Ch6
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Diseases and Disorders of the Cardiovascular System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
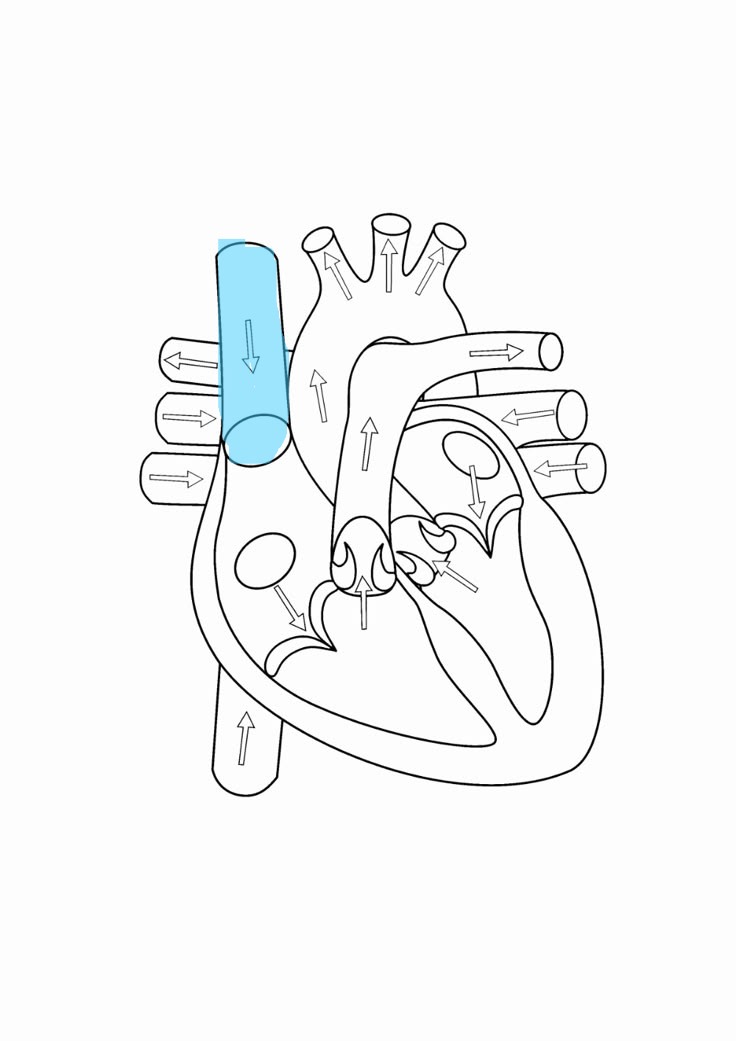
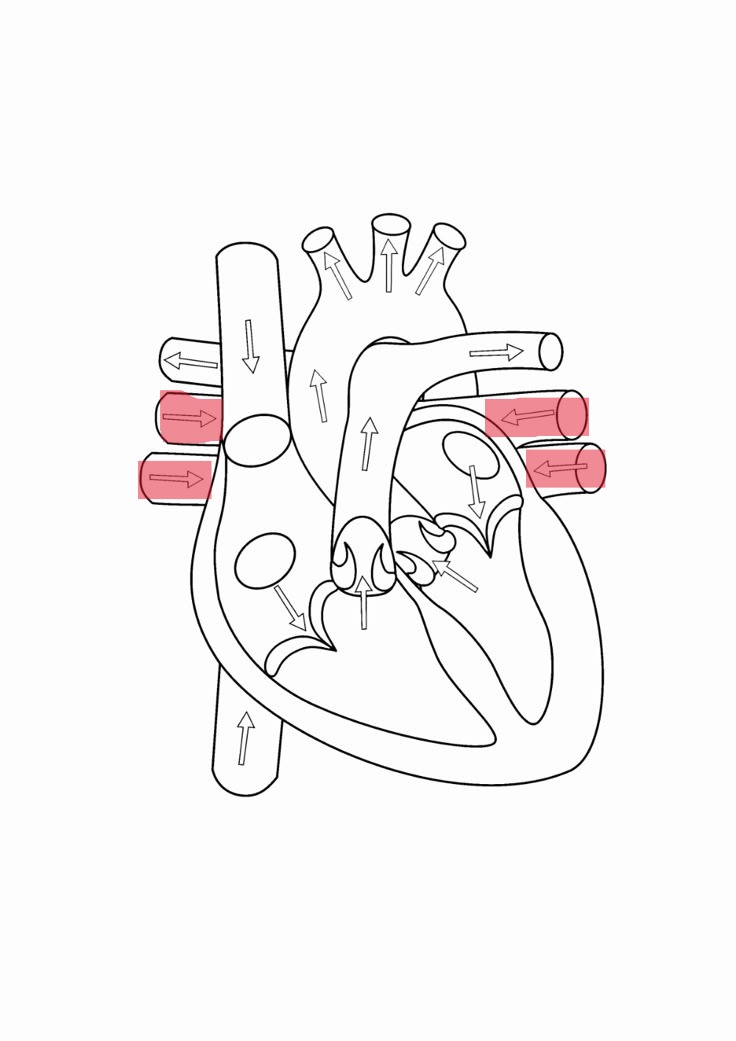
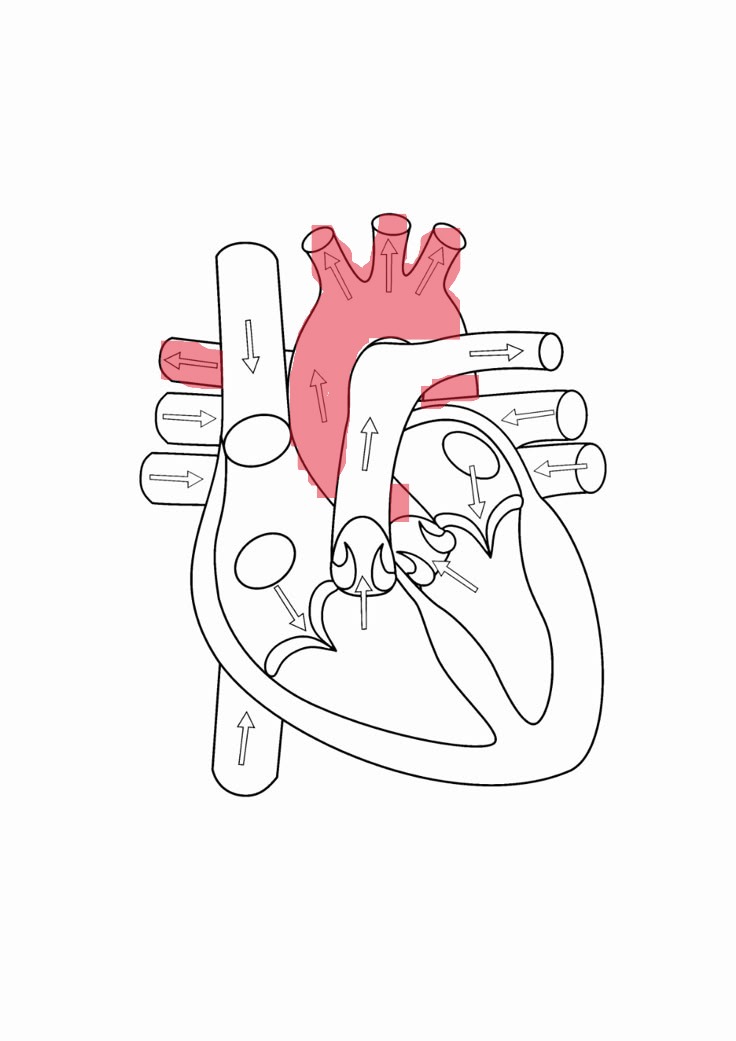
superior vena cava
brings deoxygenated blood from the head and arms to right atrium
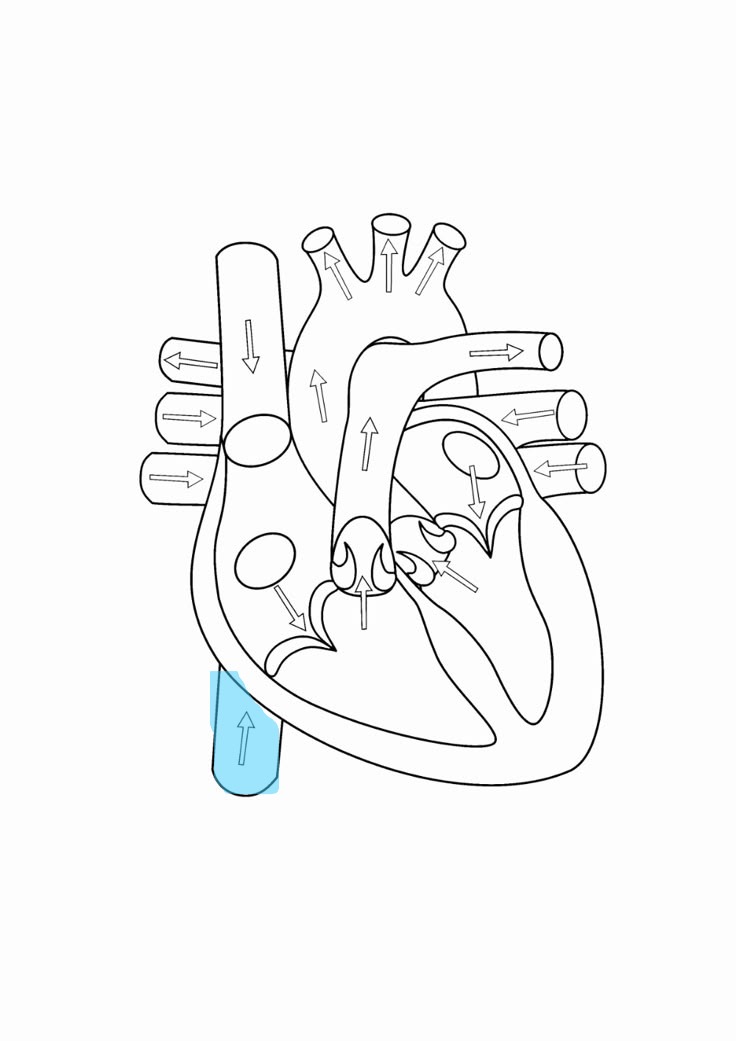
inferior vena cava
brings deoxygenated blood from trunk and legs to right atrium
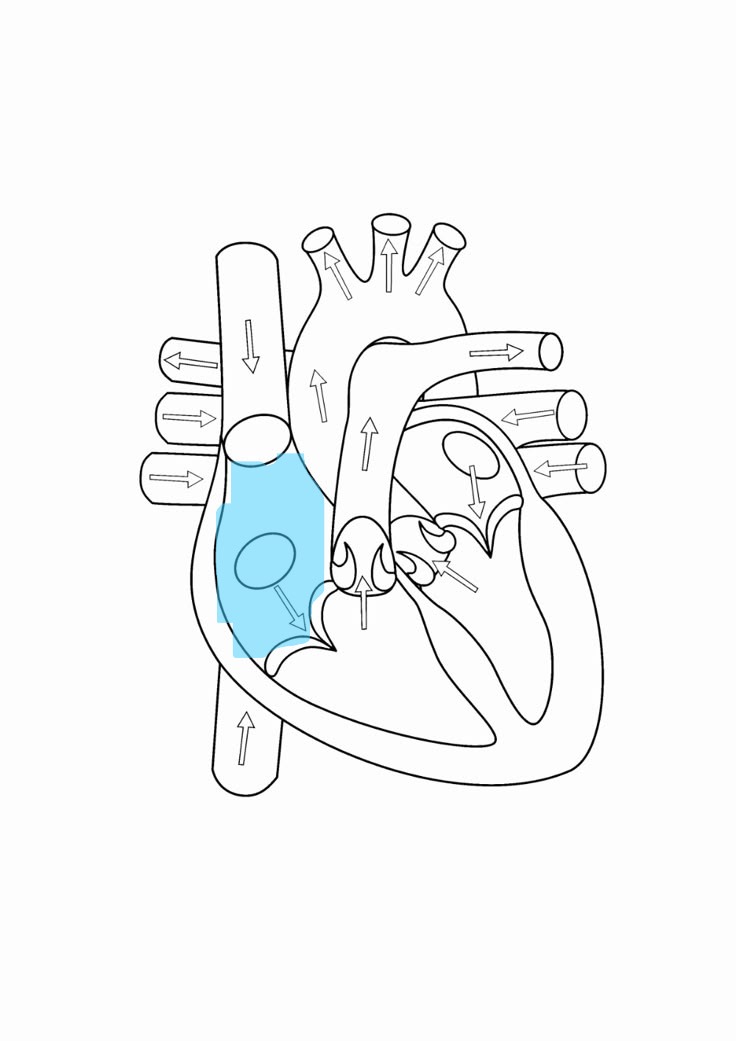
right atrium
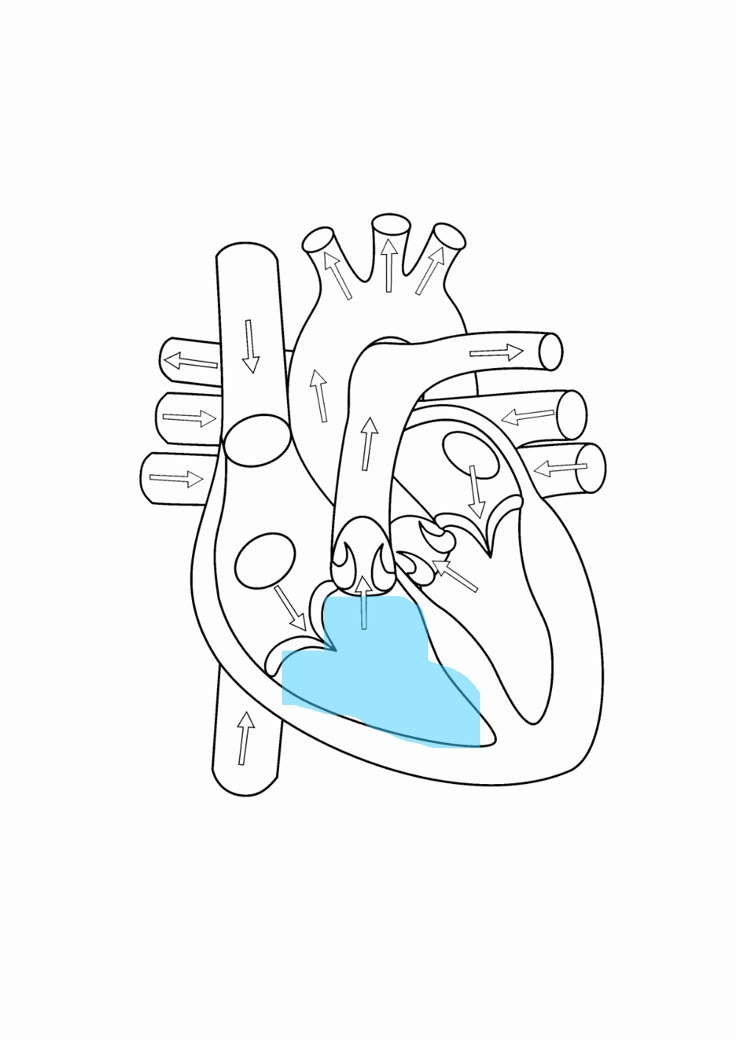
right ventricle
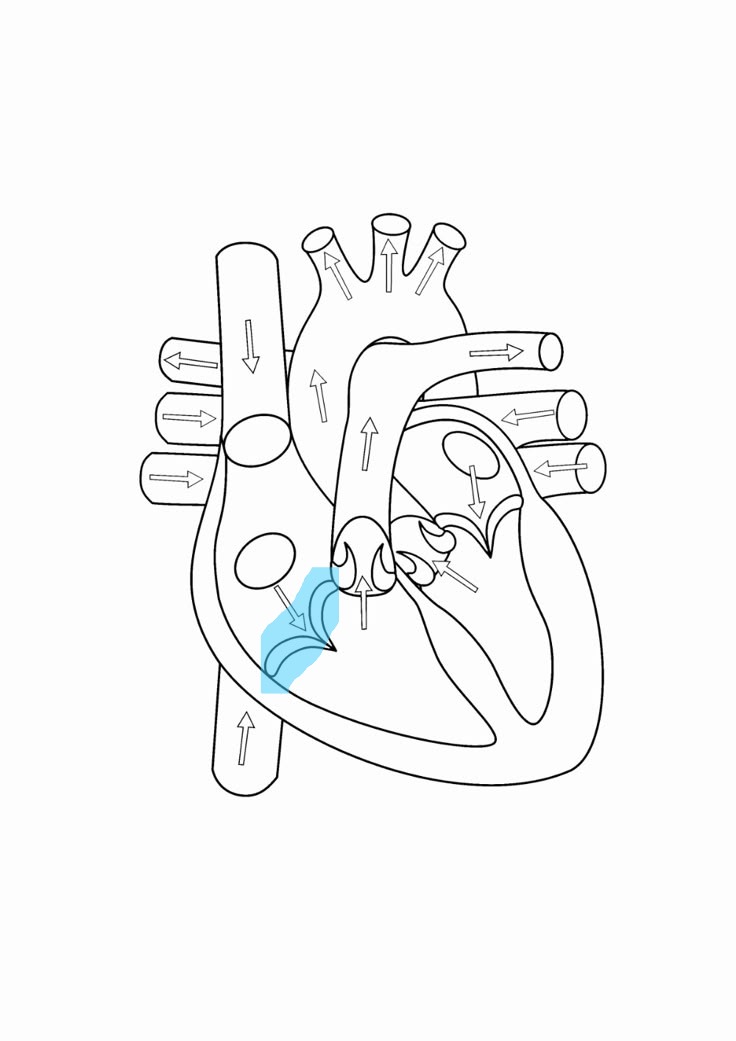
tricuspid valve
right atrioventricular valve and has 3 cusps
