MCAT Biochemistry Chapter 7- RNA and the Genetic Code
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
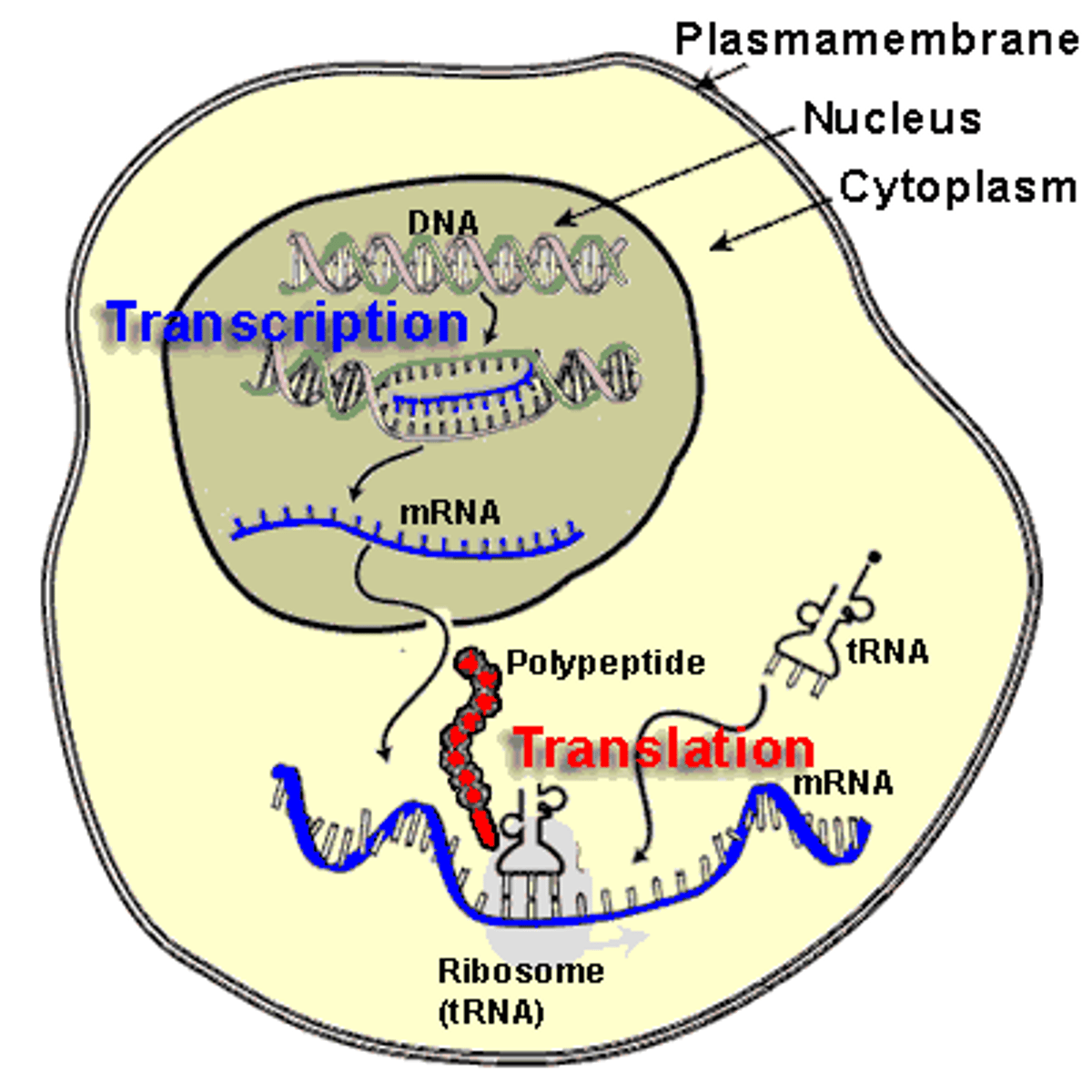
Central Dogma
transfer of genetic information
DNA-->RNA-->proteins
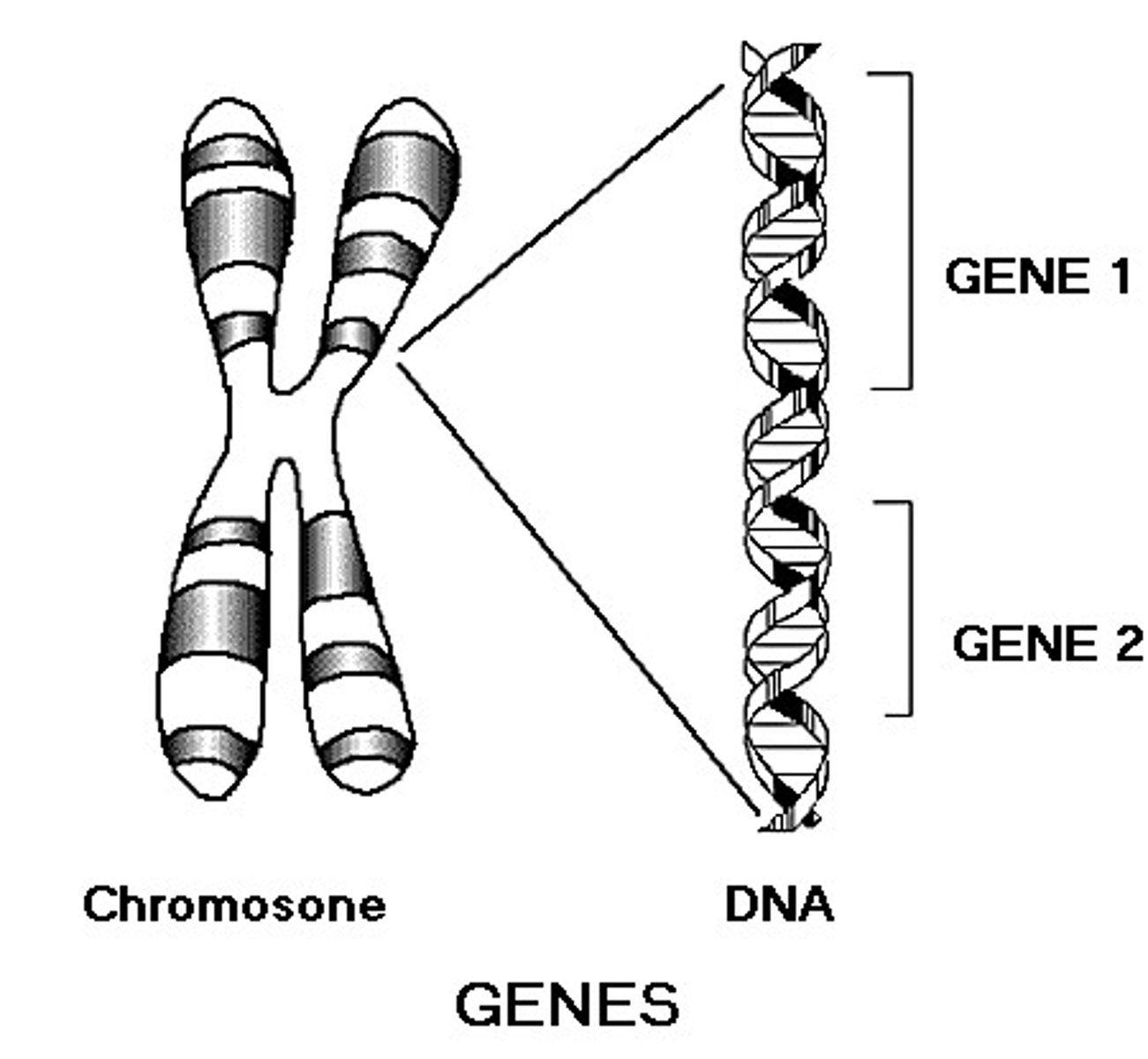
Gene
unit of DNA on a chromosome that is encoded with the instructions for a single protein or RNA, and expressed in transcription and translation
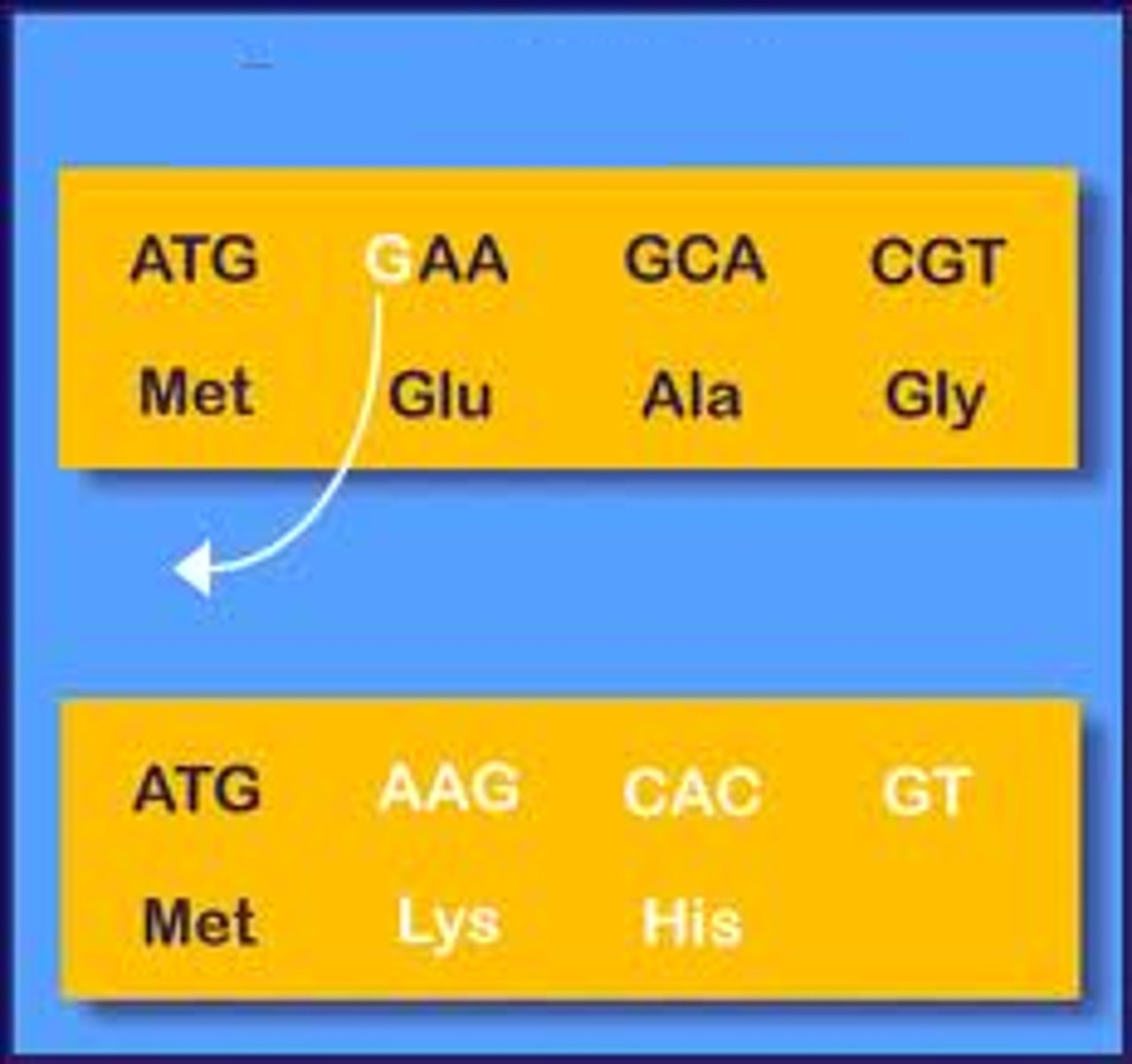
Degenerate code
- genetic code
- more than 1 codon can specify a single AA (except Met and Try)
- allows for mutation in DNA that doesn't always result in altered protein structure or fucntion
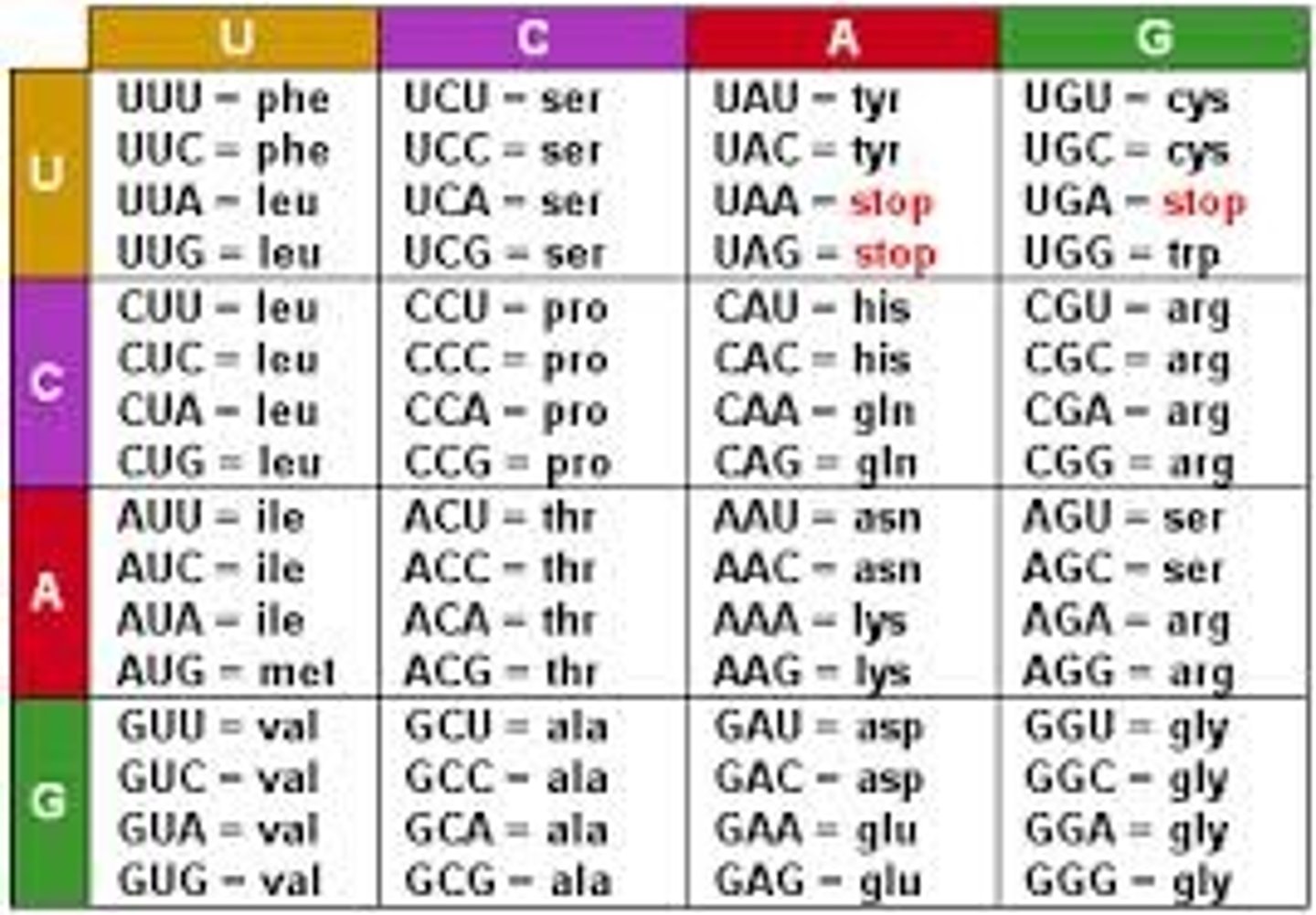
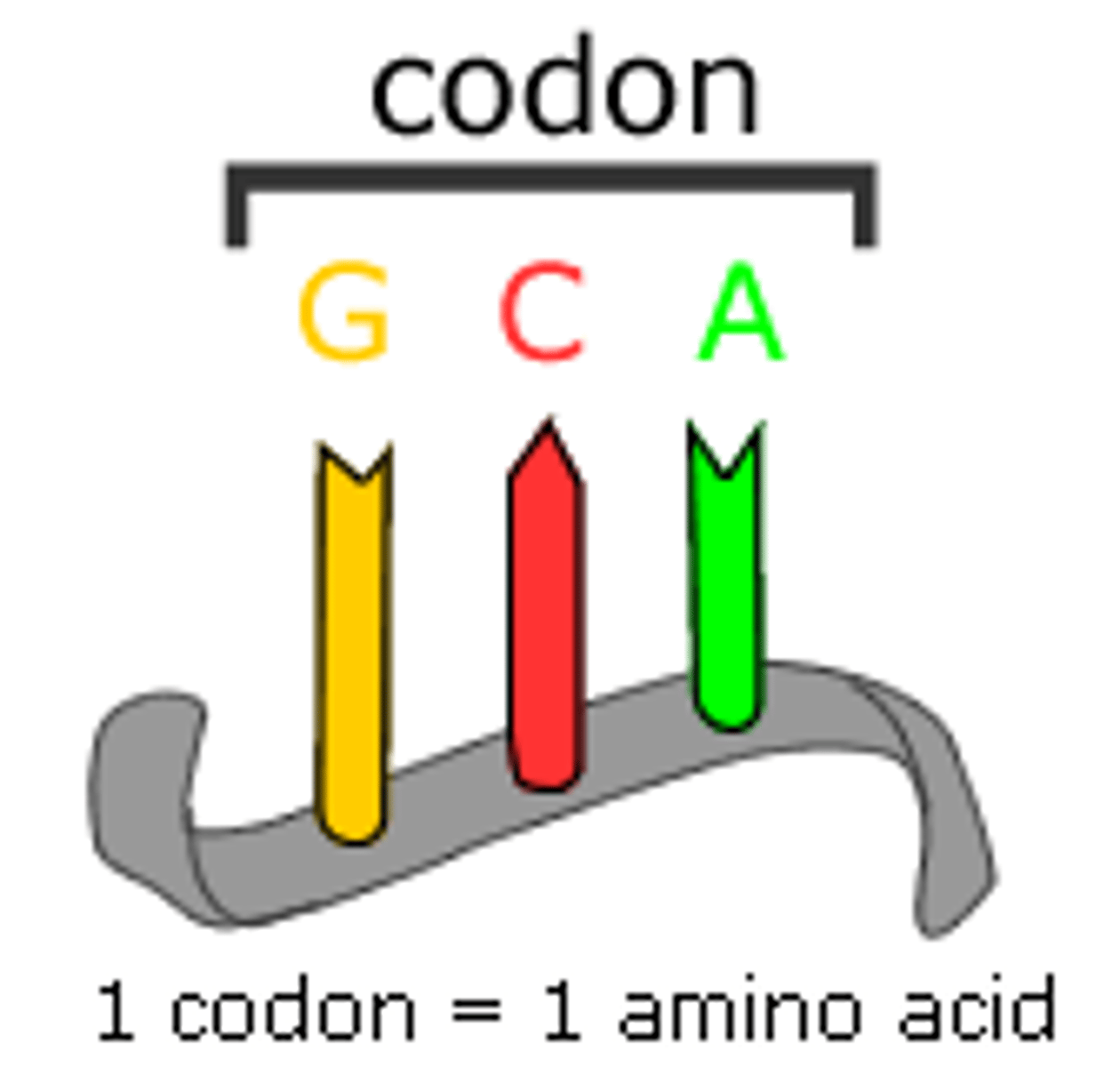
codon
read in three nucleotide segments to translate into aa
- 64 codons possible (61 codon for 20 aa; 3 codons for termination of translation - UAA, UAG, UGA)
- 5' to 3'
- 1 codon = 1 aa
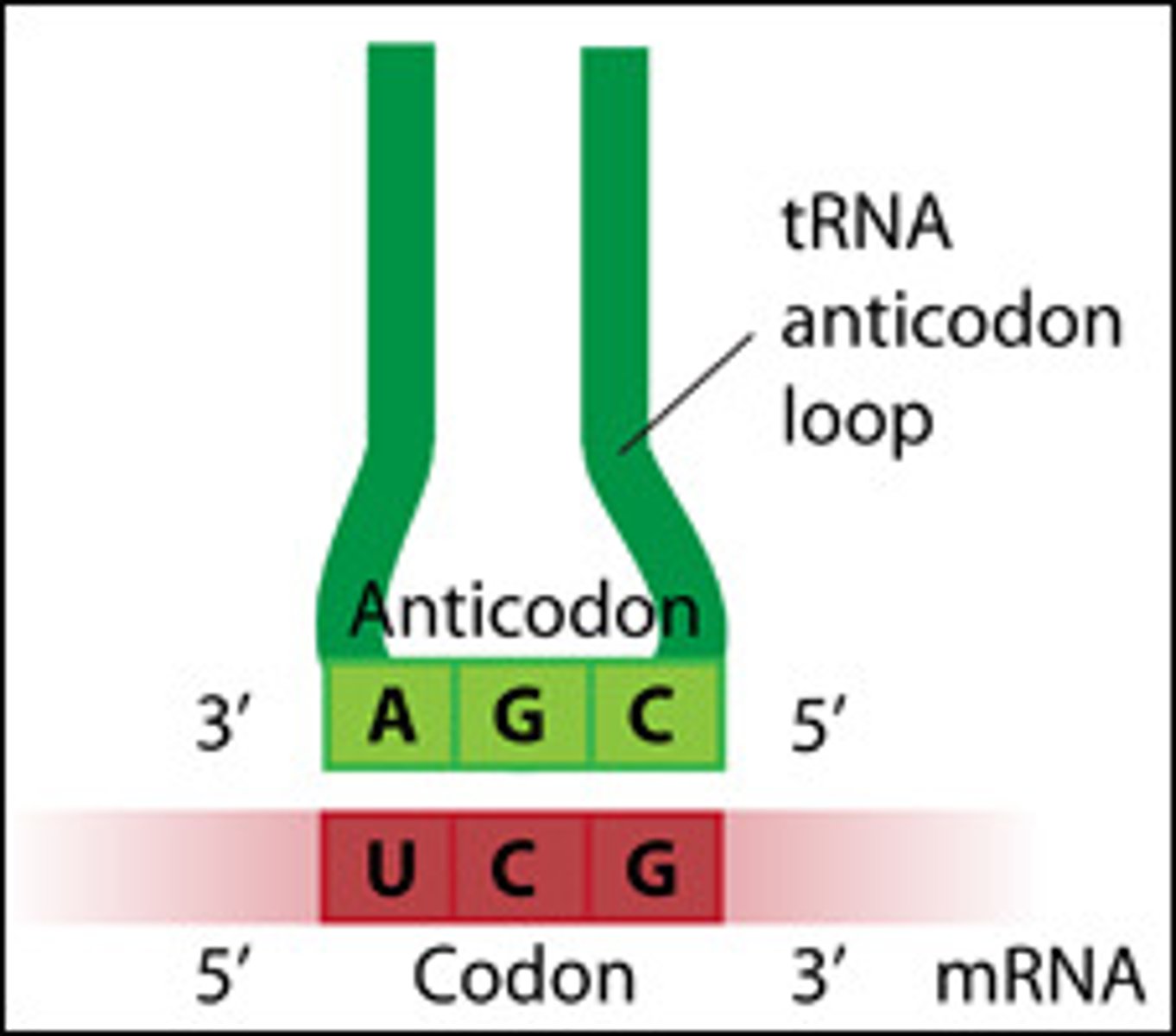
Anticodon
codon on tRNA, recognized by complementary mRNA
codon of mRNA is recognized by a complementary anticodon on a tRNA
Start codon
AUG (methionine)

Stop codons
UGA, UAA, UAG
mnemonic
UAA = U are annoying
UGA = U go away
UAG = U Are Gone

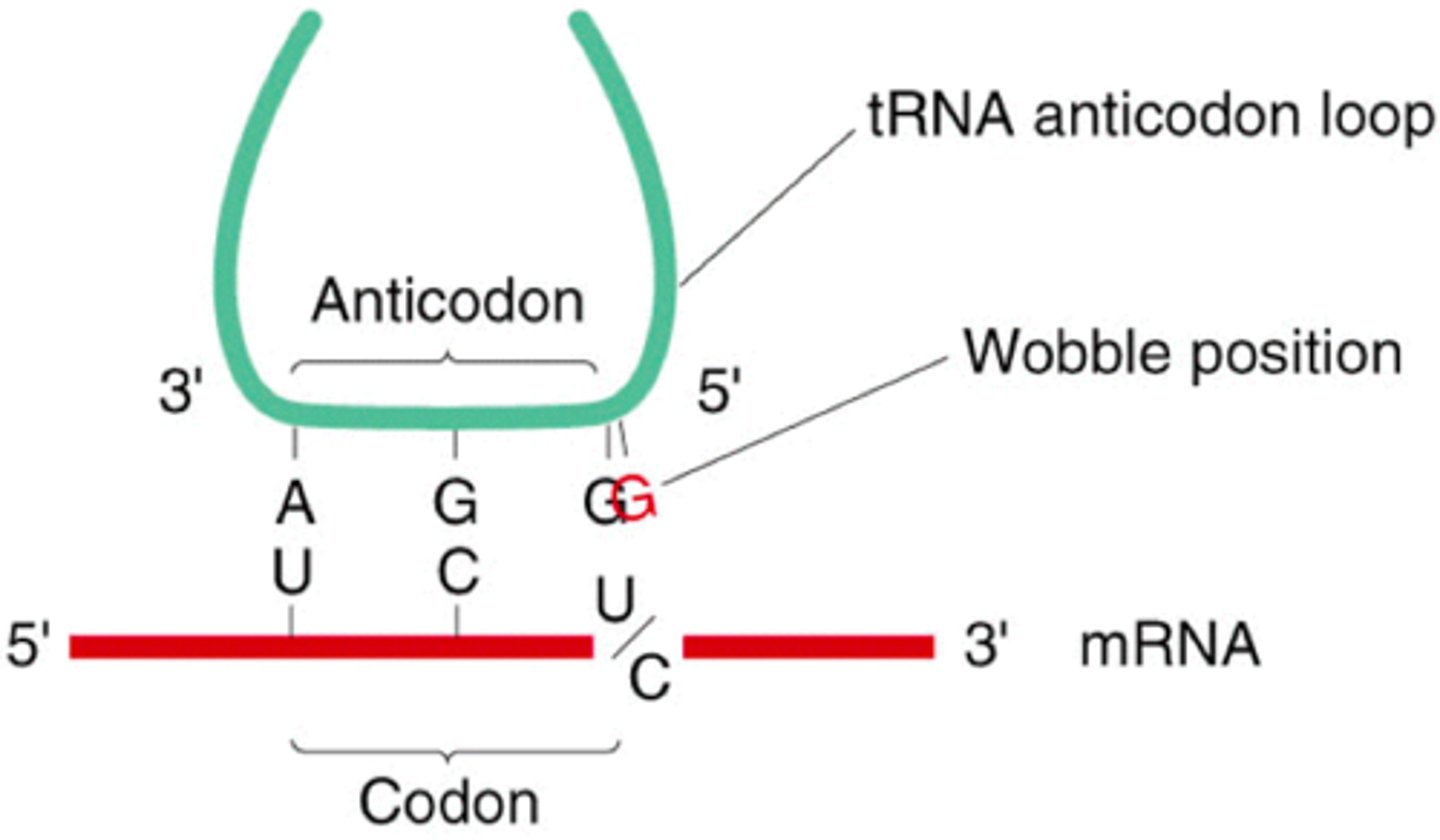
Wobble position
- third base in the codon is variable (1st and 2nd = same)
-an evolutionary development designed to protect against mutations in the coding region of our DNA
- mutation in wobble position = silent or degenerate = no effect on express of AA or polypeptide sequence
Point mutation
nucleotide changed in a codon = missense or nonsense mutation
- expressed mutations
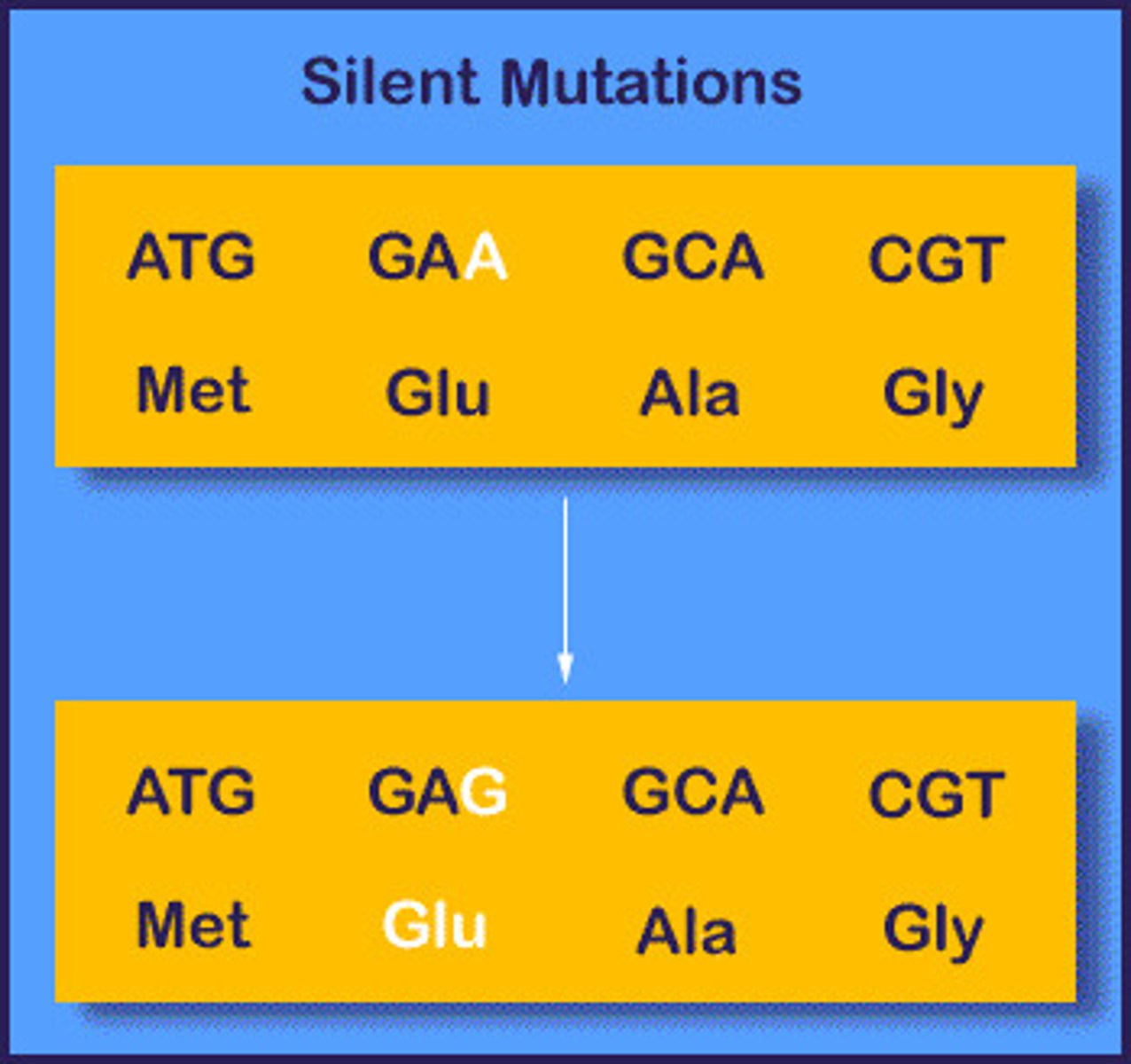
Silent mutation
no effect on protein synthesis
1 nt change --> same codon
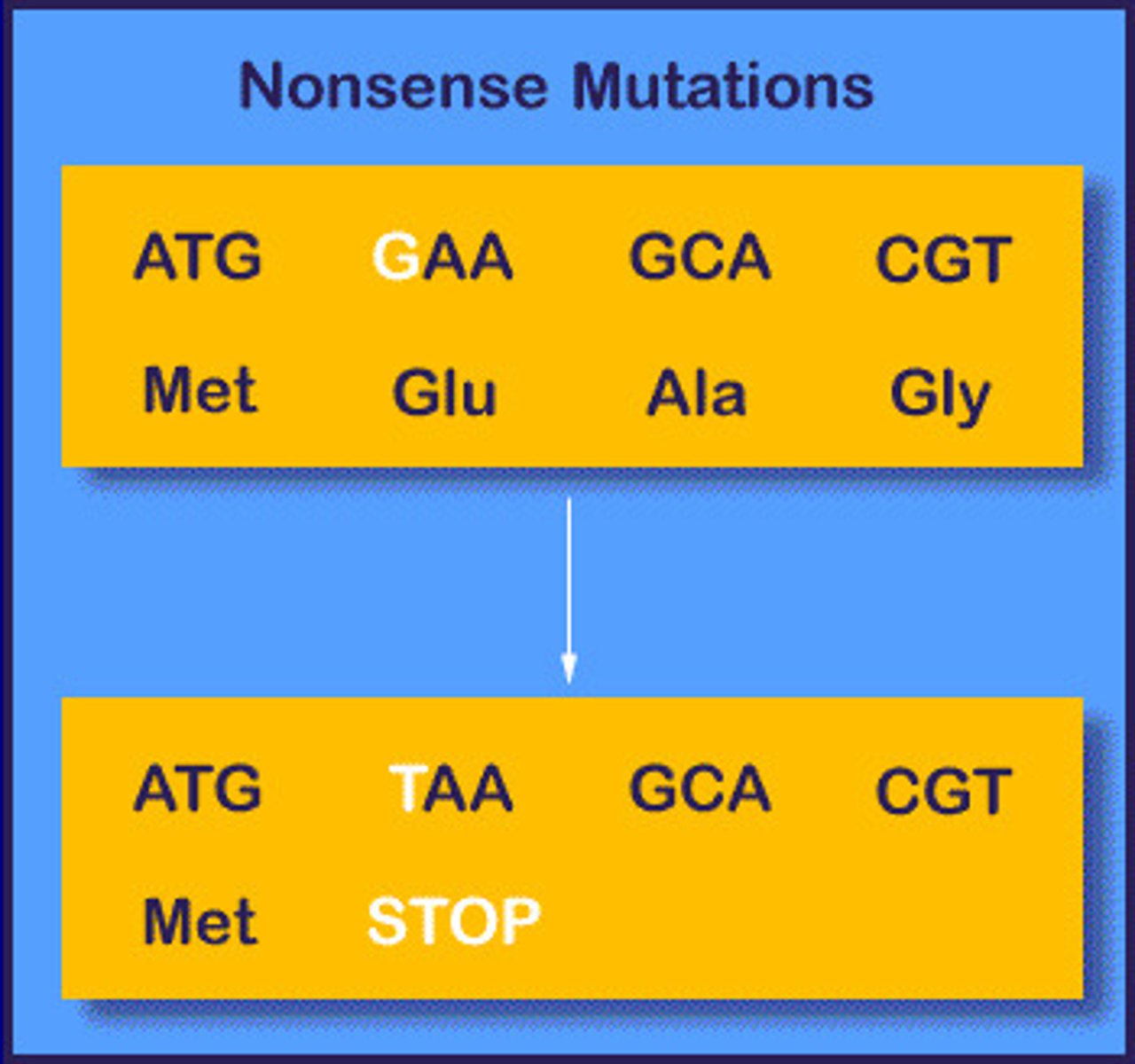
Nonsense mutation (truncation mutation)
produce a premature stop codon
1 nt change --> stop codon
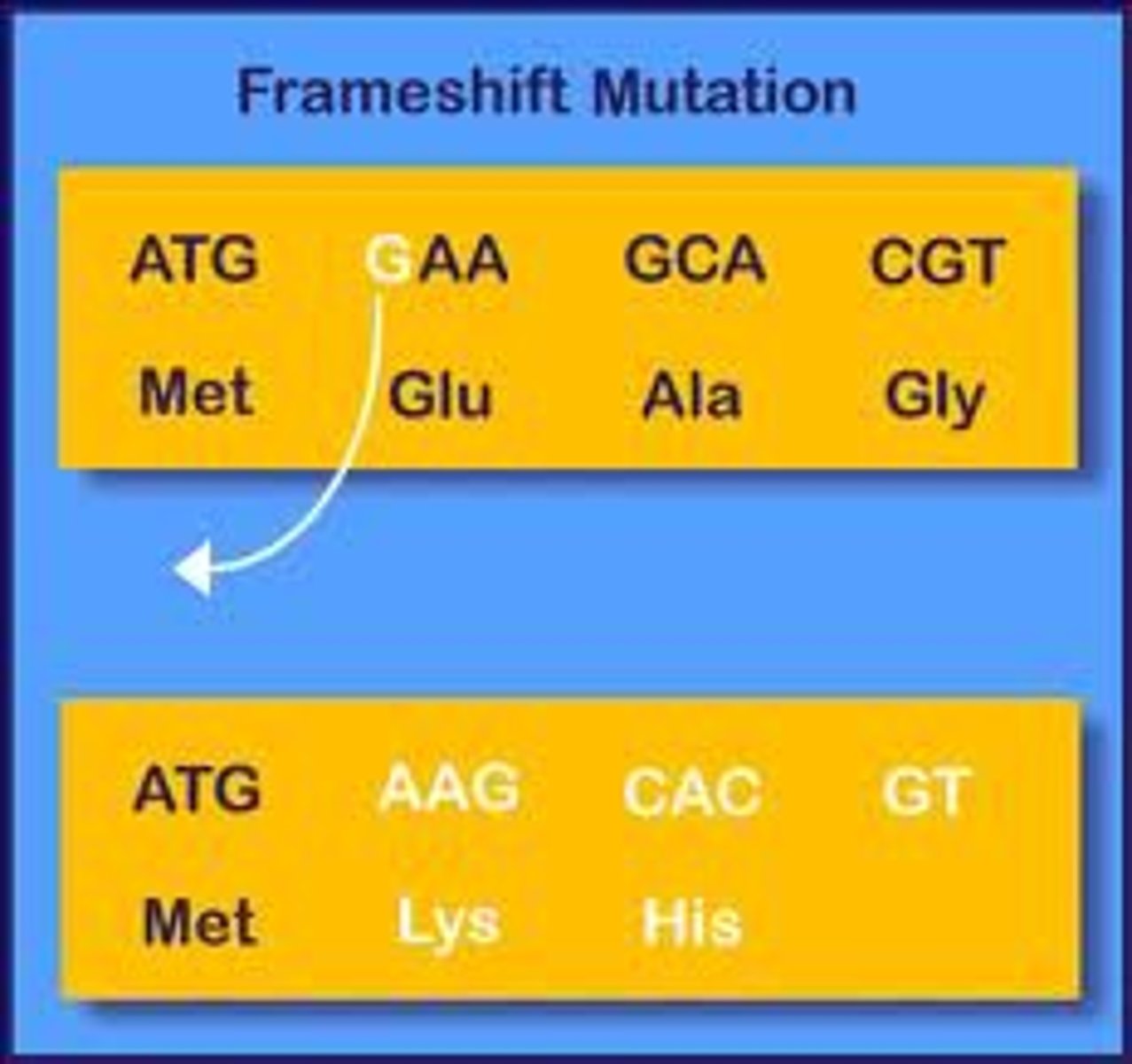
Frameshift mutation
