Carbon Group
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What oxidation states are common in Group 14?
Carbon & silicon: only +4
Germanium, tin, lead: +2 and +4
Lead prefers +2 due to the inert pair effect
How does bonding character change down Group 14?
Carbon: nonmetal, covalent
Silicon, germanium: metalloids, covalent
Tin, lead: borderline metals, more metallic but still with covalent character
Why are π bonds common in carbon but not in silicon?
Carbon’s shorter bond lengths and small p orbitals allow strong p–p overlap; silicon’s larger orbitals weaken π bonding.
What type of π bonding becomes stronger down the group?
p–d π bonding, due to increased orbital size and favorable lobe orientation.
Why can silicon be pentavalent, but carbon cannot?
Silicon’s larger size and available d orbitals allow expanded valence shells; carbon lacks d orbitals.
What structure do carbon, silicon, and germanium adopt in the solid state?
Diamond-like tetrahedral structures.
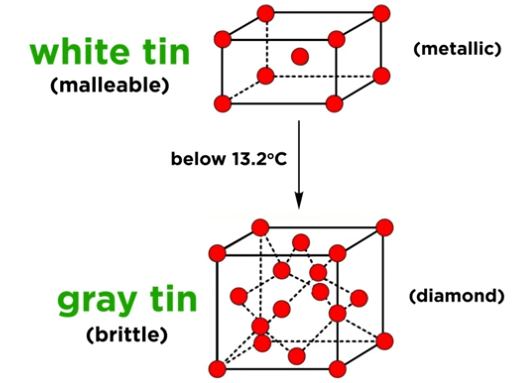
What are the two allotropes of tin, and what happens at cold temperatures?
White tin: metallic, shiny, malleable
Gray tin: brittle, diamond-like
Cold triggers transformation to gray tin → structural breakdown (tin pest)
What are interstitial carbides, and how are they formed?
Carbon atoms fit into octahedral holes in metal lattices (e.g., steel), forming hard, high-melting alloys.
Which carbon bonds are especially strong and important in coordination chemistry?
C–O bonds → CO ligand
C–N bonds → CN ligand
What are silanes, silicones, and silicates?
Silanes: Compounds like tetramethylsilane (TMS)
Silicones: Si–O–Si backbone with R-groups
Silicates: Salts with Si–O anions
How is pure silicon prepared?
By high-temperature reduction of SiO₂:
SiO₂ + C → Si + CO
SiO₂ + Mg → Si + MgO
What are key applications of carbon?
Drugs, fuels, biomolecules, essentially limitless
What are key uses of silicon?
Microchips and semiconductors
Al/Si alloys for automotive parts
What are some uses of germanium?
Transistors, diodes
Replaces TiO₂ in glass for fiber optics
Night vision equipment
What are the uses of tin (Sn)?
Non-toxic, doesn't rust
Plating to prevent corrosion
What is lead (Pb) used for?
Lead-acid batteries
Among the first rechargeable batteries, delivers high currents