Chapter 13: Solids and Modern Materials Overview
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
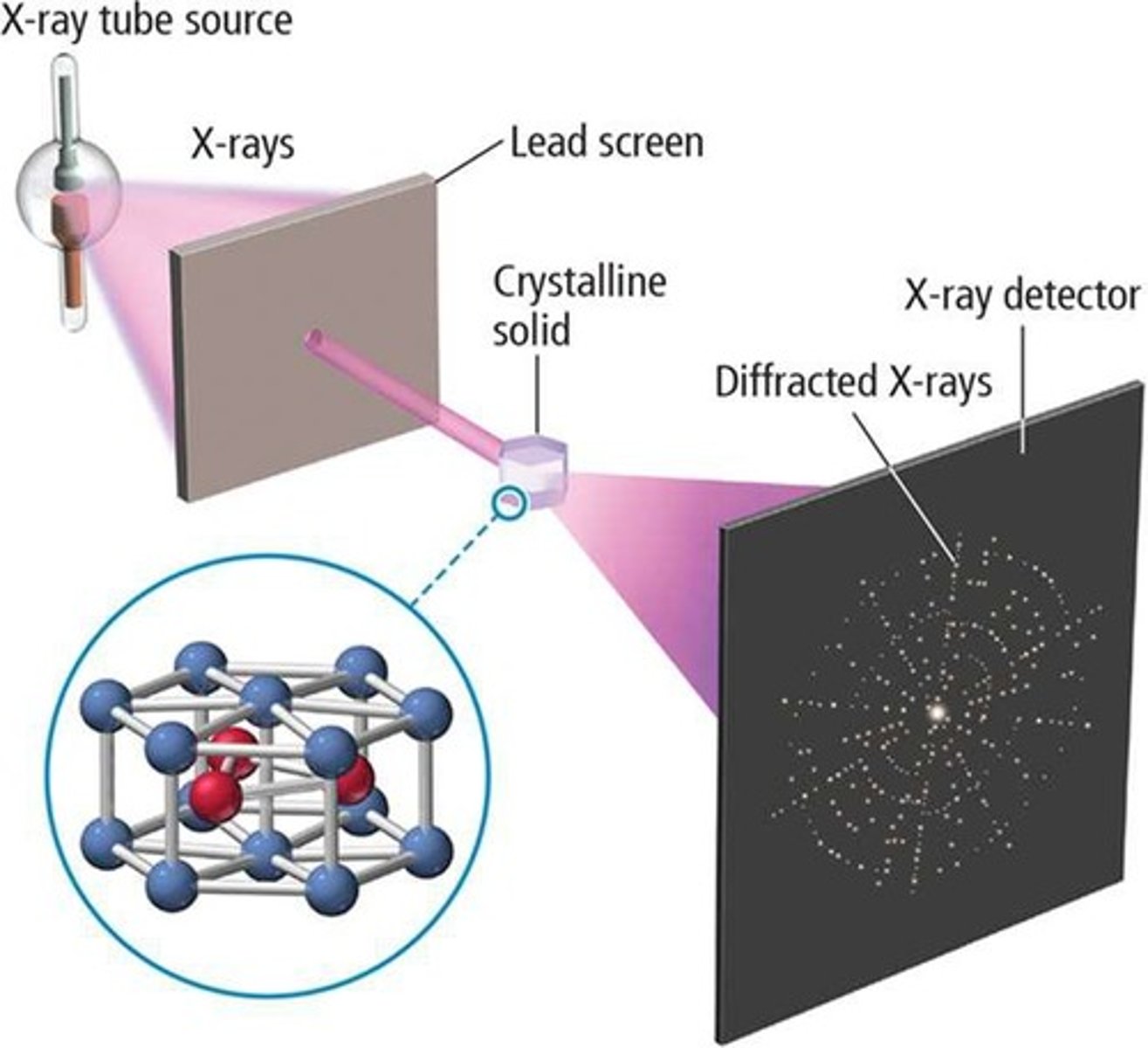
X-ray diffraction
Technique to analyze atomic arrangements in crystals.
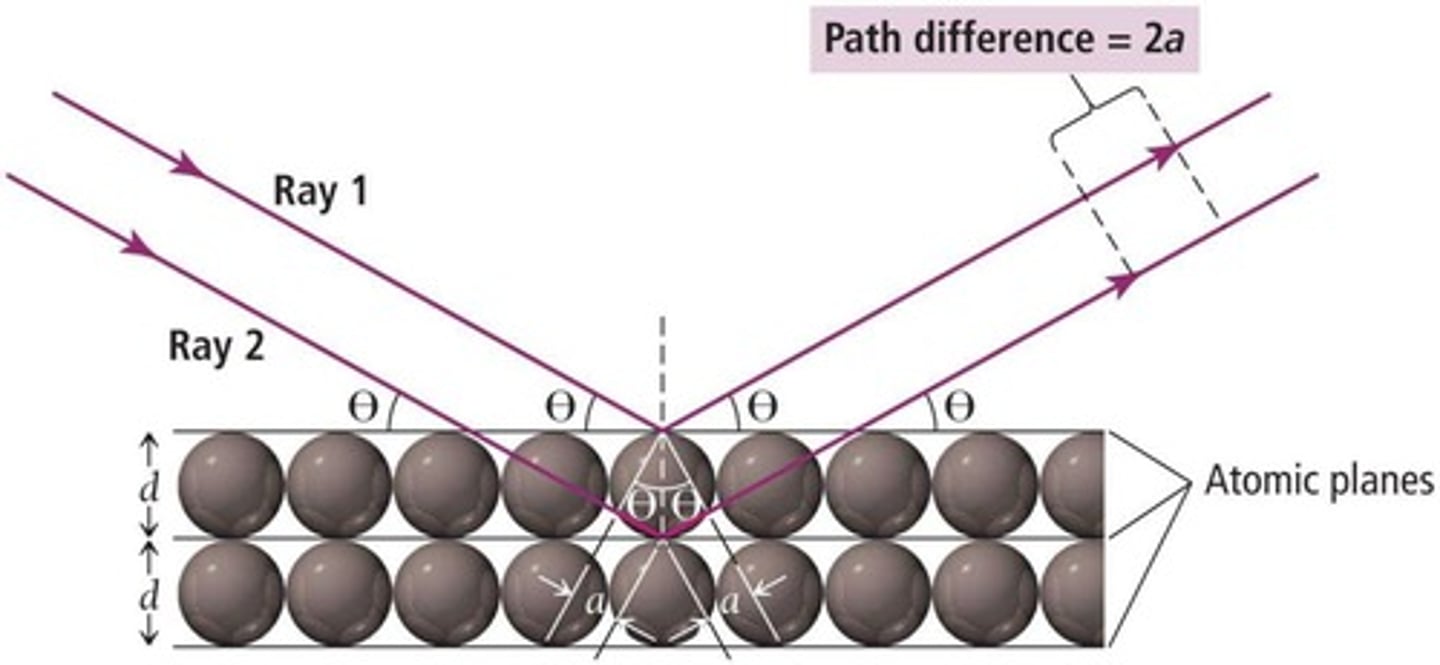
Atomic planes
Layers in crystals, spaced about 100 pm apart.