result from nucleotide addition or deletion, and change the reading frame of subsequent codons
- insertion or deletion = shift RF --> changes in aa sequence or premature truncation of protein
- more serious than point mutation
- heavily dependent on where within DNA sequence mutation occured
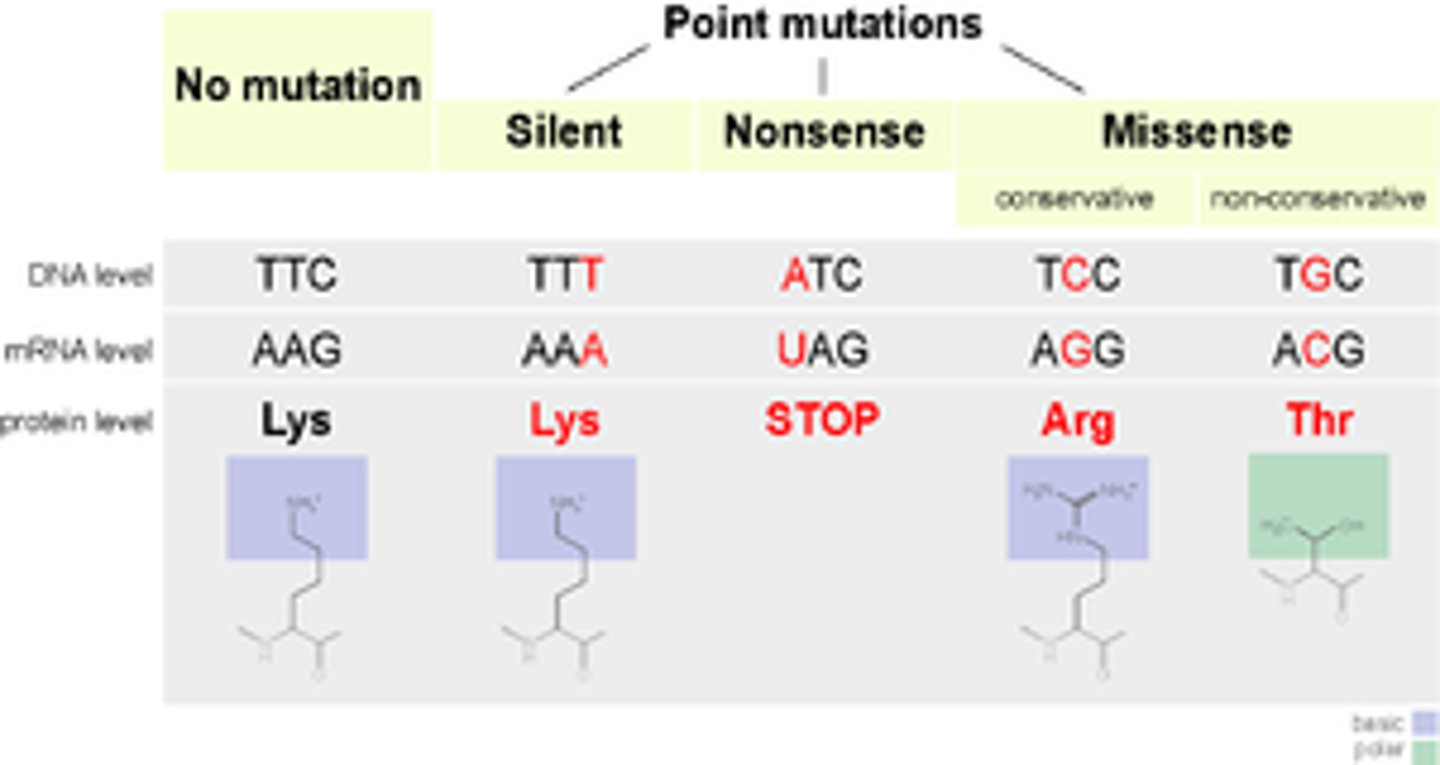
Missense mutation
produce a codon that codes for a different amino acid
1 nt change --> differ AA --> differ codon
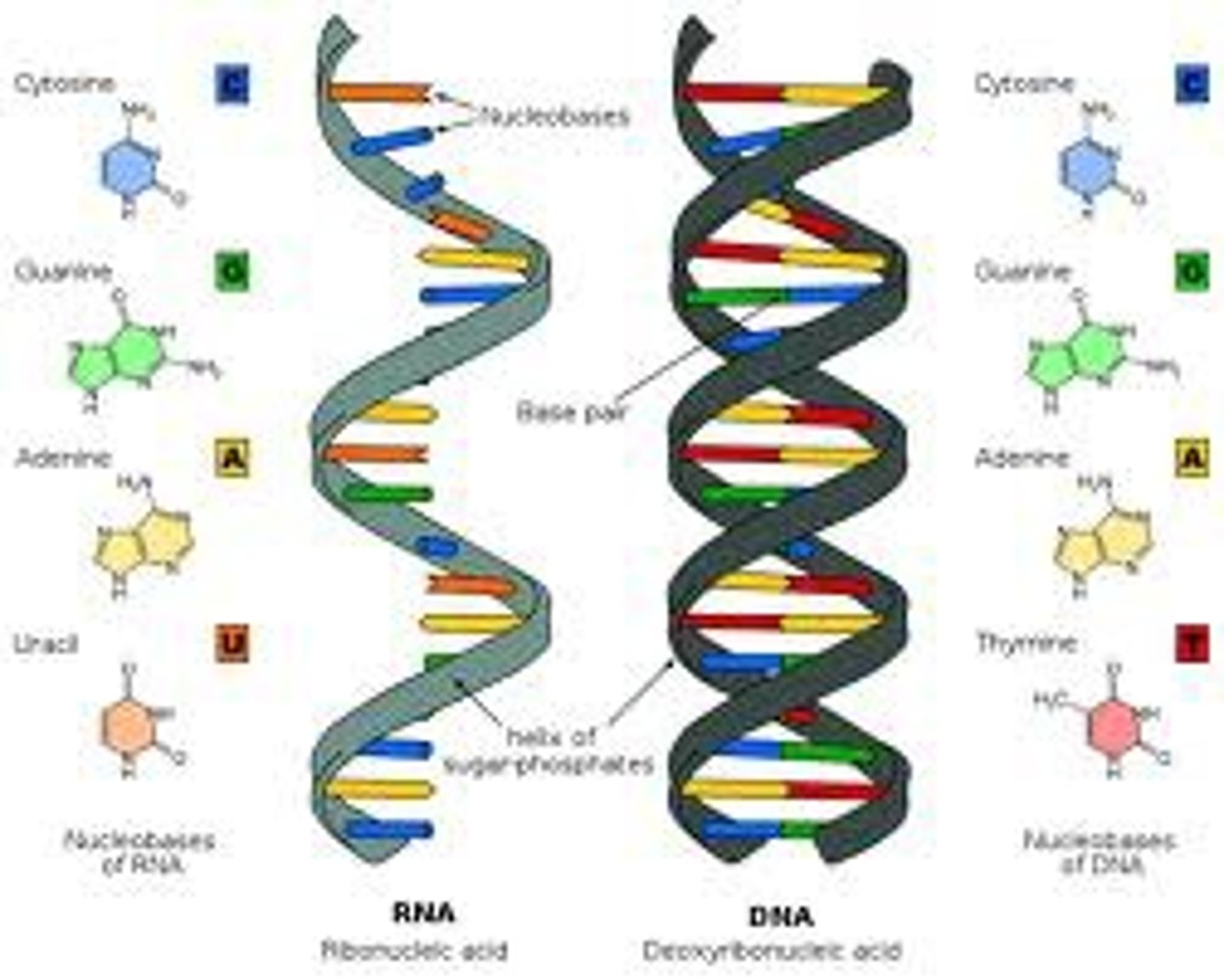
Differences between RNA and DNA
-substitution of a ribose sugar for deoxyribose
-substitution of uracil for thymine
-single-stranded instead of double-stranded
Three types of RNA
mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
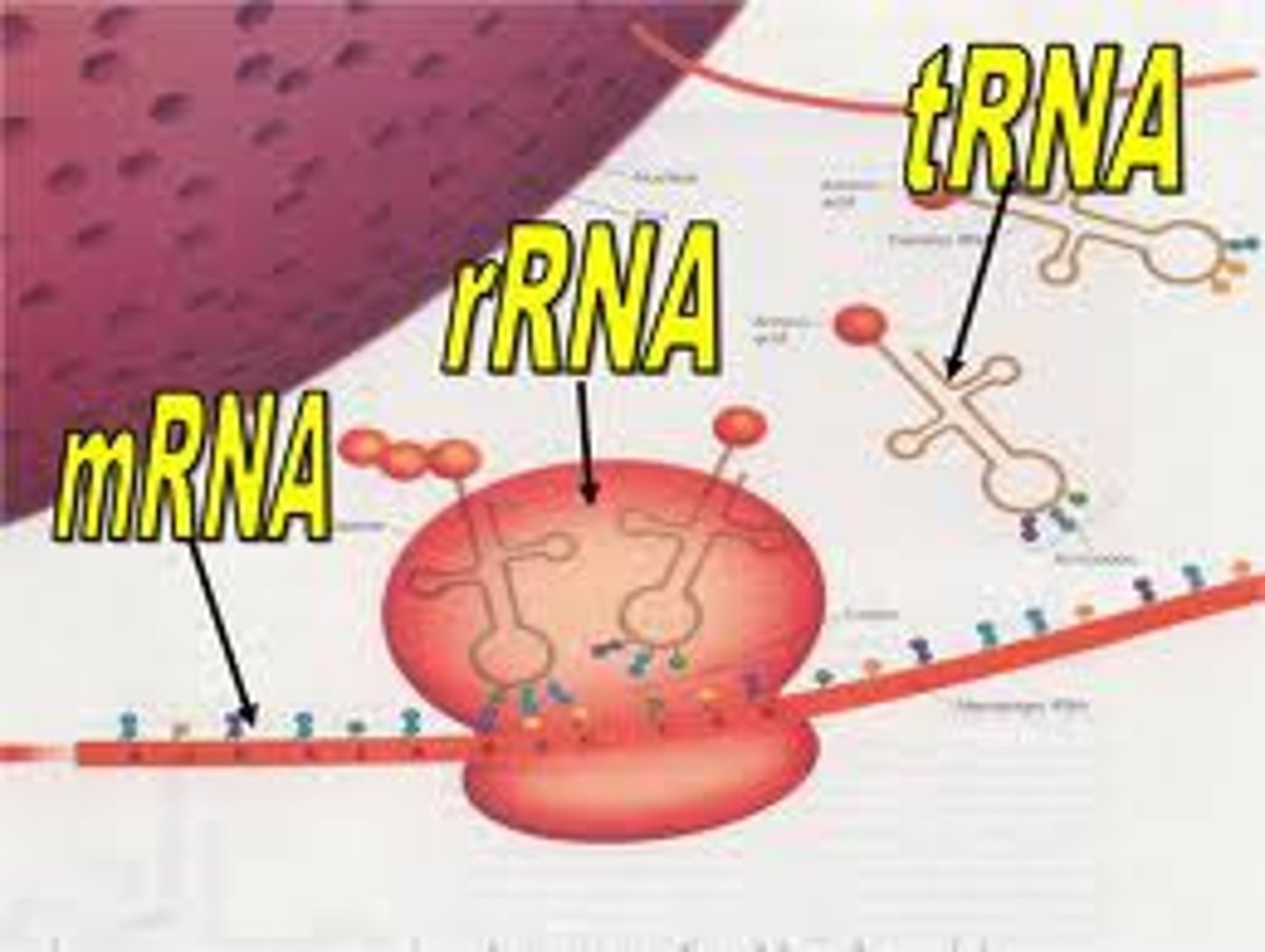
mRNA
-messenger RNA
-carries the message from DNA in the nucleus via transcription of the gene; travels into the cytoplasm to be translated
- syn mRNA strand is anitparallel and complementary to DNA template strand
- transcribed from DNA template by RNAP in cycles --> posttranscriptional modifications --> leave nucleus
- euk = monocistronic = each mRNA molecule translate into only one protein product
- prok = polycistronic = thousand of differ proteins made
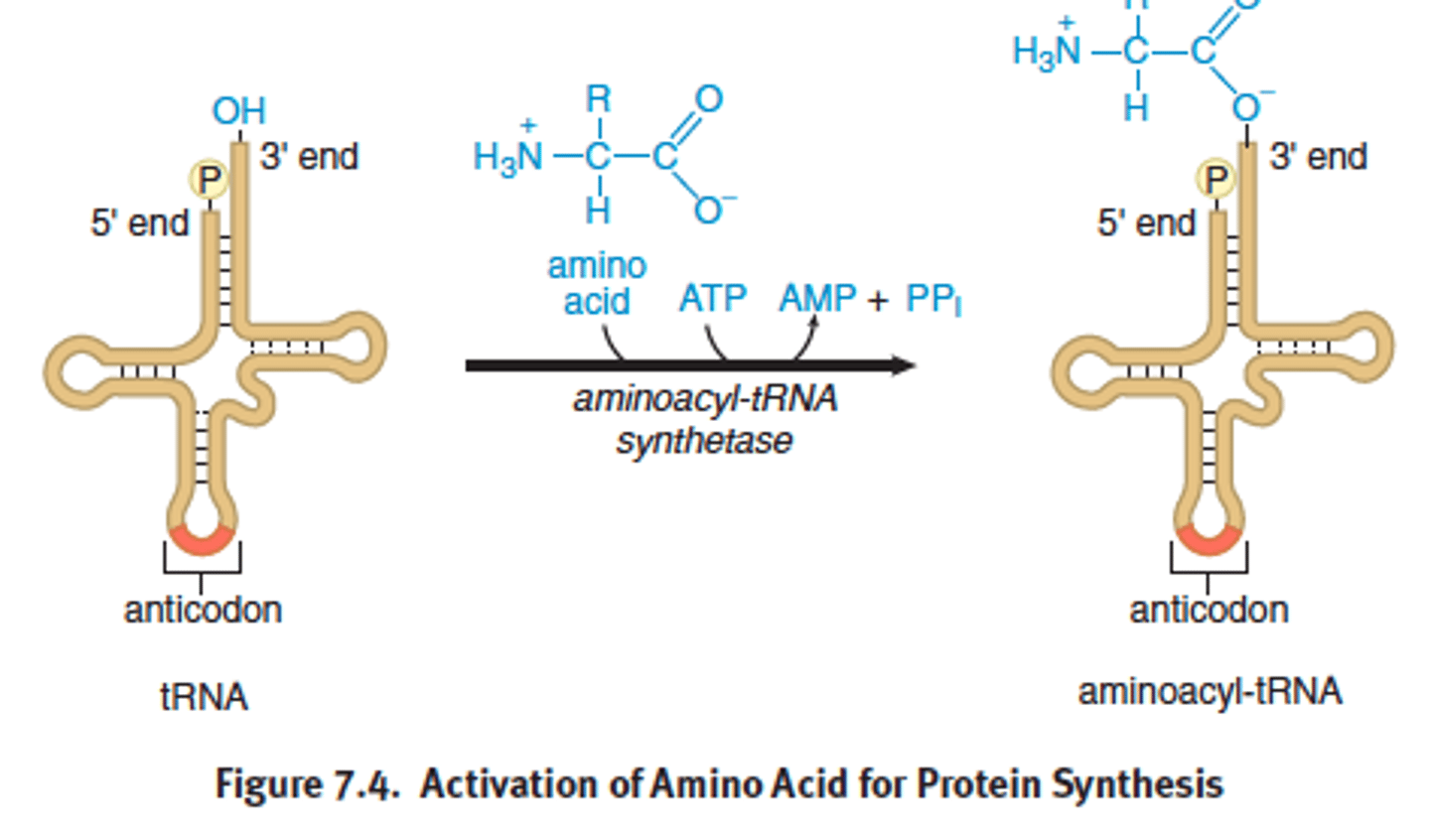
tRNA
-transfer RNA
-brings in amino acids, recognizes the codon on the mRNA using its anticodon and antiparallel
- converts nucleic acids to aa and peptides
- charged/activated by aa attaching to 3' OH + aminoacyl-tRNA synthase + ATP
- anticodon recognizes and pairs with appreciate codon on mRNA molecule while in the ribosome
- mature tRNA are in cytoplasm
- aa activated by differ aminoacyl-tRNA synthase
- each tRNA has a CCA nuclotide sequence where the aa binds
- aa-tRNA bond will be used to supply the energy needed to create a peptide bond during translation
rRNA
-ribosomal RNA
- ribozymes = made of RNA molecules
-enzymatically active
-synthesized in nucleous
- help catalyze the formation of peptide bonds and splicing introns in nucleus
