The Cell Cycle - AP Bio Ch. 12
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Up to date as of 10/3/23 notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
* What are somatic cells?
Body cells
What is the prerequisite step to mitosis?
DNA must duplicate first
* Where are sister chromatids connected?
at the Centromere
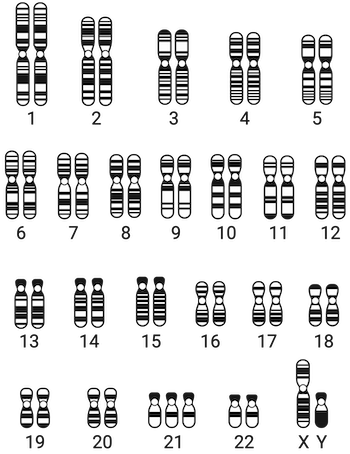
what are these
chromosomes
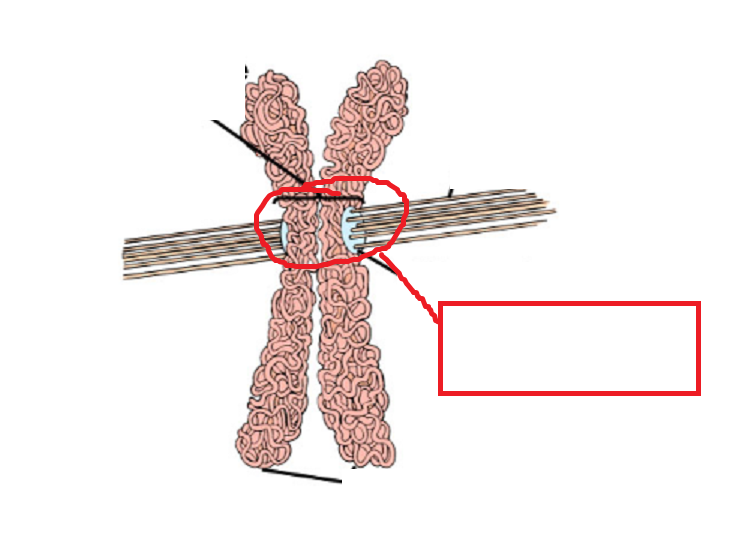
Fill in the blank
Centromere
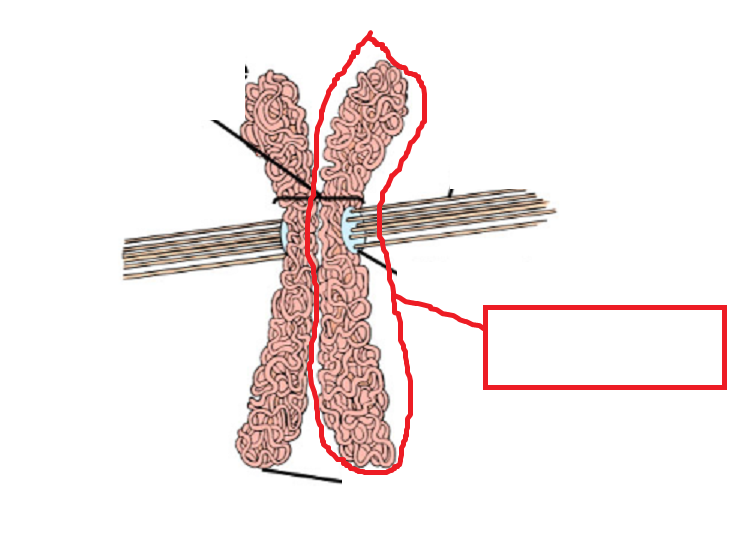
Fill in the blank
Chromatid
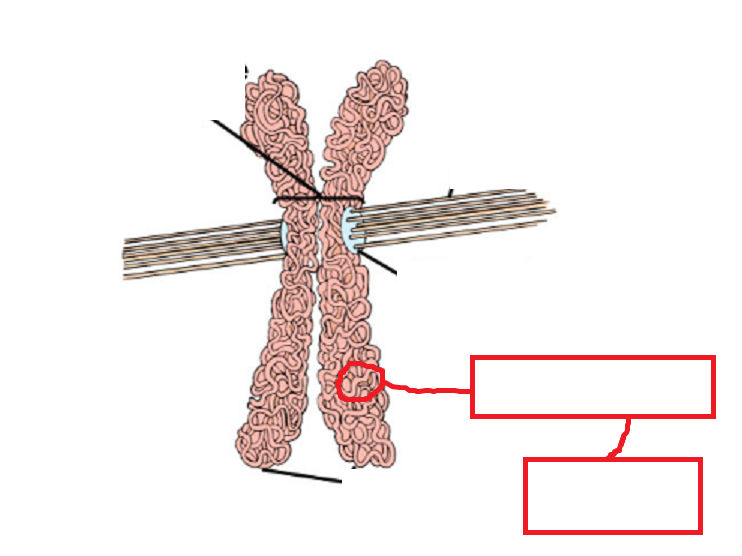
Fill in the blankz
Chromatin
DNA
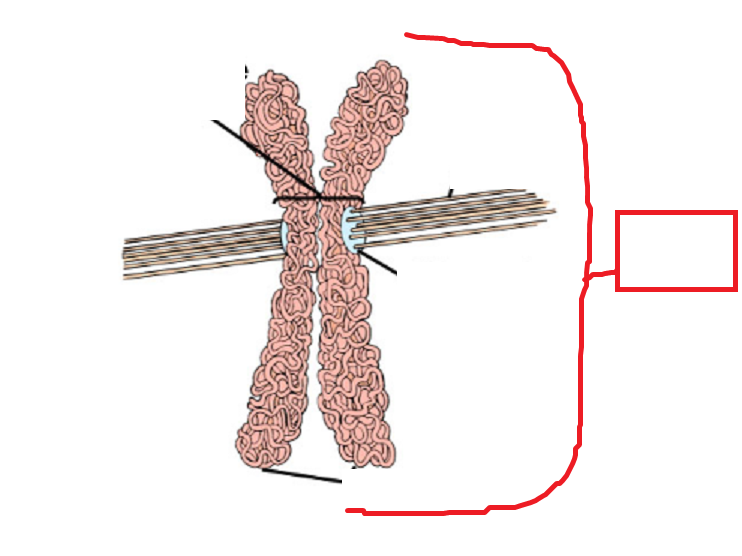
Fill in the blank
Chromosome
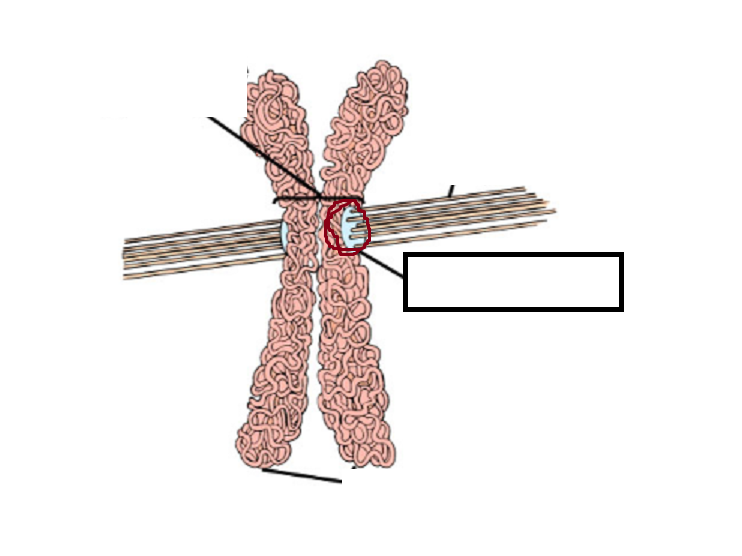
Fill in the blank
Kinetochore
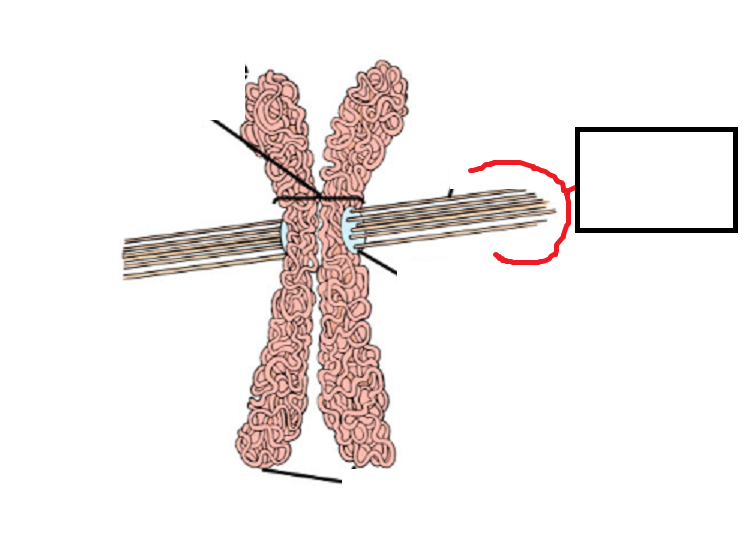
Fill in the blank
Spindles
* What happens during S of interphase?
DNA synthesis- chromosome replicationW
What is mitosis?
Division of the nucleus
What is cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm
What is binary fission?
The division of a prokaryotic cell in half
What is the entire process of binary fission?
DNA is duplicated