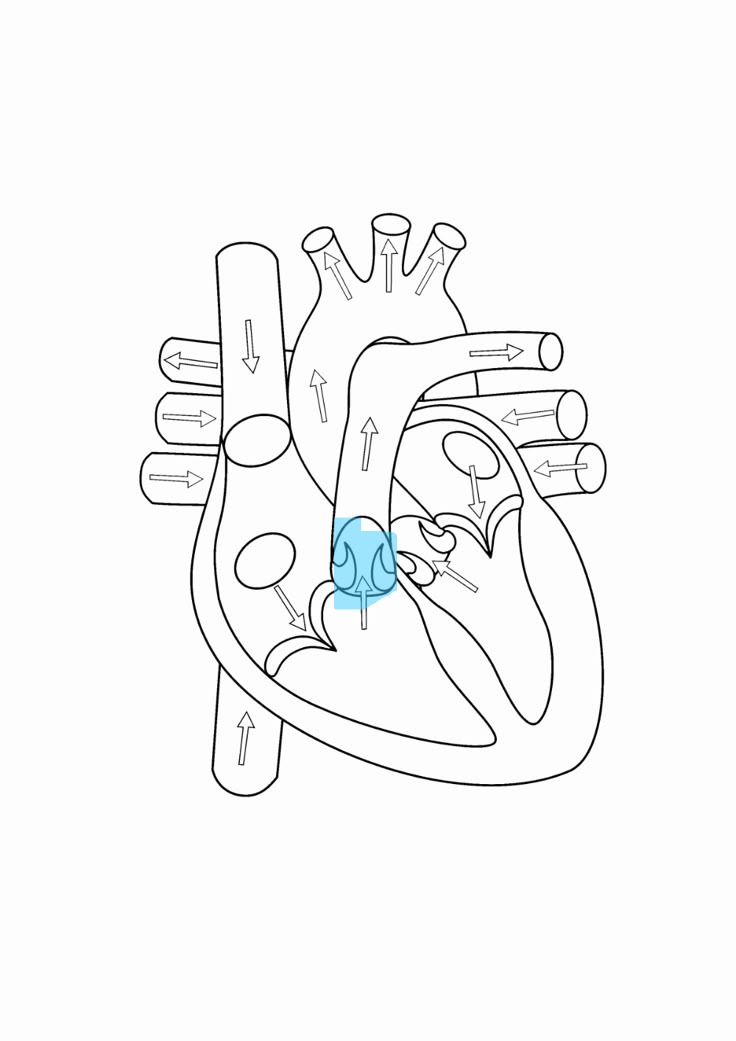
pulmonary valve
one of 2 ventricular valves, 3 cusps
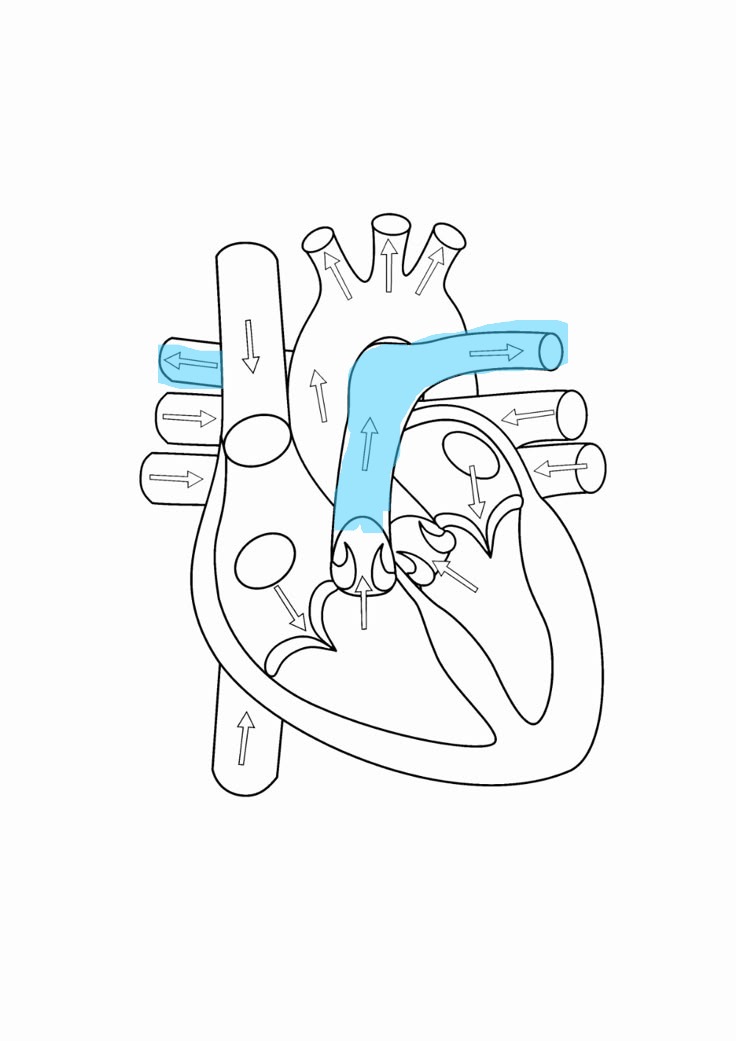
pulmonary artery
brings deoxygenated blood to respective lungs
lungs
where gas exchange occurs; blood discards co2 and picks up oxygen
pulmonary vein
transports oxygenated blood to left atrium
left atrium
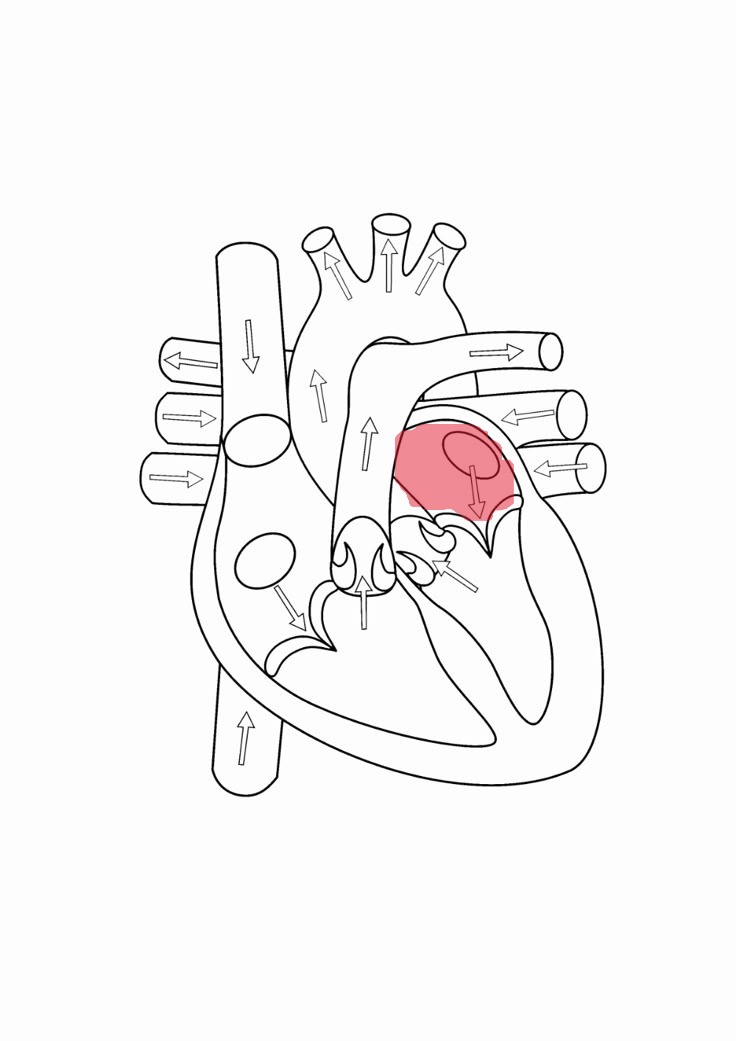
mitral/bicuspid valve
left atrioventricular valve and has two cusps
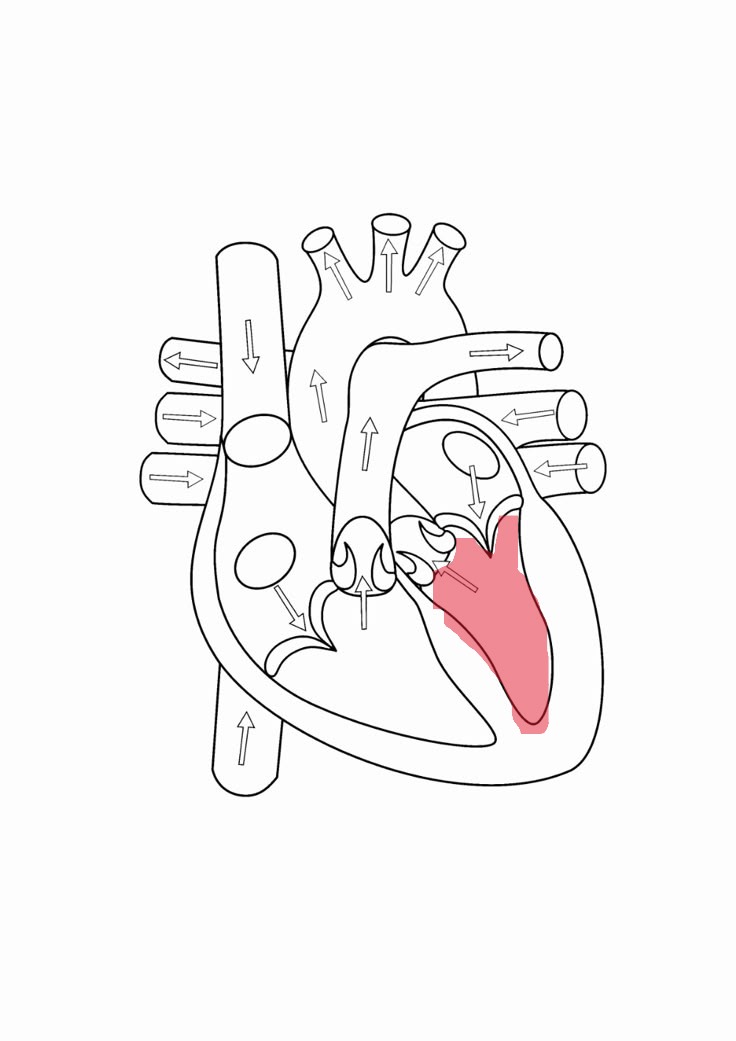
left ventricle
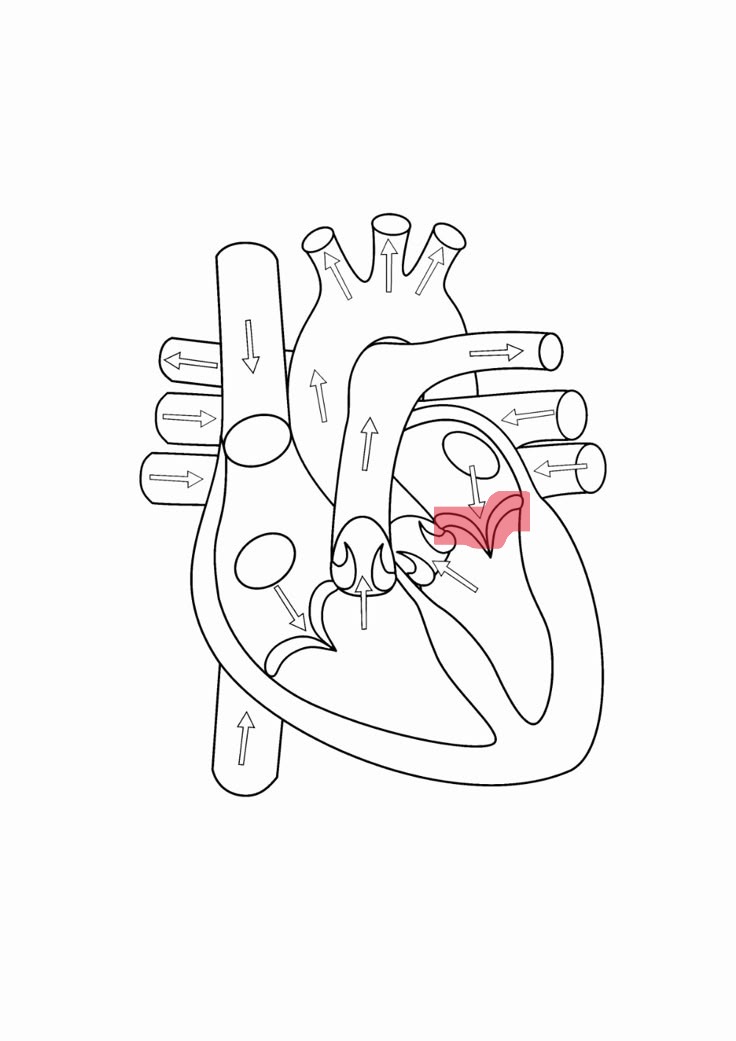
aortic valve
1 of 2 ventricular valves, 3 cusps
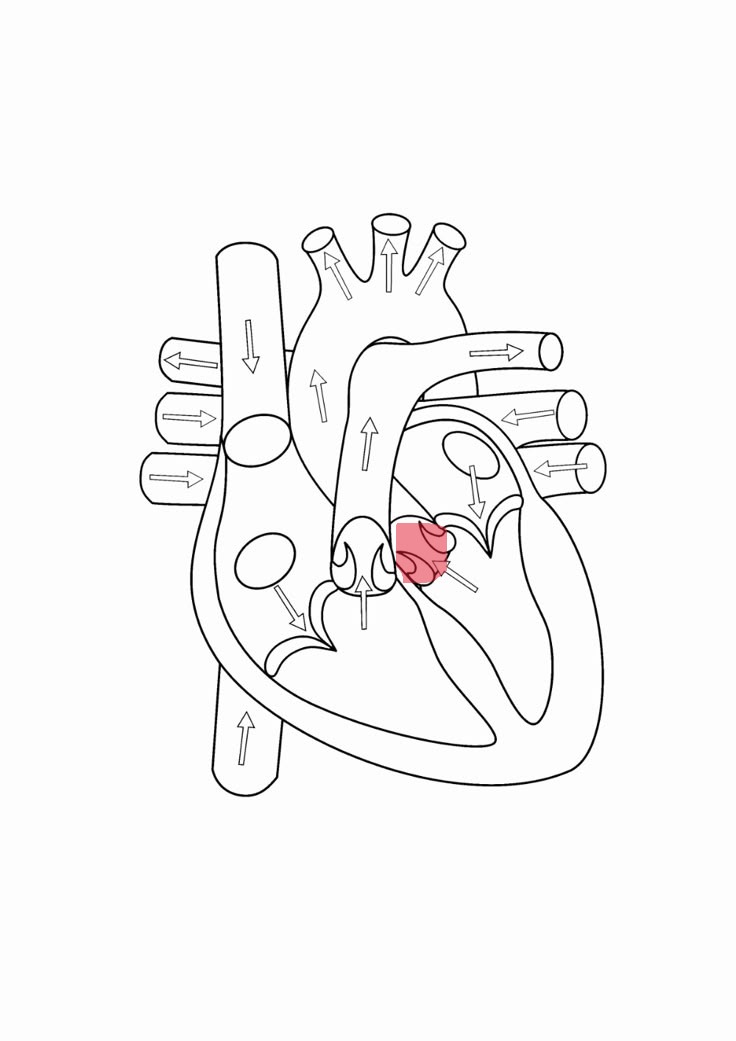
aorta
distributes oxygenates blood to the rest of the body
