Visual Fields
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
120
what is the binocular VF?
kinetic
moving target VF
fixed size & brightness
non-seeing to seeing
approaches HOV from the sides
isopter
limits of retinal sensitivity to a specific test target
static
fixed size target
intensity or brightness varies
approaches HOV from above
40
___dB is typically the least intense stimulus visible by humans
pt is probably trigger happy bc they cannot see above ~40dB
what does it tell you if the pt is getting VF values above 40dB?
III
what size stimulus is typically used for VF testing?
>0.5 sec, a head turn
typically when VF testing, a stimulus of 200ms in duration is used, if you use a stimulus of _____, it might cause _____
screening
testing strategy to make sure that the subject has at least a “statistically normal” VF; usually no attempt to measure/quantify performance
threshold
testing strategy to find the weakest stimulus seen 50% of the time; measures or quantifies performance at some or all locations & makes a “frequency of seeing” curve
frequency of seeing curve
probability of seeing stimuli over range of intensities
absolute defect
no stimulus perceived in the affected field
relative defect
VF defect changes in size inversely w/ change in size &/or intensity of stimulus (less than normal sensitivity but some stimulus is detected)
SITA - standard
threshold strategy
4 then 2dB steps
initial crossing of threshold, then reversal in 2dB steps to final crossing
SITA - fast
threshold strategy
single crossing
higher intratest variability
SITA
complex mathematical model that uses different step sizes & intelligent decision rules
½ the time w/ no loss of reproducibility or diagnostic info
high accuracy & less variability
based on age-corrected values in normal & glaucomatous populations, frequency of seeing curves around threshold values, correlations b/t adjacent test points
probability function is adjusted continuously as the test proceeds
HFA3 SITA-Faster
35% faster than SITA fast
tested in both normal & glaucoma pts
reduced dead time b/t stimuli & eliminates blind spot tracking & false negative testing
uses a gaze tracker
maybe poor sensitivity & specificity so not used much
54, 76
a 24-2 tests ___ points w/in 24deg while a 30-2 tests ___ points w/in 30deg
68
a 10-2 tests ____ points w/in the central 10deg
direct observation
gaze tracking
fixation losses (Heijl-Krakau blind spot monitoring)
what are the 3 ways to monitor fixation on a VF?
gaze deviation
an upward deflection on the gaze tracker indicates what?
blink or eye closure
a downward deflection on the gaze tracker indicates what?
fixation losses (Heijl-Krakau blind spot monitor)
# of times pt responded to stimulus that was presented in the presumed blind spot location
loss of fixation
blind spot incorrectly plotted
trigger happy
head tilt
what can cause a fixation loss?
false positive
# of times pt responds positively when pt responses are not expected
can be caused by: trigger happy or lack of understanding, anxiety
false negatives
# of times pt fails to respond when a distinctly visible stimulus (9dB or less) is presented
presented only at test point locations where threshold sensitivity has already been measured
can be caused by: FATIGUE, slow rxn time, hysteria/malingering, disease
decreased reproducibility of glaucomatous VF
what do false negatives reflect in a glaucoma pt?