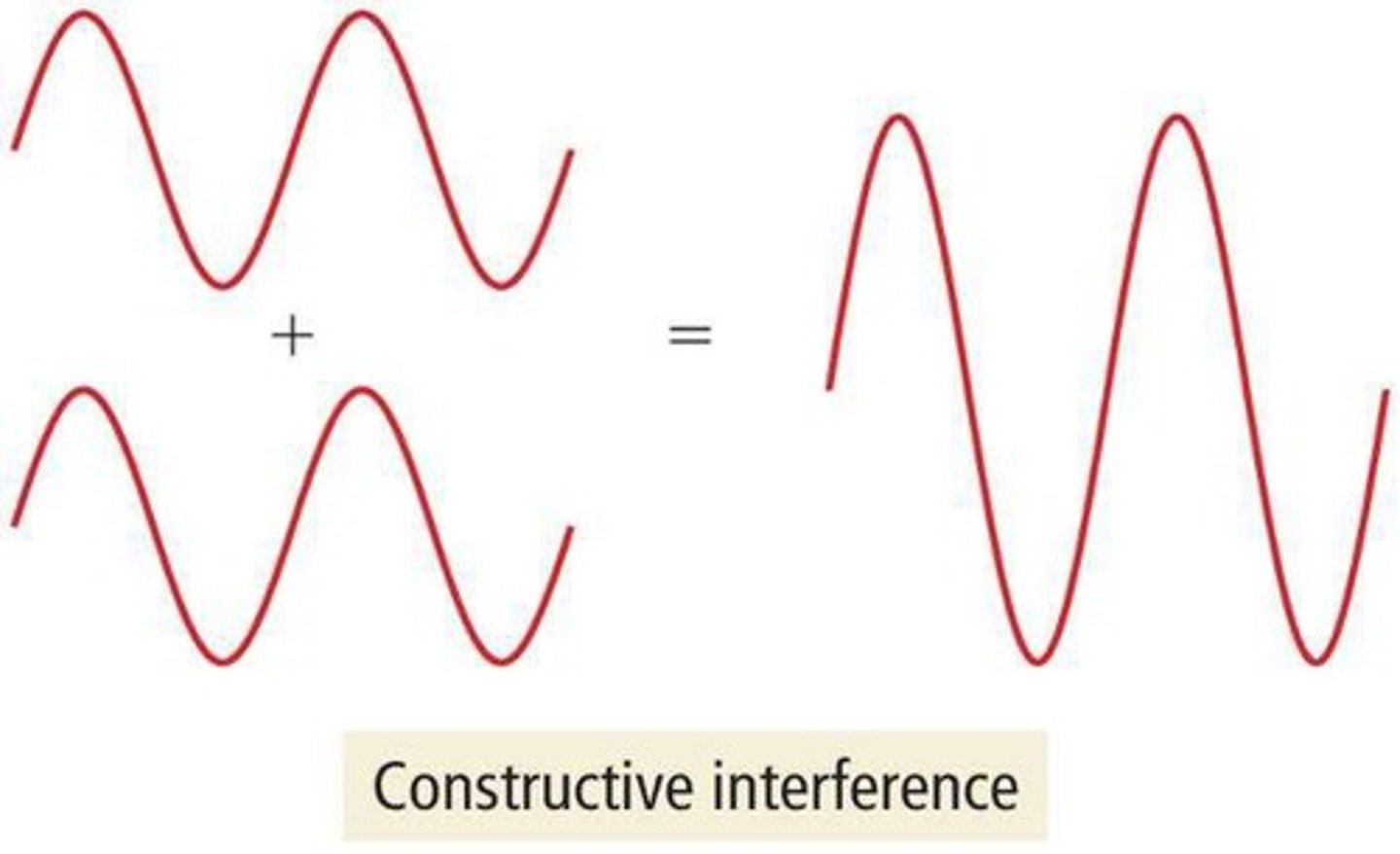
Diffraction patterns
Interference patterns formed by X-ray interactions.
Path length
Distance traveled by rays in diffraction.
Bragg's Law
nλ = 2d×sin(θ) relates wavelength and atomic spacing.
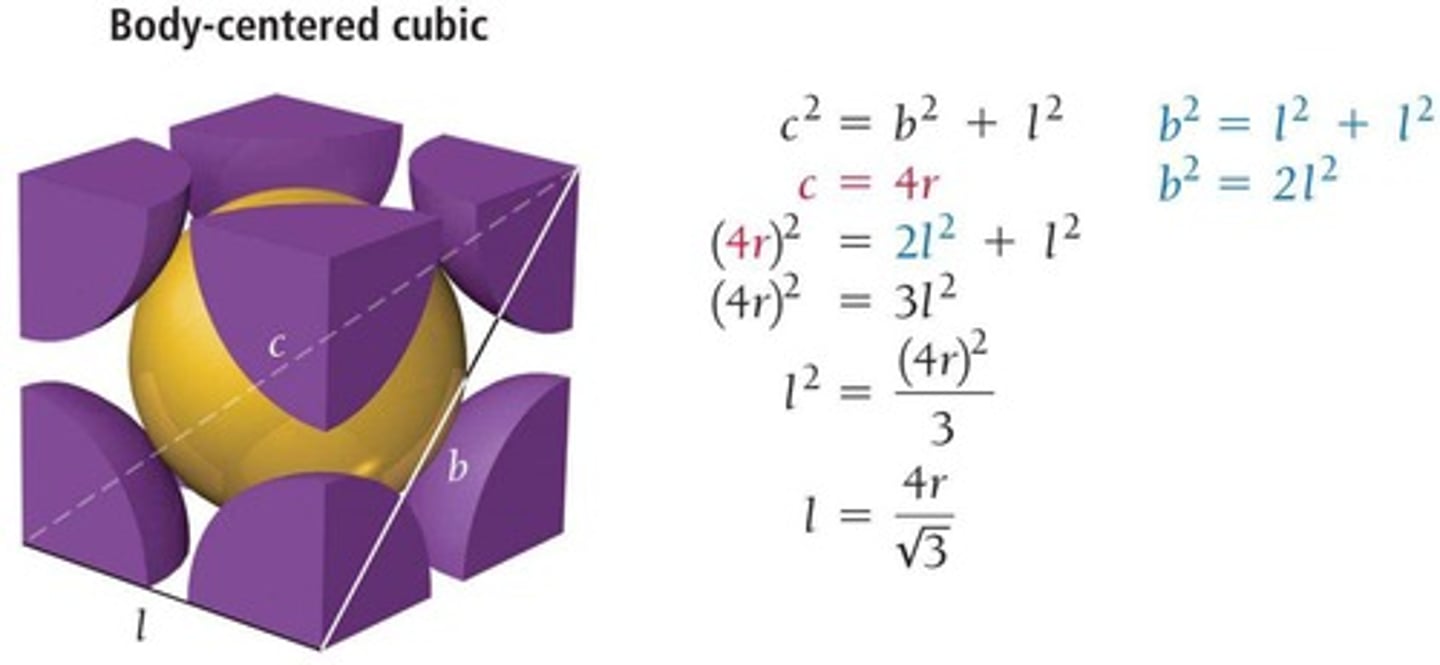
Unit cell
Smallest repeating unit showing atomic arrangement.
Crystal lattice
Regular arrangement of atoms in a crystal.
Coordination number
Number of neighboring particles in contact.
