone of Saturation
Pore space completely filled with water
Water Table
Where Saturated Zone and Unsaturated Zone meets.
Aquifer
A geological unit that carries water
Hydraulic Gradient
Difference in the height of water table of two sites connected to the same ground water system. Its the slope of the water table
Permeability
Measure of the connectedness of the pore spaces (Expressed as flow rate)
Aquitard (Confining Layer)
Geologic unit that effectively stops the flow of water
Recharge
The inflow of water into an aquifer
Discharge
The removal of water from an aquifer
Gaining Streams
Gain water from inflow of groundwater through streambed (humid env.)
Losing Streams
Lose water to groundwater system by outflow through streambed (Arid env.)
Unconfined Aquifer
An Aquifer with no aquiclud between the water table and land surface
Potentiometric Surface
The level to which water rises under pressure either in pipes (artificial) or above the level of the aquifer (confined groundwater system)
Artesian Well
A well that taps a confined aquifer.
2 Types:
Non-flowing artesian well
Flowing artesian well
Non-Flowing Artesian Well
Potentiometric surface below ground level
Flowing artesian well
Potentiometric surface above ground level
Well
A hole dug or drilled into the ground for the purpose of accessing groundwater
Cone of Depression
The area around a well where the height of water table is lowered because water is being removed faster than it is replaced
Karst Regions
Carbonate regions with dissolution features
Speleothem
Rock formation deposited in a cave
Stalactites
Speleothems forming downward from the cave roof
Stalagmites
Speleothems forming upward from the cave floor
Karst Topology
Landforms on and under the ground in areas where dissolution is important
Sinkholes
Collapse of the surface into a below ground cavity (can be from dissolution or other causes) are arguably the most news worthy karst-related hazard
Glacier
A mass of ice that is large enough to deform under its own weight and to flow down slope and/or outward
Valley Glacier
Type of glacier confined by the rock walls of a valley that prevent it from spreading laterally
Continental Glacier
A glacier whose flow is largely unconstrained by hills and valleys