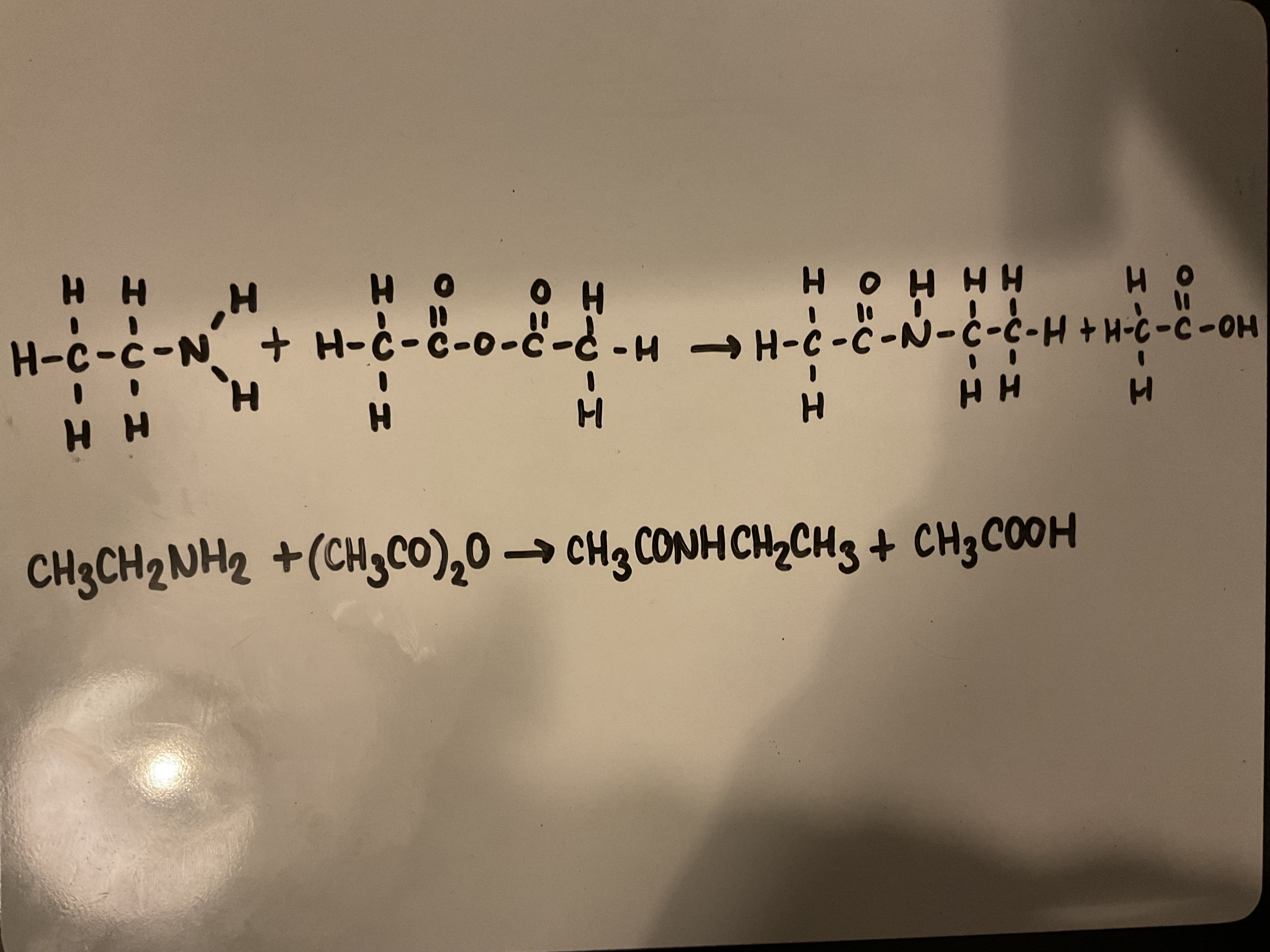Esters, Amines, Amides, Polymers & Analytical Techniques
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
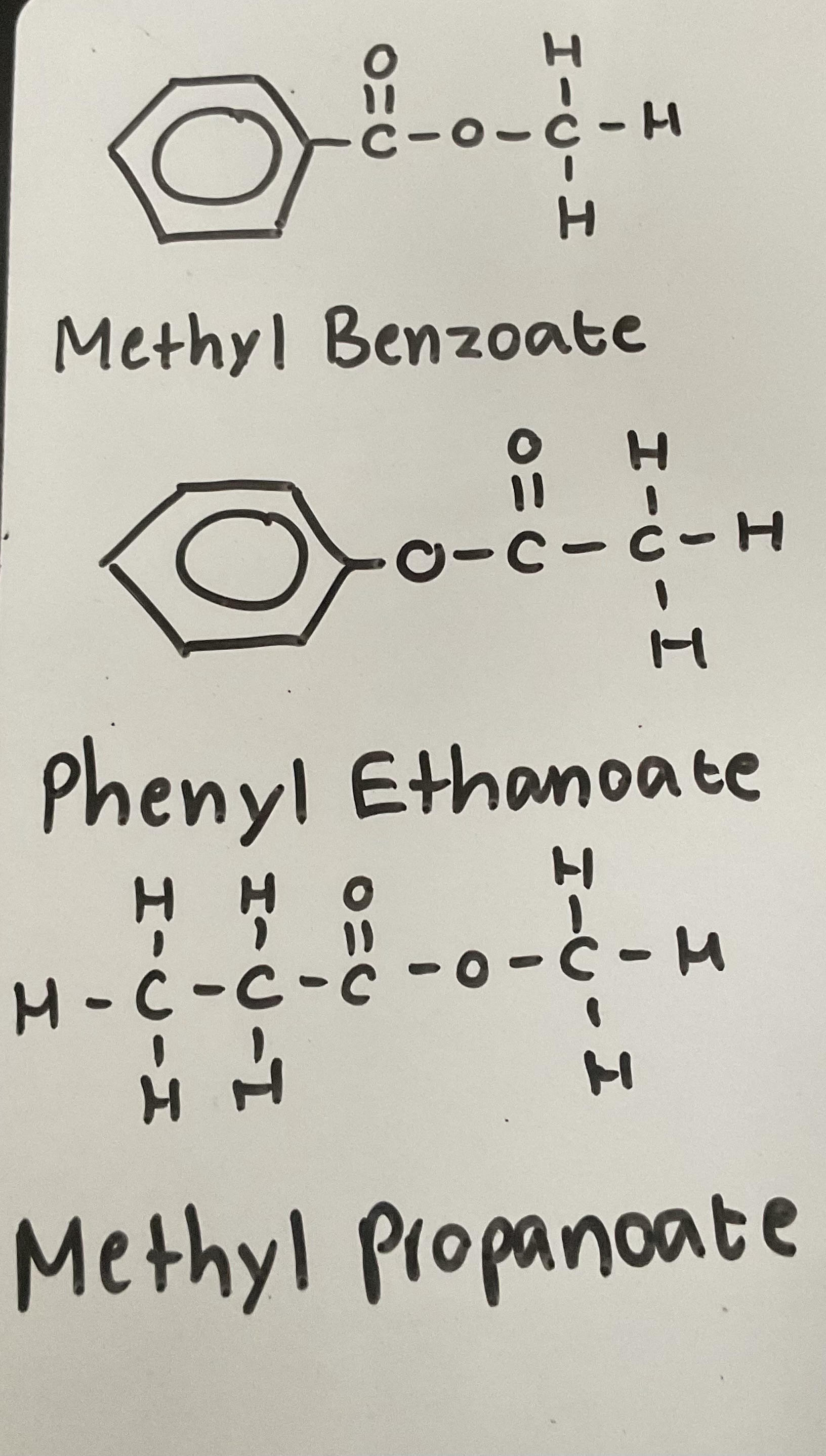
What is the general rule for naming esters
Alcohol part comes first (name it like a branch - methyl, ethyl, phenyl)
Ending is the anion of the carboxylic acid (e.g ethanoate, butanoate)
Examples:
What are the physical properties of esters
______ melting and boiling point than carboxylic acids because _________
Usually insoluble because _____________
Sweet fruity smell
What are the physical properties of esters