20, 15, 15-30
suspect reliability issues in normal pts if: fixation losses are >__%, false positives are >___%, and/or false negatives are >___%
unilateral
_______ VF defect: 1 eye is affected
bilateral
______ VF defect: both eyes are affected but due to different lesions (same or different disease)
binocular
______ VF defect: the same lesion is affecting both eyes
central
scotoma that involves fixation
cecocentral
scotoma that involves fixation to the blind spot
paracentral
scotoma that is adjacent to fixation
arcuate scotoma & nasal step
Bjerrum’s area
coincides w/ RNFL anatomy
extends from the blind spot
does not cross nasal horizontal midline of VF
can be an isolated scotoma w/in Bjerrum’s
altitudinal
VF defects that respect the horizontal meridian
heteronymous
VF defect in opposite sides of visual space for each eye
bitemporal or binasal
lesion usually at the chiasm
homonymous
VF defect in same side of visual space for each eye
right vs left
lesion is posterior to the chiasm
quadrantanopia
VF defect that respects the vertical & horizontal meridian
hemianopia
VF defect that affects 2 adjacent quadrants & respects the vertical meridian
F
T/F: you have to specify heteronymous in the VF defect description
complete
no vision at all in the affected half of the VF
incomplete
partial vision in affected half of the visual field
congruous
VF coincide when superimposed
more similar by angle of defect border & depth of defect
congruous
ischemic events will usually cause more _______ VF defects
incongruous
compressive lesions like tumors will usually cause more _______ VF defects
posterior
more ________ lesions in the visual pathway usually cause more congruous defects
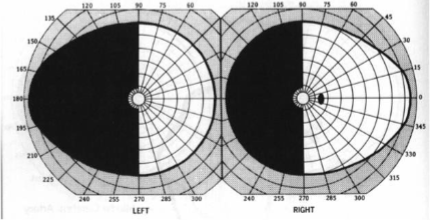
bitemporal hemianopia
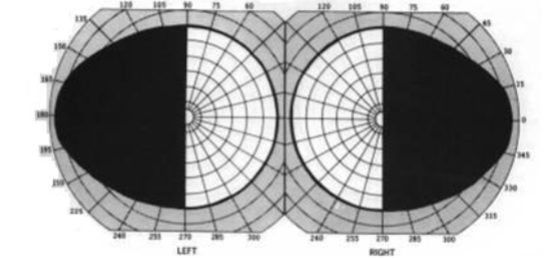
right complete homonymous hemianopia w/ macular splitting
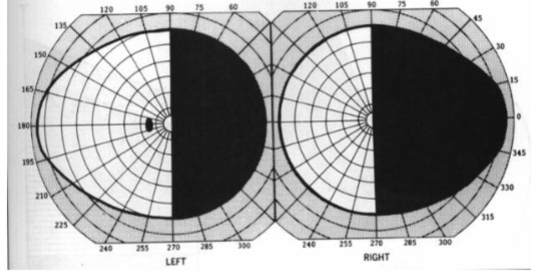
left incomplete congruous homonymous hemianopia
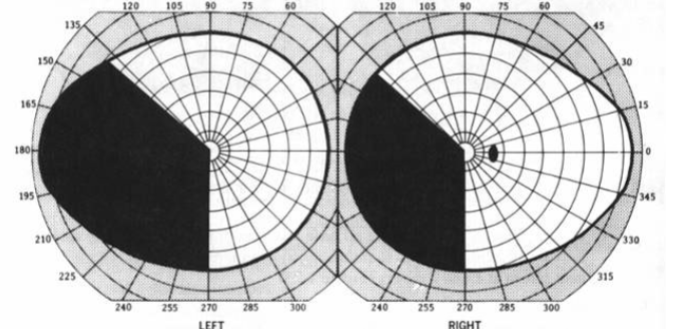
OD double arcuate VF defect, inferior > superior w/ inferior nasal step
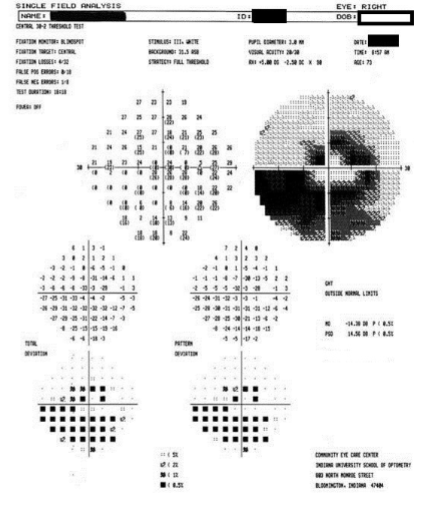
left incomplete incongruous homonymous hemianopia
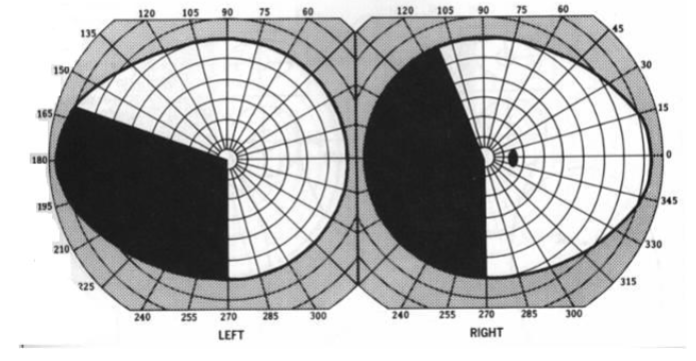
temporal
macular ganglion cells enter the _______ portion of the ONH
nasal
the peripheral nasal ganglion cells enter the _______ portion of the ONH
superior & inferior
the ganglion cell axons temporal to the disc (other than macular fibers) enter the __________ portion of the ONH
reduced VA
light brightness diminished
reduced color perception
RAPD (if unilateral or asymmetric)
VF defect
what are some s/sx of optic neuropathy?