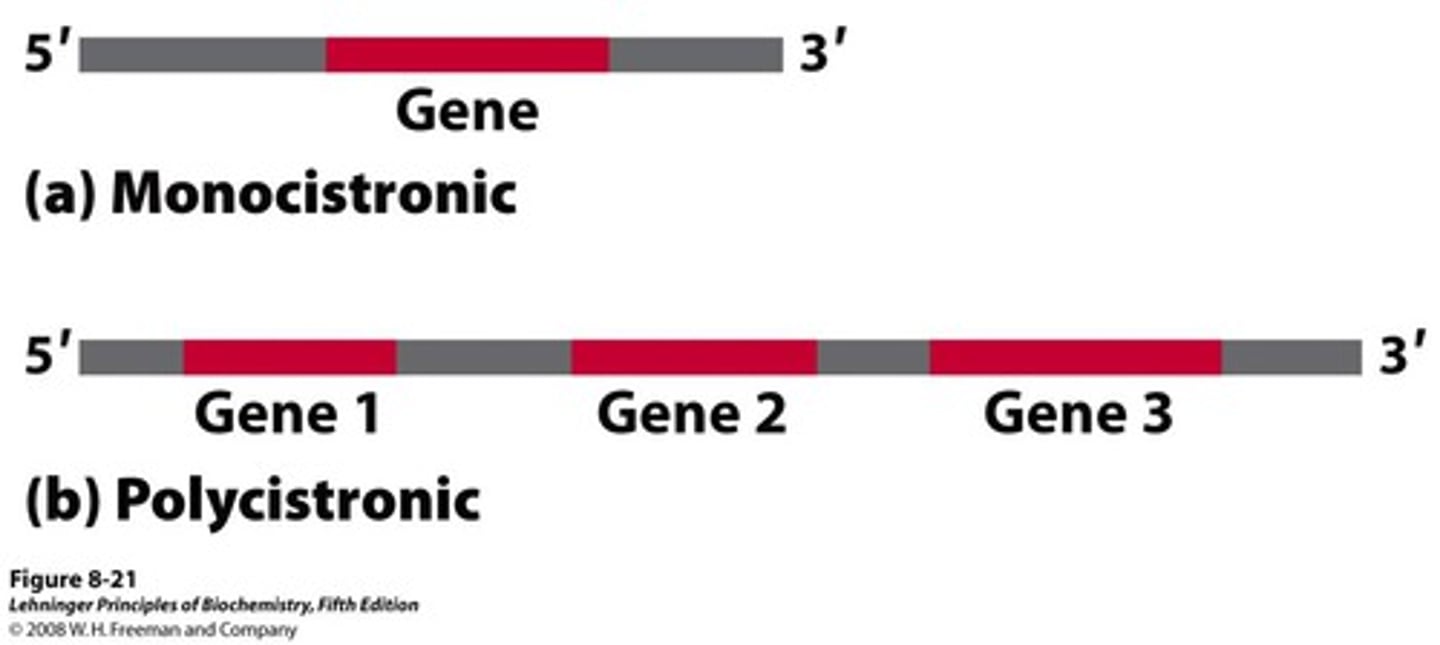
Monocistronic
each mRNA molecule translates into only one protein product
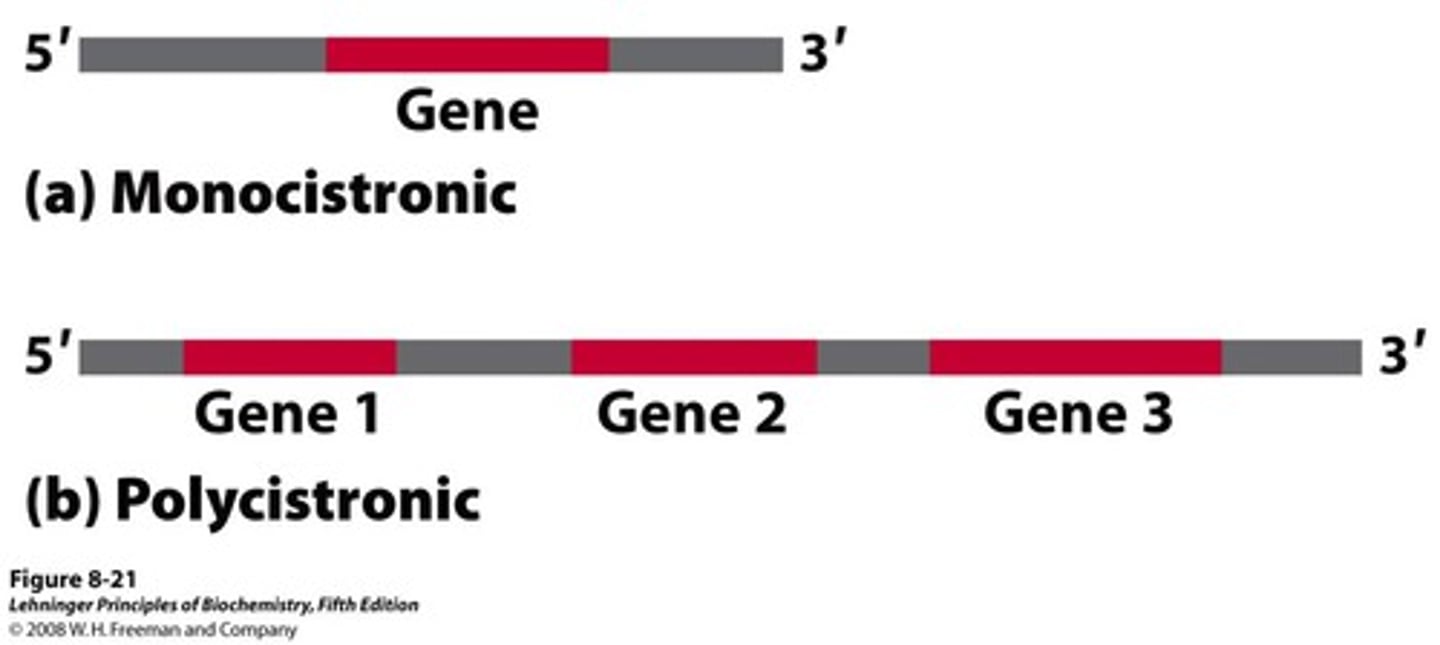
Polycistronic
starting the process of translation at different locations in the mRNA can result in different proteins
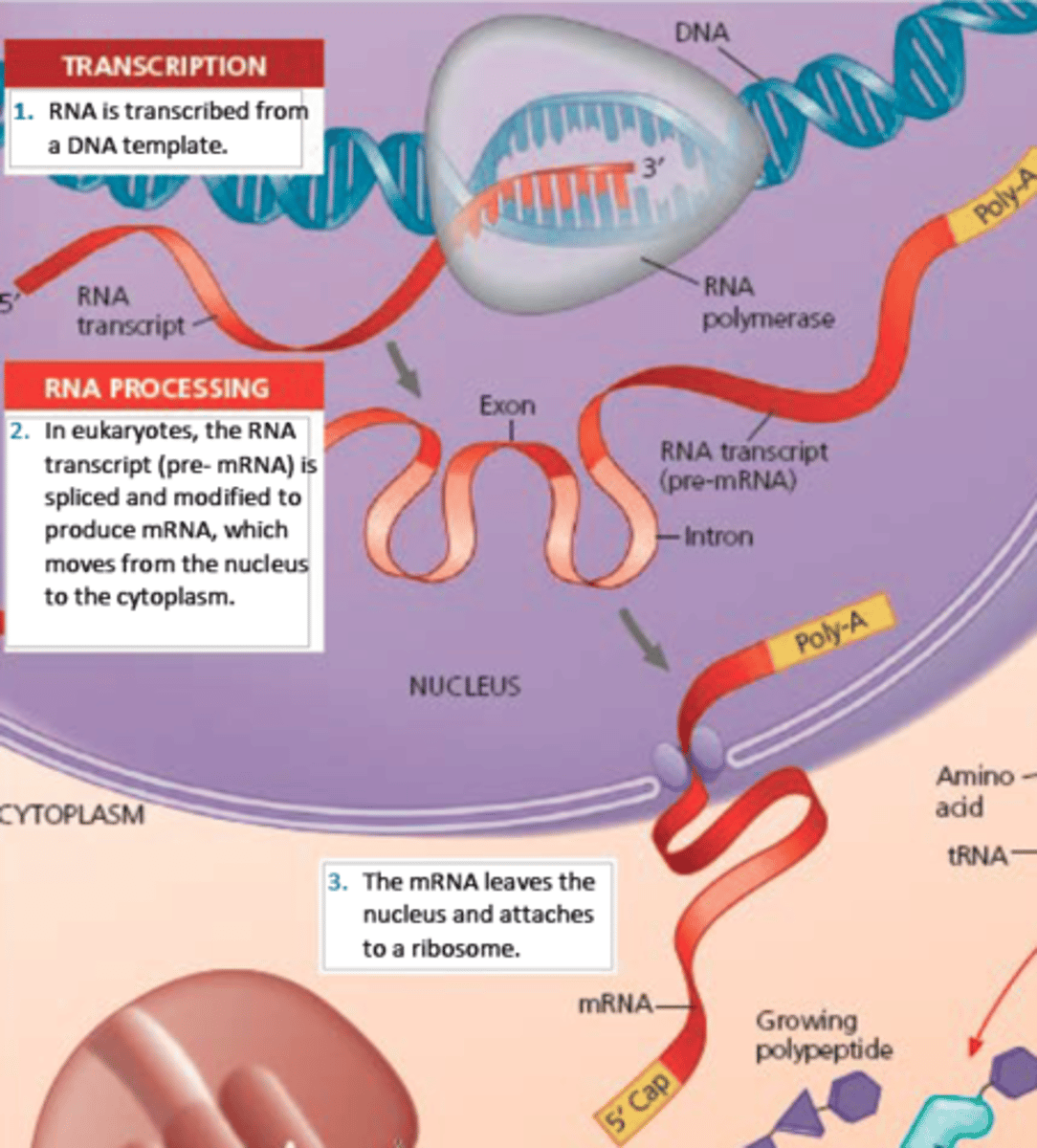
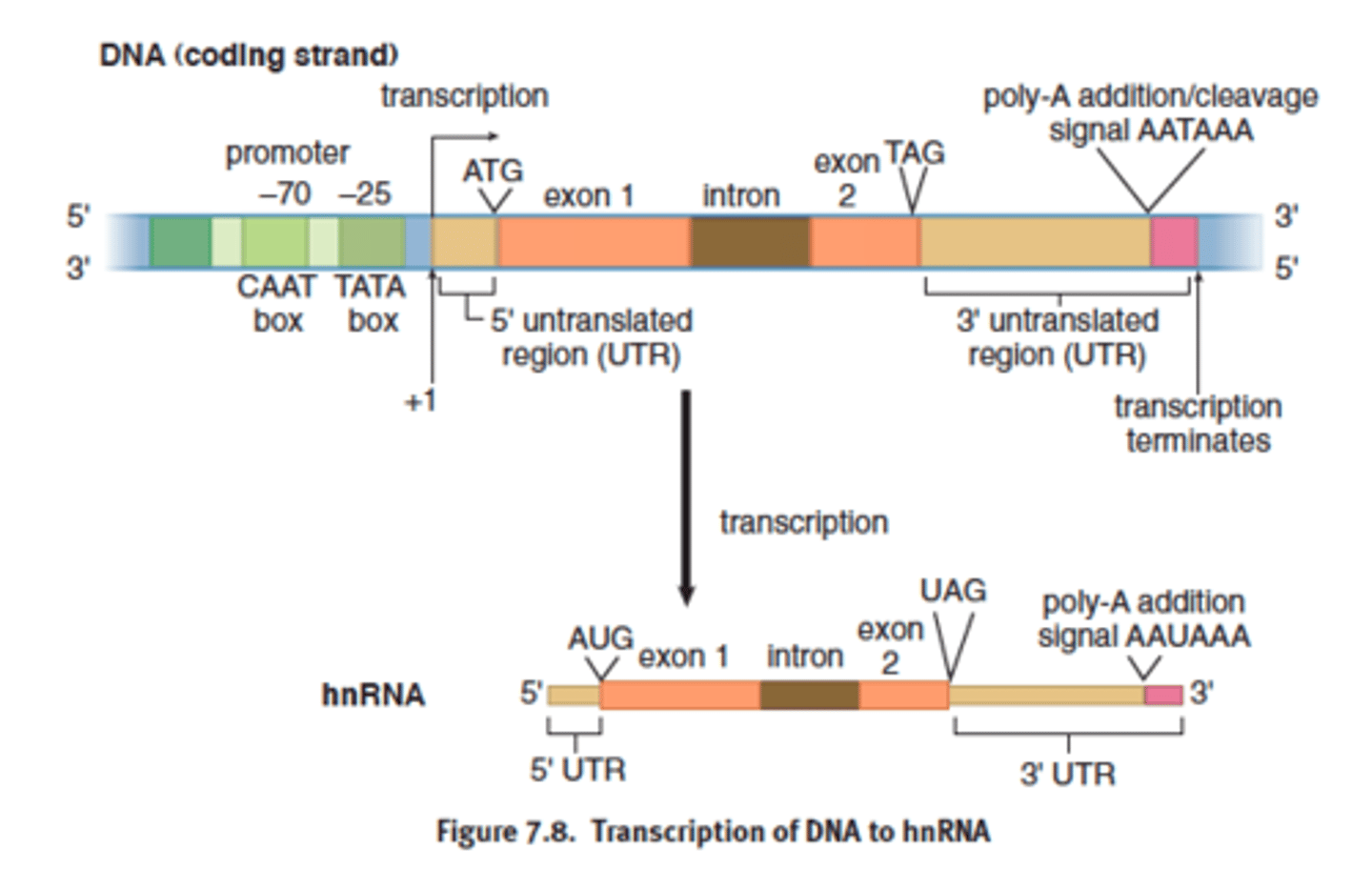
Transcription
the creation of mRNA from a DNA template
we transcribe information, we
use the same language to write it
down
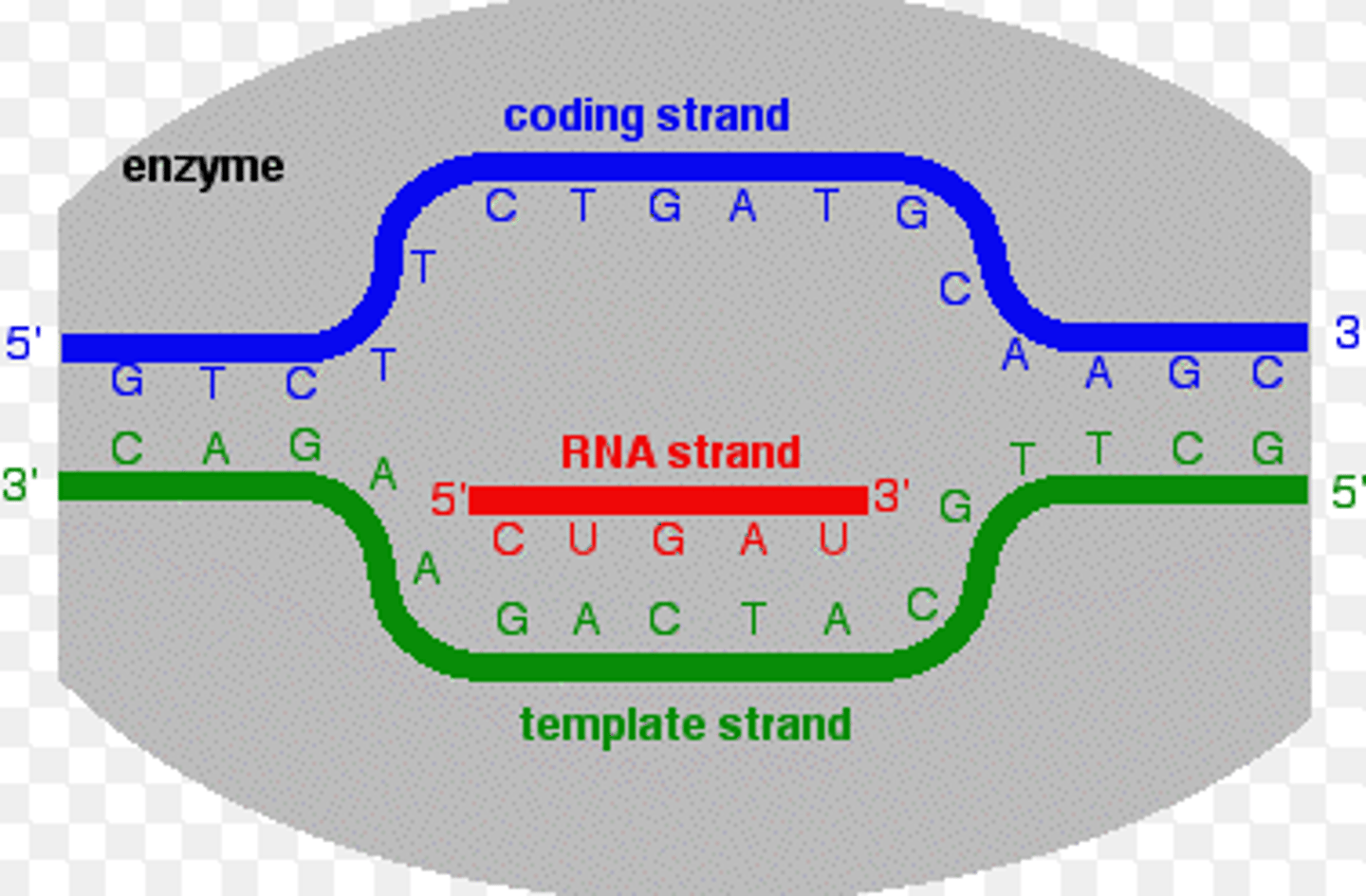
Template strand
-aka antisense strand
-used to synthesize the single strand of mRNA
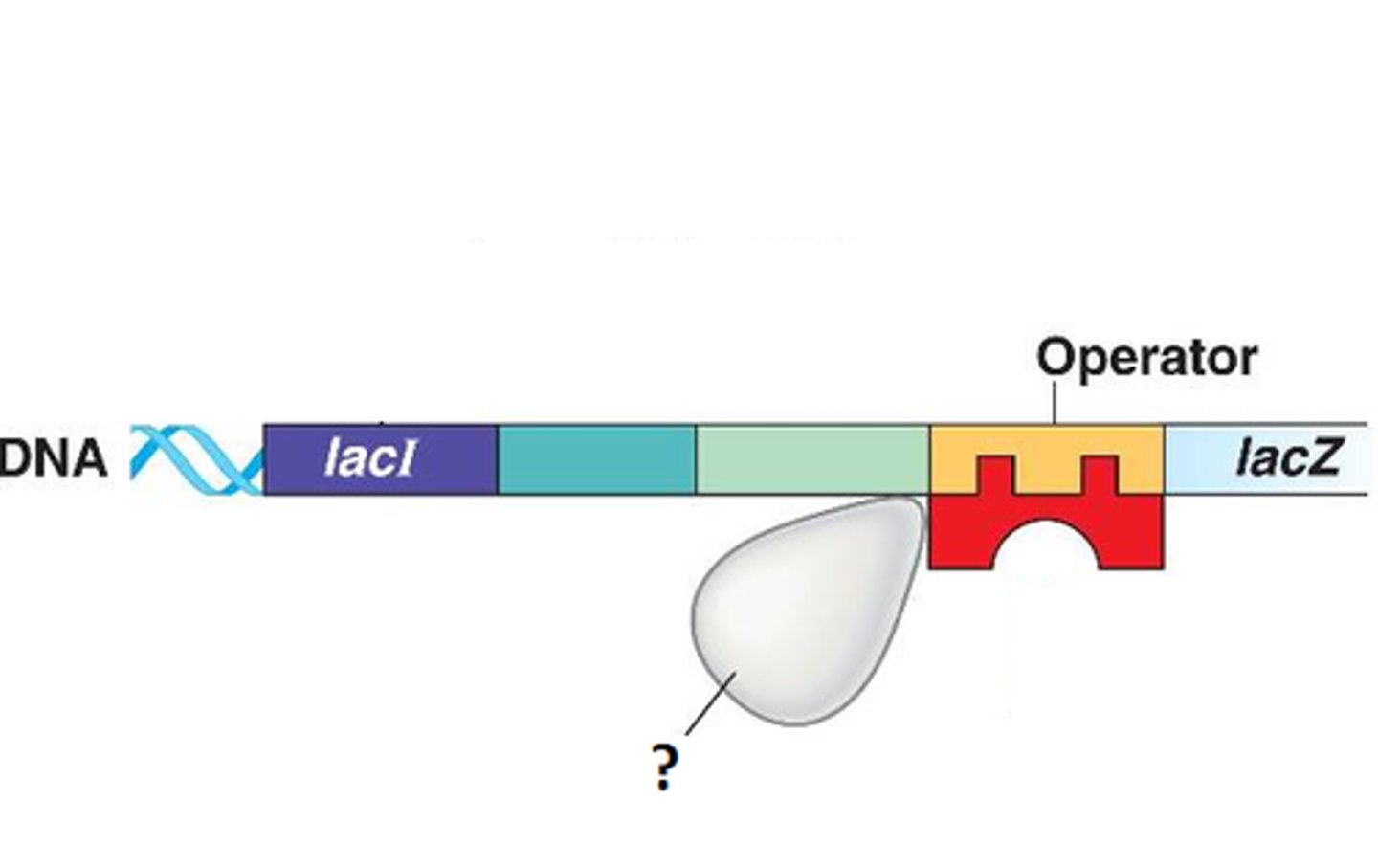
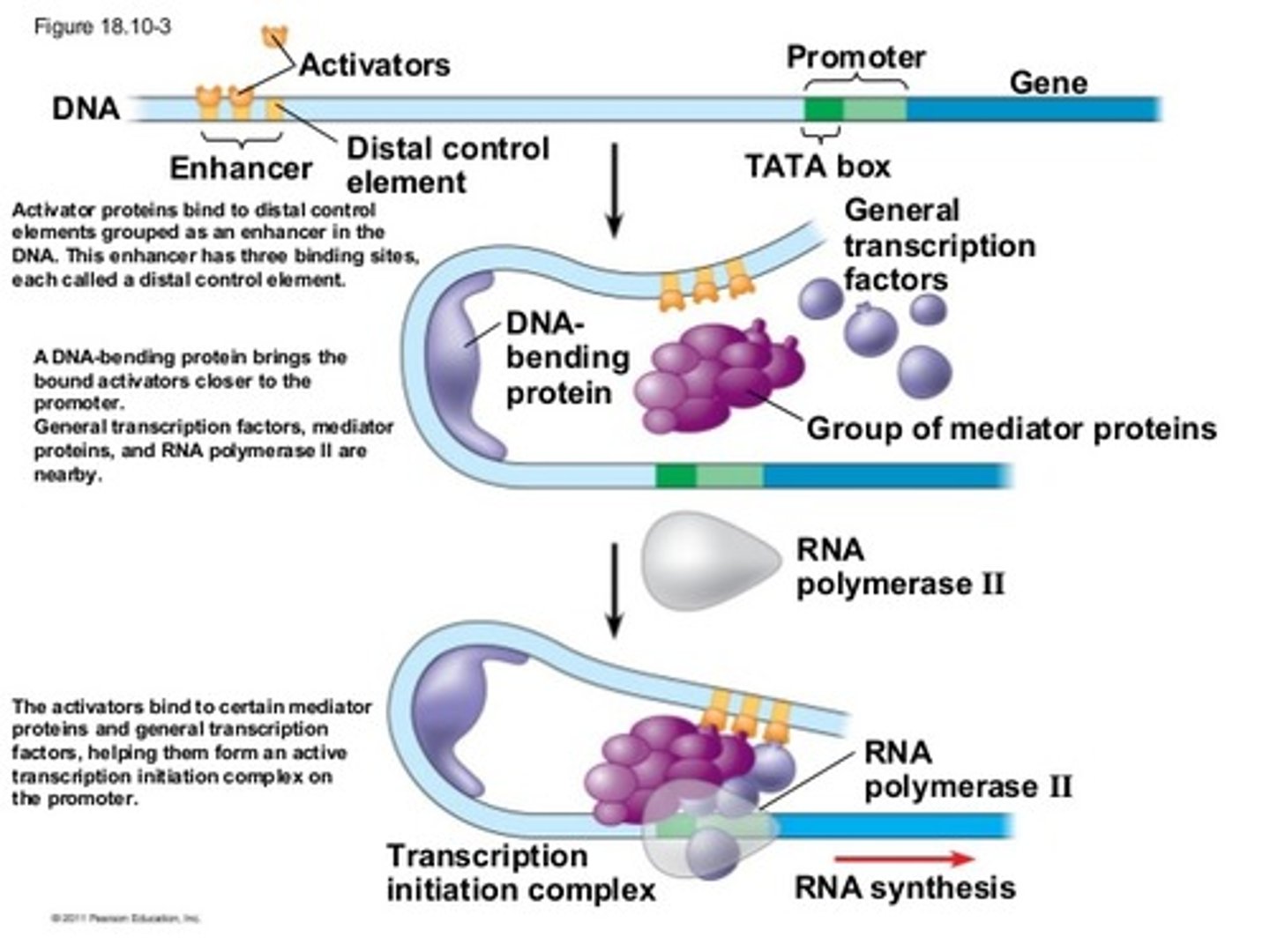
Promoters
-portion of DNA upstream from a gene
-contains the TATA box, which is the site where RNA polymerase II binds to start transcription
Transcription factors
help the RNA polymerase locate and bind to the promoter region of the DNA, helping to establish where transcription will start
RNAP
travel along template strand in 3' to 5'
transcribed 5' to '
doesn't proofread
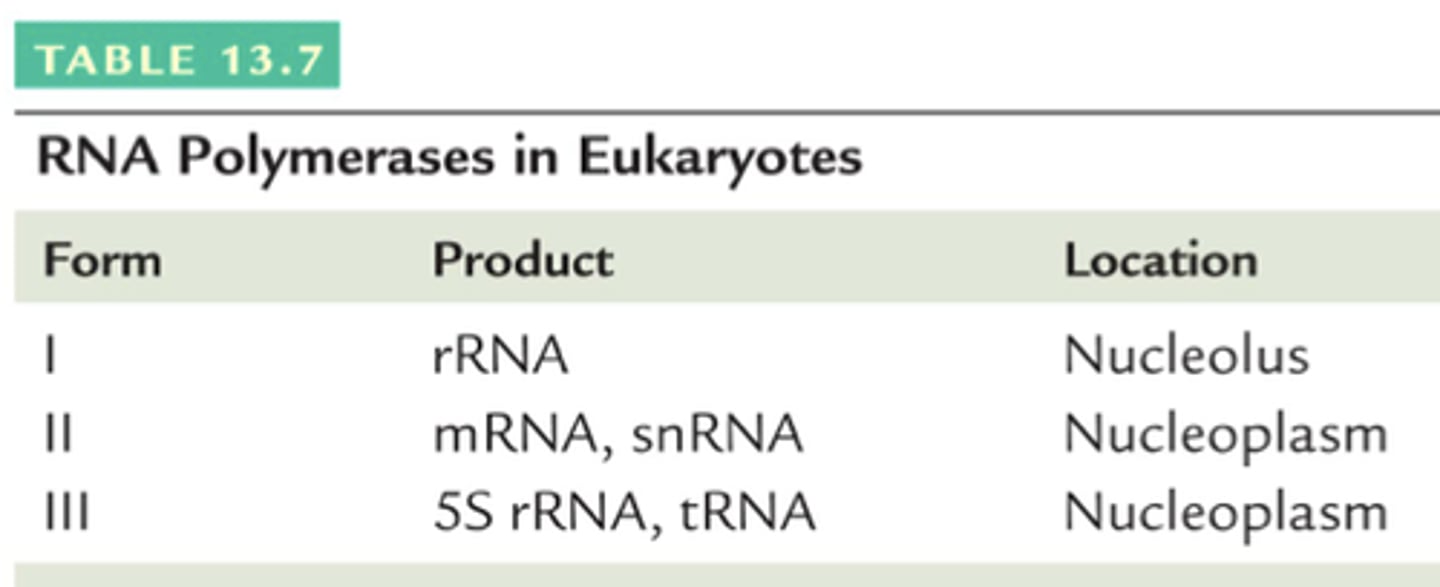
RNA polymerase I
located in the nucleolus and synthesizes rRNA
RNA polymerase II
transcription in eukaryotes and binds to TATA box (promoter) (associated w/ TF to help bind to promoter)
located in the nucleus and synthesizes hnRNA (pre-processed mRNA) and some small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
RNA polymerase III
located in the nucleus and synthesizes tRNA and some rRNA
- dont require primer
TATA box
-25 upstream (toward 5' end)
where RNA polymerase II binds
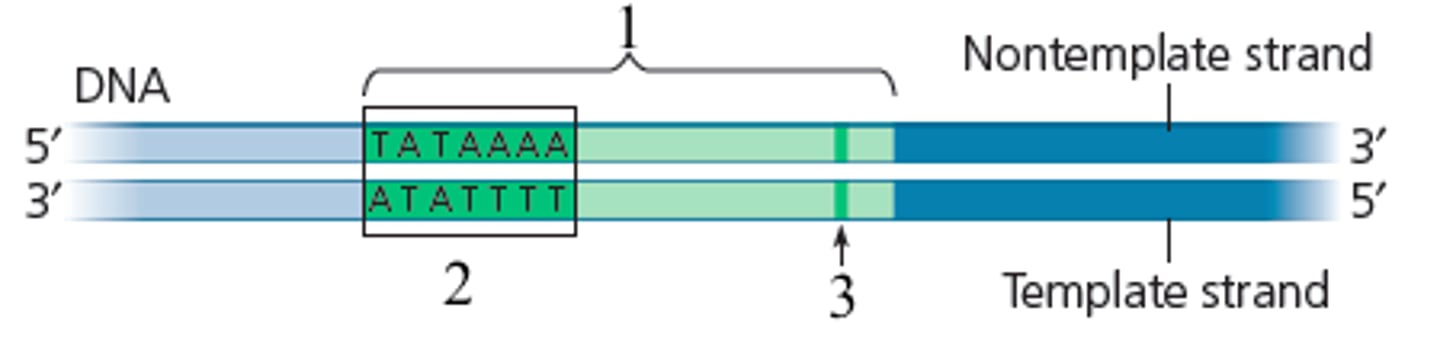
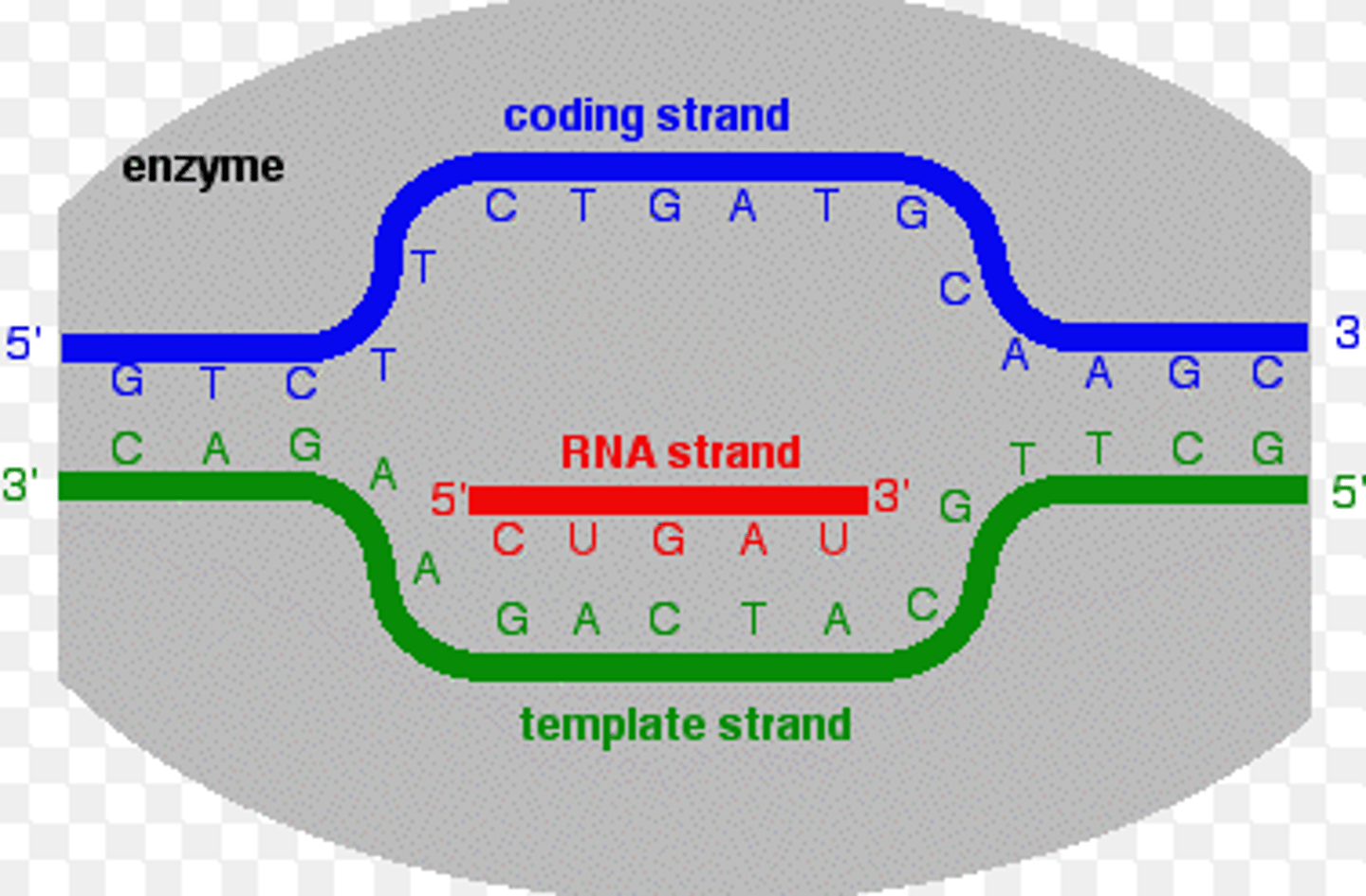
coding strand
the strand of DNA that is not used for transcription and is identical in sequence to mRNA, except it contains uracil instead of thymine
complementary to template strand
hnRNA (like preMrna)
- preprocessed mRNA
Heterogeneous nuclear RNA; the primary transcript made in eukaryotes before splicing.
