Chapter 28: Pacific Art
Key Notes
- Time Period: From Ancient Times to Present
- Culture, beliefs, and physical settings
- The Pacific has 1,500 inhabited islands, each with a distinct ecology.
- Australia was populated 30,000 years ago. The Lapita people migrated east about 4,000 years ago.
- Pacific peoples are seafaring.
- The sea is a major theme in Pacific art.
- Cultural interactions
- Pacific art has been influenced by ecology, colonialism, social structure, missionary activity, and commerce.
- Europeans encountered the Pacific in the sixteenth century. Later, they divided the region into three distinct zones: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia.
- Material Processes and Techniques
- Pacific art is seen as a whole: the work of art exists in the context of events, media, and ceremonies. There is a wide variety of materials used in Pacific art.
- Among the materials used in Pacific art are bone, seashell, fiber, wood, stone, and coral, as well as tortoise shell.
- Materials are likely to create a response in the audience; i.e., precious objects denote wealth.
- Audience, functions, and patron
- Pacific art is related to forces in the spiritual world. One’s vital force, or mana, was often wrapped or shielded to be protected. Sometimes mana could represent a whole community. The act of protecting the mana through rituals or wrapping is called tapu.
- Pacific art is often performed using dance, singing, costuming, scent, and cosmetics.
- Objects often illustrate familial and societal history. Others are created to be performed and later destroyed.
- Sacred ceremonial spaces are common in the Pacific. Masks are key elements in Pacific performances.
- Rituals and performances often involve exchanging prearranged items that have symbolic value.
- A symmetry of relationships is often sought. Opposing forces, such as gender, are placed within a balancing situation in many rituals.
- Theories and Interpretations
- Pacific art is an expression of a collection of beliefs and social relationships.
- Creating or destroying a work of art often carries great significance, sometimes more significant than the object itself.
- The act of performance contains the work’s meaning.
- The objects in that performance contain no meaning unless brought to life by rituals.
Historical Background
- Some areas of the Pacific are among the oldest inhabited places on earth, while others are among the newest.
- Aborigines reached Australia around 50,000 years ago.
- Remote Pacific islands like Hawaii, Easter Island, and New Zealand were occupied only in the last thousand years.
- Seafarers reached Fiji in the central South Pacific around 1300 B.C.E.
- Technological development of sailing craft enabled greater territories to be mapped and charted for possible occupation.
- Tonga was reached in 420 B.C.E. and Samoa in 200 B.C.E. using the particularly effective twin-hulled sailing canoe.
- The discovery of New Zealand by the ancestors of the Maori happened perhaps as early as the tenth century, but certainly by the thirteenth century.
- European involvement in the Pacific began with the circumnavigation of the globe by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and his crew.
- Explorers of the eighteenth century were followed by occupiers from the nineteenth century, who implanted European customs, values, religions, and technologies onto the indigenous population.
- Many areas of the Pacific achieved independence in the twentieth century.
Patronage and Artistic Life
- Pacific society had clear gender roles
- Men were responsible for wood carving
- Women were responsible for sewing and pottery
- Women in the Pacific still weave barkcloth or tapa
- Inner bark of the mulberry tree is harvested and made malleable by soaking
- Strips of bark are placed in a pattern and fused together by beating
- Designs are added by stenciling or painting directly onto the surface
- The result is a cloth of refined geometric organization and intricate patterning
Key Terms
- ‘Ahu ‘ula: Hawaiian feather cloaks
- Malagan: a large, traditional ceremony from Papua New Guinea, as well as the masks and costumes used in that ceremony
- Mana: a supernatural force believed to dwell in a person, or a sacred object
- Moai: large stone sculptures found on Easter Island
- Tapa: a cloth made from bark that is soaked and beaten into a fabric
- Wapepe: navigation charts from the Marshall Islands
Micronesia
➼ Nan Madol
Details
- Saudeleur Dynasty
- c. 700–1600
- basalt boulders and prismatic columns
- Found in Pohnpei, Micronesia
Form
- 92 small artificial islands connected by canals, about 170 acres in total.
- Built out into the water on a lagoon—similar to Venice, Italy.
- Seawalls 15 feet high and 35 feet thick acted as breakwaters.
- Canals were flushed clean with the tides.
- Islands were arranged southwest to northeast to take advantage of the trade winds.
- Walls were made of prismatic basalt; roofs were thatched.
Function: Ancient city that acted as the capital of the Saudeleur Dynasty of Micronesia.
Context
- City built to separate the upper classes from the lower classes.
- King arranged for the upper classes to live close to him, to keep an eye on them.
- Curved outer walls point upward at edges, giving the complex a symbolic boat-like appearance.
Image

➼ Female Deity
Details
- c. 18th to 19th century
- Wood
- Found in Nukuoro, Micronesia
Form
- Simple geometric form.