optic neuritis, neuroretinitis, toxic & nutritional optic neuropathies, compressive lesions, optic pit w/ central serous choroidopathy
what are some pathologies that might cause a cecocentral scotoma?
papilledema, peripapillary atrophy (POHS, posterior staphyloma, high myopia)
what are some pathologies that might cause an enlarged blind spot (Seidel scotoma)?
AION, glaucoma, BRAO, RD
what are some pathologies that might cause an altitudinal VF defect?
ipsilateral
temporal fibers from nasal VF pass directly through the optic chiasm to the _______ optic tract
contralateral
nasal fibers from temporal VF pass through the optic chiasm to the ______ optic tract
posteriorly
superior nasal fibers from the inferior VF decussate ________ in the optic chiasm
anteriorly
inferior nasal fibers from the superior VF decussate _________ in the optic chiasm
junctional scotoma
lesion at the anterior chiasm & posterior optic nerve
VF defect: unilateral temporal or ipsilateral central scotoma & contralateral superior temporal defect
fixation
where do chiasmal VF defects originate?
vertical
chiasmal VF defects respect which meridian?
T
T/F: an optic tract lesion may produce a greater VF defect in the contralateral eye & a mild RAPD compared w/ a chiasmal lesion
ONH drusen, tilted optic discs, ON hypoplasia
what are some pathologies that can cause pseudo-bitemporal hemianopia?
T
T/F: when the optic tract is damaged, 6-9mo later optic atrophy can be seen at the disc
eye w/ the temporal VF defect
if an optic tract lesion causes an APD, which eye will it be in?
bow tie/band optic atrophy
occurs w/ damage to crossing fibers
lesion in the optic chiasm or optic tract
retrograde atrophy w/ cell death
decreased pain sensation, contralateral body weakness
what are some systemic s/sx that may accompany VF defects w/ damage to the LGN?
F
T/F: there will be an APD w/ an LGN lesion
anterior choroidal artery & posterior choroidal artery
what supplies blood to the LGN?
keyhole defect/sector-sparing homonymous hemianopia
VF defect that can result from an anterior choroidal artery occlusion
respects the vertical meridian
homonymous horizontal sectoranopia (incomplete hemianopia)
VF defect that can result from a posterior choroidal artery occlusion
respects the vertical meridian
points to fixation
Meyer’s loop
formed by the inferior fibers from superior VF coursing anteriorly around the lateral ventricle from LGN to the temporal lobe
incomplete homonymous hemianopia or superior homonymous quadrantanopia
what type of VF defects can result from a lesion to the optic radiations in the temporal lobe?
unusual taste/smell, hallucinations, seizures, dysphasia, anomia
what are some systemic s/sx that can accompany VF defects from a temporal lobe lesion?
posteriorly
superior fibers from the inferior VF course _________ from the LGN into the parietal lobe
complete or incomplete homonymous hemianopia
what VF defect is created from a lesion to the optic radiations in the parietal lobe?
inferior
if the VF defect from a lesion to the parietal lobe optic radiations is incomplete, which side is denser?
seizures, loss of tactile discrimination, hypotonia, ataxia
what are some systemic s/sx that can accompany VF defects seen in parietal lobe lesions?
altitudinal
if there is a quadrantanopia from an occipital lobe lesion, it may be _________ if bilateral
there is dual arterial supply to the macular cortex
macular fibers project to both hemispheres
what are the theories behind macular sparing vs macular splitting in occipital lobe lesions?