Packing efficiency
Volume percentage occupied by particles in unit cell.
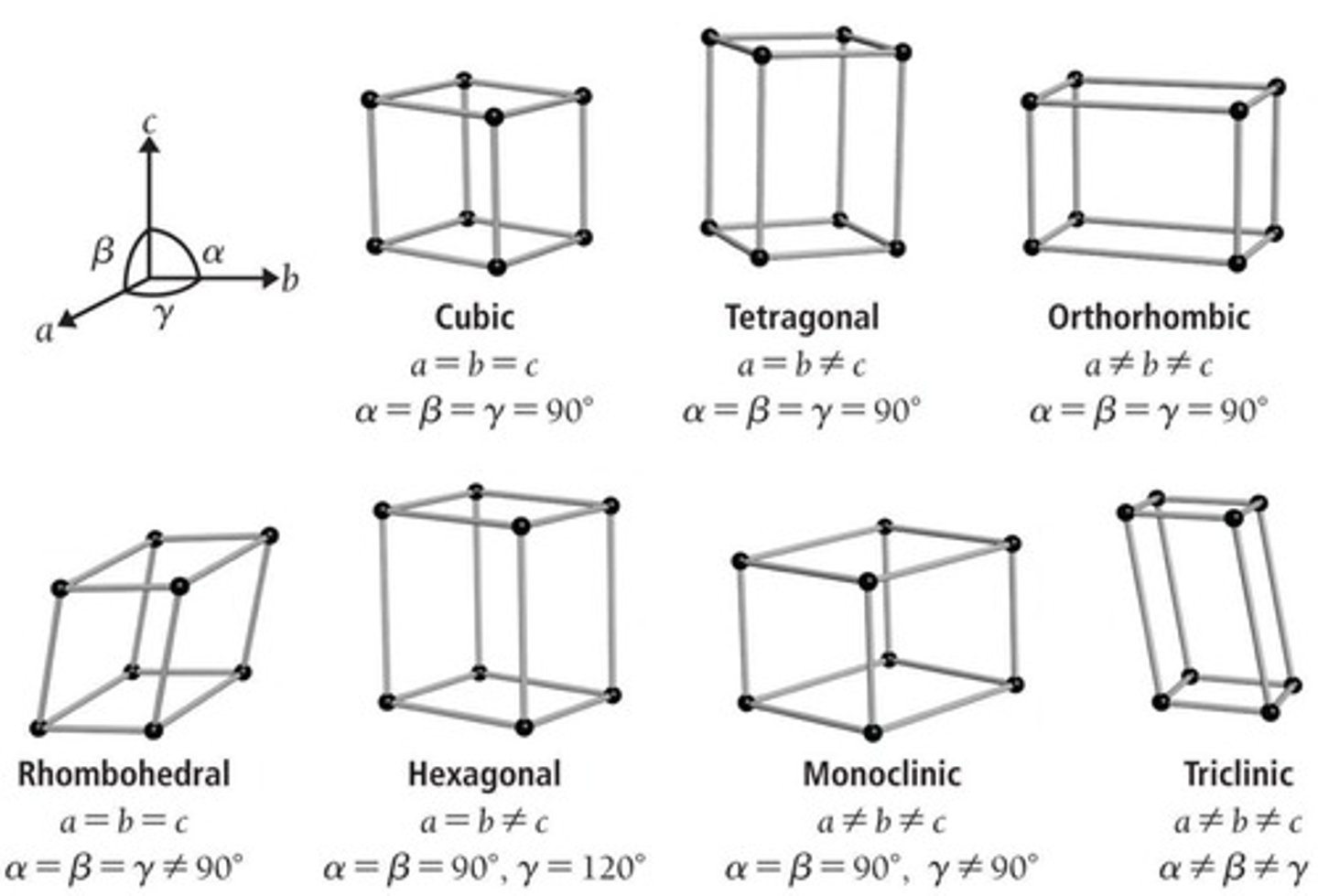
Cubic unit cells
Unit cells with 90° angles and equal edge lengths.