- Erect pose, long arms, broad chest.
- Chin drawing to a point; no facial features.
- Horizontal lines were used to indicate kneecaps, navel, and waistline.
Function: Female deity.
Context
- Many were kept in religious buildings belonging to the community.
- They represent individual deities.
- Sometimes they were dressed in garments; may have been decorated with flowers.
- Taken by missionaries who did not record anything about the sculptures.
Image

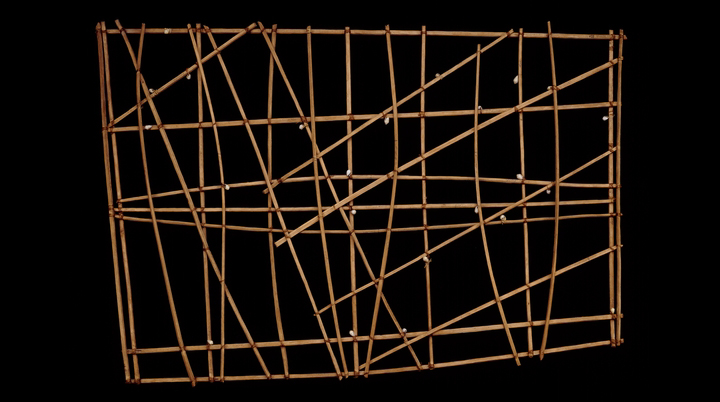
➼ Navigation Chart
Details
- From Marshall Islands, Micronesia
- 19th to early 20th century
- wood and fiber
- British Museum, London
Form
- Chart is made of wood, therefore waterproof and buoyant.
- Small shells indicate the position of the islands on the chart.
- Horizontal and vertical sticks support the chart.
- Diagonal lines indicate wind and water currents.
- Charts indicate patterns of ocean swells and currents.
Function
- Charts meant to be memorized prior to a voyage; not necessarily used during a voyage.
- Charts enabled navigators to guide boats through the many islands to get to a destination. Charts were individualized to their makers; others cannot read the chart.
Context
- Marshall Islands are low lying and hard to see from a distance or from sea level.
- Charts are called wapepe in the Marshall Islands.
Image
Hawaii
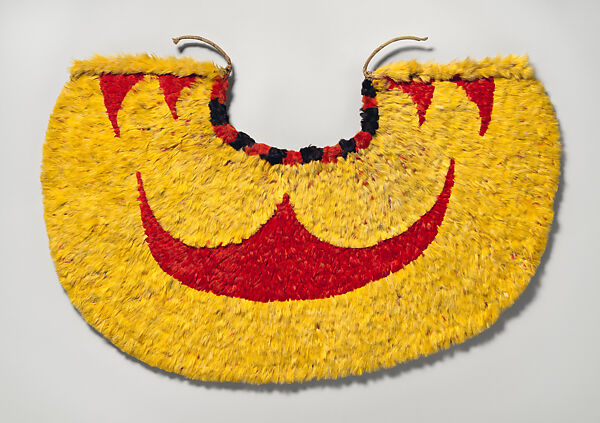
➼ ‘Ahu ‘ula (Feather Cape)
Details
- late 18th century
- feathers and fiber,
- Found in British Museum, London
Materials
- The cape is made of thousands of bird feathers.
- Feathers numbered 500,000; some birds had only seven usable feathers.
- The feathers were tied to a coconut fiber base.
Function: Only high-ranking chiefs or warriors of great ability were entitled to wear these garments; worn by men.
Context
- Red was considered a royal color in Polynesia; yellow was prized because of its rarity.
- The cape was created by artists who chanted the wearer’s ancestors to imbue their power onto it.
- It protected the wearer from harm.
- The concept of “mana:” a supernatural force believed to dwell in a person or sacred object.
- Many capes have survived, but no two capes are alike.