Cell elongates and splits in half
the end
* What are checkpoints?
A point in the cell cycle where certain conditions are “looked for” by molecules
What is the most important checkpoint?
G1
What stage is where cells go if they do not pass a checkpoint and are not preparing to divide?
G0 stage
What is the G0 stage
A stage where cells go if they do not pass a checkpoint and where they are not preparing to divide
**What two molecules drive the checkpoint system?
Kinases
Cyclin
**What are kinases? What is their concentration?
Kinases are enzymes with a constant concentration in a cell
**What is the family member of the kinase family?
CDK: cyclin dependent kinase
**What is cyclin? What is its concentration?
A protein that attaches to kinase; its concentration fluctuates/cycles
*What is it called when CDK and cyclin attach to each other?
Maturation promoting factors (MPFs)W
*What are maturation promoting factors (MPFs)?
The name of the molecule when CDK and cyclin attach to each other. they serve as one-time use “keys” to unlock checkpoints.
What would happen if there was not enough cyclin to attach to the CDK?
The CDK would just wait until it has cyclin
What is the process of a checkpoint “unlocking”
Cyclin is accumulated and bumps into CDK by chance
Cyclin + CDK attach and become MPF
Cyclin begins to degrade immediately after the checkpoint and comes apart from the CDK
Repeat :)
***When will there be the highest concentration of cyclin X?
At checkpoint X
Cyclin is like a ______. Once it is used, it ________ be used again.
Coupon; cannot
How important is cyclin degrading?
Super
Cyclin + _____ = MPF
CDK
______ + CDK = MPF
Cyclin
Cyclin + CDK = ______
Can a hypothetical MPF A open checkpoint B?
No
What does CDK stand for
Cyclin dependent kinase
What builds cyclin
Ribosomes
What is the centromere?
The region where chromatids are attached to eachother
What is a chromatid?
A replicated chromosome
How many centromeres are there if there are 40 chromatids in a cell?
20 centromeres
True or false: Mitosis produces new nuclei w/ exactly the same chromosomal endowment as the parent nucleus?
True
True or false: The mitotic spindles in prokaryotic cells are composed of microtubules.
False!!
This is a trick question!! Prokaryotes do not have spindles!!