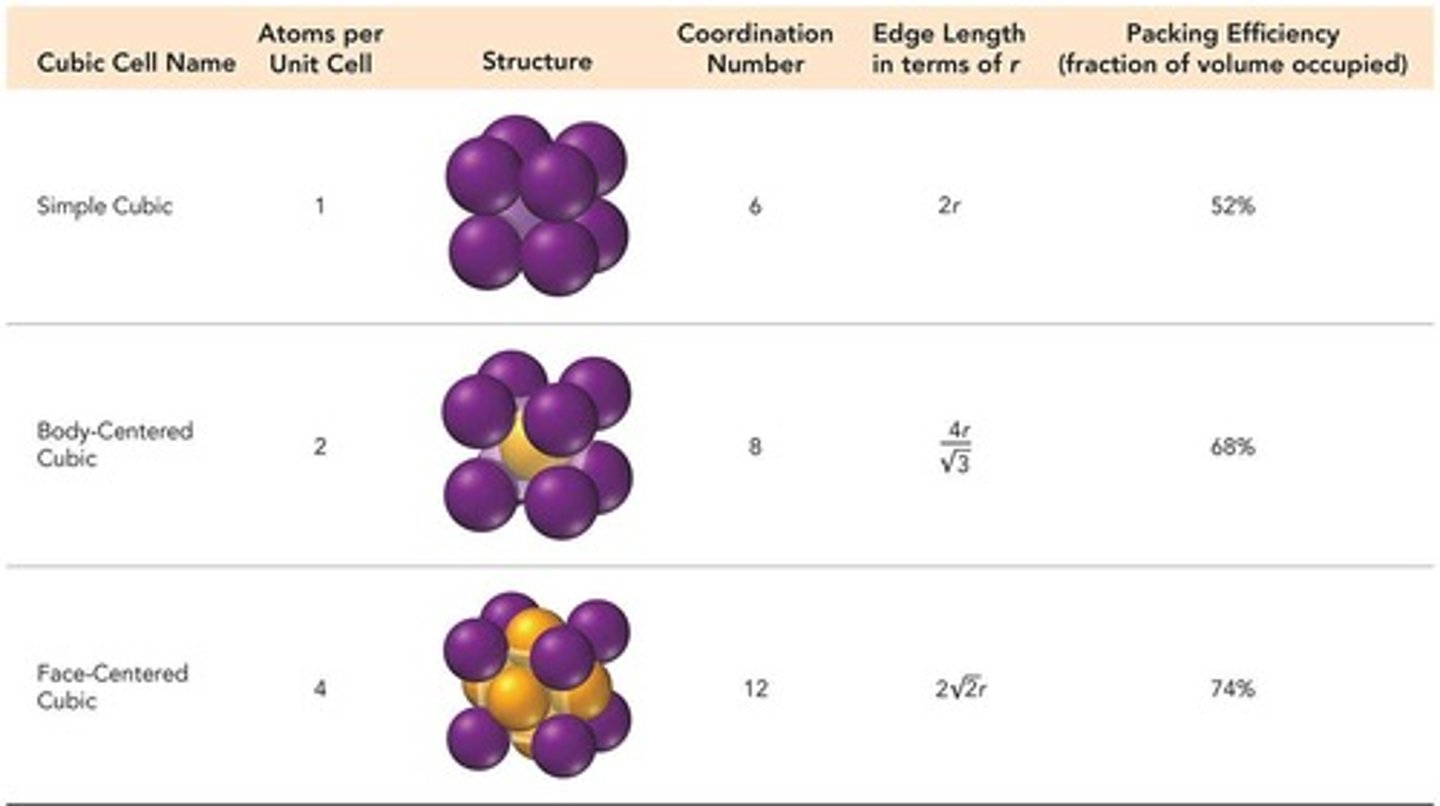
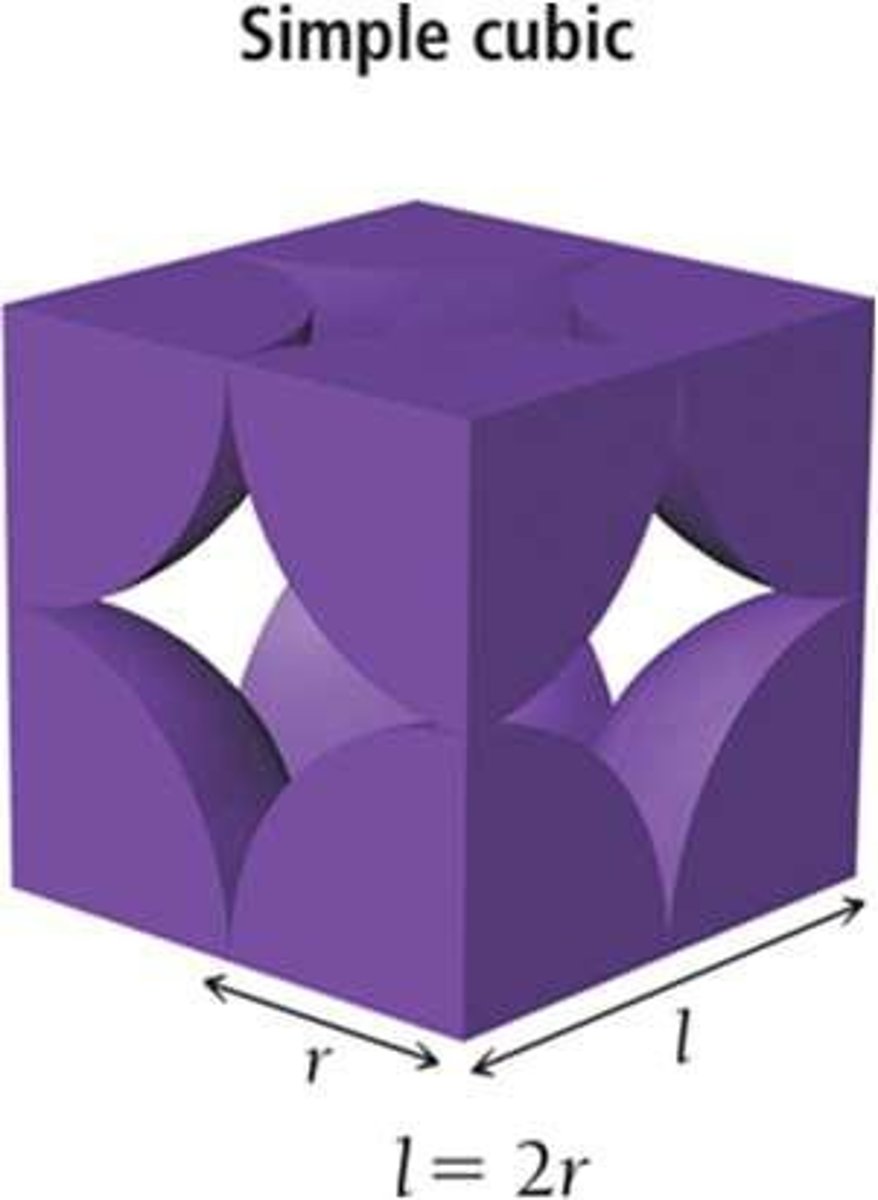
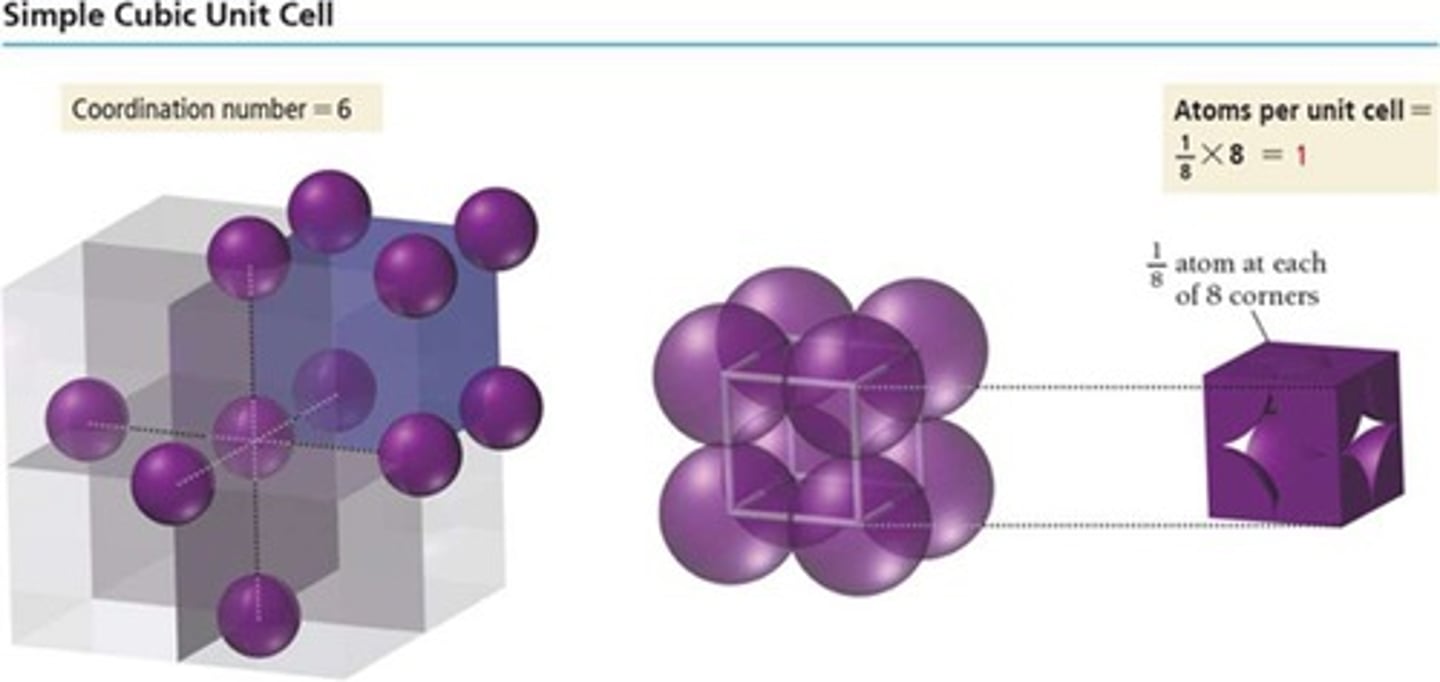
Simple cubic
Unit cell with one particle per cell.