- primary transcript formed
- mRNA derived from hnRNA via post transcriptional modification
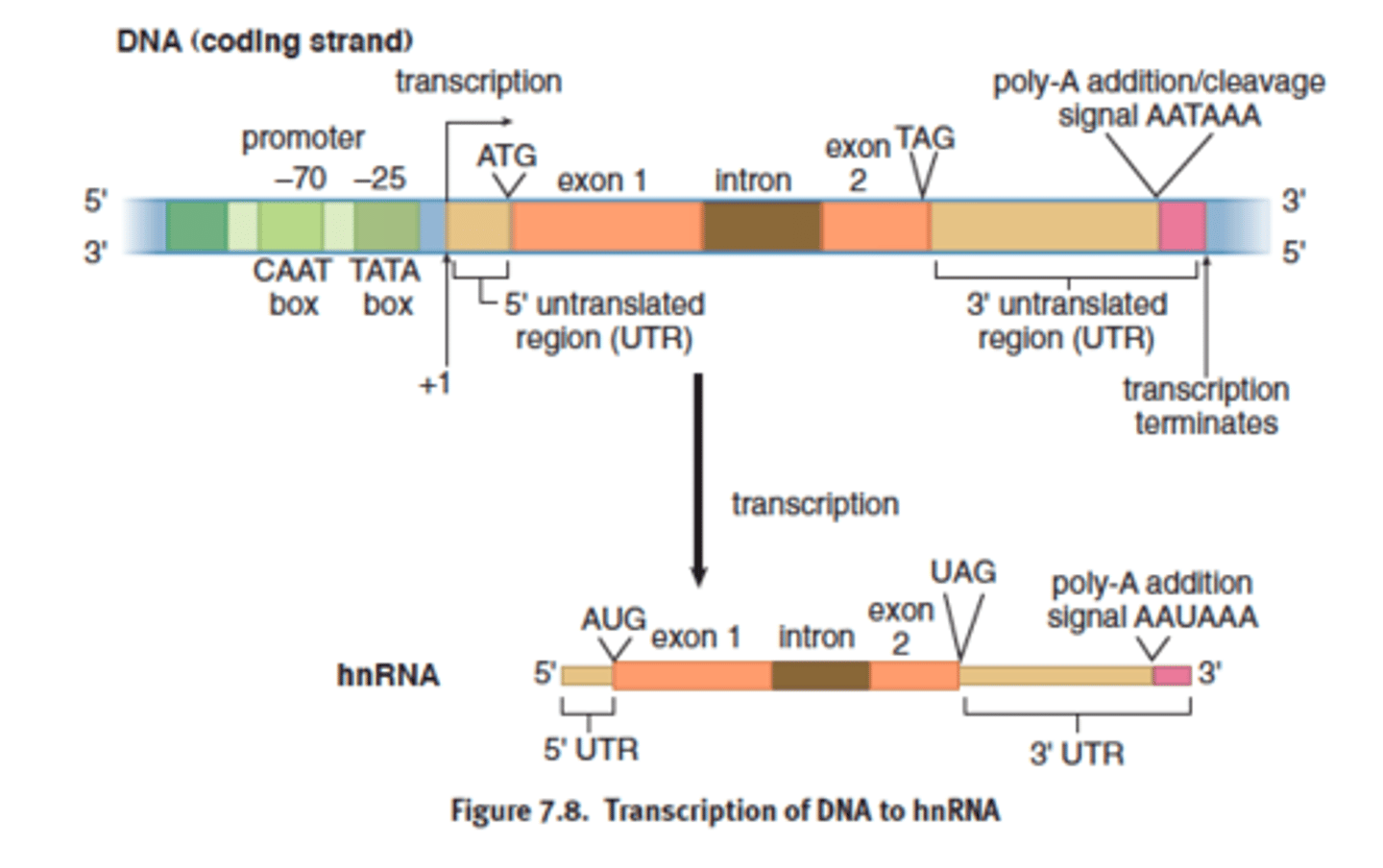
Types of post transcriptional processing (mRNA )
-splicing
-5' cap
-3' poly-a tail
*Note: only occurs with eukaryotic mRNA
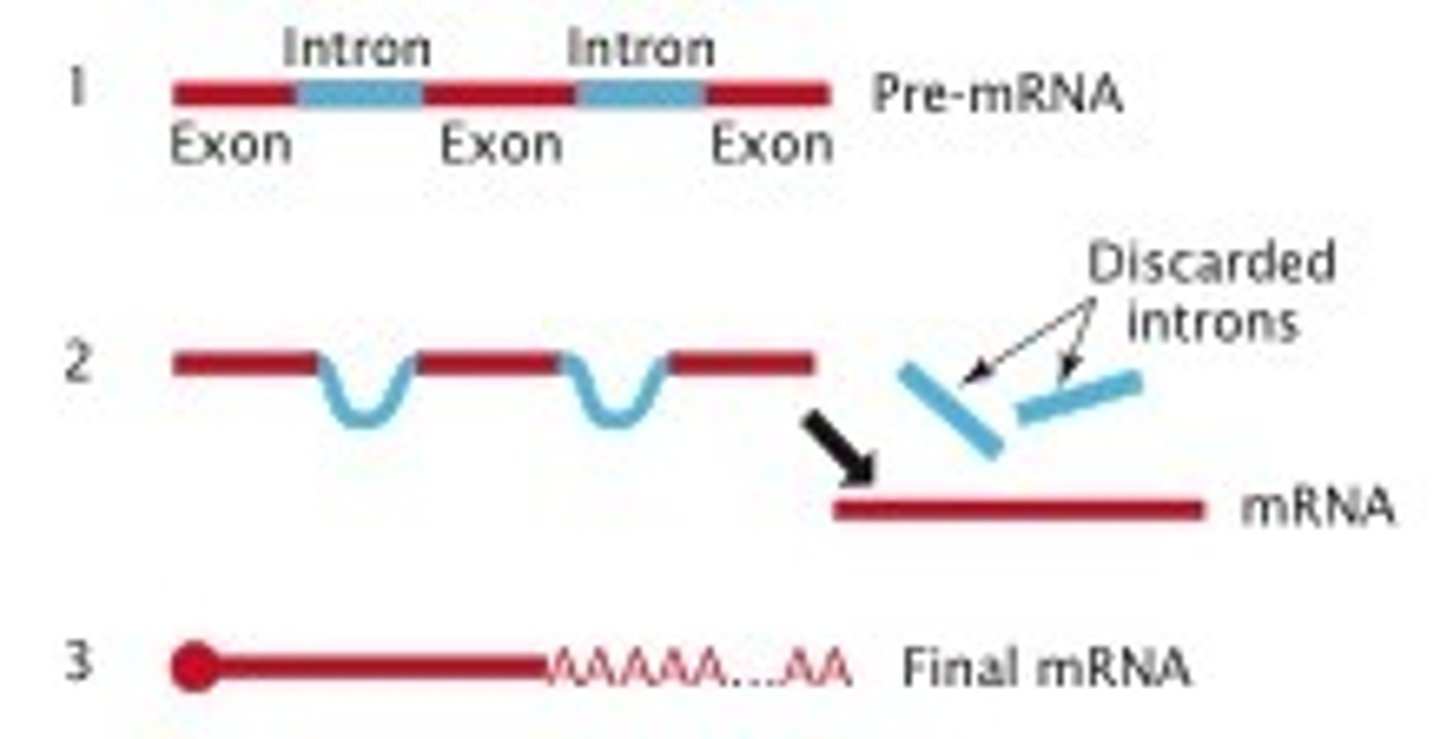
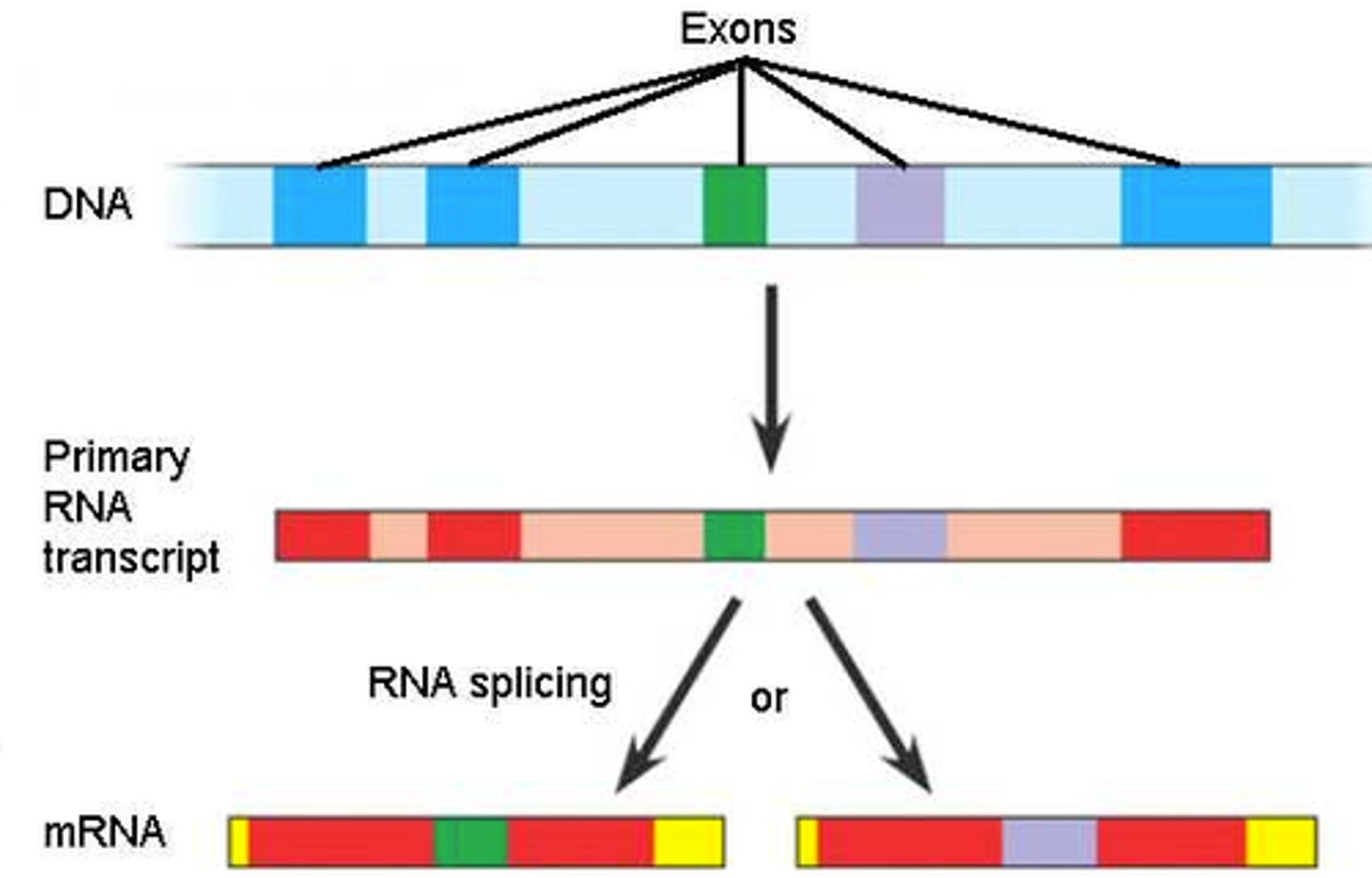
Splicing: Introns and Exons
-remove noncoding sequences (introns) and ligate coding sequences (exons) together\
-accomplished by the spliceosome
- introns stay in nucleus; exons exit nuclease as part of the mRNA
- maturation of hnRNA includes splicing of the transcript to remove non coding sequences and ligate coding sequence
- accompanied by spliceosme - small nuclear RNA (snRNA) with proteins - small nuclear ribonuceloproteins (snRNP)
- recognizes both 5' and 3' split sites of the introns
- noncodifn sequenze are excised in form of variant and degraded
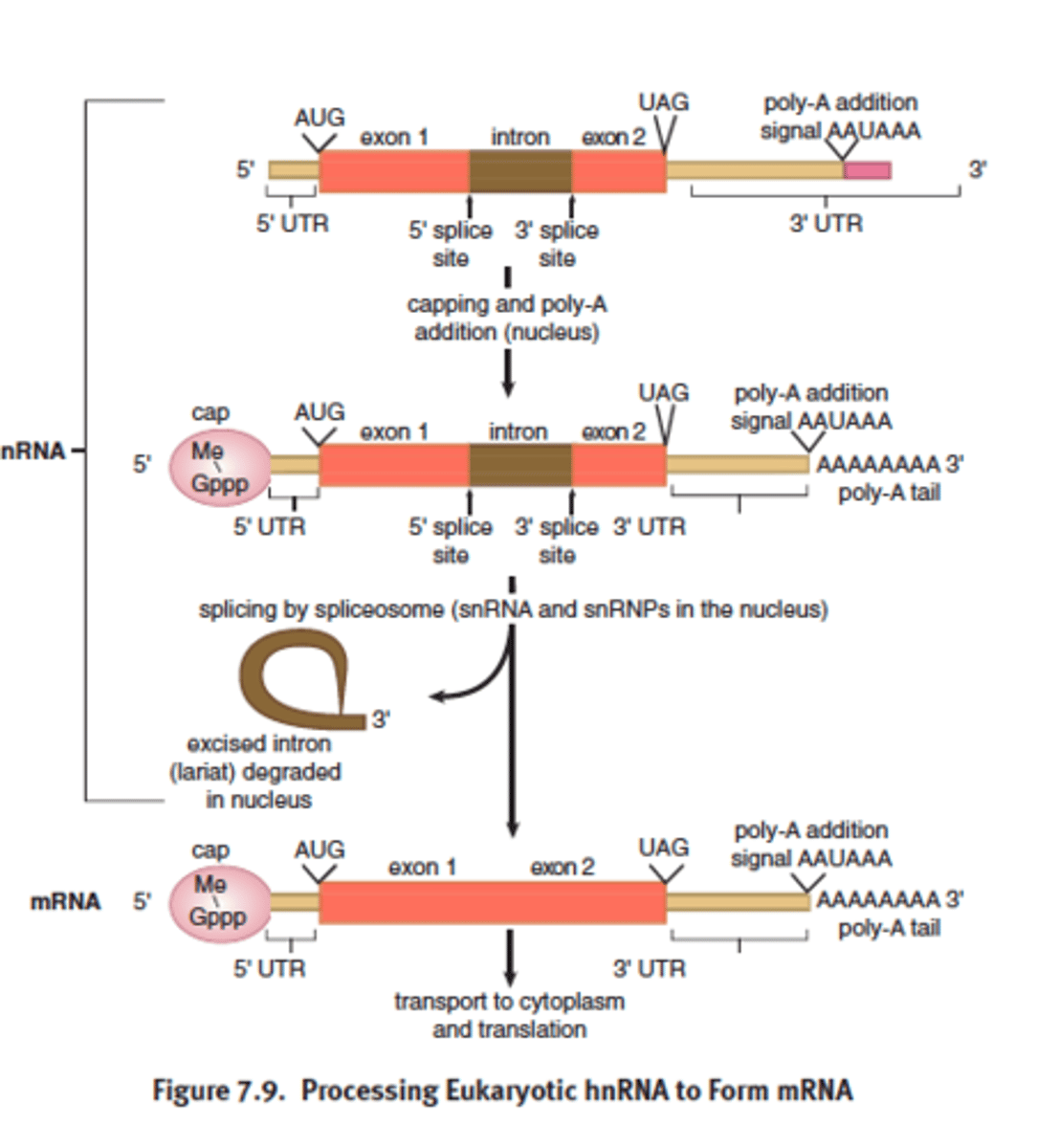
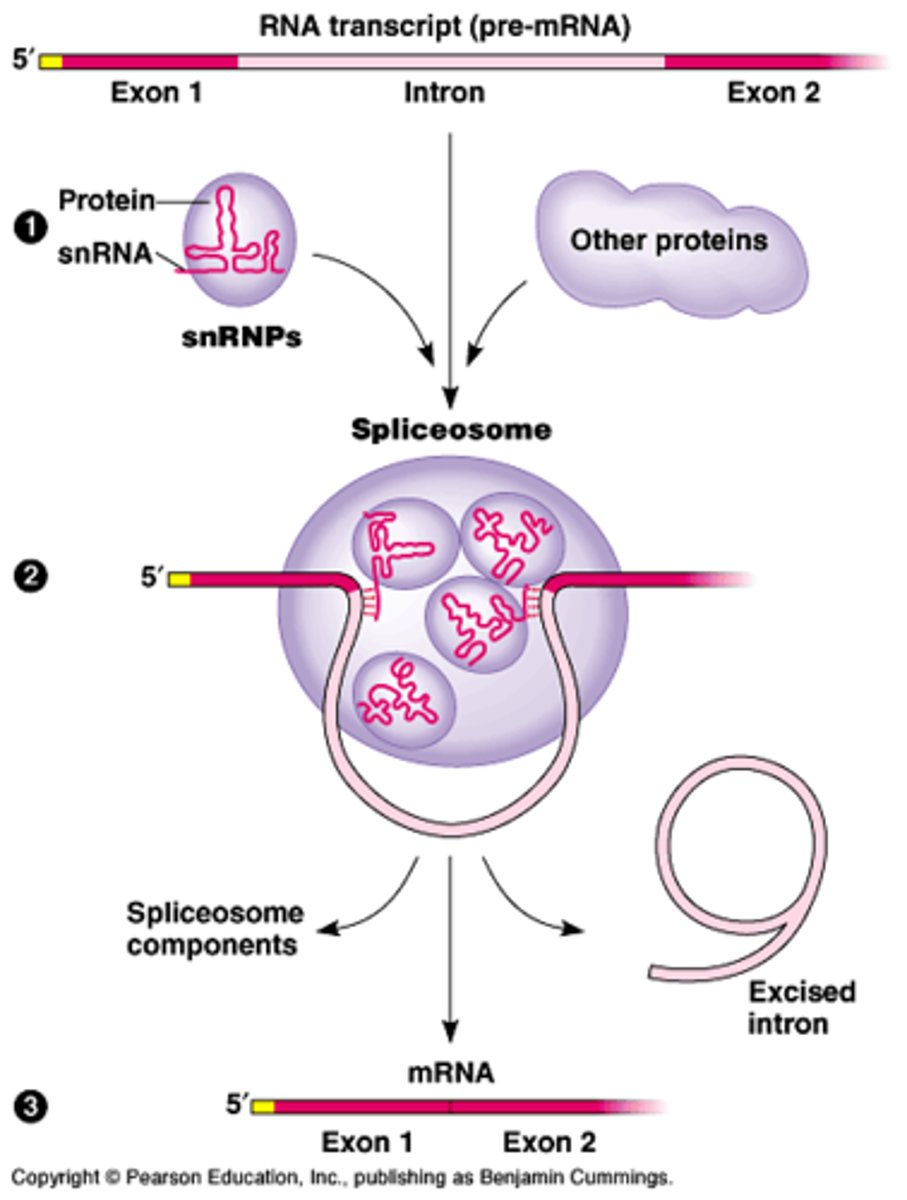
Spliceosome
-small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules couple with proteins known as small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs)
-recognizes both the 5' and 3' splice sites of the introns
-noncoding sequences are excised in the form of a lariat and then degraded
introns evolution
regulation of cellular gene expression levels and in maintaining the size of our genome
- rapid protein evolution
- mutation = won't change the protein sequence because introns are cleaved out of the mNA transcript prior to translation
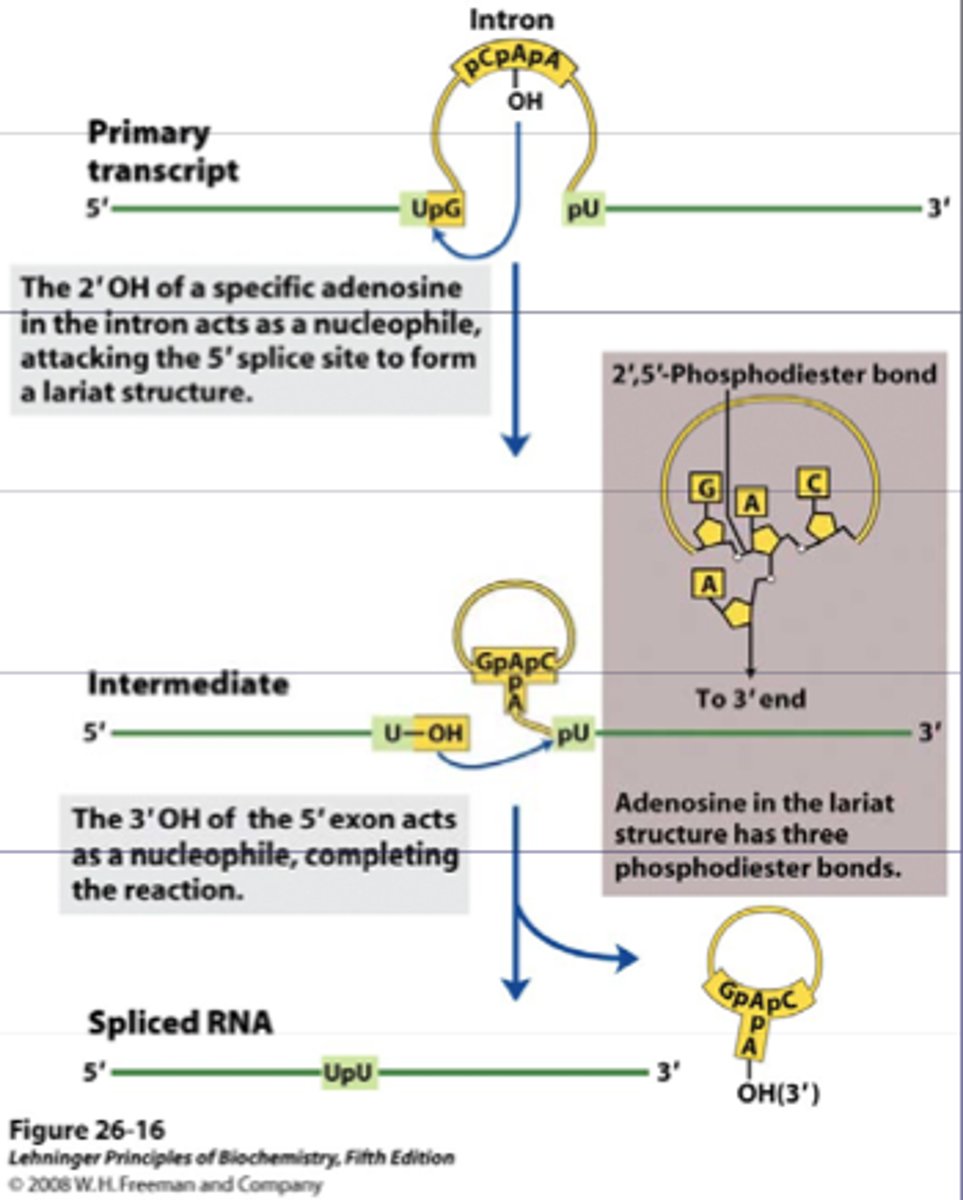
lariat
non-coding sequences are excised in the form of lasso shaped structure and degraded
5' cap
- 5' end of hnRNA
-7-methylguanylate triphosphate cap (inverted Guanine residue that is methylated on position 7; 2 OH --> 2 CH3)
- added by capping enzyme complex (CEC) coupled with RNAP during the process of transcription when 5' end emerged from RNAP
- recognized by the ribosome as the binding site
- regulation of nuclear export
- protects mRNA from degradation in the cytoplasm
- promote splicing of exon closest to the 5' end of mRNA
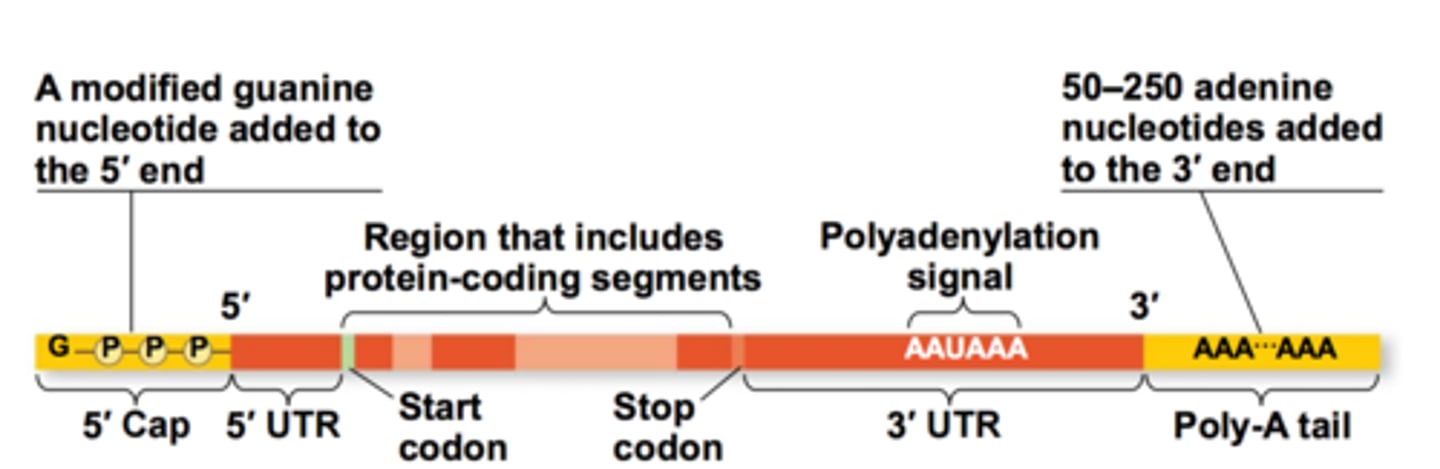
3' poly-a tail
- polyadenosyl (poly) tail = composed of adenine bases
- added to the 3' end of the mRNA transcript after splicing
- protects the message against rapid degradation
- also assists with export of the mature mRNA from the nucleus
- untranslated region still exist at 5' and 3' edges bc ribosome initates translation at the start codon and end at stop codon
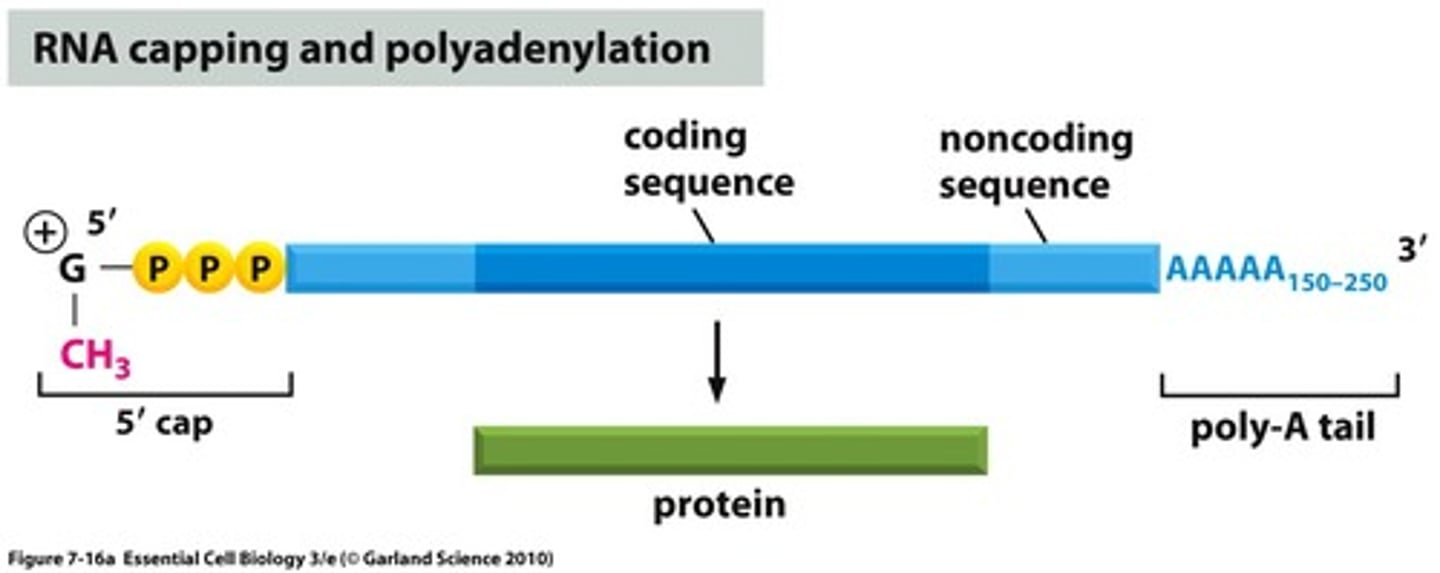
mature mRNA
- only exon remain
- cap and tail added