Image

Cook Islands
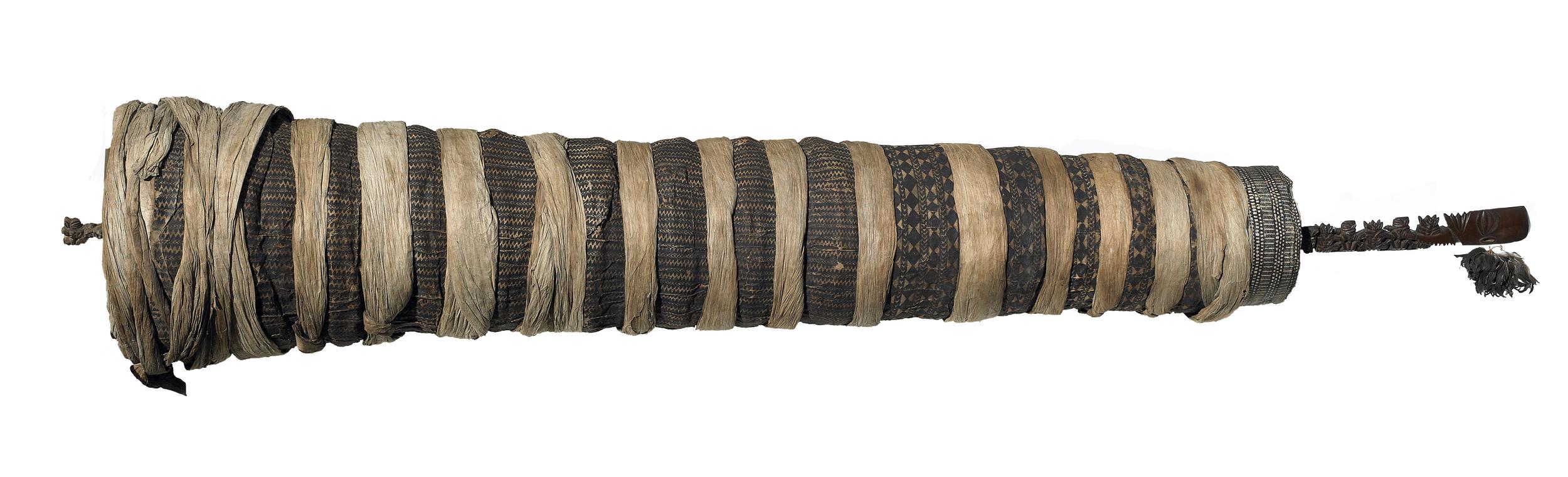
➼ Staff God
Details
- From Rarotonga, Cook Islands, central Polynesia
- late 18th to early 19th century
- wood, tapa, fiber, and feathers
- Found in British Museum, London
Form and Content
- Large, column-like, wooden core mounted upright in village common spaces; the wooden core is wrapped with tapa cloth.
- The wooden sculpture placed on top features a large carved head with several smaller figures carved below it).
- The shaft is in the form of an elongated body.
- The lower end had a carved phallus. Some missionaries removed and destroyed the phalluses, considering them obscene.
- The soul of the god is represented by polished pearl shells and red feathers, which are placed inside the bark cloth next to the interior shaft.
Context
- Most staff gods were destroyed; only the top ends were retained as trophies.
- This is the only surviving wrapped example of a staff god.
- In the contextual image from a book by an English missionary (not shown), the staff gods have been thrown down in the village square in front of a European-style church; it represents the fall of one faith and the adoption of another.
- The contextual image is the only visual evidence that indicates how these staff gods were used.
- Reverend John Williams observed that the barkcloth contained red feathers and pieces of pearl shell, known as the manava or the spirit of the god. He also recorded seeing the islanders carrying the image upright on a litter.
Image

Polynesia
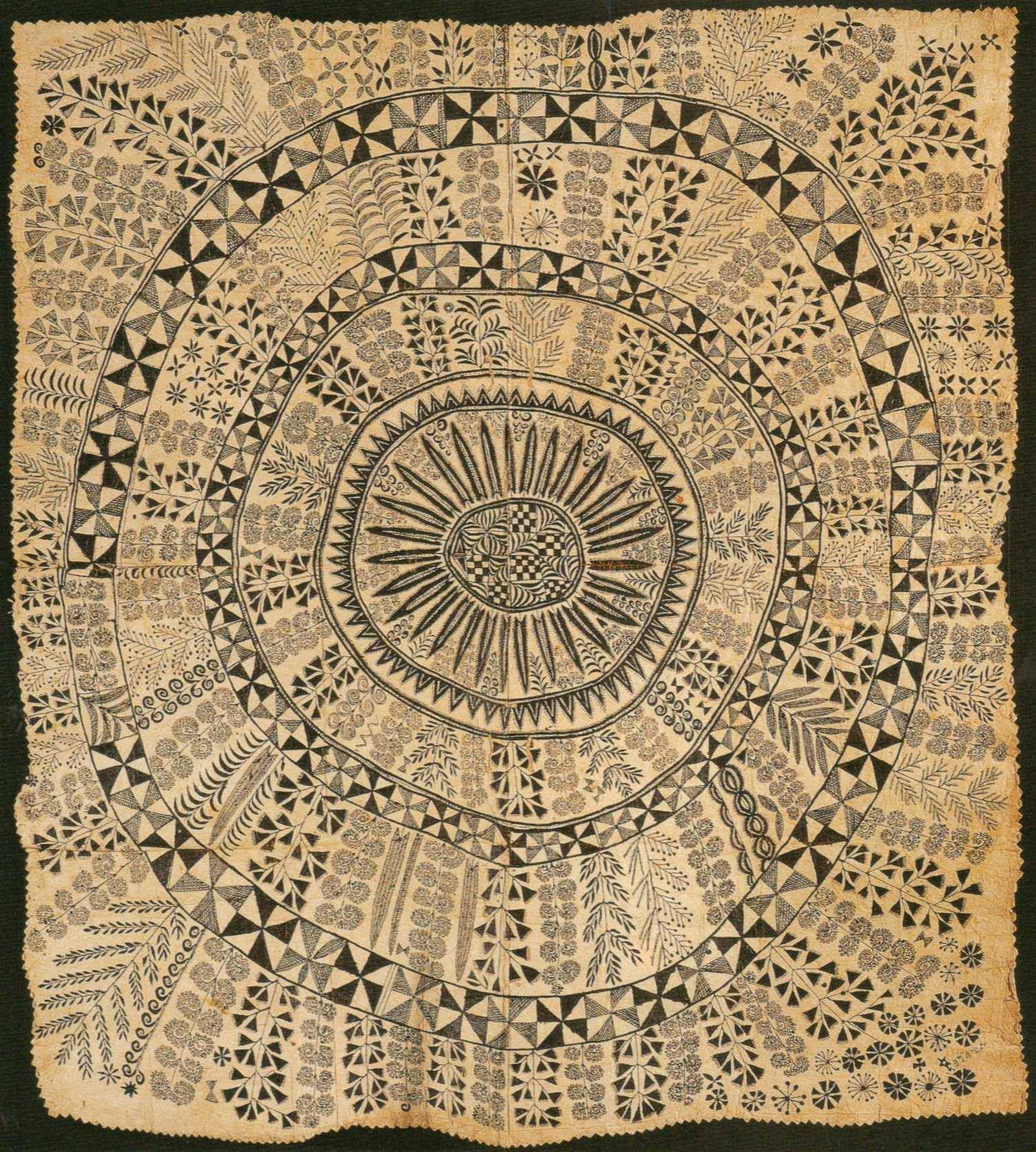
➼ Hiapo (Tapa)
Details
- from Niue
- c. 1850–1900
- tapa or bark cloth, freehand painting
- Found in Auckland War Memorial Museum, New Zealand
Technique
- Tapa is cloth made from tree bark; the pieces are beaten and pasted together.
- Using stencils, the artists dye the exposed parts of the tapa with paint.
- After the tapa is dry, designs are sometimes repainted to enhance the effect.