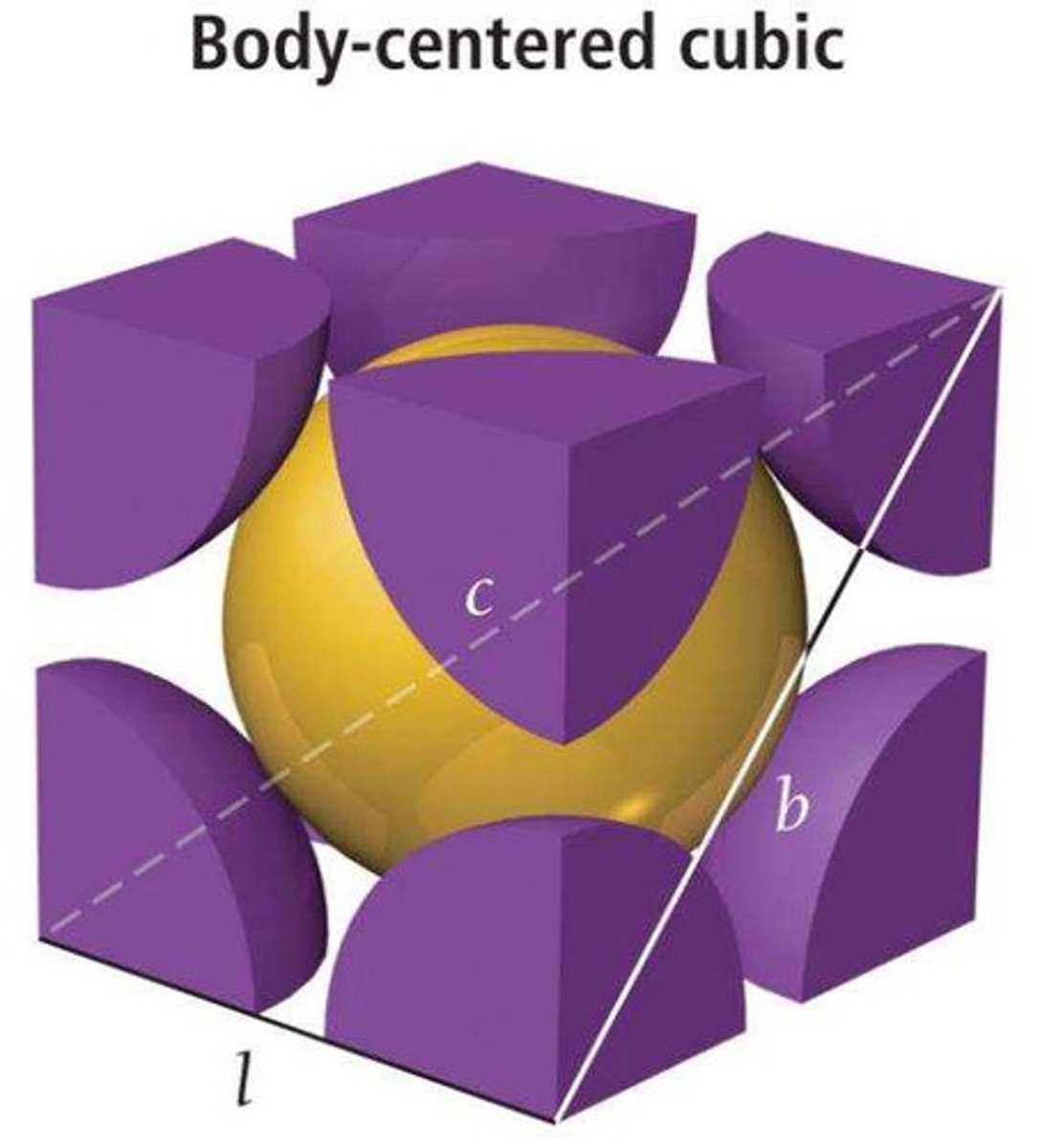
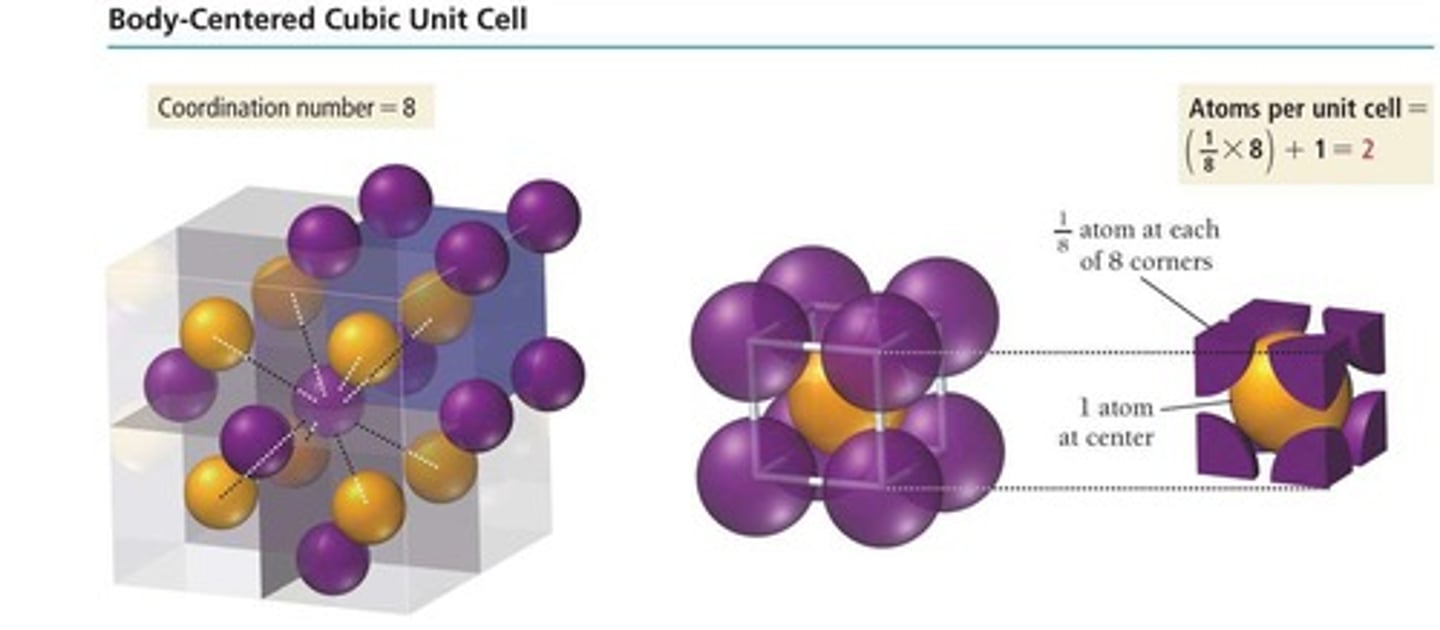
Body-centered cubic
Unit cell with two particles, one at center.