- transport to cytoplasm for protein translation
- untranslated regions = still exists 5' to 3' edges bc the ribosome initiates translation at start codon (AUG) and and at stop codon (UAA, UGA, UAG)
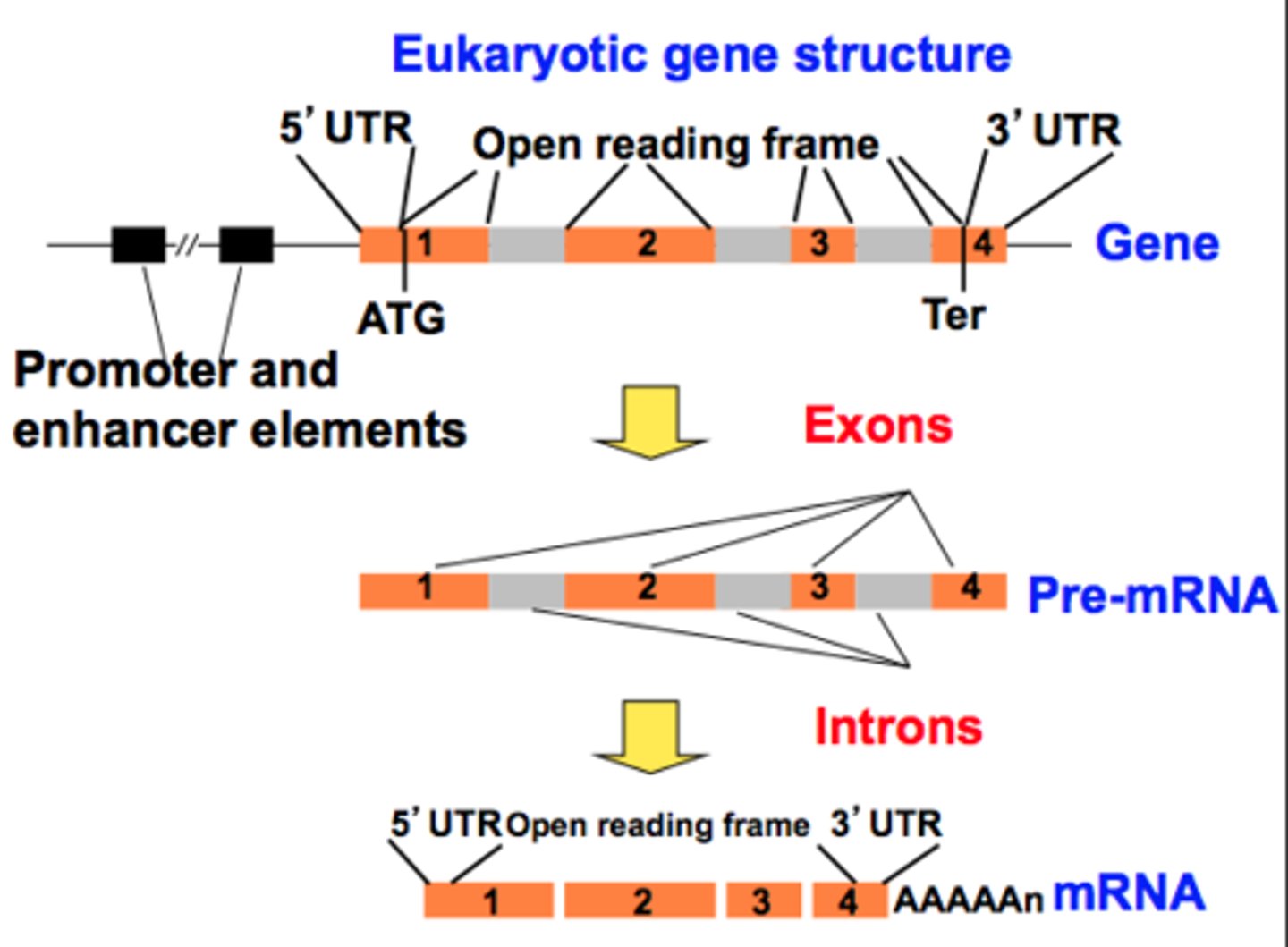
Alternative splicing
combing different exons in a modular fashion to acquire different gene products - lead to different encoded proteins
- function in regulation of gene expression + generates protein diversity
-produce multiple variants of proteins encoded by same original gene
nuclear pores (in translation)
transcript mRNA pass through to go to cytoplasm and find a ribosome to begin translation
Translation
-converting mRNA transcript into a functional protein
-requires mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, amino acids, and energy in the form of GTP
- occurs in cytoplasm
Terminology and 5'-->3'
DNA _RNA _PROTEIN
DNA=replication; new DNA synthesized in 5'--3' direction
-DNA-> RNA=transcription; new RNA synthesized in 5'-->3' direction (template is read 3'-->5')
-RNA-->protein
=translation; mRNA read in 5'-->3' direction
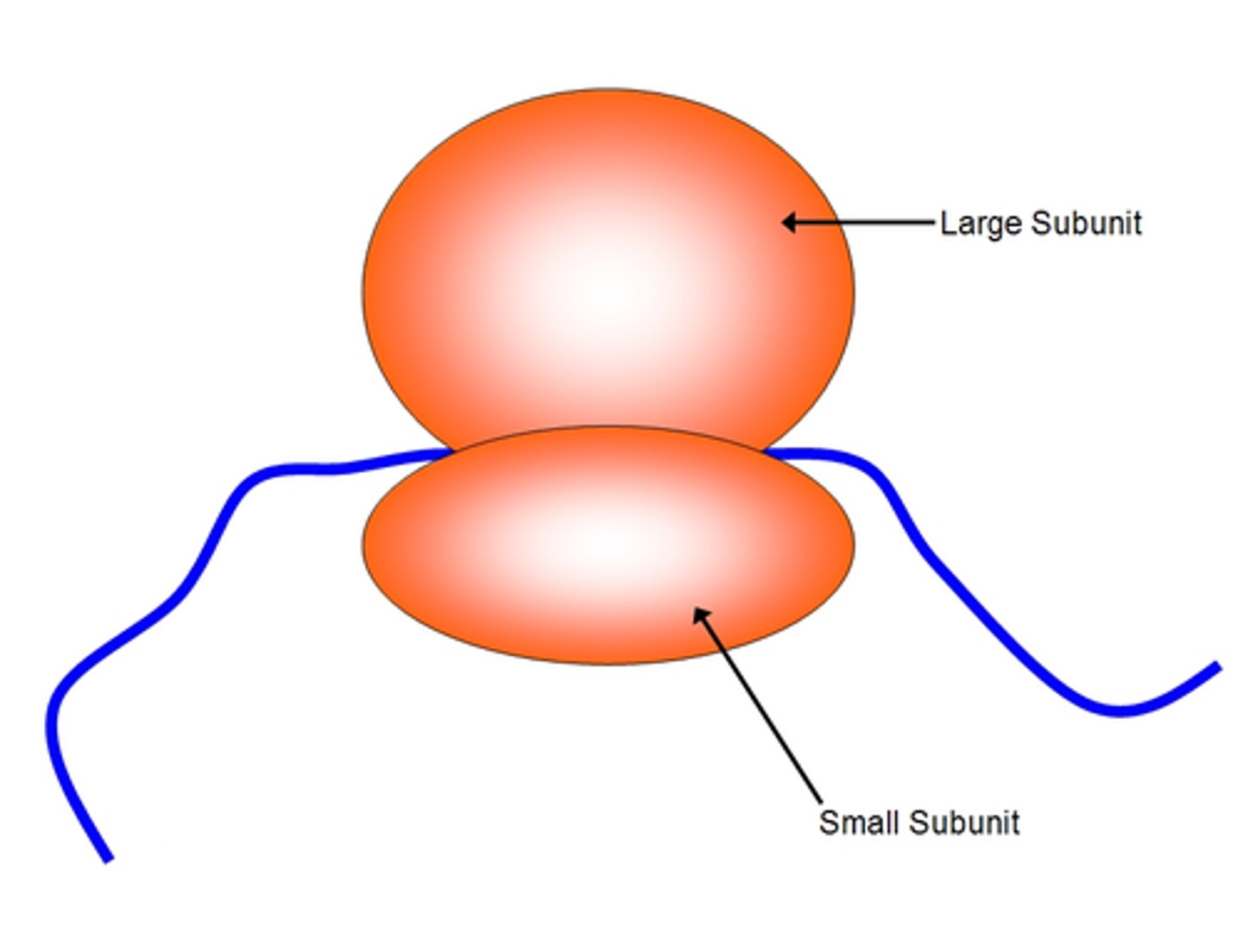
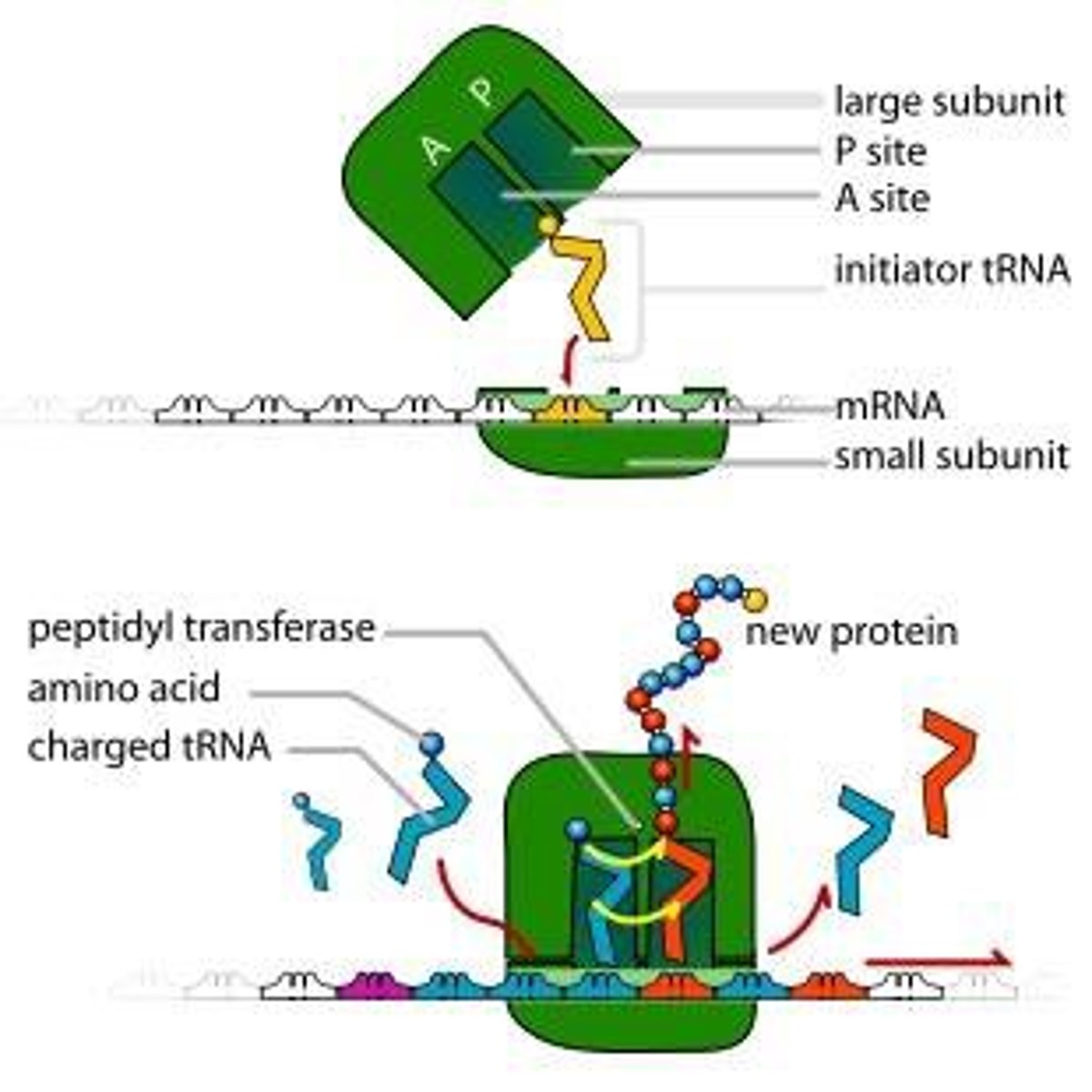
Ribosomen(in translation)
-factories where translation occurs
-composed of proteins and rRNA
-made of large and small subunits
- different in pork than eek (allowing antibiotics to target the ribs of prokaryotes and prevent translation of proteins)
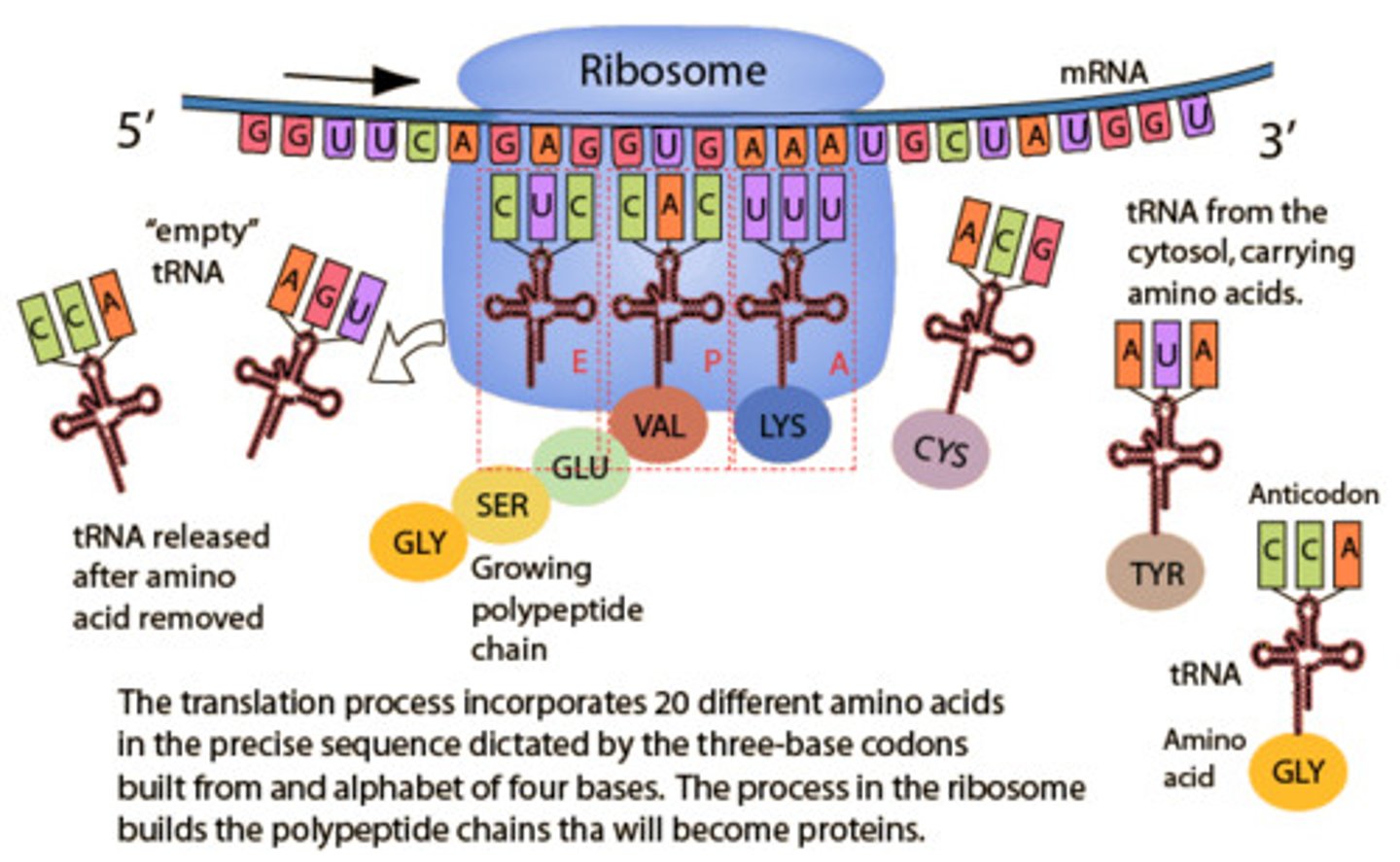
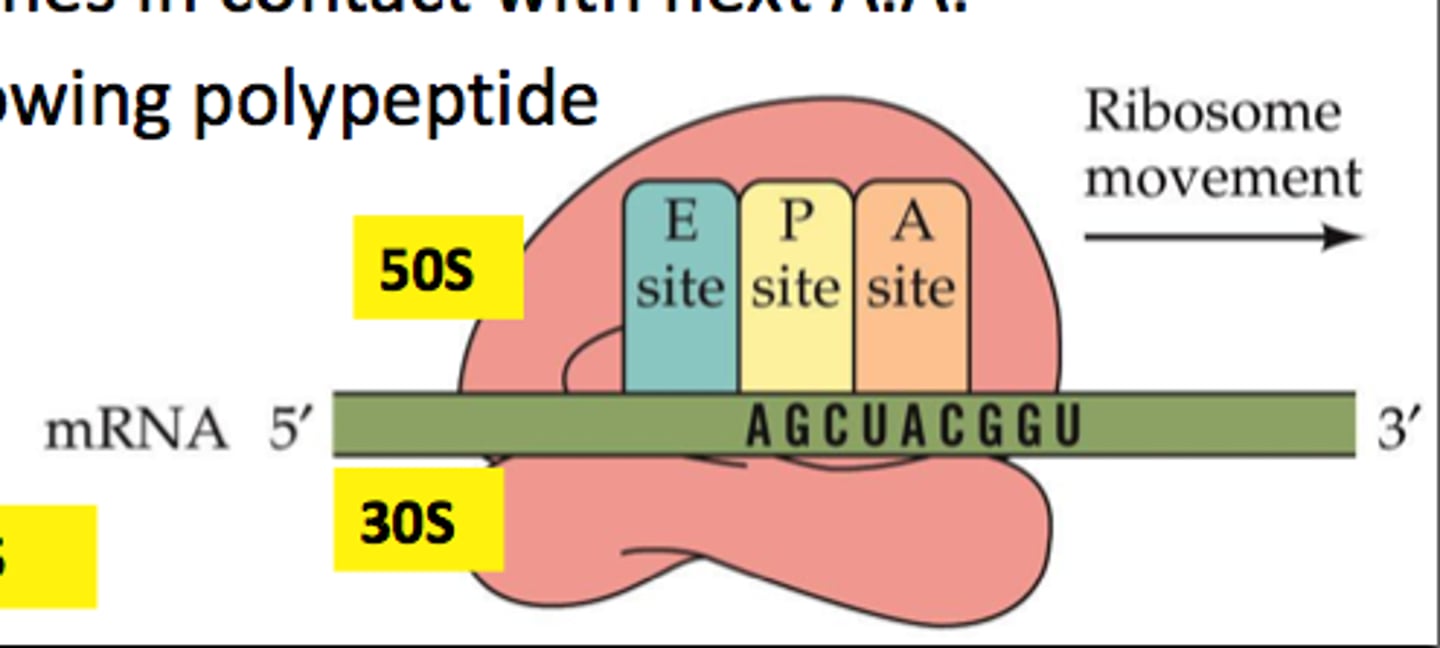
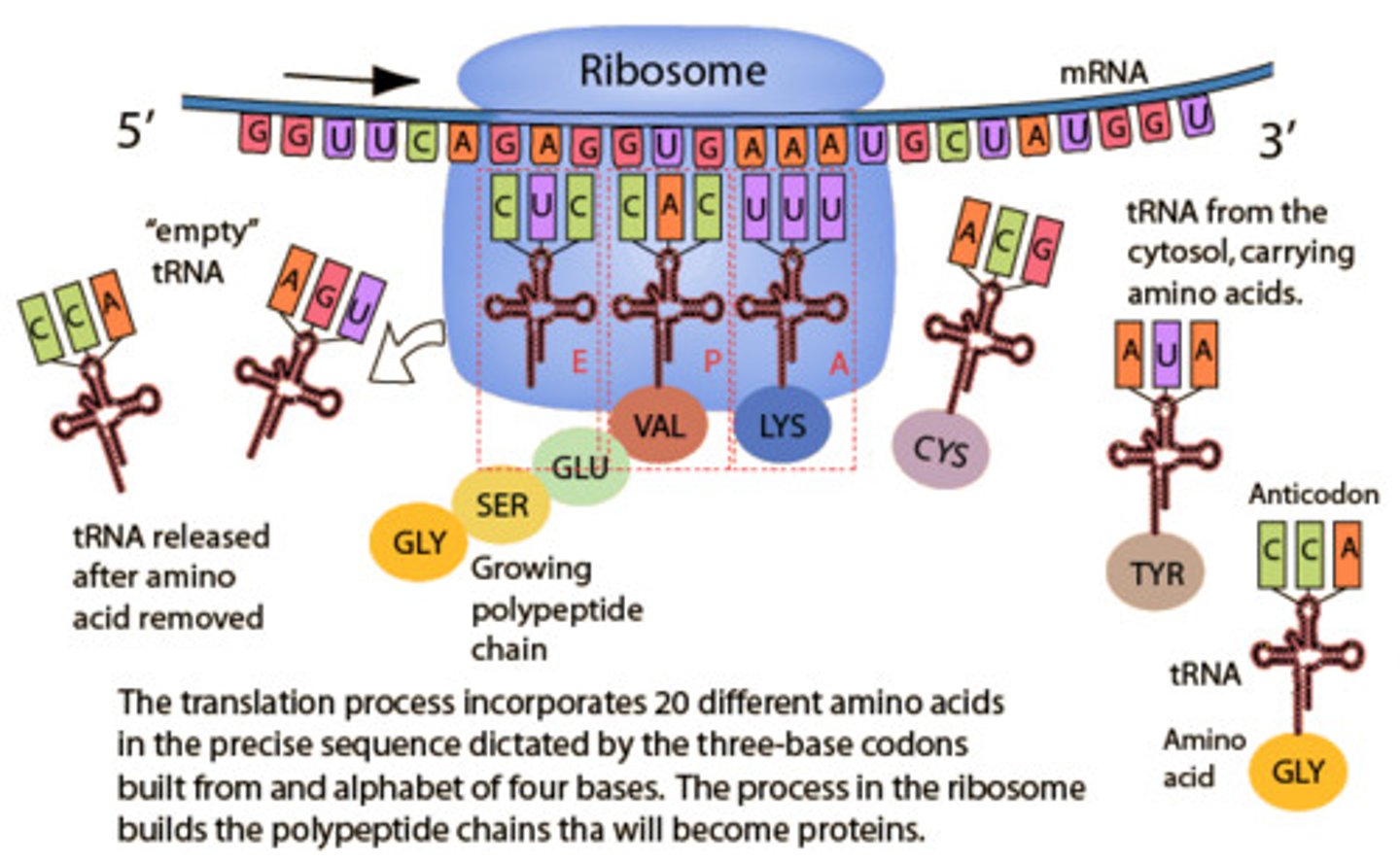
Three binding sites in ribosome
-A site= aminoacyl (lands)
-P site= peptide (builds)
-E site= exit
(APE order)
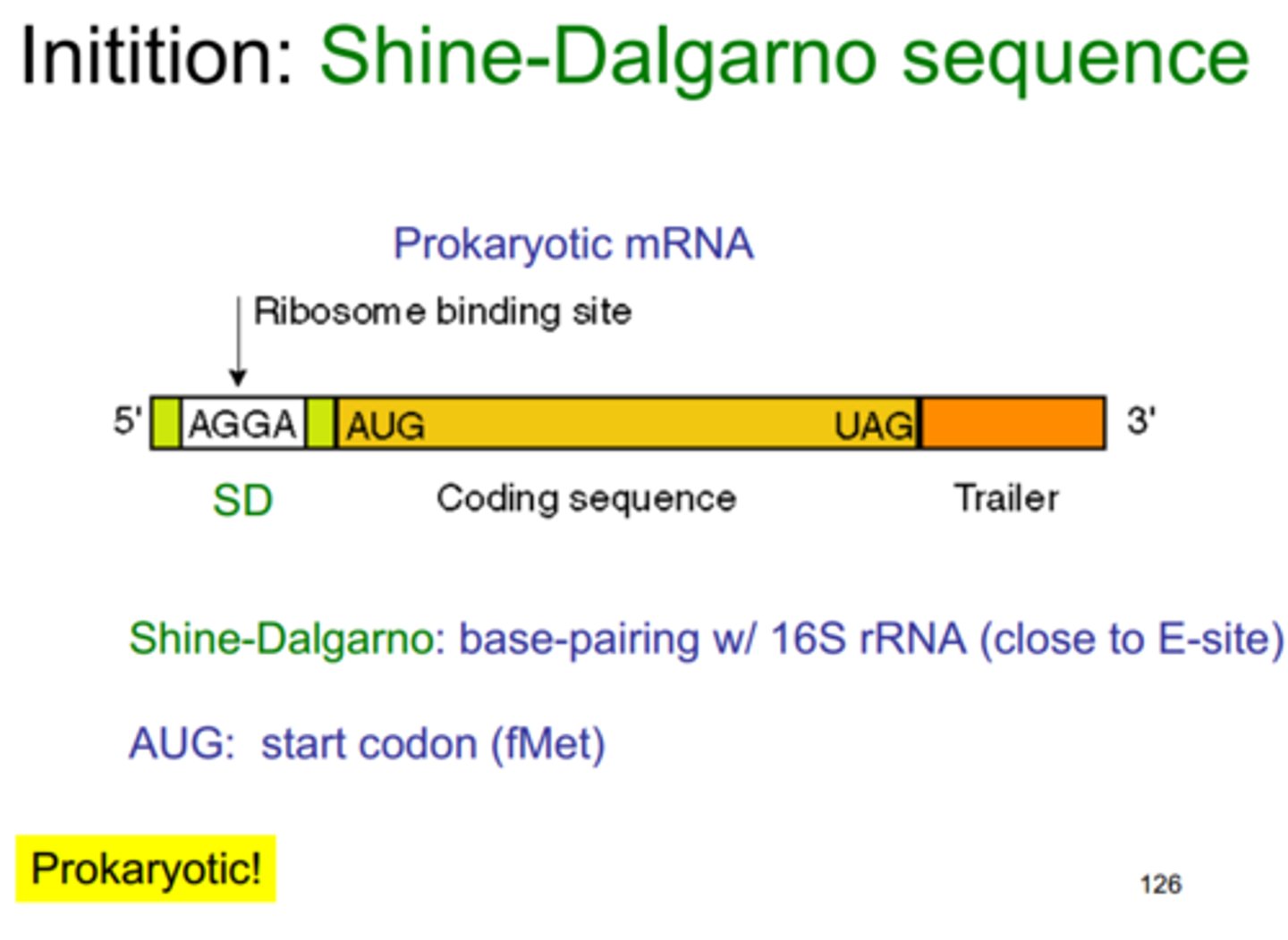
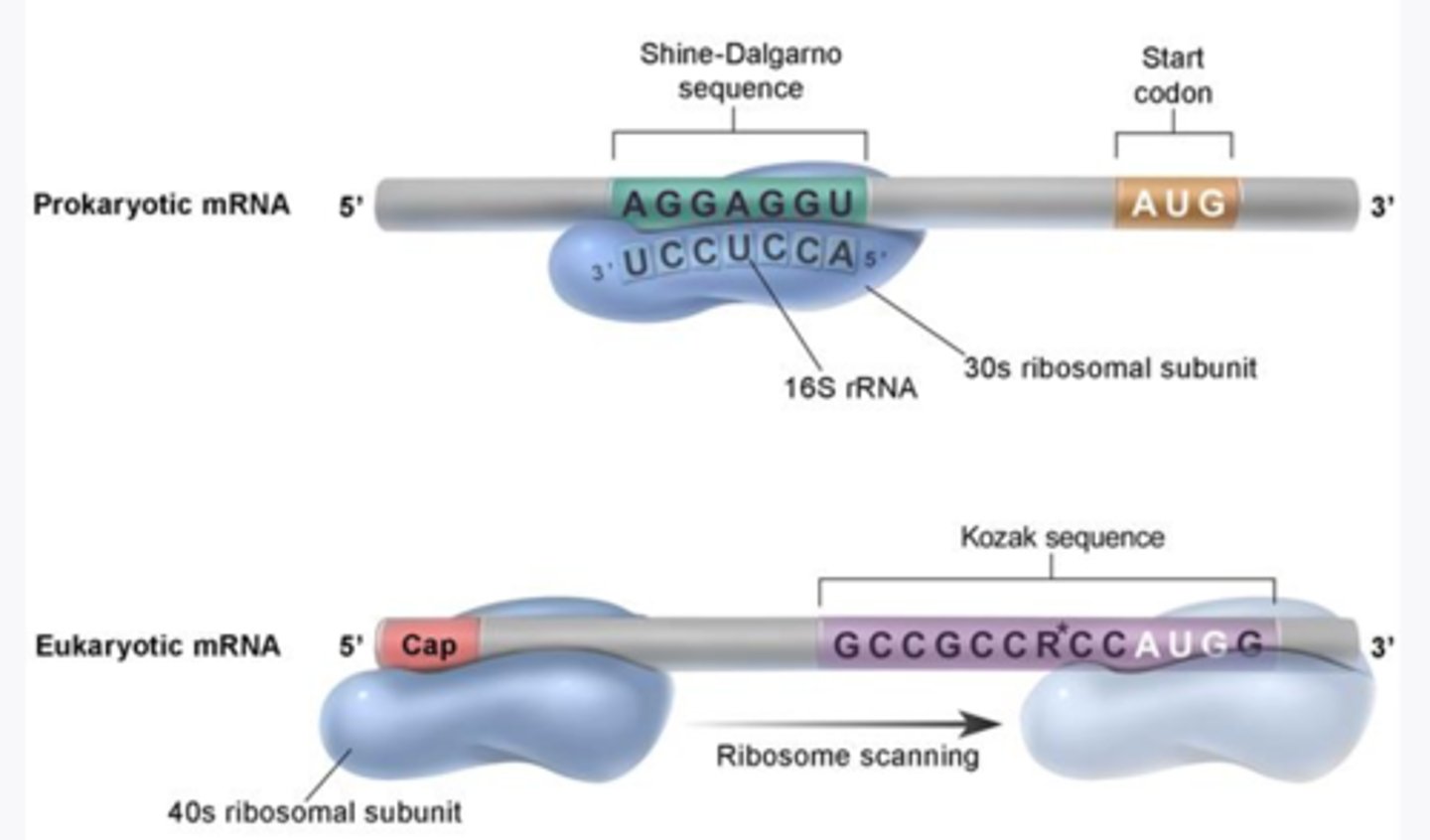
Initiation in prokaryotes of translation
-occurs when 30S ribosome attaches to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and scans for a start codon(AUG) to bp with anticodon (UAC) within P site
-lays down N-formlymethionine in the P site of the ribosome
- Large subunit (50S) binds to small subunit assisted by initiation factors
Initiation in eukaryotes of translation
- charged inactive tRNA binds to AUG (met) through bp with its anticodon within P site
-occurs when the 40S ribosome attaches to the 5' cap and scans for a start codon (AUG) to bp with anticodon (UAC) within P site
-lays down methionine in the P site of the ribosome
- Large subunit (60S) binds to small subunit assisted by initiation factors
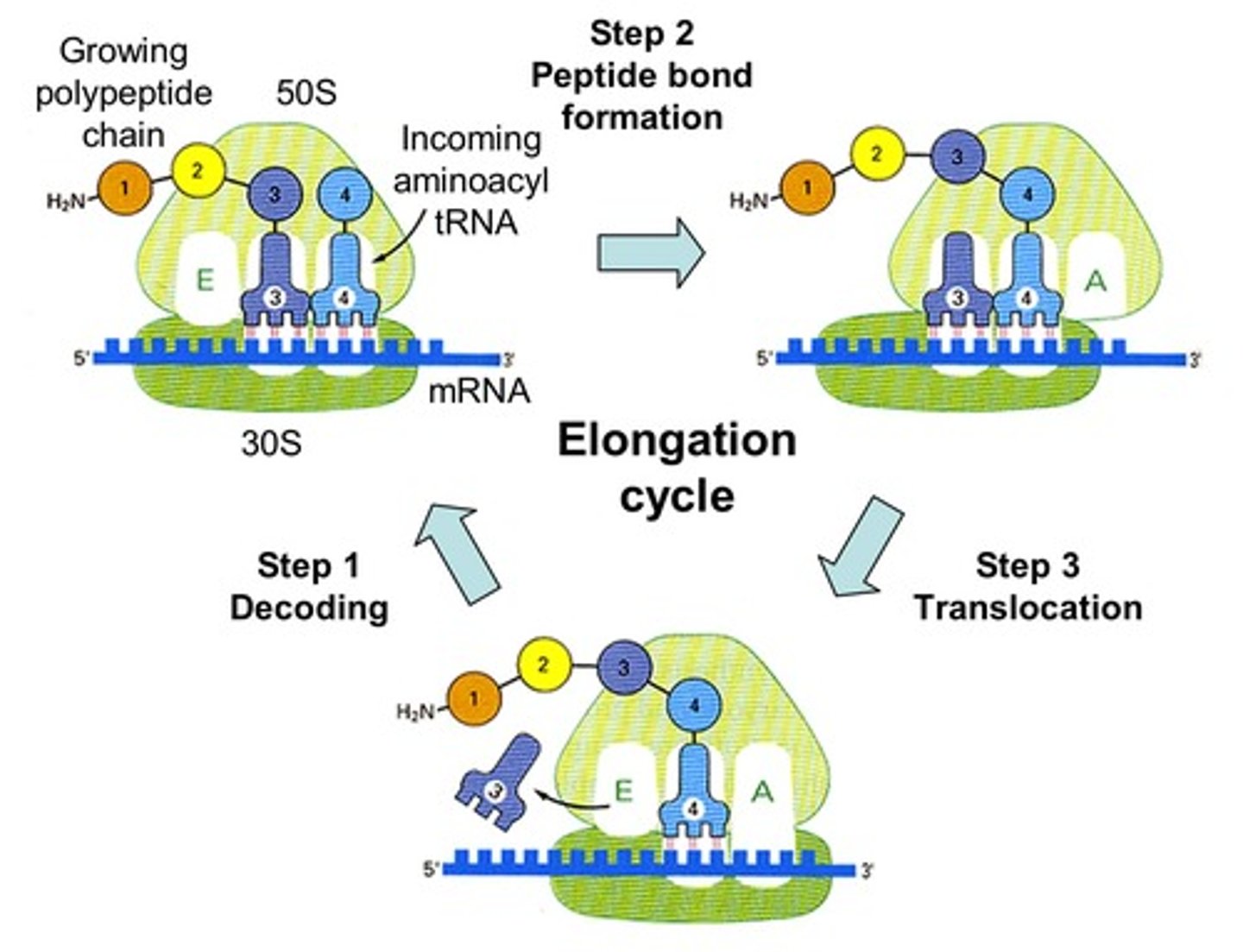
Elongation in translation
- ribosome moves 5' to 3' discretion along mRNA, synthesizing the protein from N to C terminus adds to the methionine.