Function: Traditionally worn as clothing before the importation of cotton.
Context
- Hiapo is the word used in Niue for tapa (bark cloth).
- Tapa takes on a special meaning: commemorating an event, honoring a chief, noting a series of ancestors.
- Tapa is generally made by women.
- Each set of designs is meant to be interpreted symbolically; many of the images have a rich history.
Image

New Zealand
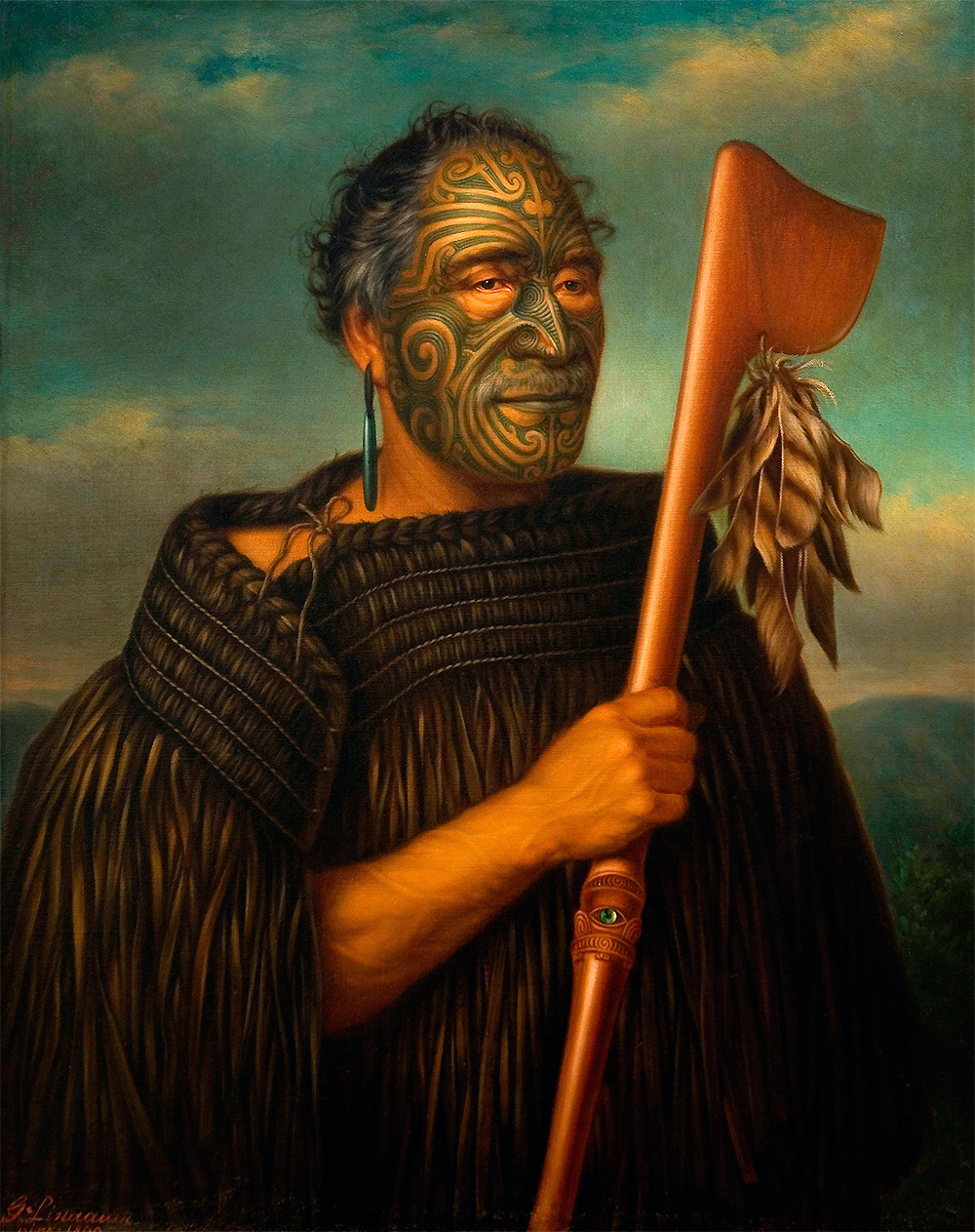
➼ Tamati Waka Nene
Details
- By Gottfried Lindauer
- 1890
- oil on canvas
- Found in Auckland Art Gallery, Auckland, New Zealand
Subject
- Subject is Tamati Waka Nene (c. 1780–1871), Maori chief and convert to the Wesleyan faith.
- Painting is posthumous, based on a photograph by John Crombie.
Content
- Emphasis is placed on symbols of rank: elaborate tattooing with Maori designs, staff with an eye in the center, feathers dangling from the staff.
- Ceremonial weapon has a finely wrought blade with dangling feathers and abalone shell as a focal point or eye.
- Status is revealed in oversize greenstone earring, which contains his power, or “mana,” and kiwi feather cloak.
Context
- The painter was born in Bohemia and was famous for portraits of Maori chieftains upon his arrival in New Zealand in 1873–1874 until his death in 1926.
- He was a journeyman painter and tradesman who worked on commission.
- This is a European-style painting in its use of oil paint, canvas backing, coloring, modeling, shading, and atmospheric perspective.
- Conflicting interpretations of works such as these:
- Maori may see the portraits as an embodiment of the spirit of a person, and as a link between past and present.
- Westerners may see the paintings as a commercial adventure with a monetary value.
- Some may see the portrait as a record of a vanishing culture.
- Others may interpret the work as anthropology highlighting aspects of Maori costuming and physiognomy, and what they could mean.