visceral pericardium
covering of the heart
parietal pericardium
lining of the sac
epicardium
covers the external heart surface
endocardium
inner layer of heart which also covers valves and is continuous with the endothelium that lines the vessels
myocardium
layer between external and internal layers, the thickest; contracts to pump blood out of the heart
coronary artery
brings blood to the myocardium (heart muscle)
left coronary artery
branches into left anterior descending artery (LAD) and circumflex artery, supplies blood to both arteries
right coronary artery
branches to right marginal and posterior interventricular branch, supplies back wall of heart
systole
when ventricles contract
diastole
when ventricles relax and fill with blood
echocardiogram
heart ultrasound that can see tissue damage, pump capacity, size and shape of heart; demonstrates left ventricular hypertrophy by measuring the wall of the left ventricle
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
evaluate heart by measuring electrical activity
cardiac arrhythmia
disturbance in impulses from sinoatrial node or through conductive tissue; heart flutters, contractions, cardiac arrest
Myocarditis
usually caused by virus such as coxsackie, adenovirus, or echovirus, can present as active inflammation and progress to cardiac failure
viral myocarditis
treatment is conservative with bedrest and treatment of underlying condition
cardiomyopathy
dilated, hypertrophic, or restrictive left ventricles
cardiomyopathy
treatment include medications, surgically implanted devices, or heart transplant
Stenosis
narrowing of passageways/valve, decreases blood flow
regurgitation
leaking in valve, blood flows in wrong direction
strep
People who are not properly treated for ____ are at a higher risk for rheumatic heart disease.
rheumatic heart disease
complication include valve stenosis, valve regurgitation, damage and weakening of heart muscle
sometimes mitral of aortic valve damage so severe, requires surgical replacement of valve
mitral valve prolapse