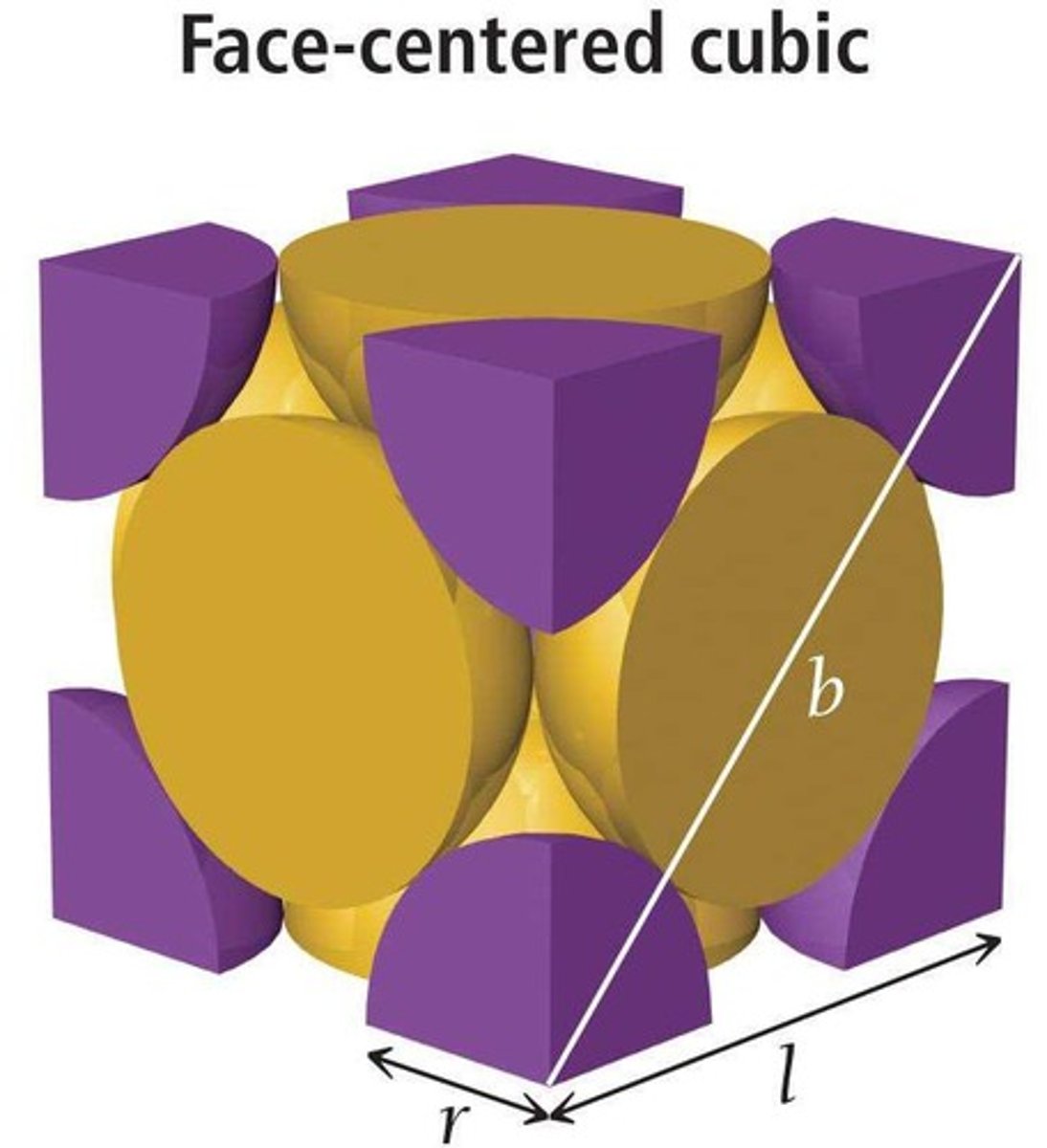
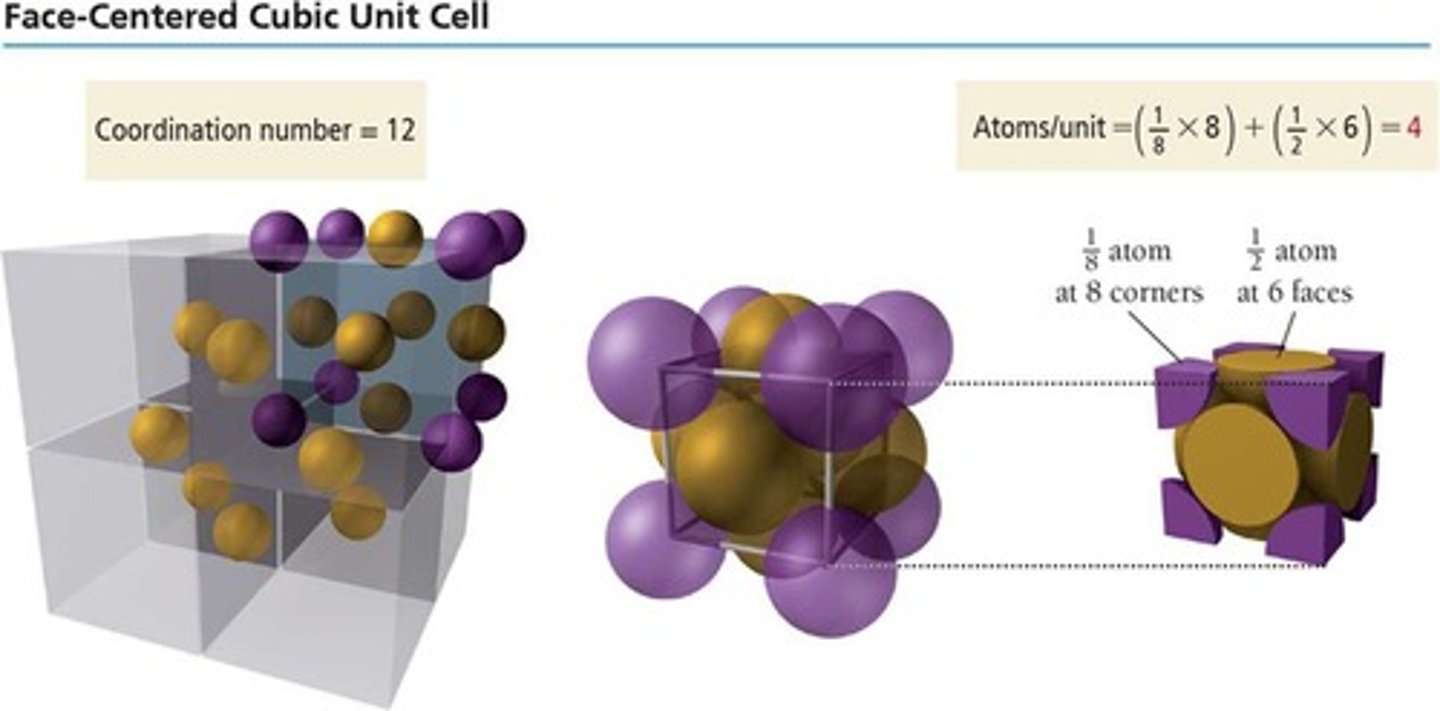
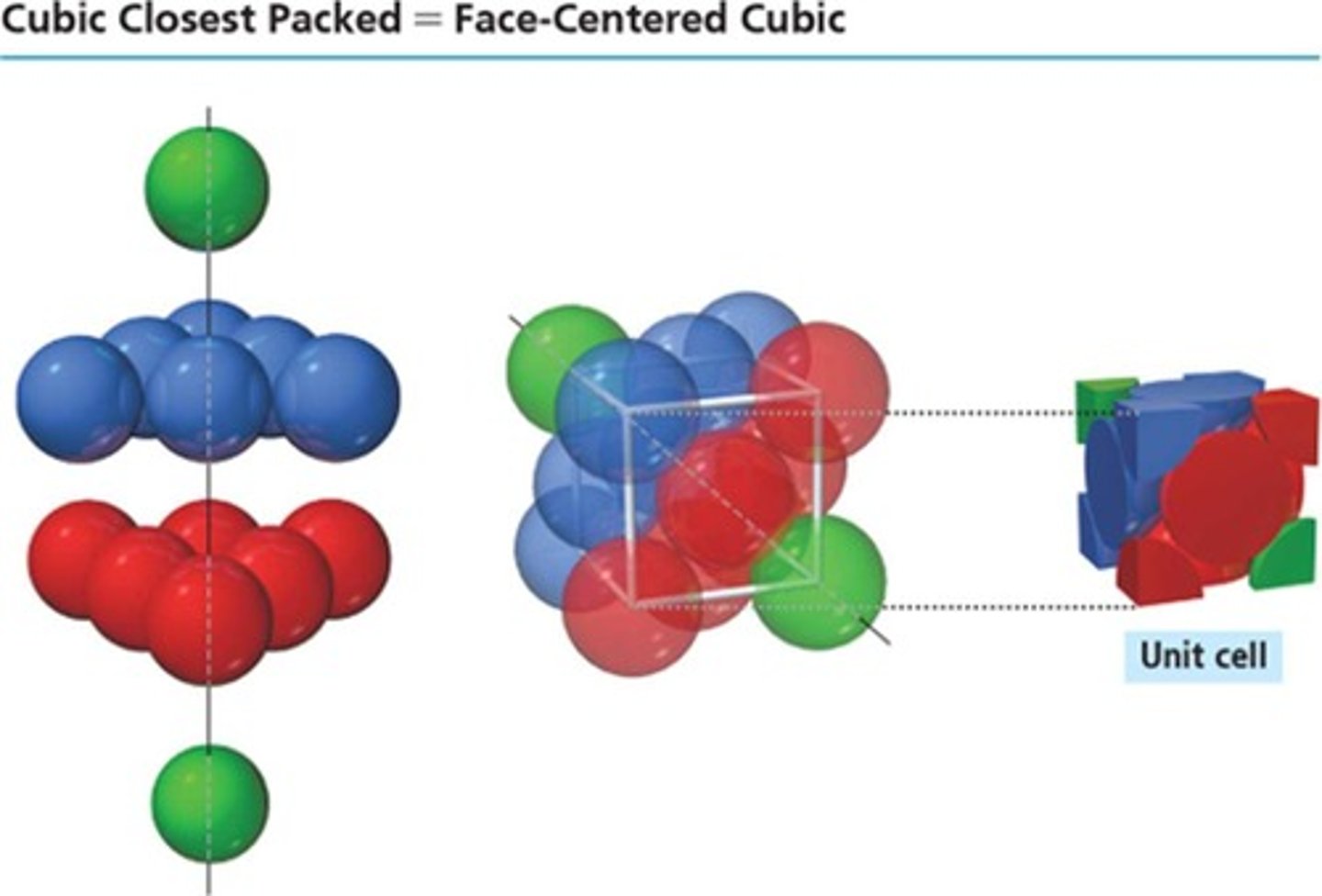
Face-centered cubic
Unit cell with four particles, one at each face.
Coordination number of simple cubic
6, due to corner particle contacts.
Coordination number of body-centered cubic
8, due to center particle contacts.