-the addition of a new aminoacyl-tRNA into the A site of the ribosome and transfer of the growing polypeptide chain from the tRNA in the P site to the tRNA in the A site
-now inactivated (uncharged) tRNA pauses in the E site before exiting the ribosome
A site in translation
aminoacyl-tRNA binds to w/ GTP + EFs
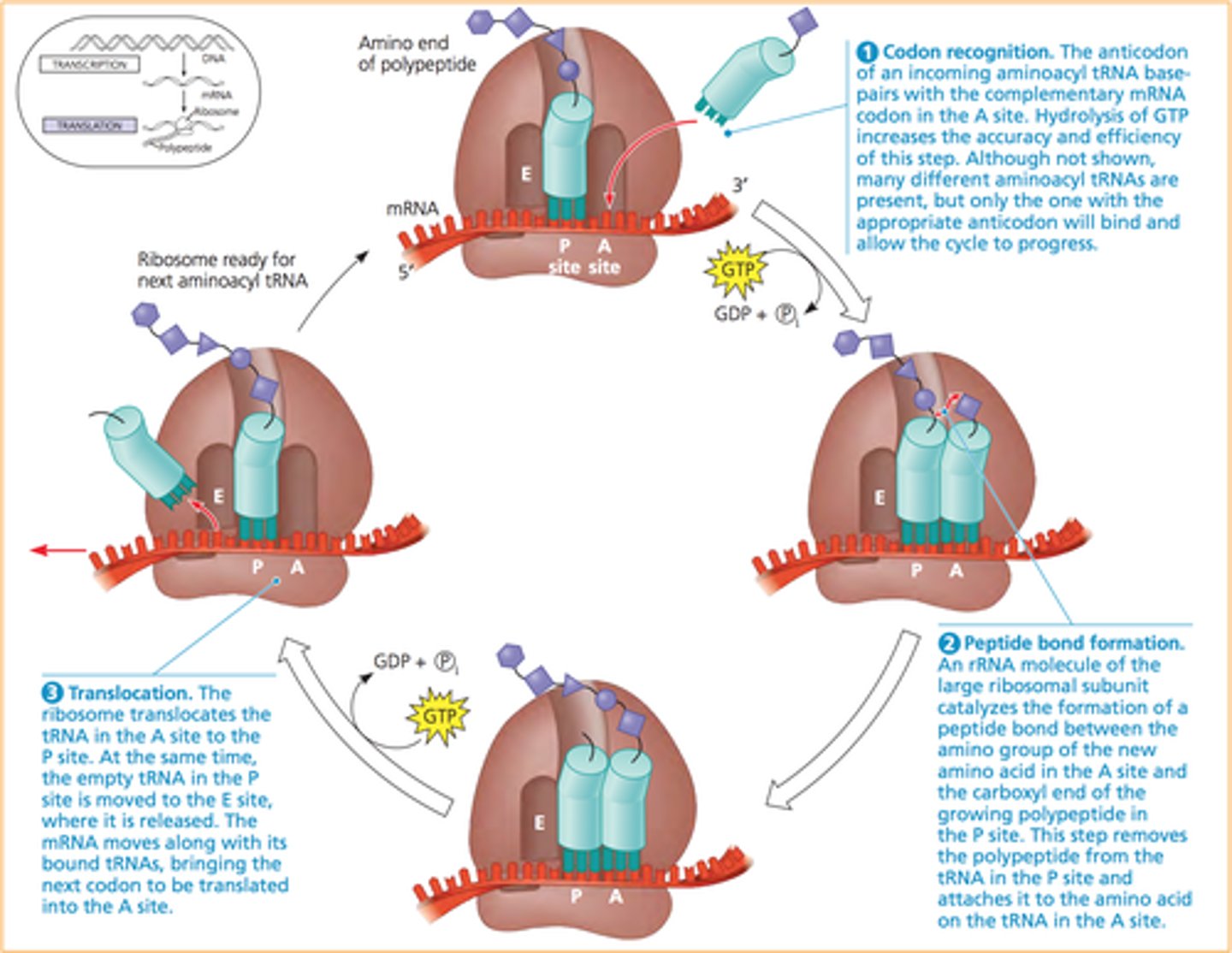
P site in translation
holds the tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide
peptide bond forms using peptidyltransferase in large subunit
GTP = energy
E site in translation
inactivated tRNA pauses transiently before existing ribosome
translation of ribosome 3 nucleotides alone the mRNA + GTP + EFs
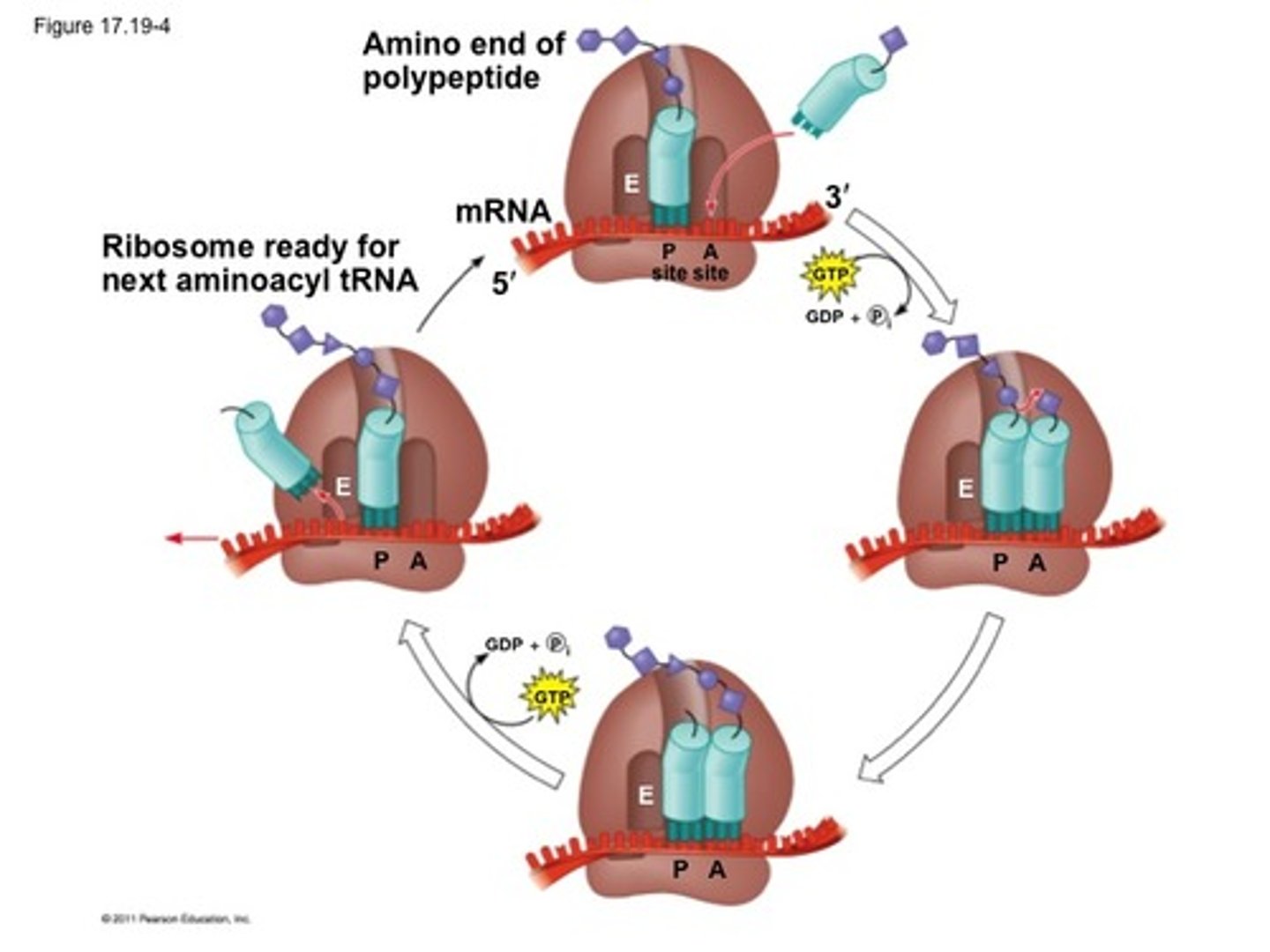
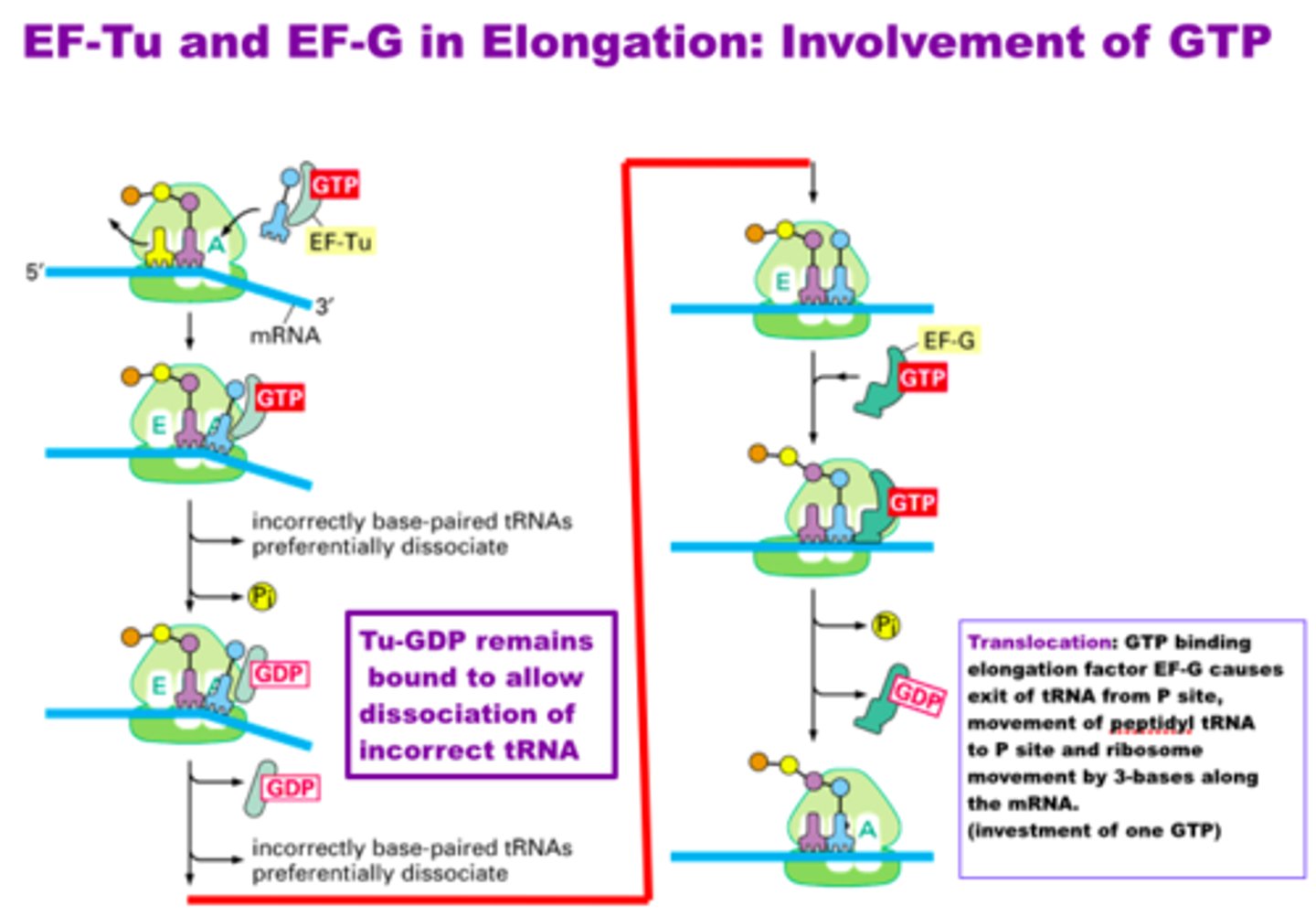
Elongation factors (EF)
assist by locating and recruiting aminoacyl-tRNA along with GTP, while helping to remove GDP once the energy has been used
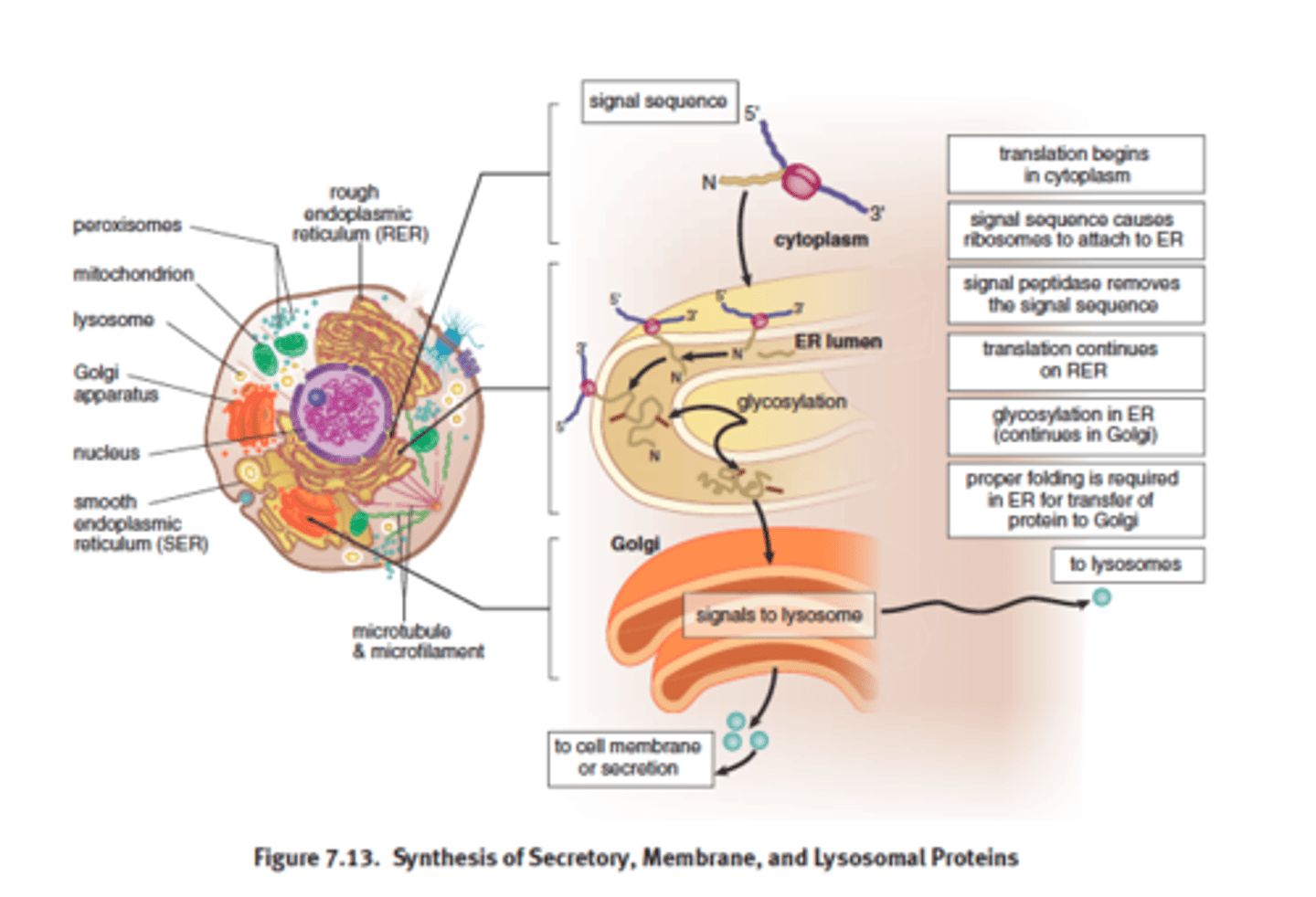
signal sequence
some eukaryotic proteins contain to direct ribosome to move the ER so that protein can be translated directly into the lumen of RER --> Golgi --> vesicle via exocytosis
OR direct proteins to nucleus, lyosomes or CM
Postranslation modifications
-folding by chaperones
-formation of quartenary structure
-cleavage of proteins or signal sequences
-covalent addition of other biomolecules
proper protein
functioning. For example, several
clotting factors, including prothrombin,
require posttranslational carboxylation
of some of their glutamic acid residues
in order to function properly. Vitamin K
is required as a cofactor for these reactions;
thus, vitamin K deficiency may
result in a bleeding disorder.
covalent addition of other biomolecules
Phosphorylation—addition of phosphates by protein kinases to activate or
deactivate proteins
• Carboxylation—addition of carboxylic acid groups, usually to serve as
calcium-binding sites
• Glycosylation—addition of oligosaccharides as proteins pass through the ER
and Golgi apparatus to determine cellular destination
• Prenylation—addition of lipid groups to certain membrane-bound enzymes
Termination
-occurs when the codon in the A site is a stop codon
-release factor places a water molecule on the polypeptide chain and thus releases the protein
- peptidyly transferase and termination factors to hydrolyze complete polypeptide chain from final tRNA
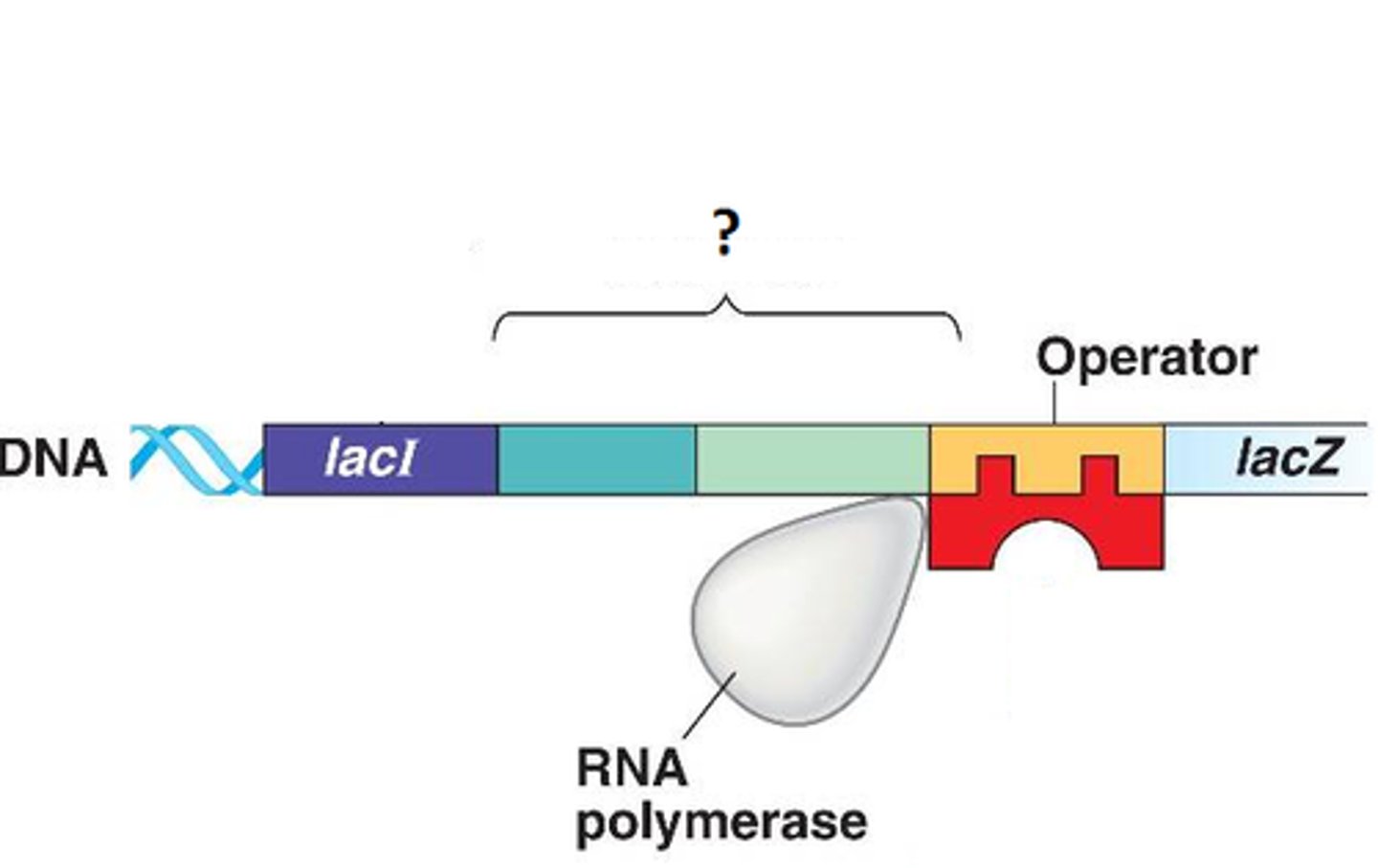
Operon
-a cluster of genes transcribed as a single mRNA
-both inducible and
repressible systems, and offer a
simple on-off switch for gene control in
prokaryotes.