the parietal lobe contains visual association area for directing smooth eye movements
explain why OKR and OKN are disrupted w/ a parietal lobe lesion?
towards
a disruption in OKR and OKN will occur when the target moves ______ the side of the parietal lobe lesion
normal
describe the OKN with an occipital lobe lesion
cecocentral scotoma
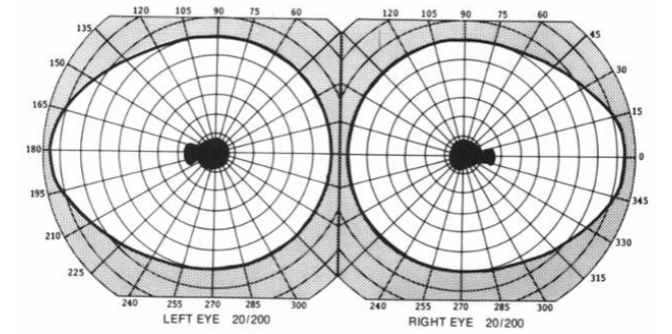
enlarged blindspot

altitudinal VF defect
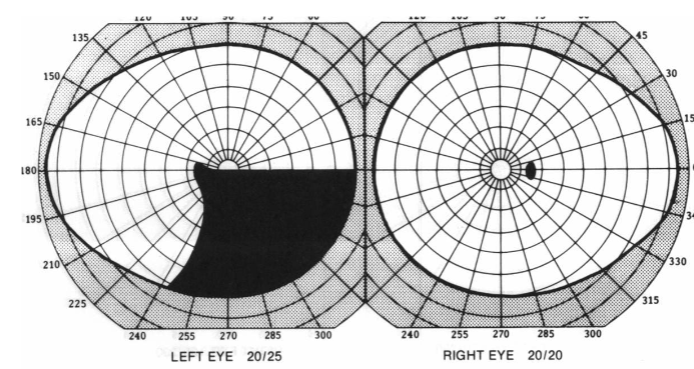
junctional scotoma
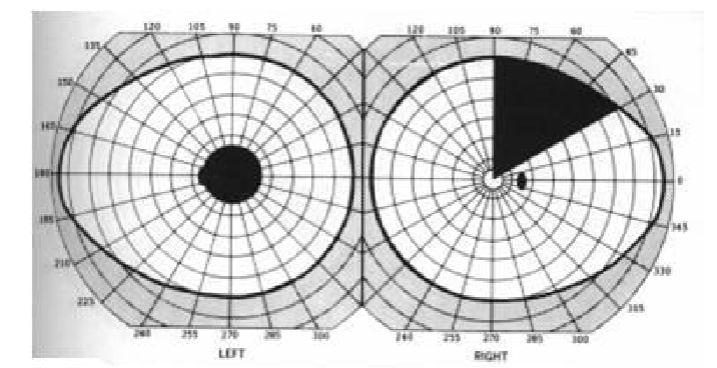
bitemporal hemianopia
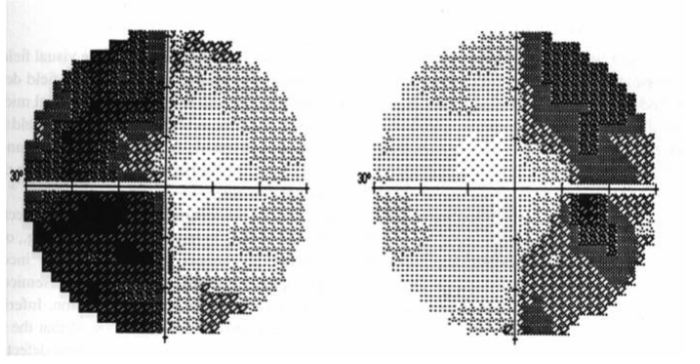
pseudo-bitemporal hemianopia
