Science Contact Forces Quiz
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Newtons third law of motion
For every action there is and equal and opposite reaction.
What is Kinetic Energy
KE is moving energy. More speed-more KE, Less speed-less KE
Define Force:
Force is the push or pull on an object. (can cause damage in/to an object)
Model a soccer player getting hit in the head by a ball. Explain how the contact force is equal.
The contact force is both equal and opposite because of Newton's third law, when the soccer player gets hit with the ball the force from the ball to player is the same from the force of the player to ball.
Difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. (Net force/acceleration)
Net force shows overall motion (unbalanced/balanced). Net force is a number- acceleration/motion to the side with more force.
Come up with your own force diagram word problem using tug or war and pull forces.
Kiera and Lucy are playing tug or war. Kiera pulls the rope 20n to the left, whereas Lucy pulls the rope 25n to the right. What is the net force?
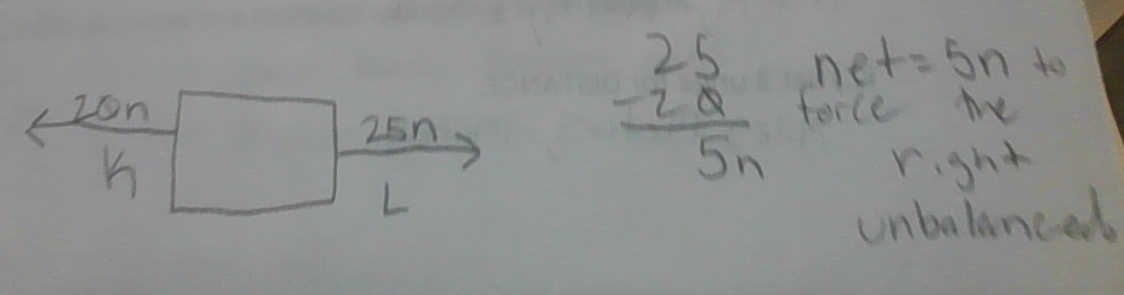

Player 84 hits player 13 with a force of 5n. What is the force exerted on player 84? What is the force exerted on player 13?
The force exerted on each player is 5n because of Newton's third law.

Which system has the least KE? Why?
System C has the least KE only one out of the two things are moving so only one of the two objects that have KE. Whereas in system A and B both objects (Soccer ball & player + player & player) are moving so both have KE.

Which system had the lowest collision force? Why?
System C also has the lowest collision force because it has the lowest KE. Since system C just has one object moving (the player) it has less KE and collision force than both system A and B.

Which system(s) invole both objects having KE when they collide?
Both system A and B insole both objects have KE because both objects are in motion. But in system A if the ball was the only thing moving and not the player then it would not have both objects moving.
3 units for speed or rate:
miles/hr, m/min, inches/sec.
3 units for distance:
Miles, meters, inches.
How do you find distance?
Time x Rate or Speed
How do you find time?
Distance/Rate or Speed
How do you find Rate or Speed?
Distance/Time
Explain the difference between: stopping distance, reaction time, and braking distance.
Reaction time is the time it takes your brain to process there is trouble and then slam on the brakes. Braking distance is the distance it takes for your car to stop. Stopping distance is the total reaction time and braking distance.
Explain how AIRBAGS work in a car crash:
AIRBAGS spread out the force so there is less pressure in one area.
Explain how seatbelts work in a collision using the term INERTIA
Inertia keeps your body moving until the seatbelt stops your motion.
Energy of motion
Kinetic Energy
stored energy
Potential energy
energy moving from one object to another
KE Energy transfer
Energy changing from one type to the next.
Energy transformation
Energy cannot be created or destroyed- only transferred or transformed
Law of Conservation of Energy
Do things BEND when they collide?
yes
Do all things break in a collision?
no
KE transferring from object to object.
Motion
Measured in newtons, push or pull.
force
Force opposite motion as an object passes through the air
Air resistance
a force that acts between two objects that are in contact with one another
Friction
how fast an object moves
Law of Conservation of Energy