- Jacob- Monod model describes the structure
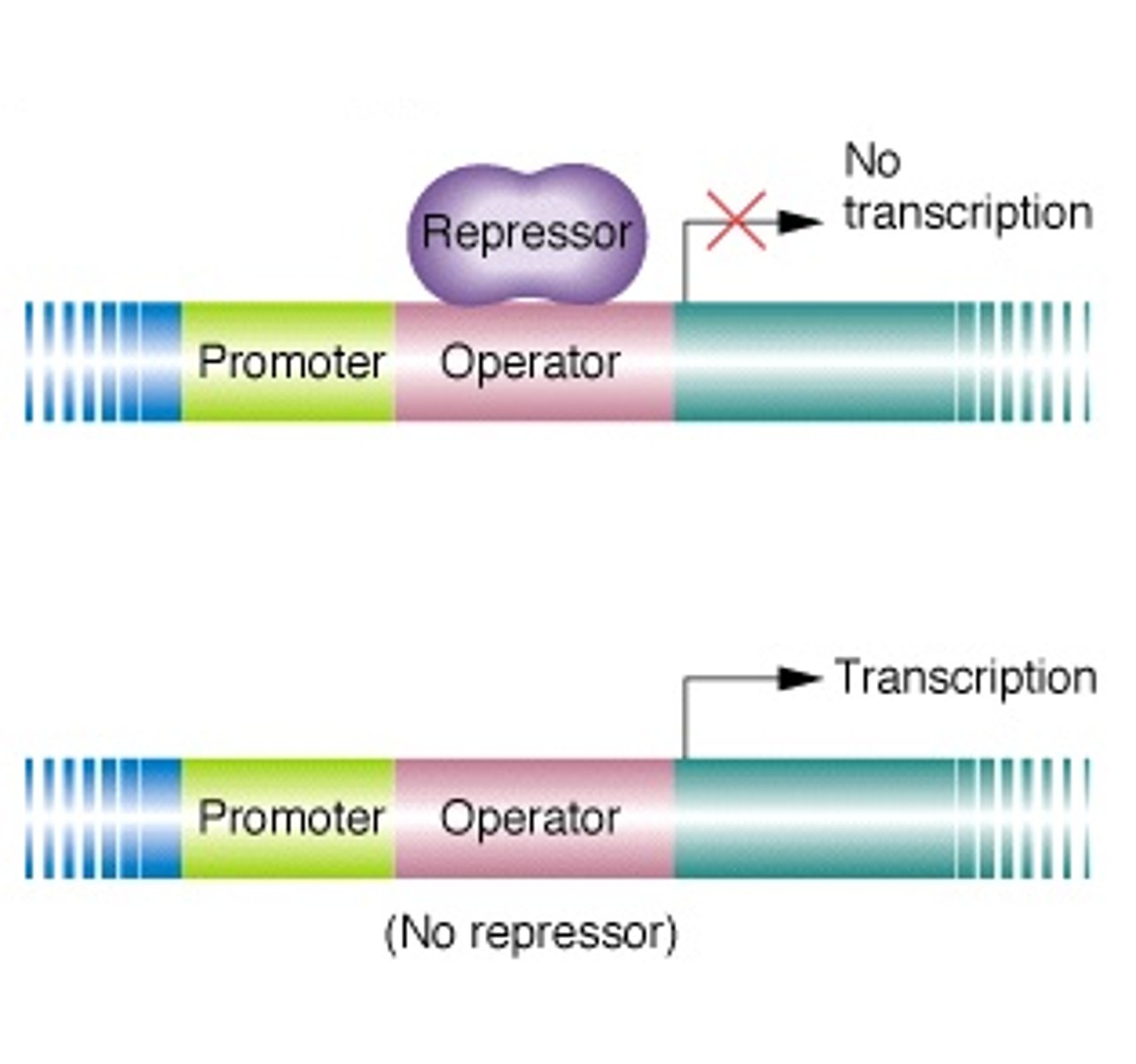
What do operons contain
-structural genes
-operator site
-promoter site
-regulator gene
Structural gene in lac operon complex
codes for protein of interest
Operator site in lac operon complex
-nontranscribable region of DNA that is capable of binding a repressor protein
-upstream of structural gene
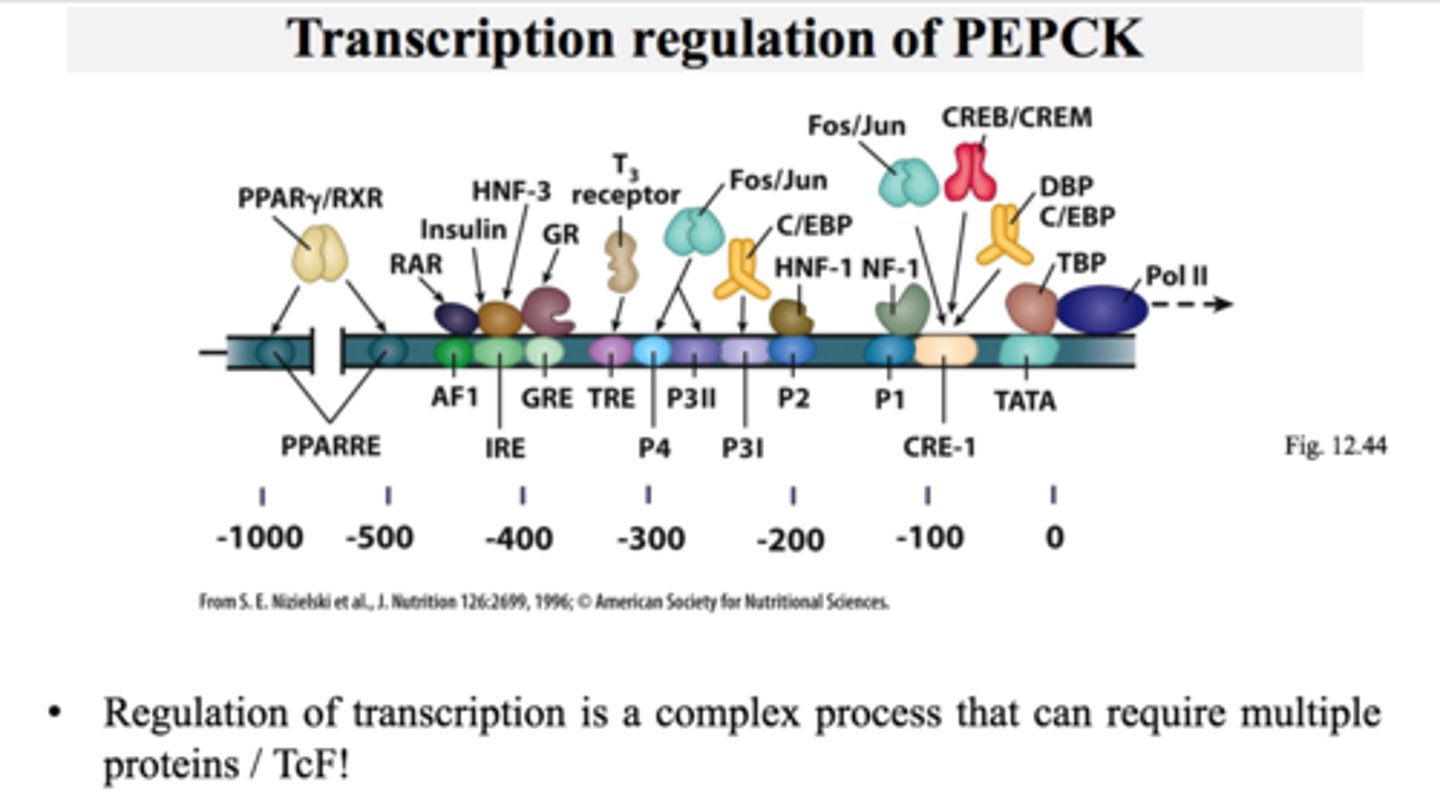
Promoter site in lac operon complex
-further upstream of operator
-similar in function to promoters in eukaryotes
-provides a place for RNA polymerase to bind
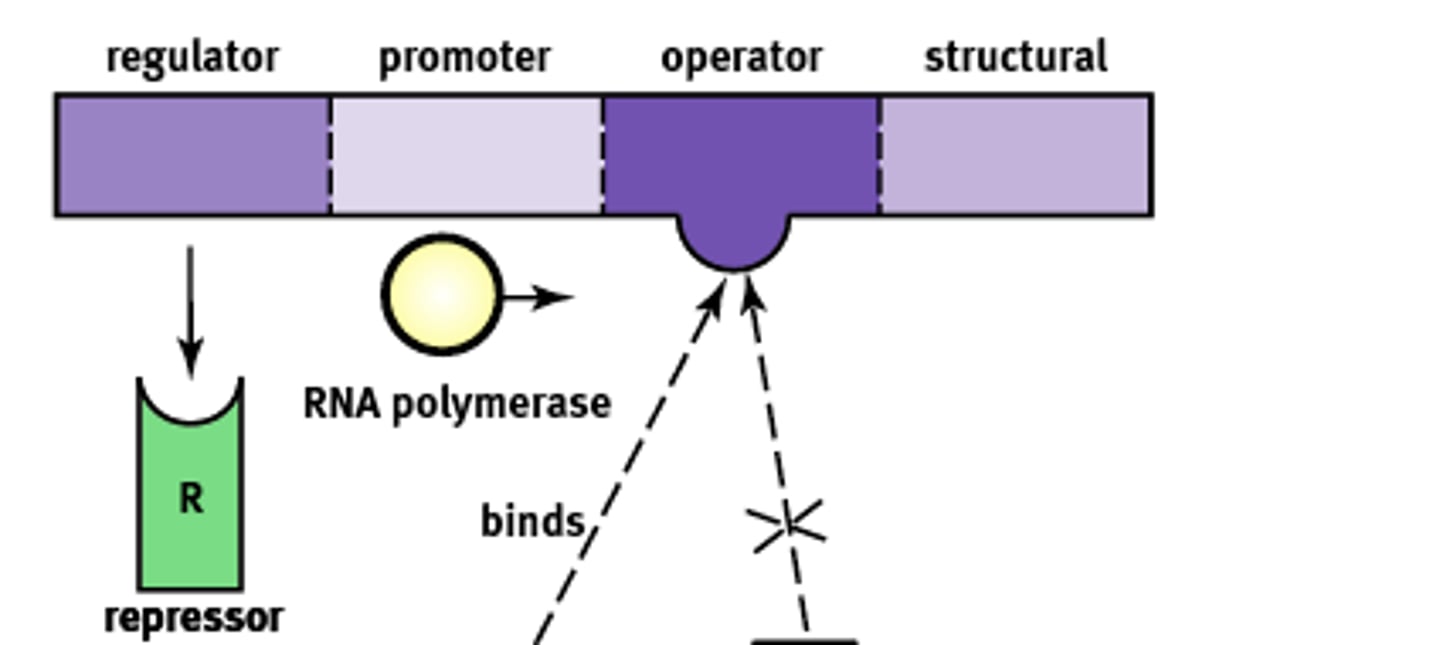
Regulator gene in lac operon complex
-furthest upstream
-codes for protein known as the repressor
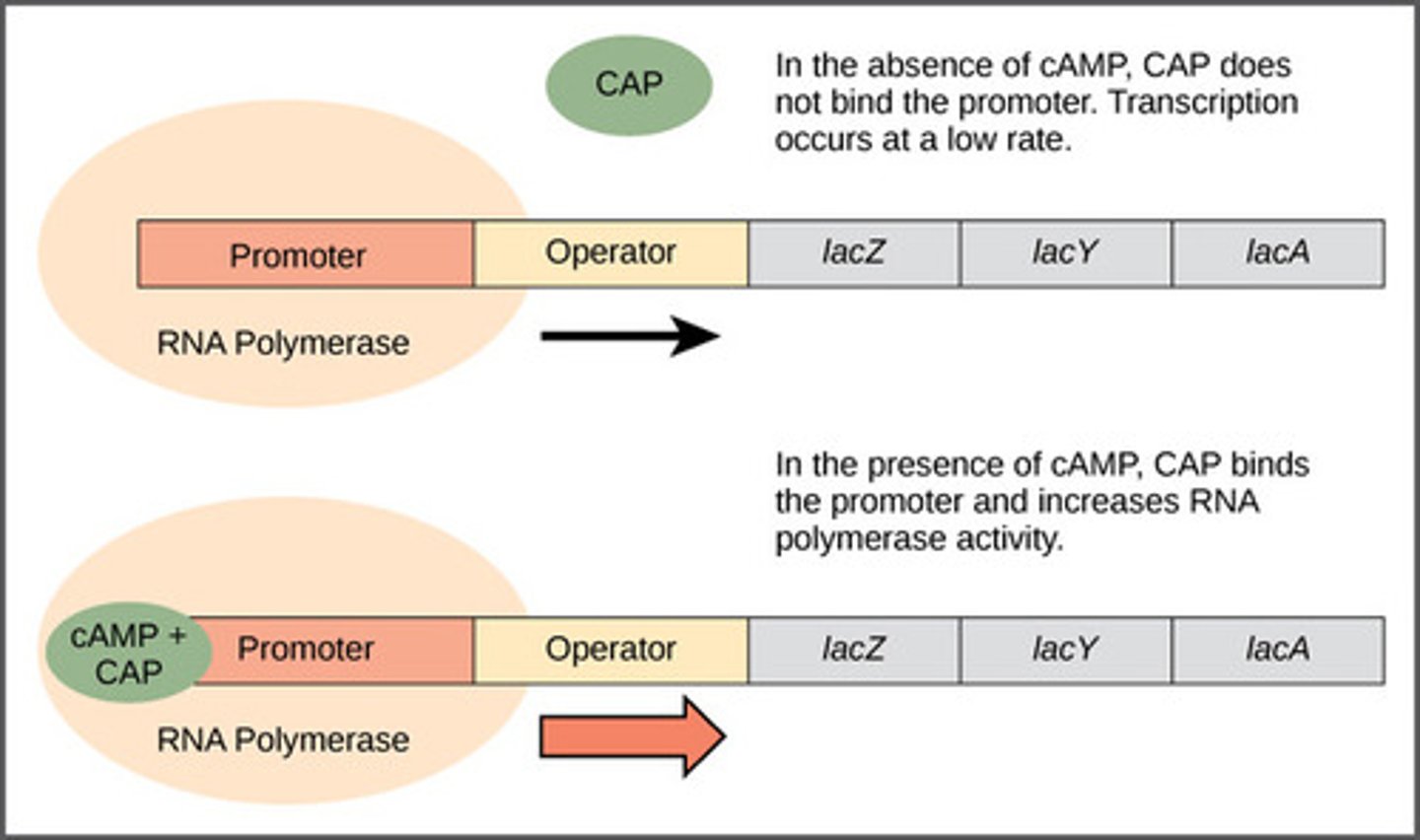
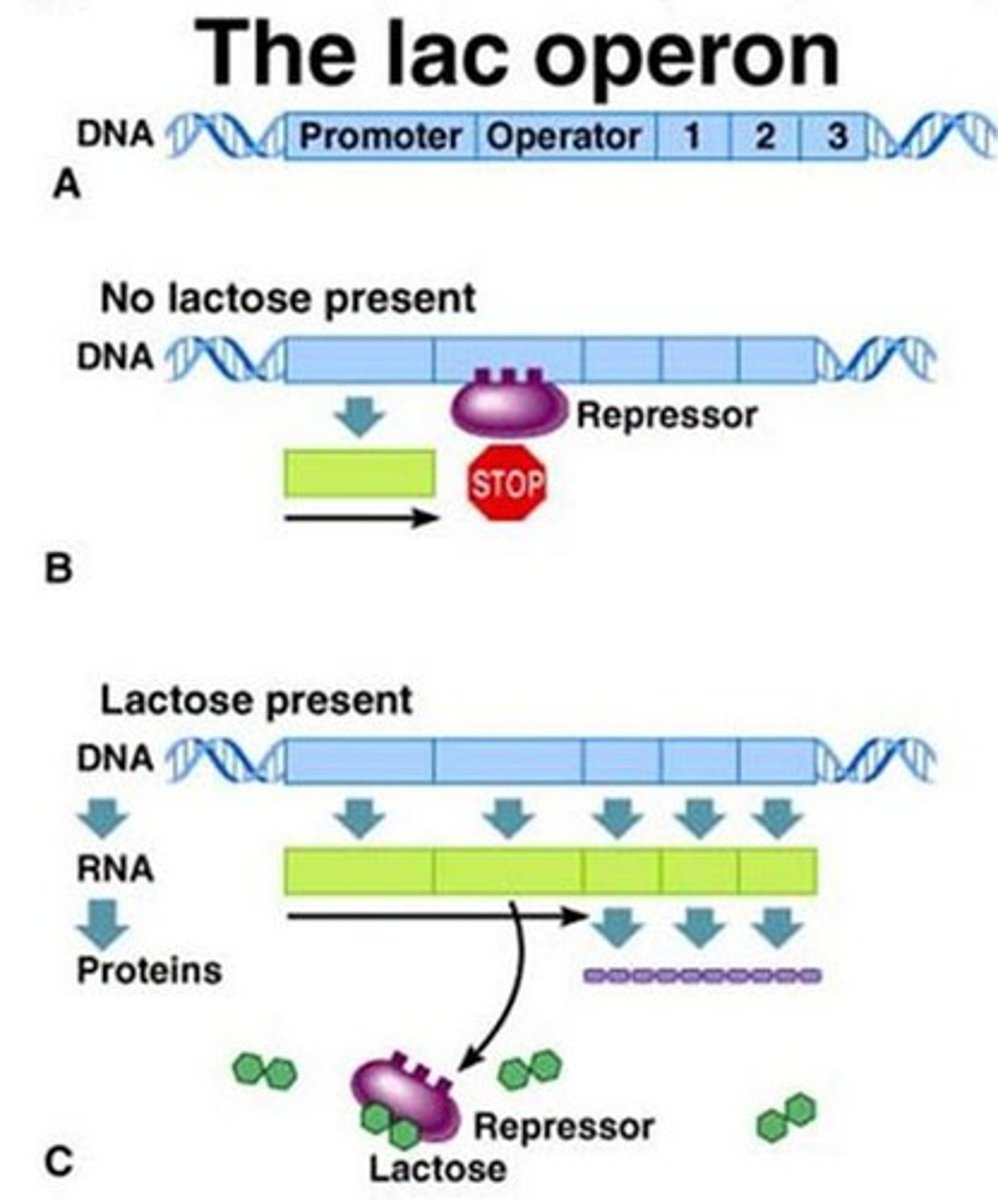
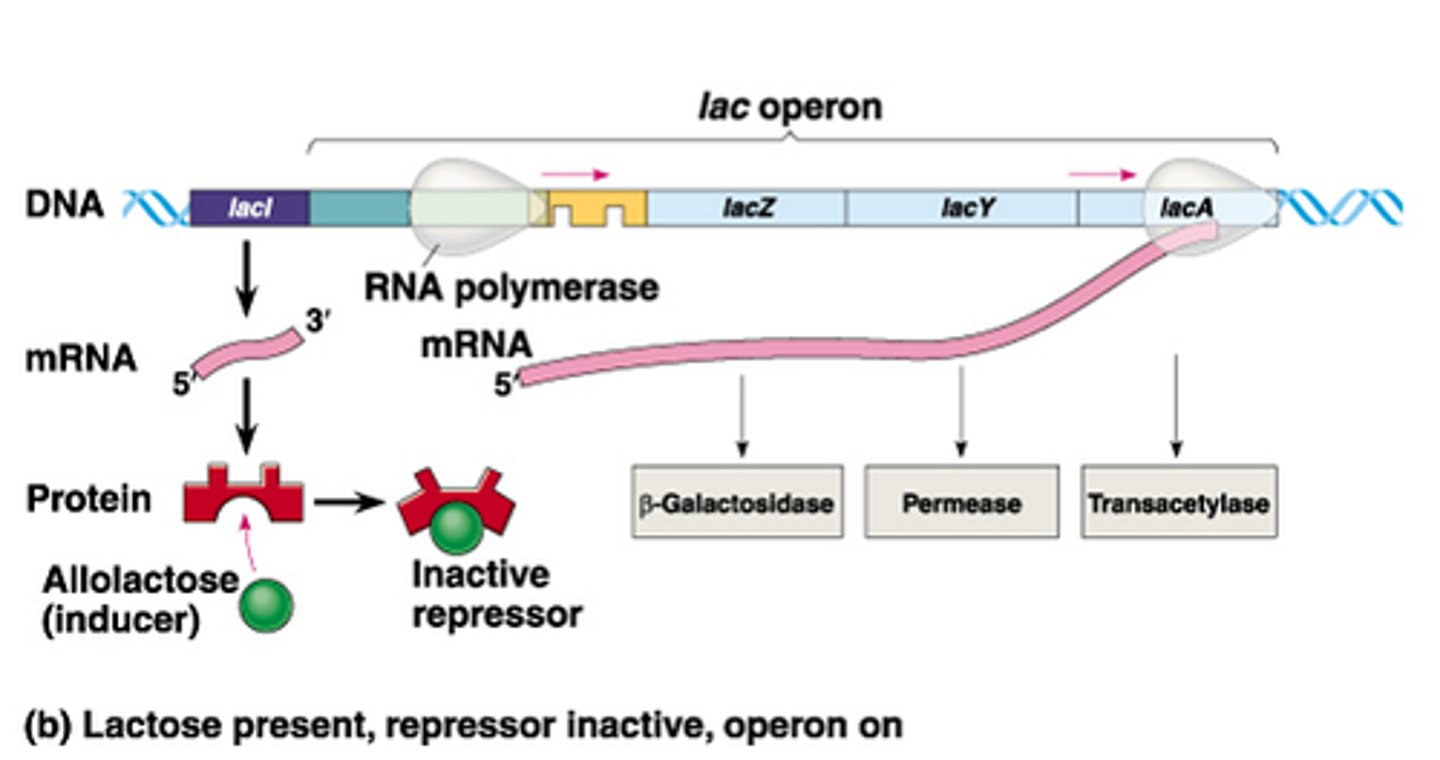
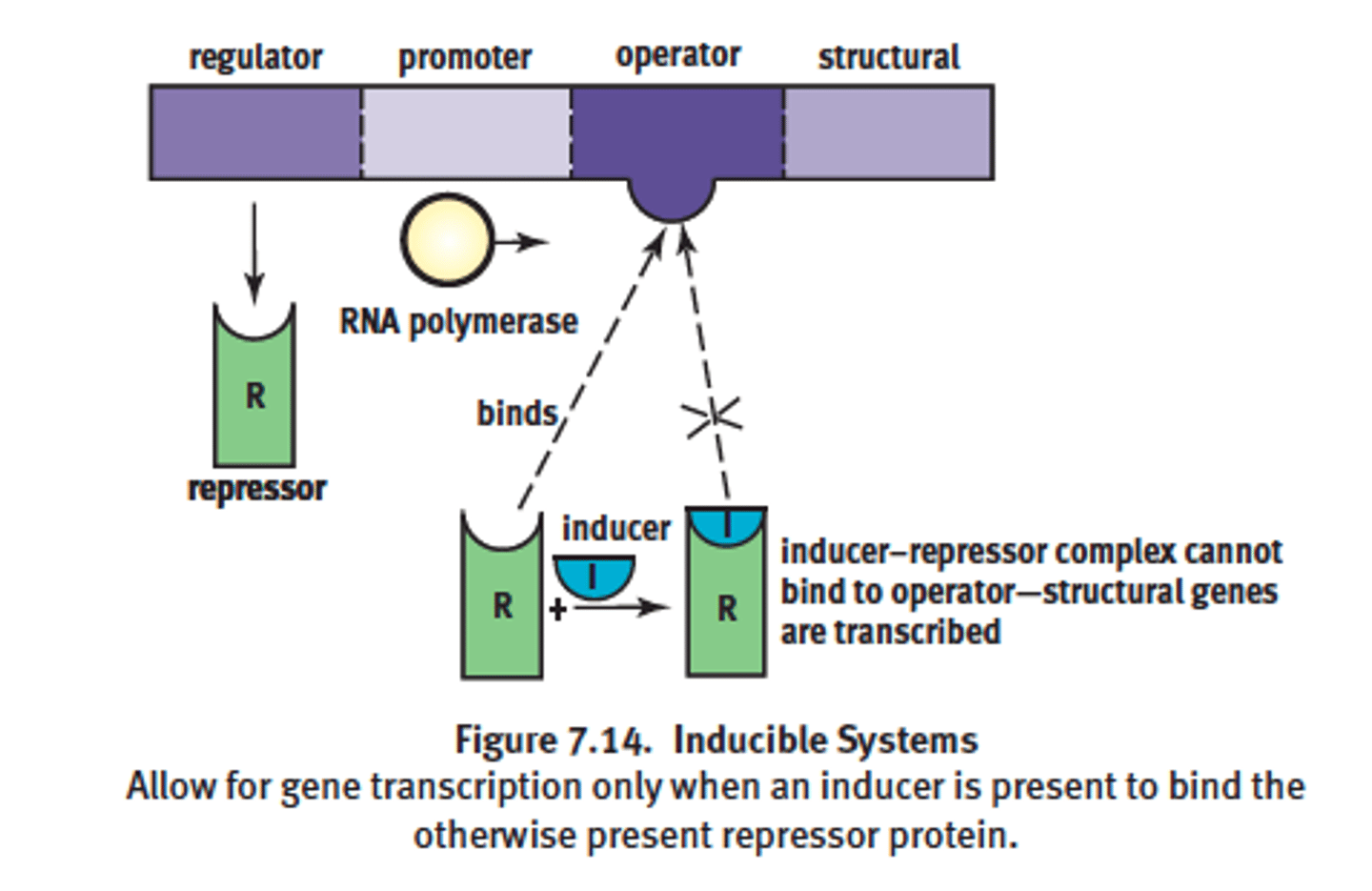
Inducible system in lac operon complex
- repressor binds blocking RNAP bind to promoter = reduces transcription avidity = negative control
- competitive inhibition = remove repressor by adding more inducers
- example: Lac operon system
-goes by positive control mechanism
-bound by a repressor under normal conditions
-can be turned on by an inducer pulling the repressor from the operator site
Repressible system in Trp operon complex
example: Tryptophan operon
-goes by negative control mechanisms
-transcribed under normal conditions
-can be turned off by a corepressor coupling with the repressor and the binding of this complex to the operator site
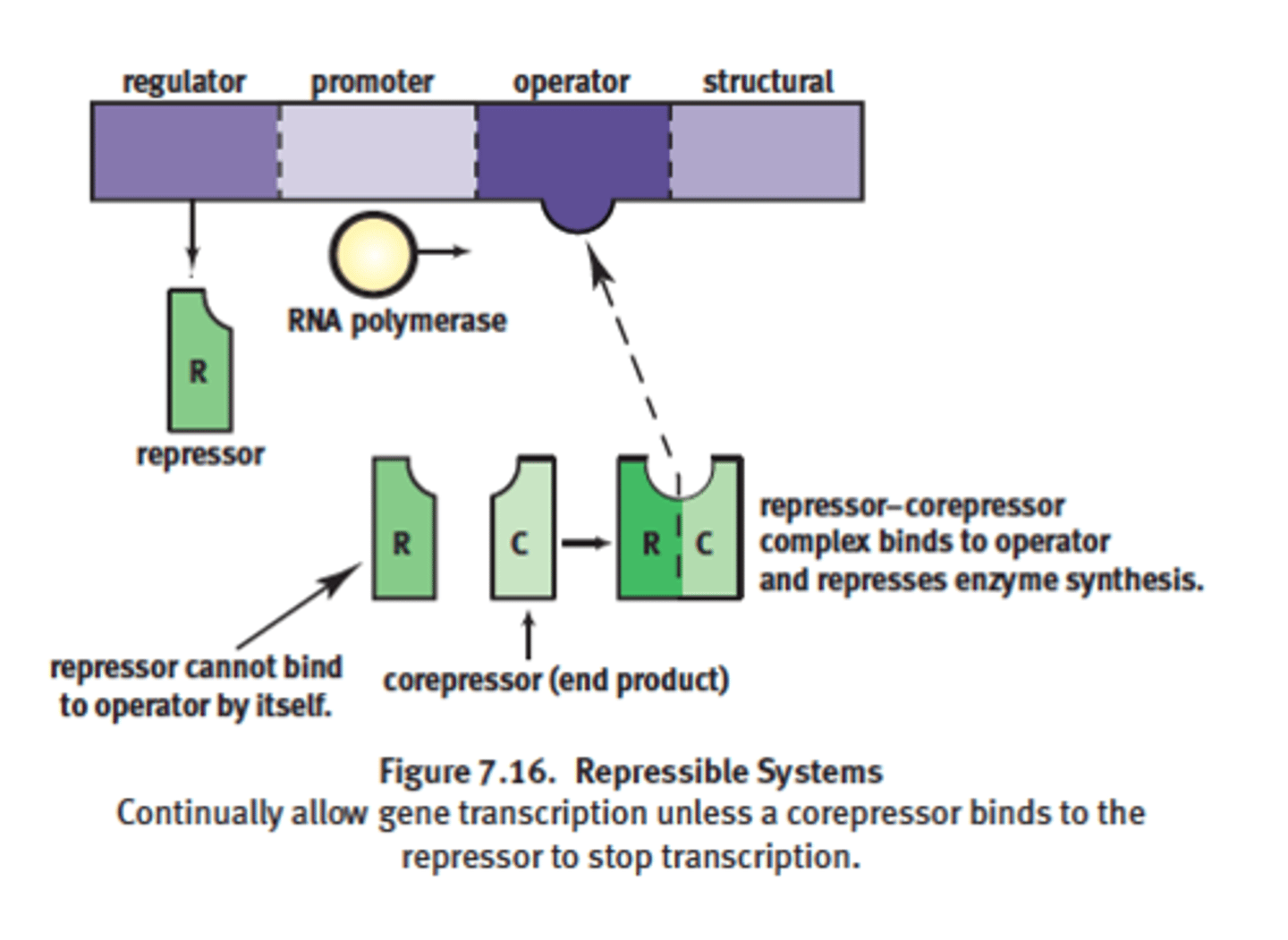
operon systems
positive and negative (how do they work?)