- Still others may see the portraits as expressions of colonial dominance.
Image

Papua New Guinea
➼ Malagan Mask
Details
- From New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea
- c. 20th century
- wood, pigment, fiber, and shell
- Found in Dallas Museum of Art, Dallas, Texas
Form
- Masks are extremely intricate in their carving.
- They are painted black, yellow, and red: important colors denoting violence, war, and magic.
- Artists are specialists in using negative space.
Function
- Sculptures of the deceased are commissioned; they represent the individual’s soul, or life force, not a physical presence.
- The mask indicates the relationship of a particular deceased person to a clan and to living members of the family.
- The large haircomb reflects a hairstyle of the time; masks are not physical portraits, only portraits of the soul.
Context
- Malagan ceremonies send the souls of the deceased on their way to the otherworld.
- Sometimes ceremonies begin months after death and last an extended period of time.
- During the time after death the sponsors must organize the ceremonies and the feasts. They must also hire the sculptors who will carve the structures for the event.
- An expensive undertaking: families often combine their wealth and honor several individuals.
- The commissioned malagan sculptures are exhibited in temporary display houses. Each sculpture honors a specific individual and illustrates his or her relationships with ancestors, clan totems, and/or living family members.
- During the course of the ceremony it is believed that the souls of the deceased enter the sculptures.
- The ceremonies free the living from the obligation of serving the dead.
- Structures are erected to suit a purpose; after the ceremony, the structures are considered useless and usually destroyed or allowed to rot—they have fulfilled their function.