Coordination number of face-centered cubic
12, due to face particle contacts.
Lattice parameters
a, b, c: lengths of unit cell edges.
Unit cell volume
Measured in ų or pm³, describes cell size.
Spherical particles
Assumed shape for unit cell calculations.
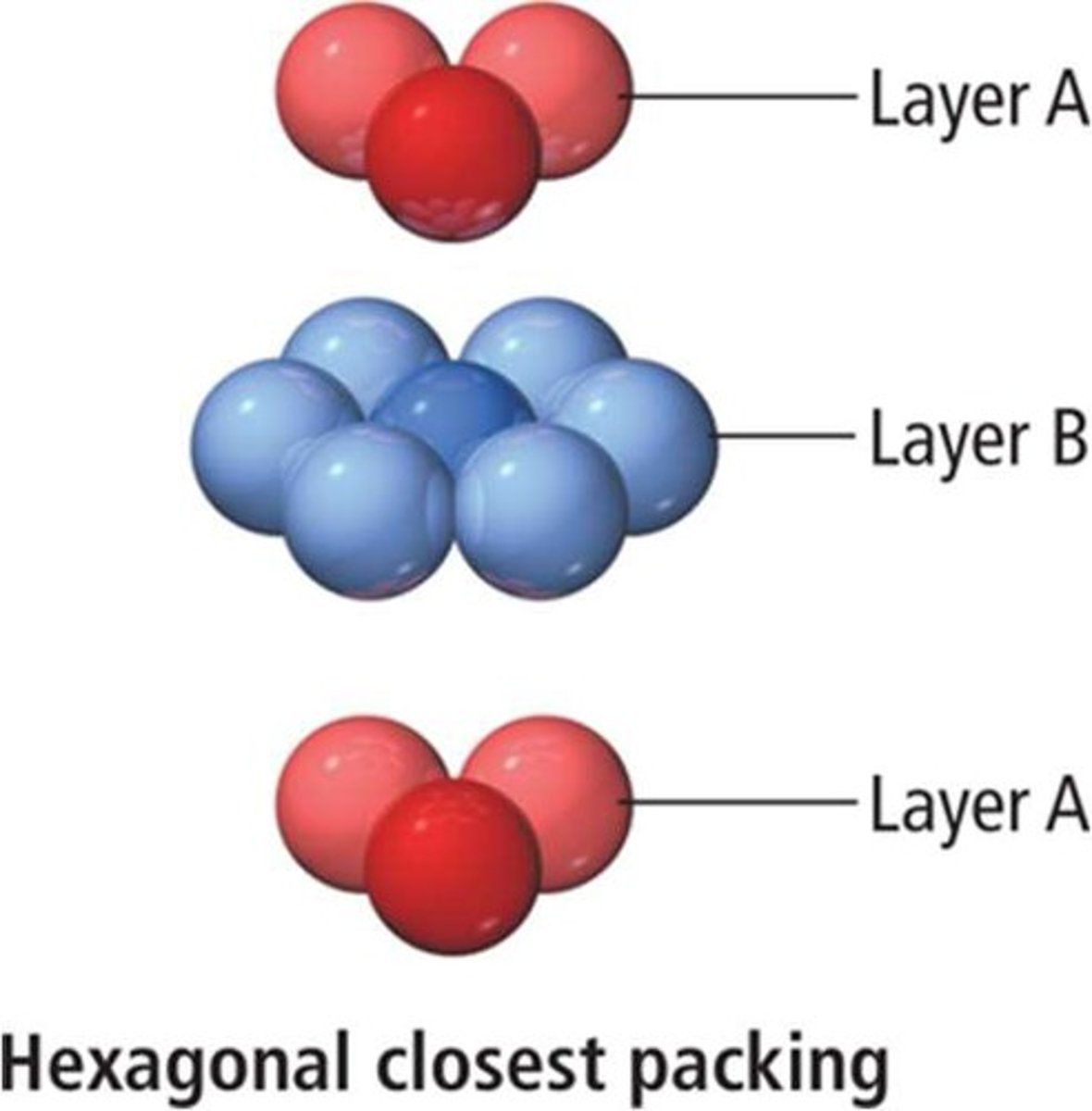
Hexagonal close packing
Efficient arrangement of spheres in layers.
