Types of Muscle Tissue
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Skeletal muscle
Consists of long, cylindrical, striated fibers
→ Vary greatly in length & have multiple nuclei & mitochondria
Location: usually attached to bones via tendons
Function: motion, posture, heat production, & protection

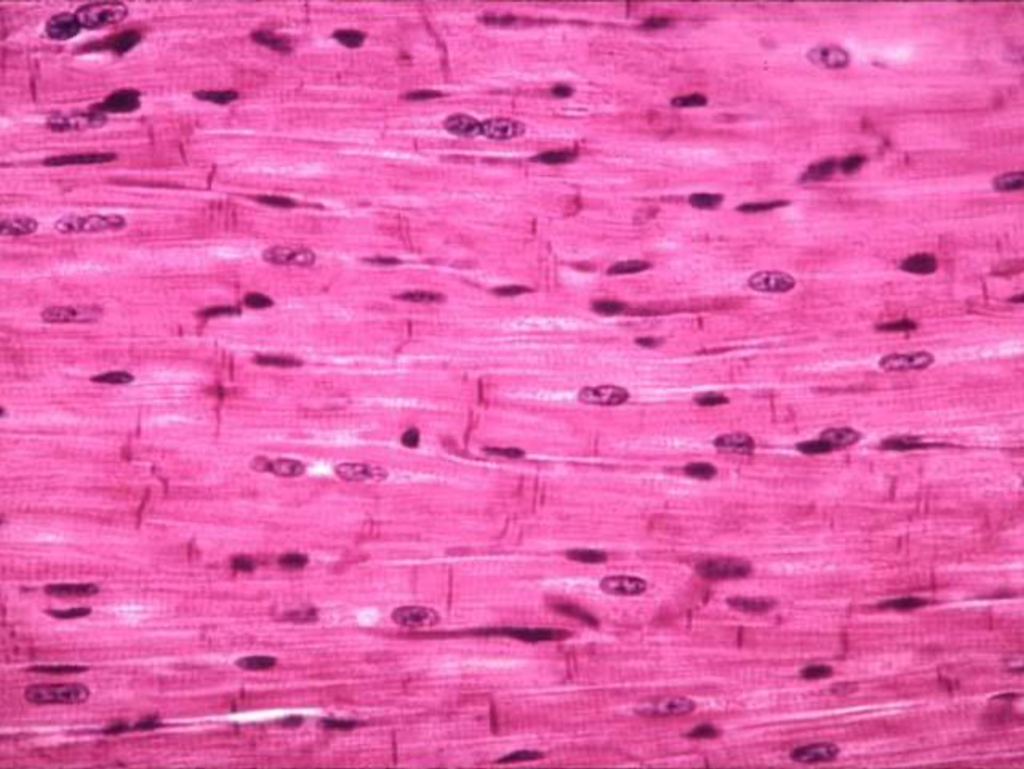
Cardiac muscle
Consists of striated, branching fibers
→ Typically has one nucleus but SOMETIMES has two nuclei
Join end-to-end via intercalated discs
→ Contain desmosomes (strengthen & hold fibers together during contractions) & gap junctions (facilitate quick conduction of electrical signals)
Location: Heart wall
Functions: Pumps blood to all parts of the body
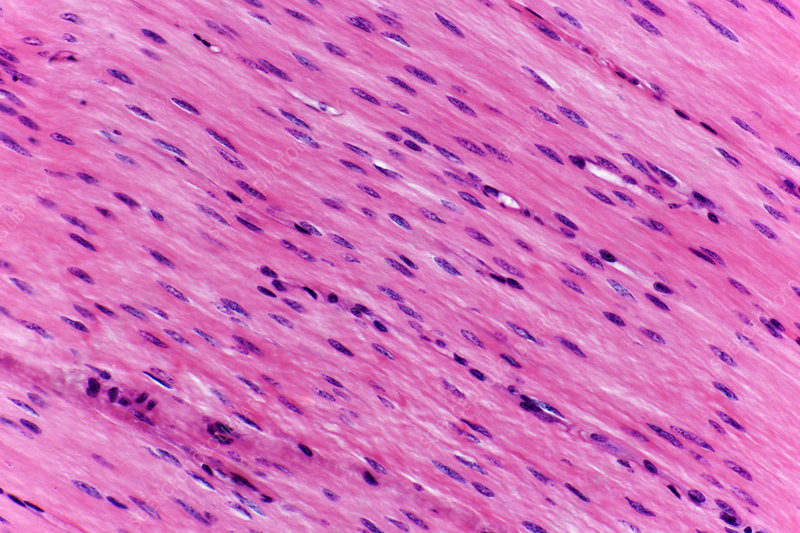
Smooth muscle
Consists of non-striated, spindle-shaped fibers
→ Has one nucleus per cell, usually involuntary, usually connected by gap junctions
Functions: motion (constriction of blood vessels & airways, propulsion of food through the intestinal tract, & contraction of urinary bladder)
Location: Iris of the eyes; hollow walls of internal structures like blood vessels, airways to lungs, stomach, intestines, gallbladder, bladder, & uterus
Muscular tissue
Consists of elongated cells celled muscle fibers or myocytes
Use ATP to generate force
Produce body movements, maintains posture, provides protection, & generates heat