Image

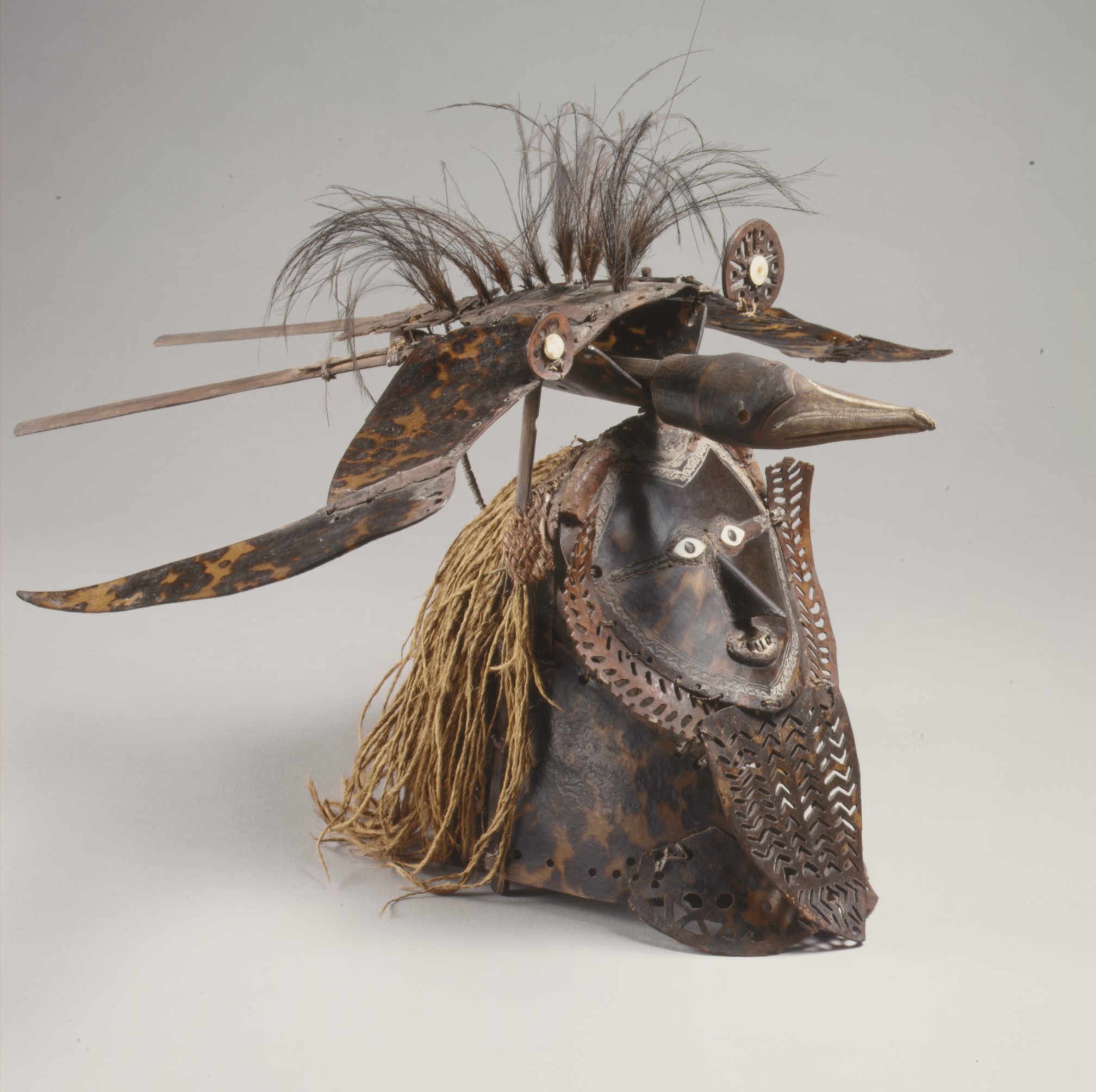
➼ Buk (Mask)
Details
- From Torres Strait
- mid- to late 19th century
- turtle shell, wood, fiber, feathers, and shell
- Found in Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
Form
- Some masks combine human and animal forms; this mask shows a bird placed on top.
- Turtle shell masks are unique to this region.
Function
- The mask, like a helmet, is worn over the head.
- Part of a larger grass costume used in ceremonies about death, fertility, or male initiation, perhaps even to ensure a good harvest.
- Ceremonies involved fire, drum beats, and chanting; recreating mythical ancestral beings and their impact on these people in everyday activities.
Context
- Torres Strait is the water passageway between Australia and New Guinea.
- Human face may represent a cultural hero or ancestor.