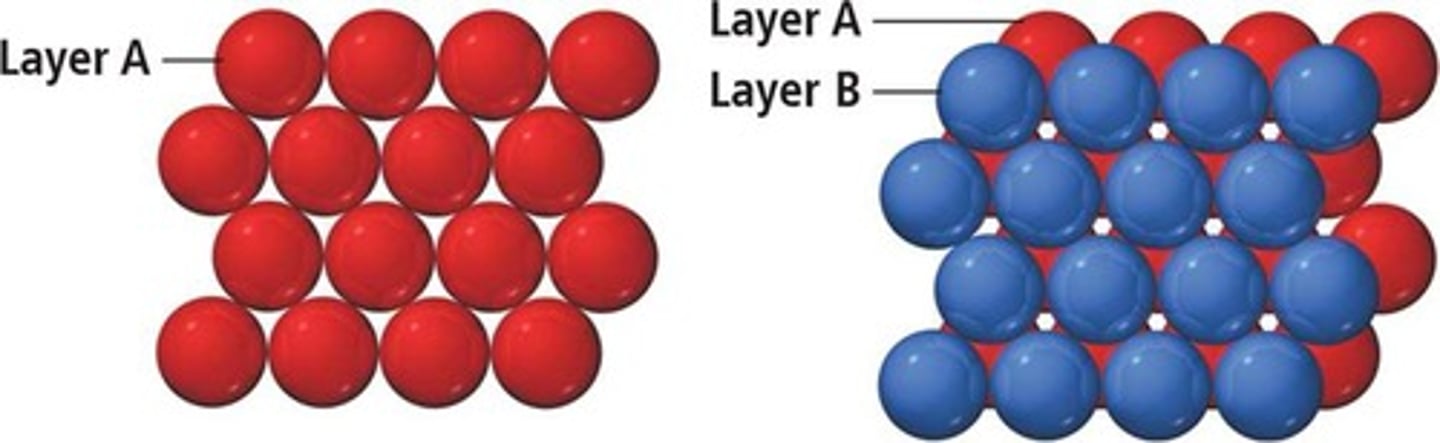
Edge length of unit cell
Denoted as l or a, critical for calculations.
Density calculation
Mass per unit volume, important for element identity.
Atomic weight
Mass of one mole of atoms, in g/mol.
Hexagonal Closest-Packed
Atoms arranged in close-packed hexagonal layers.
Cubic Closest-Packed
Atoms arranged in cubic closest-packed layers.
Crystalline Solids
Solids with ordered particle arrangements.
Molecular Solids
Solids composed of molecules at lattice sites.
Ionic Solids
Solids made of ions occupying lattice sites.
Atomic Solids
Solids classified by attractive forces between atoms.
Polymorphs
Different crystalline structures of the same compound.
Coordination Number
Number of close cation-anion interactions in crystals.
Coulombic Forces
Strong forces holding ionic solids together.
Metallic Bonding
Bonding involving a sea of mobile electrons.
Nonbonding Atomic Solids
Held together by weak dispersion forces.
Metallic Atomic Solids
Held together by metallic bonding, varying melting points.
Network Covalent Solids
Held together by covalent bonds, very hard.
Dispersion Forces
Weak intermolecular forces in molecular solids.
Dipole-Dipole Attractions
Intermolecular forces between polar molecules.
Hydrogen Bonds
Strong intermolecular forces involving hydrogen atoms.
Melting Points
Temperature at which solids transition to liquids.
CsCl Structure
Coordination number of cesium chloride is 8.
NaCl Structure
Coordination number of sodium chloride is 6.
Zinc Blende Structure
Coordination number of zinc blende is 4.
Atomic Radii
Average size of atoms in a crystal structure.
Density Calculation
Determining density using unit cell dimensions.
S2-
Anion occupying corners and faces in unit cell.
Zn2+
Cation located in tetrahedral holes of ZnS.
Tetrahedral holes
Spaces in crystal lattice for cation placement.
Density calculation
Mass per unit volume, expressed in g/cm³.
Fluorite Structure
CaF2 arrangement with F- and Ca2+ ions.
Coordination number
Number of nearest neighbors surrounding an ion.
CaF2
Calcium fluoride, 1:2 cation to anion ratio.
Antifluorite structure
Occurs with cation:anion ratio of 2:1.
Network Covalent Solids
Solids with atoms bonded by covalent bonds.
Graphite
Carbon allotrope with layered structure and dispersion forces.
Bond length in graphite
142 pm, distance between bonded carbon atoms.
sp2 hybridization
Carbon bonding with three sigma and one pi bond.
Diamond
Carbon allotrope with tetrahedral sp3 bonding.
High melting point
Temperature around 3800 °C for carbon allotropes.
Buckminsterfullerenes
C60 carbon structure resembling a soccer ball.
Nanotubes
Cylindrical structures made of interconnected carbon rings.
Single-walled nanotubes
One layer of interconnected carbon rings.
Multiwalled nanotubes
Concentric layers of interconnected carbon rings.
Silicates
Compounds containing SiO4 tetrahedra, major crust component.
Quartz (SiO2)
Common silicate mineral with tetrahedral structure.
Ceramics
Inorganic solids made from powders and heat.
Aluminosilicates
Silicates containing aluminum, used in ceramics.
Kaolinite
Clay mineral, Al2Si2O5(OH)4, used in ceramics.
Oxide Ceramics
Common ceramics like Al2O3 and MgO.
Refractory Materials
Materials used in high-temperature applications.
Nonoxide Ceramics
Ceramics like Si3N4, BN, and SiC.
Si3N4
Network covalent solid similar to silica.
BN
Isoelectronic with C2, forms diamond-like structure.
Portland Cement
Powdered mixture mainly of limestone and silica.
Concrete
Widely used building material made from cement.
Borosilicate Glass
Glass with added boric acid for durability.
Vitreous Silica
Hard, low thermal expansion, transparent to UV.
Leaded Glass
Glass containing PbO, high refractive index.
Soda-Lime Glass
Common window glass, 70% silica content.
Molecular Orbitals
Formed from combining atomic orbitals.
Band Theory
Describes delocalized orbitals in solids.
Valence Band
Band of bonding molecular orbitals.
Conduction Band
Band of antibonding molecular orbitals.
Band Gap
Energy gap between valence and conduction bands.
Conductors
Continuous valence and conduction bands.
Semiconductors
Have band gap, can conduct electricity.
Insulators
Large band gap restricts electron promotion.
Doping
Adding impurities to increase semiconductor conductivity.
n-type Semiconductors
Doped with electron-rich impurities.
p-type Semiconductors
Doped with electron-deficient impurities.
Diode
Allows current flow in one direction.
Polymers
Large molecules formed from repeated monomers.
Monomers
Small molecules that link to form polymers.
Polymerization
Process of linking monomer units together.
Condensation Polymerization
Involves elimination of small molecules during formation.