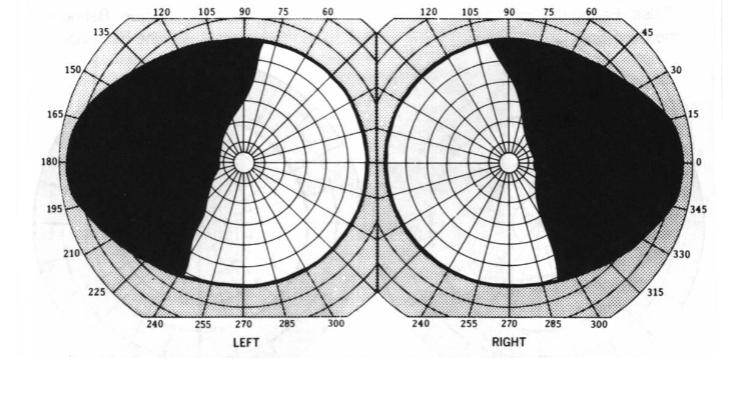
left incomplete incongruous homonymous hemianopia
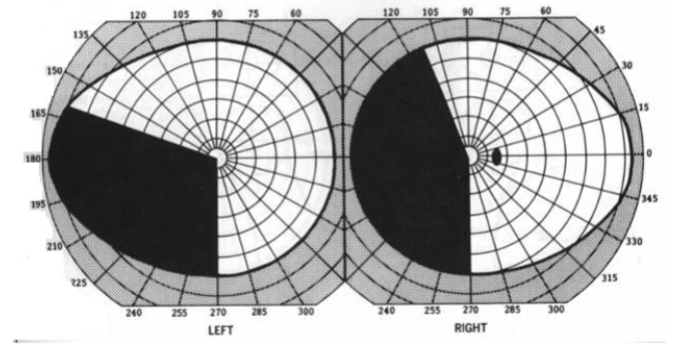
sector-sparing homonymous hemianopia (keyhole defect)
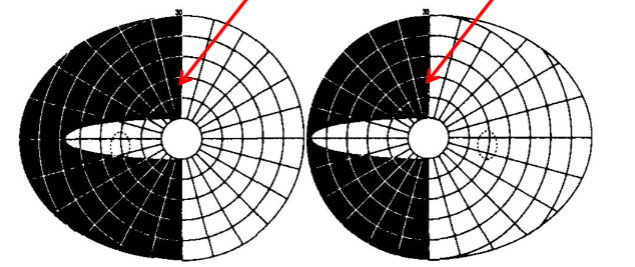
homonymous horizontal sectoranopia
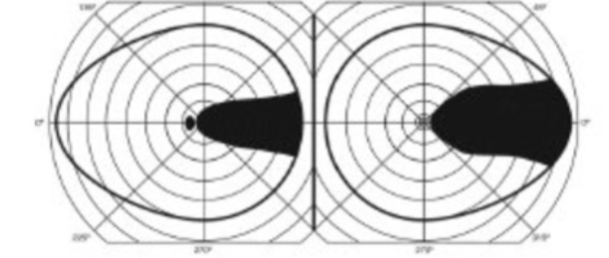
right incongruous homonymous superior quadrantanopia
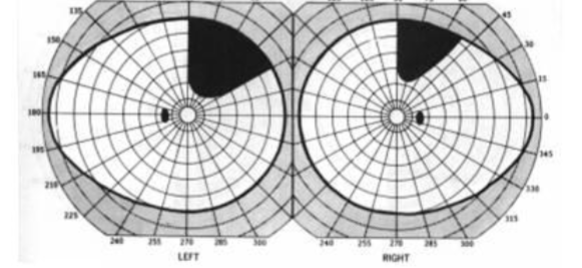
left incomplete homonymous quadrantanopia, denser inferior (incomplete left inferior quadrantanopia)
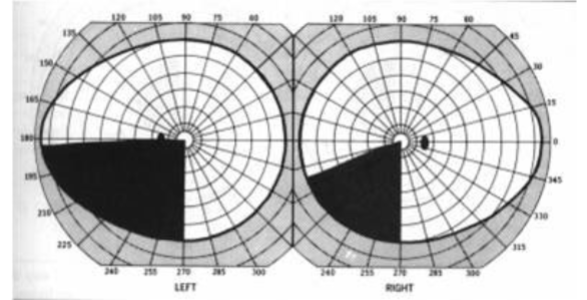
left incomplete congruous homonymous hemianopia w/ macular sparing