Image

Fiji
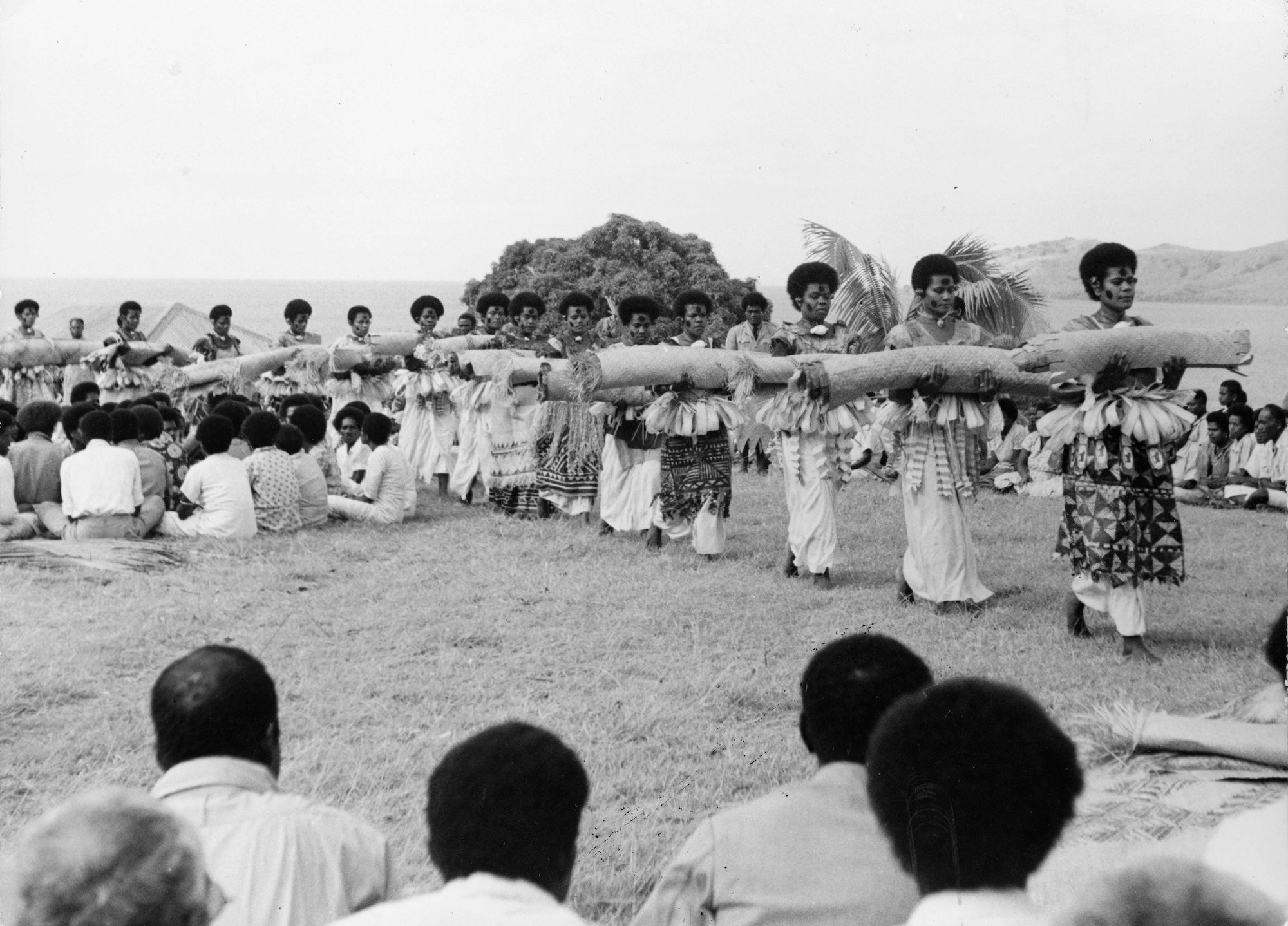
➼ Presentation of Fijian mats and tapa cloths to Queen Elizabeth II during the 1953–1954 royal tour
Details
- 1953
- multimedia performance, photographic documentation,
- Found in Alexander Turnbull Library, Wellington, New Zealand
Materials
- Costume, cosmetics including scent.
- Chant; movement; pandanus fiber/hibiscus fiber mats.
Technique
- Men oversee the growth of the mulberry trees that produce the tapa; women turn the bark into cloth.
- Bark is removed from the tree, soaked in water, and treated to make it pliable.
- Clubs are used to beat the strips into a long rectangular block to form pieces of cloth.
- The edges of these smaller pieces are then glued or felted together to produce large sheets.
- The tapa is decorated according to a local tradition; sometimes stenciled, sometimes printed or dyed.
Function: Enormous tapa clothes were made and presented to Queen Elizabeth II in 1953 in commemoration of her visit to Fiji on the occasion of her coronation as queen of England.
Context: The presentation to the queen is an example of performance art.