leaflets of the mitral valve bulges into the left atrium when ventricle contracts
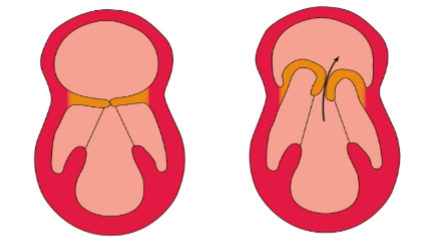
cardiac echo
how is prolapse mitral valve diagnosed?
beta blockers
how is prolapse mitral valve most commonly treated?
antibiotic prophylaxis
recommended for severe mitral regurgitation before dental procedure to reduce risk of infective endocarditis
High-density Lipoprotein (HDL)
transports cholesterol from heart to liver
Low-density Lipoproteins
transports cholesterol from liver to heart
hyperlipidemia
aka high cholesterol; high levels of lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) in blood
coronary artery disease
buildup of plaque specifically in the arteries of the heart
Women; men
___ have higher HDL levels than ___.
angiogram
dye is injected and one can see blood vessels and plaques
angioplasty
catheter in inserted into vessel, balloon is inflates and pushes plaque into wall + widens the artery
arteriosclerosis
artery walls are thickened, hardened, and inflexible
atherosclerosis
umbrella term for plaque buildup throughout body
atheroma
term for the irregular mass or yellow, mushy debris or plaque
stable plaque
surrounded by fibrous tissue, causes permanent narrowing of vessel
aspirin
interferes w/ platelet function of clotting and reduces risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke
varicose veins
dilated, spider-like veins due to incompetent valves
compression sclerotherapy
angina pectoris
chest pains from coronary heart disease
nitroglycerin
treatment for angina pectoris
foramen ovale
hole between the left and right atrium, closes after birth to form depression
fossa ovale
depression formed between left and right atrium after birth
ductus arteriosus
shunt between pulmonary artery and aorta, blood pumped from right ventricle to pulmonary artery, allows blood to bypass nonfunctional lungs (bc fetus doesn’t have developed lungs yet)
closes after birth, sometimes doesn’t
Tetralogy of Fallot
congenital heart disease; ventricular septal defect, pulmonary valve stenosis, misplaced aorta (lies over septum), hypertrophy