negative control = binding of protein to DNA stops transcription
postive control = binding of protein to DNA increases transcription
inducible sytem = normally off but made to turn on on a given signal
repressible sytem = normally on but made to turn off on a given signal
any combination of console and system: lac operon = negative inducible system and tap operon = positive repressible system
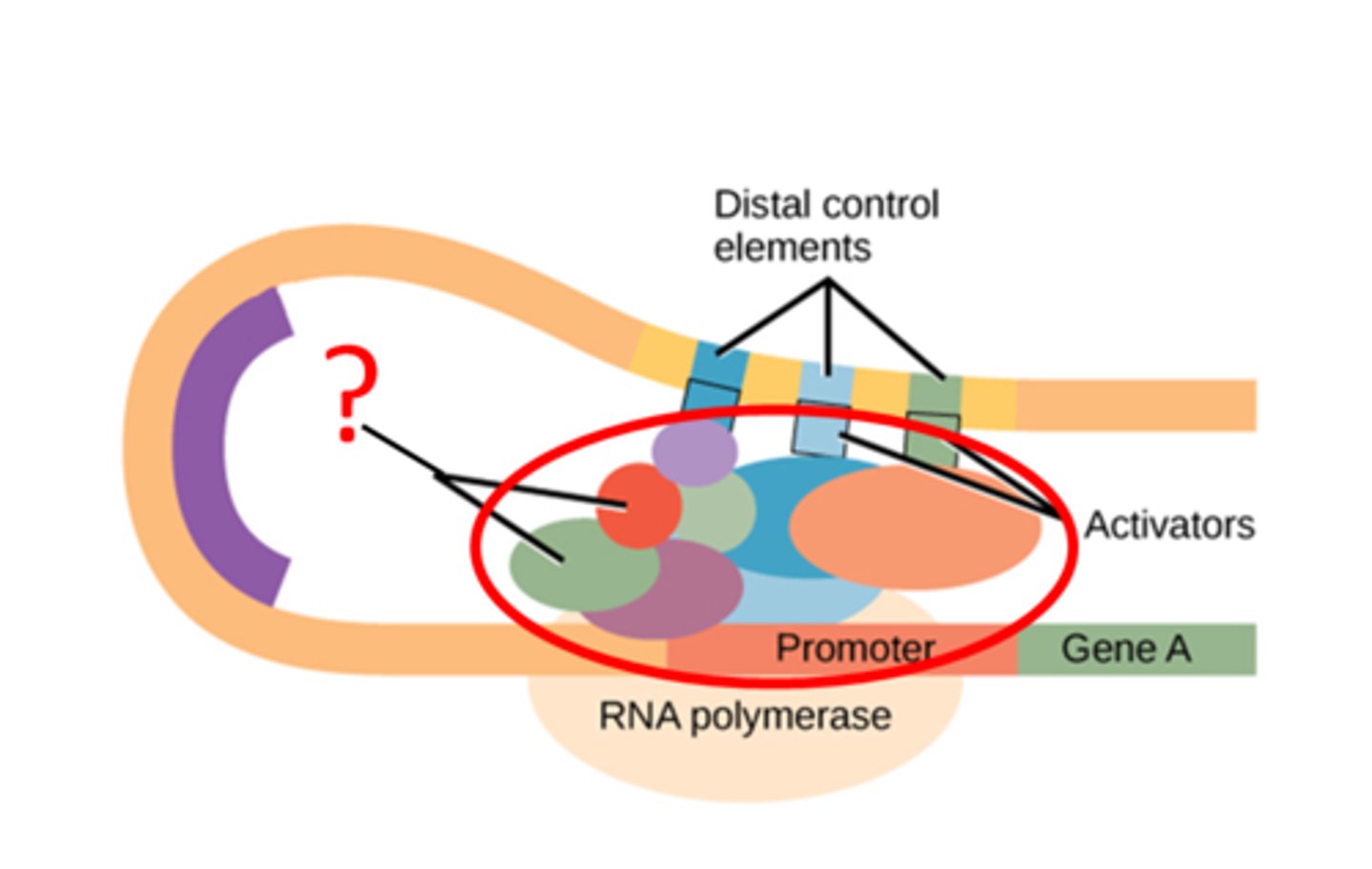
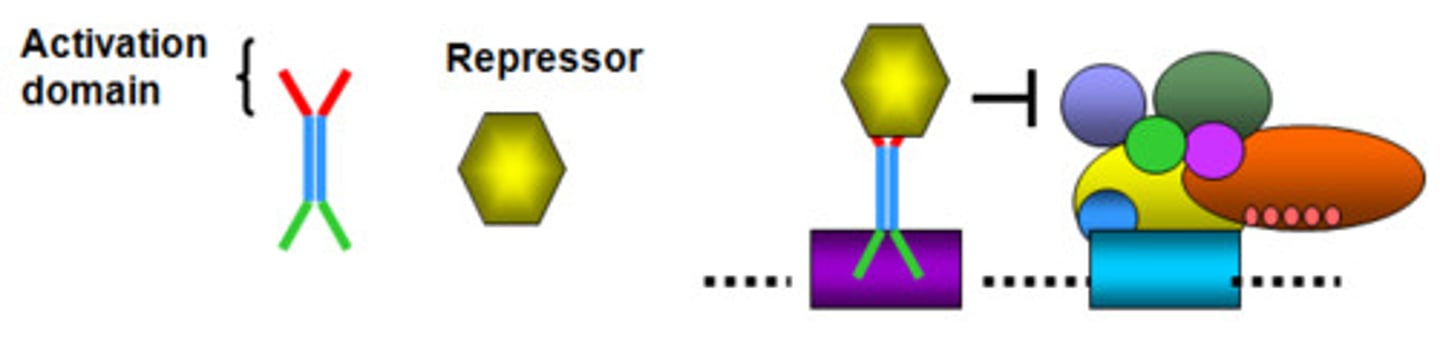
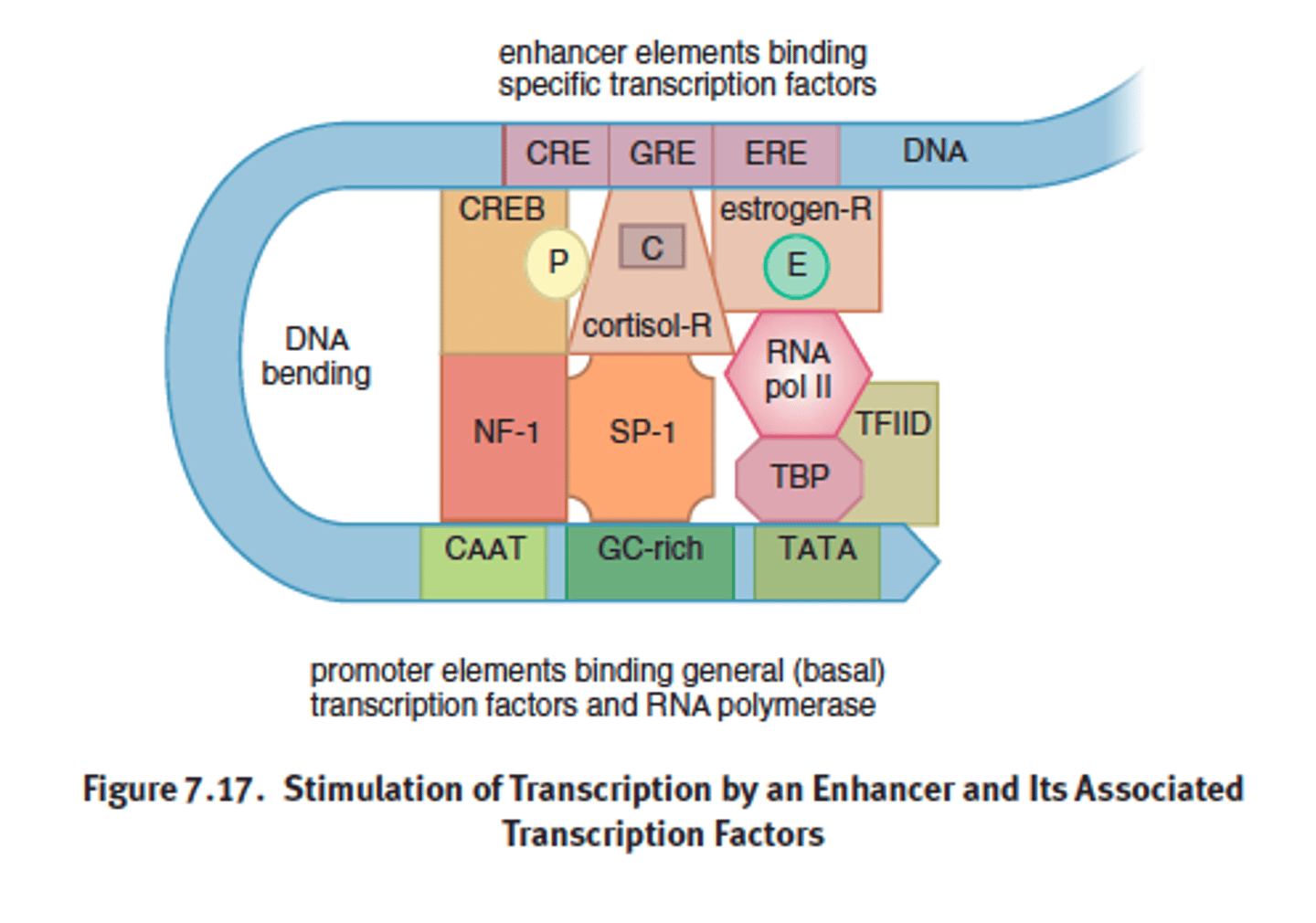
Transcription factor
-transcription-activating proteins that search the DNA looking for specific DNA-binding motifs
-have two domains, DNA-binding domain and an activation domain
- produced and translocated back to nucleus = trans regulators bc they travel through the cell to their point of action
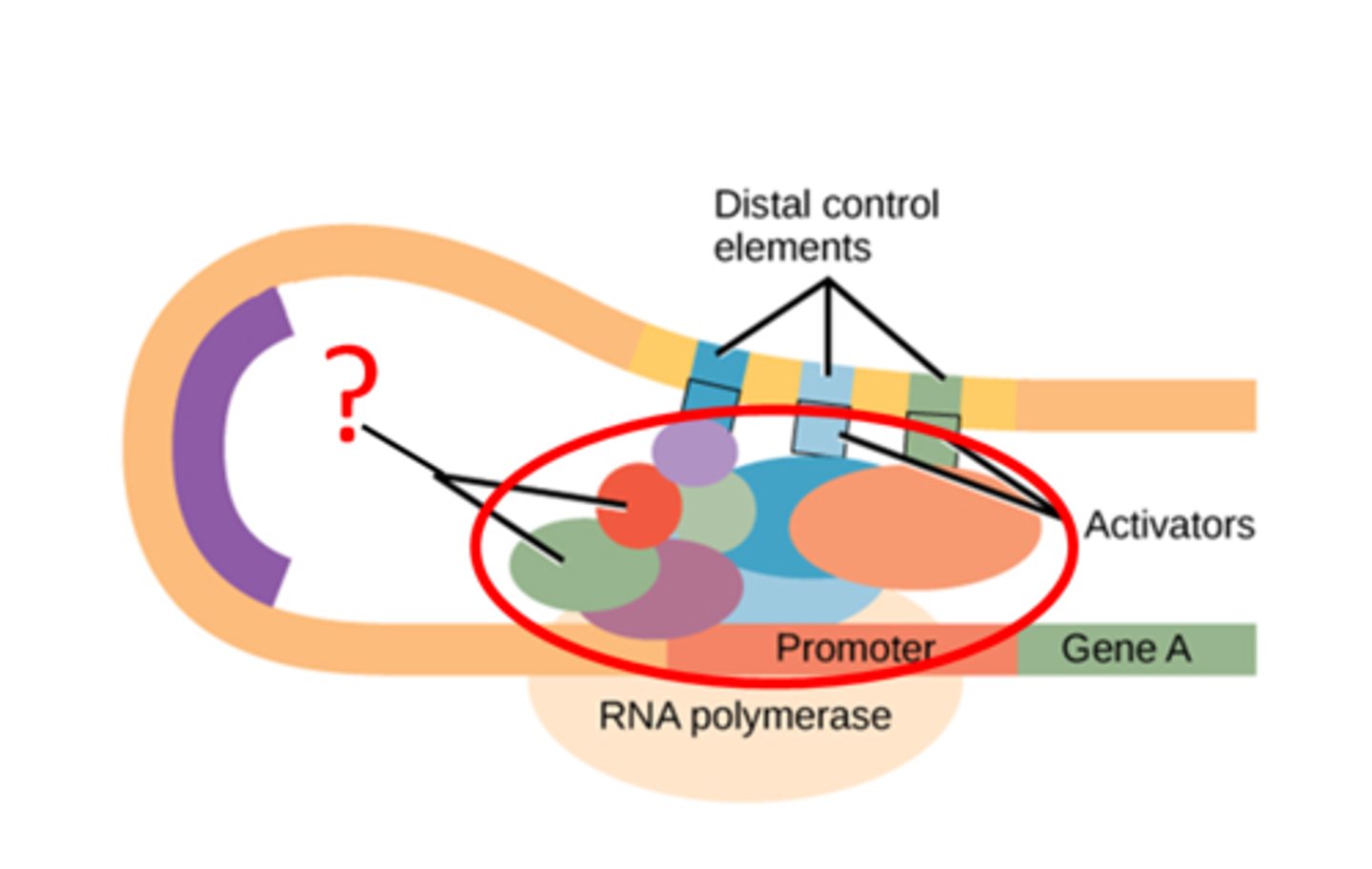
DNA-binding domain on transcription factors
binds to specific nucleotide sequence in the promoter region or to a DNA response element to help in the recruitment of transcriptional machinery
Activation domain on transcription factors
allows for the binding of several transcription factors and other important regulatory proteins, such as RNA polymerase and histone acetylases, which function in the remodeling of the chromatin structure
amplified - means what in terms of gene control and how does it do it
expression increased in response to hormones, GF, or intracellular conditions
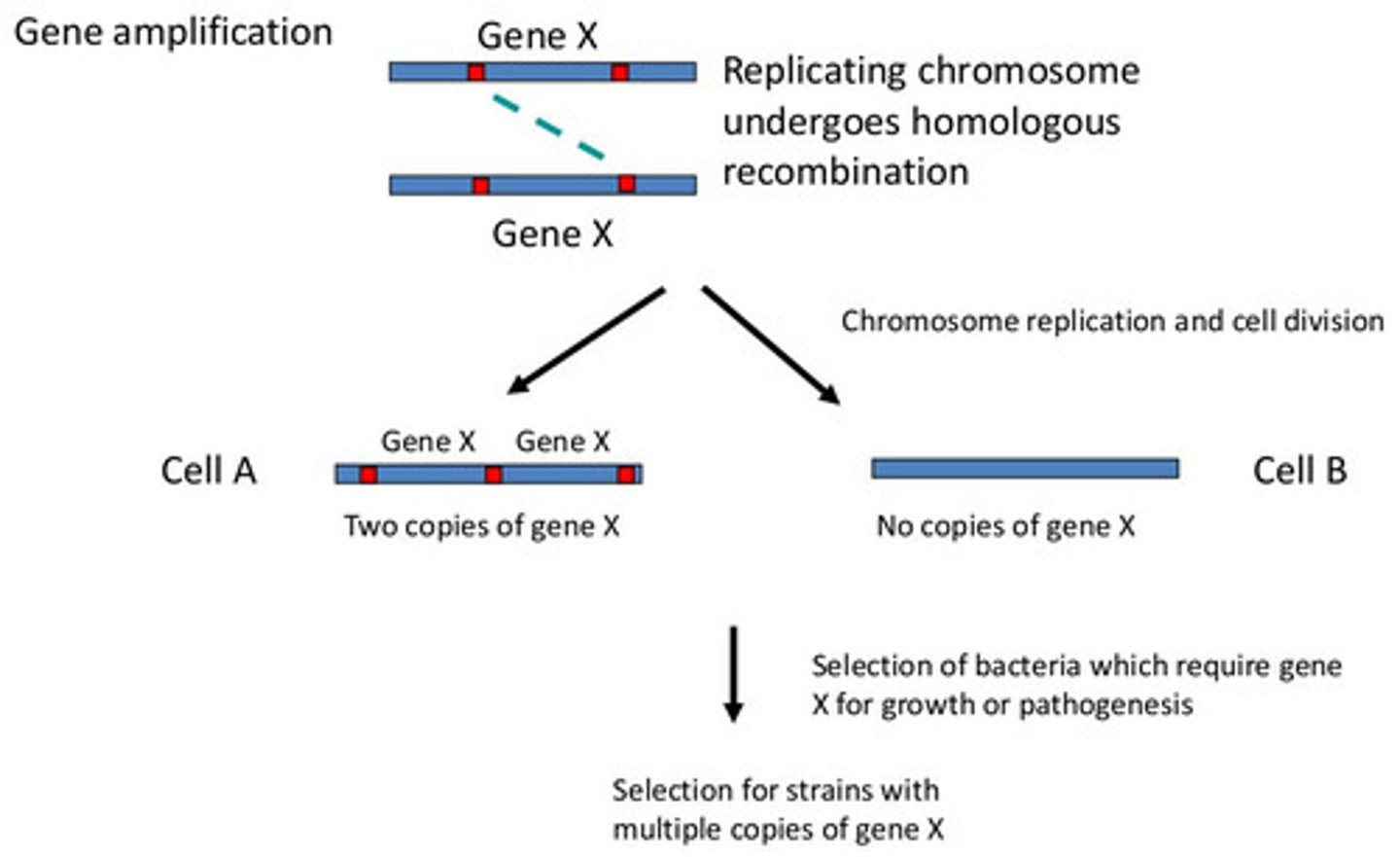
DNA regulatory base sequences
- promoters, eahnccers, response elements = cis regulators bc they are in the same vin city as the gene they control
Enhancer in gene amplification
a collection of several response elements that allow for the control of one gene's expression by multiple signal
gene duplication
duplicated in series on the same chromosome
duplicated in parallel by opening the gene with helices and permitting DNA replication only of that gene
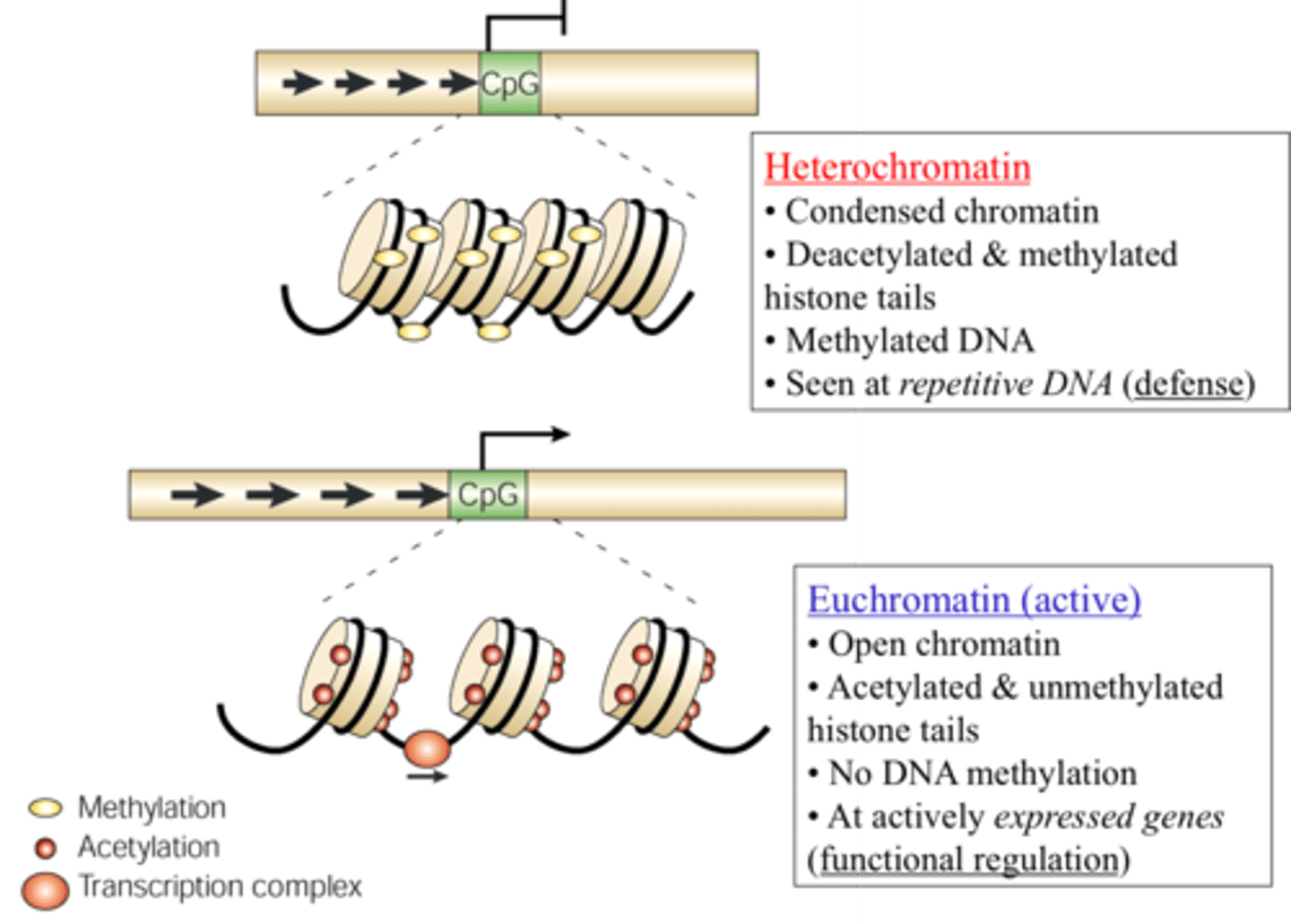
heterochromatin vs. euchromatin in terms of gene expression and structure
HeteroChromatin = Highly Condensed (transcriptionally inactive)
euchromatin = less condensed, transcriptionally active ("truly transcribed")
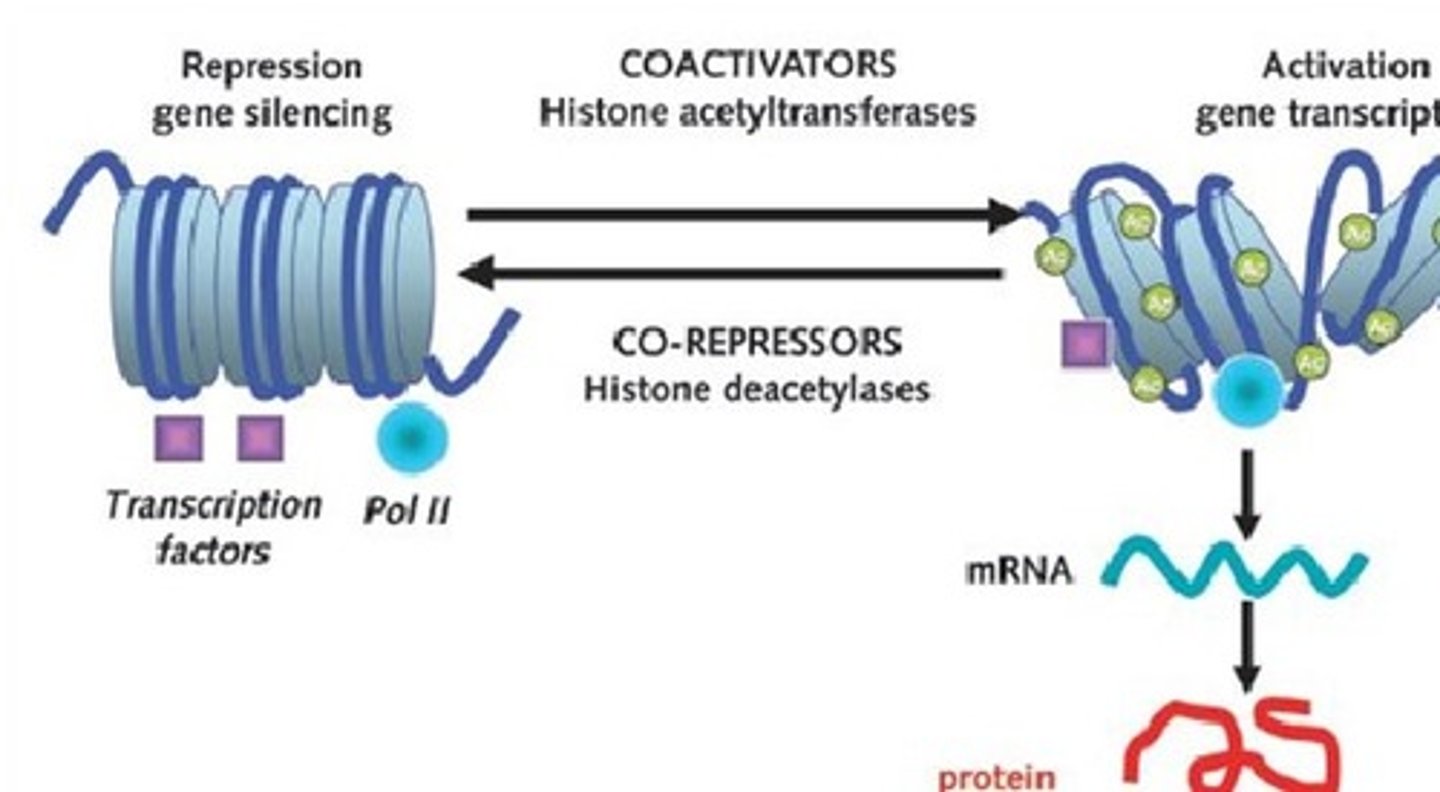
Histone acetylases
Coactivator acetylate lysine residues found in the amino terminal tail regions of histone proteins
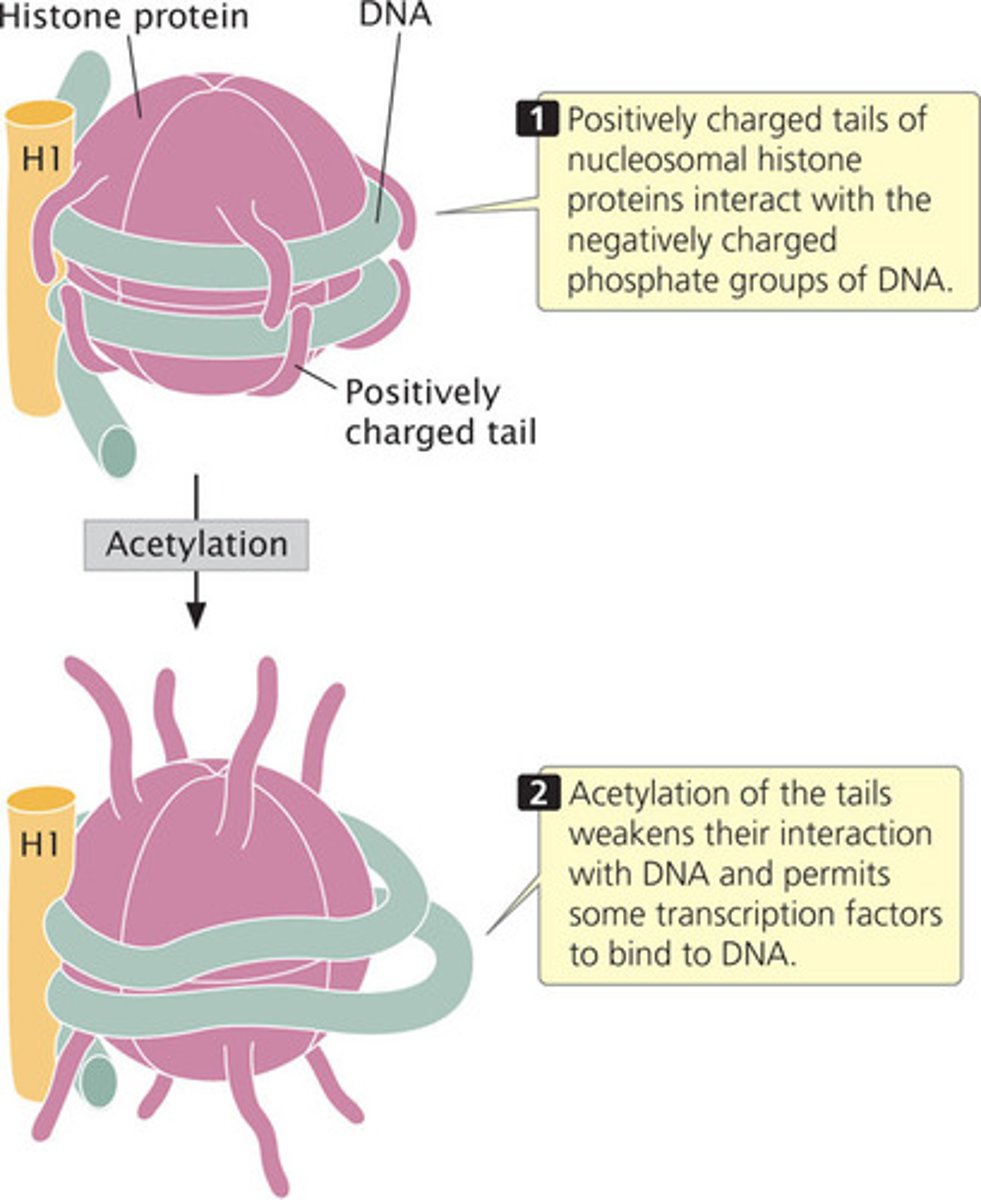
Acetylation (CH3CH) of histone proteins
decreases the positive charge on lysine residues and weakens the interaction of
the histone with DNA, resulting in an open chromatin conformation that allows
for easier access of the transcriptional machinery to the DNA.
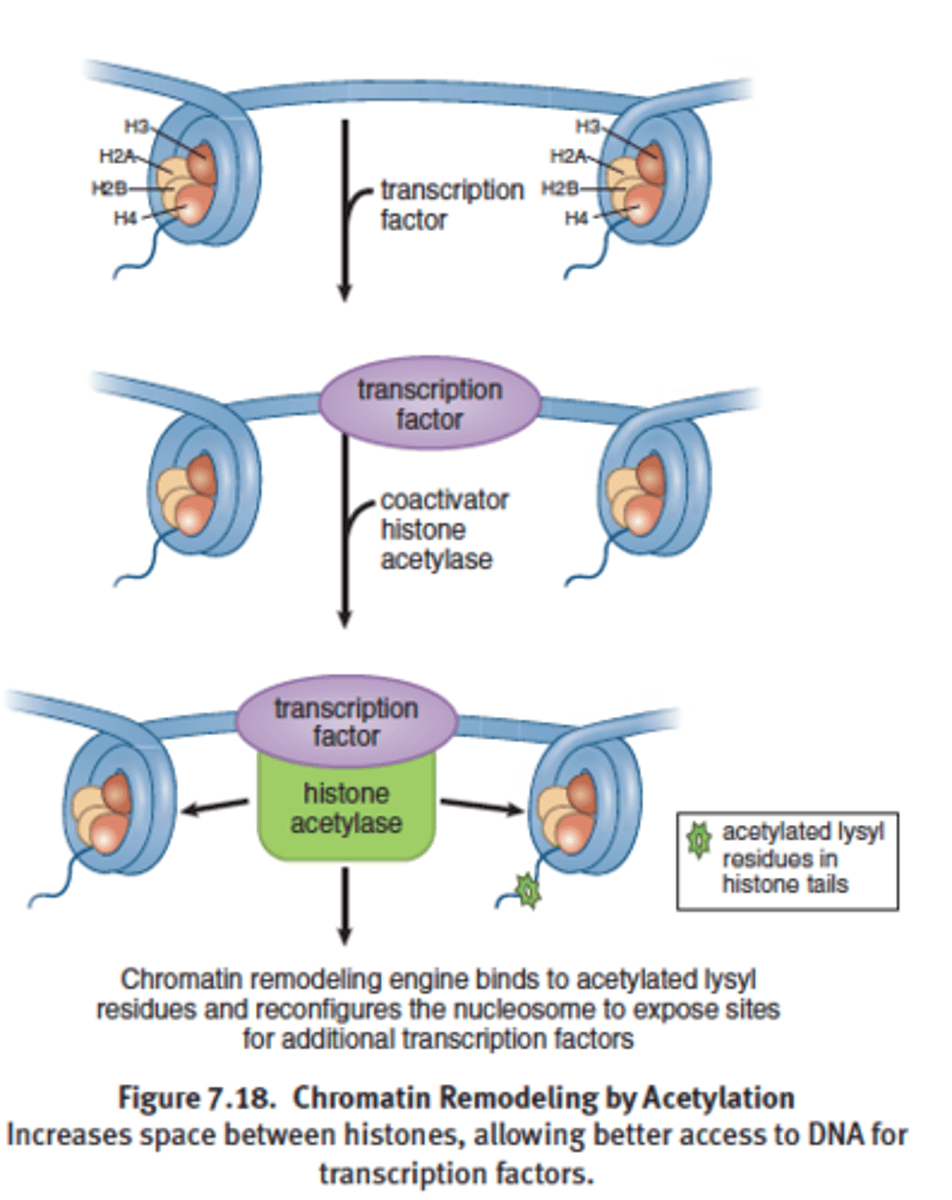
acetylation of histones
-occurs on histone proteins
-decreases the positive charge on lysine residues and weakens the interaction of the histone with DNA
-results in open chromatin conformation
- overall increase in gene expression levels in the cell
Histone deacetylases
remove acetyl groups from histones, resulting in closed chromatin conformation and overall decrease in gene expression levels in the cell
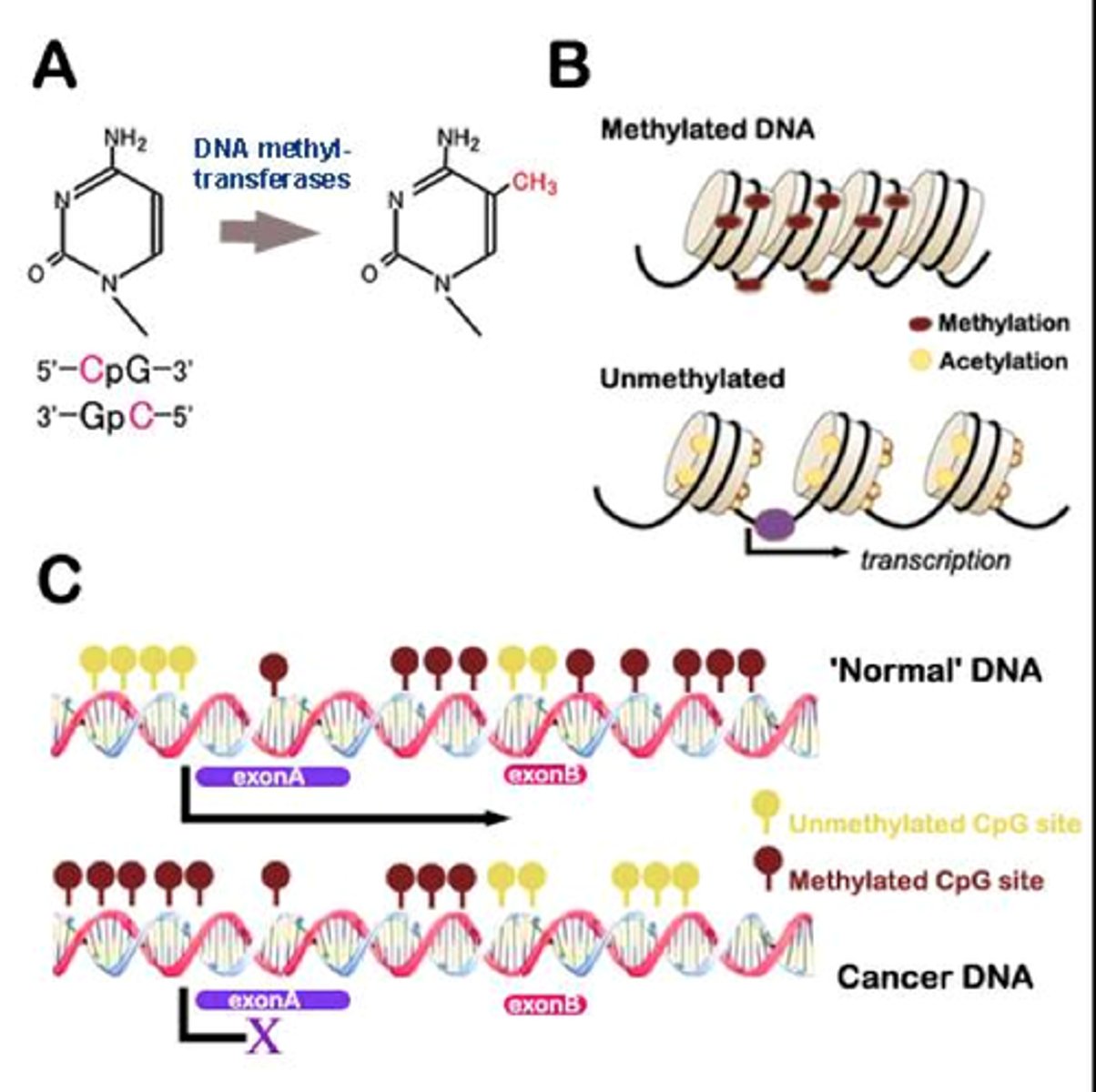
DNA methylation
-DNA methylases add methyl groups to cytosine and adenine nucleotides
-linked with silencing of gene expression
During development, methylation plays an important
role in silencing genes that no longer need to be activated. Heterochromatin
regions of the DNA are much more heavily methylated, hindering access of the
transcriptional machinery to the DNA