Image

Easter Island
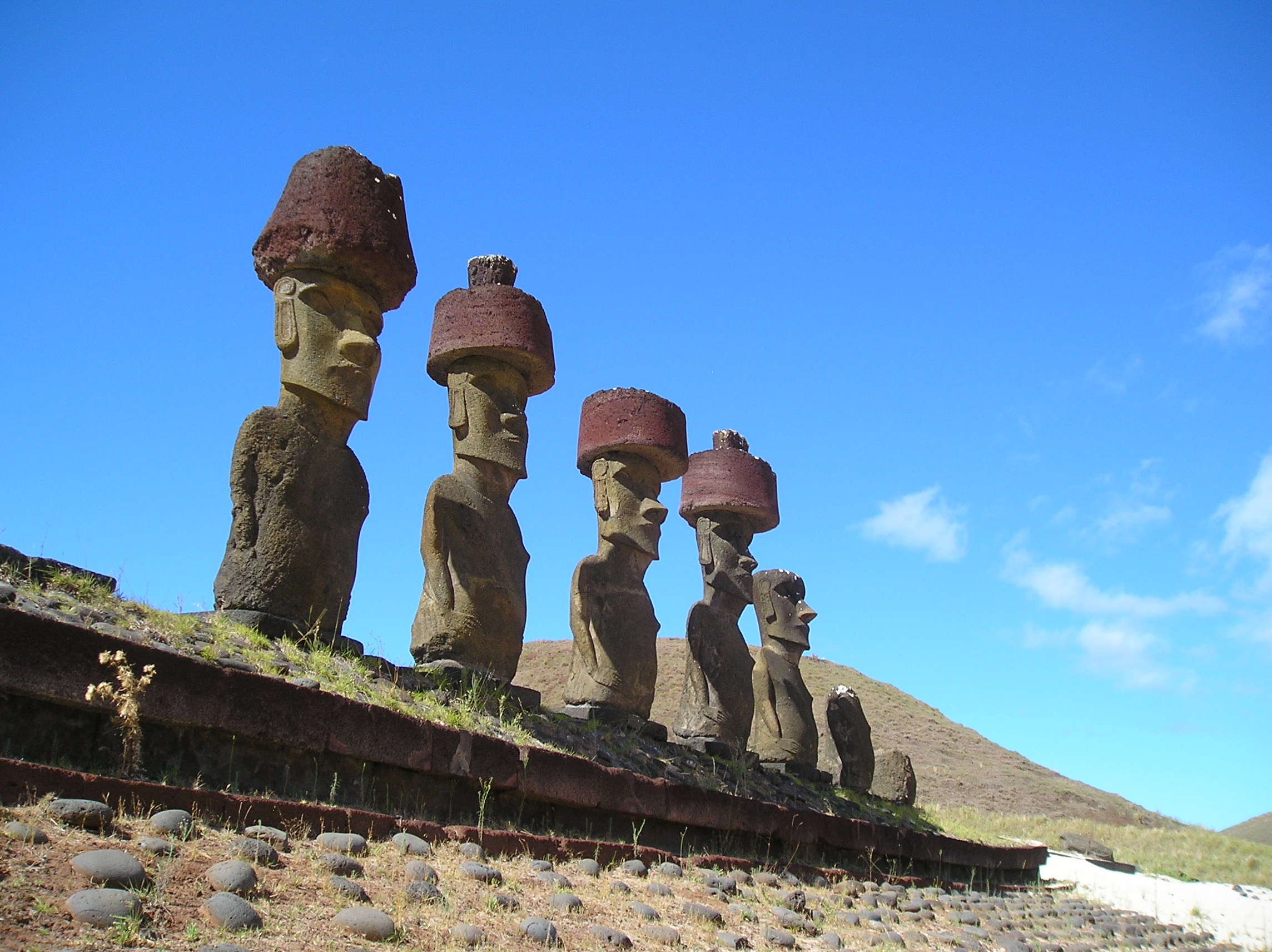
➼ Moai on Platform (Ahu)
Details
- c. 1100–1600
- volcanic tuff figures on basalt base
- Found in Easter Island (Rapa Nui)
Form
- Prominent foreheads; large broad noses; thin pouting lips; ears that reach to the top of their heads.
- Short, thin arms fall straight down; hands on hips; hands across lower abdomen below navel.
- Breasts and navels are delineated.
- Backs are tattooed.
- Topknots were added to some statues.
- White coral was placed in the eyes to “open” them.
Function: Images represent personalities deified after death or commemorated as the first settler-kings.
Context
- There are about 900 statues in all, 50 tons apiece, mostly male; almost all facing inland.
- They were erected on large platforms, called ahu, of stone mixed with ashes from cremations; the platforms are as sacred as the statues that are on them.
- After being carved, figures were said to have been “walked” into place from where they were quarried.
- Beneath an ahu is a cemetery where village elders were buried.
- The depletion of resources may have caused an ecological crisis which led to a decline in society and the destruction of the monuments.
- Monuments were toppled face down because it was believed that the eyes had spiritual power.
Image