Lower melting and boiling point than carboxylic acids because esters can’t form hydrogen bonds
Usually insoluble because esters can’t form hydrogen bonds with water
Sweet fruity smell
How can esters be formed from carboxylic acids and alcohols. Include the conditions and type of reaction
Condensation Reation
Heat under reflux
Concentrated H2SO4 catalyst
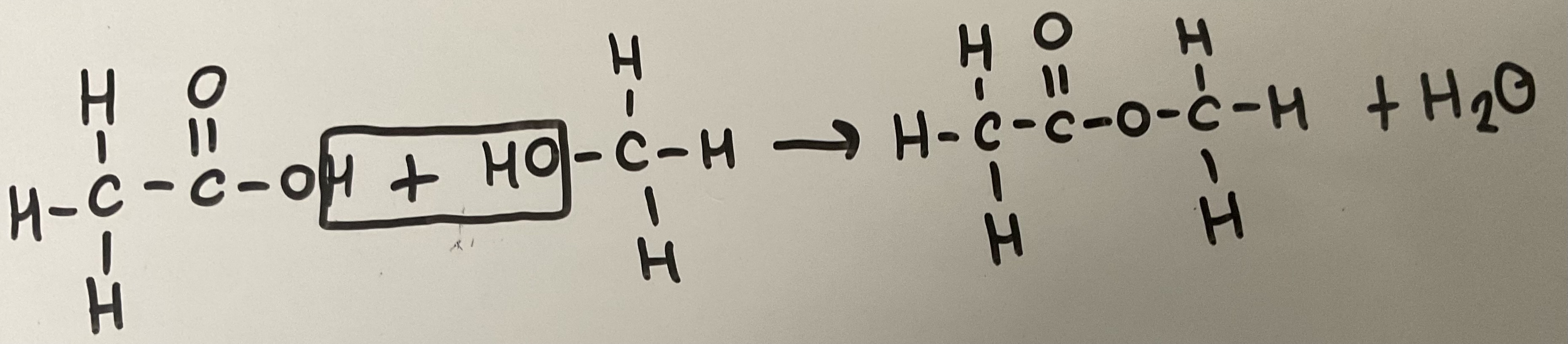
What is a primary, secondary and tertiary amine
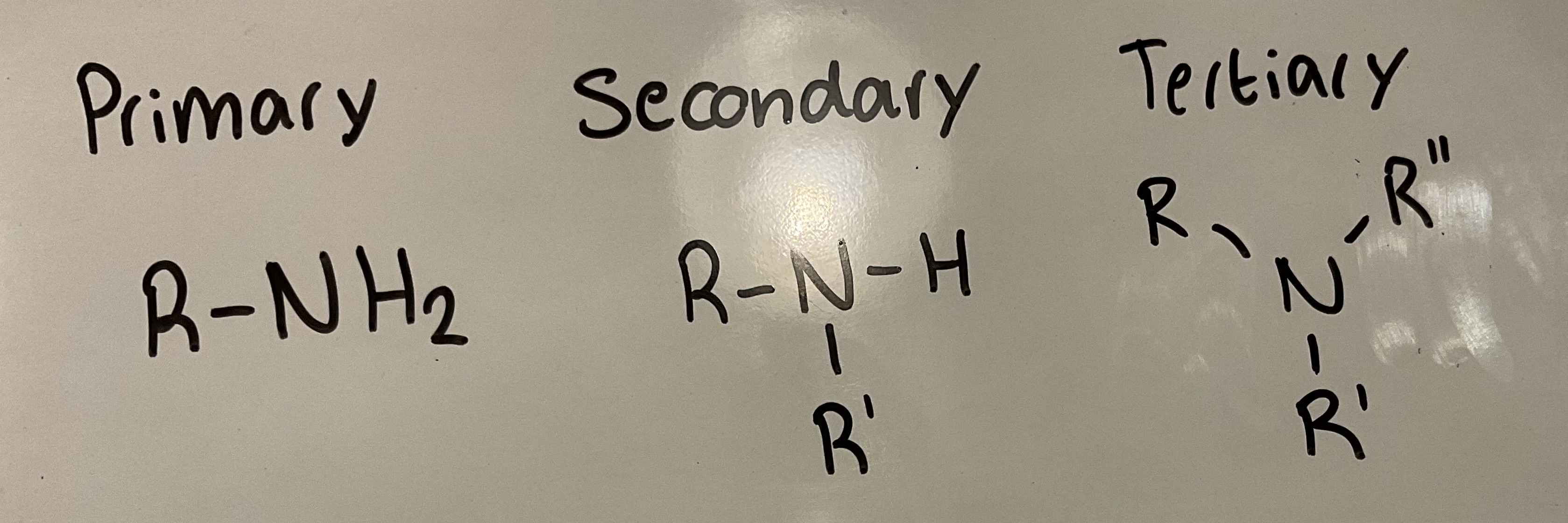
Physical properties of amines
Higher melting and boiling points than expected because _________
They are soluble in water because _________
They have a distinctive _____ smell
Physical properties of amines
Higher melting and boiling points than expected because they form hydrogen bonds
They are soluble in water because they form hydrogen bonds with water
They have a distinctive fishy smell
Chemical properties of amines:
Due to their lone pair they can act as
__________
__________
__________
Bases (proton acceptors)
Nucleophiles (electron pair donor)
Ligand (DM topic)
Amines are bases and so will react with acids to form salts. Show the equation of the reaction between methyl amine and HCI
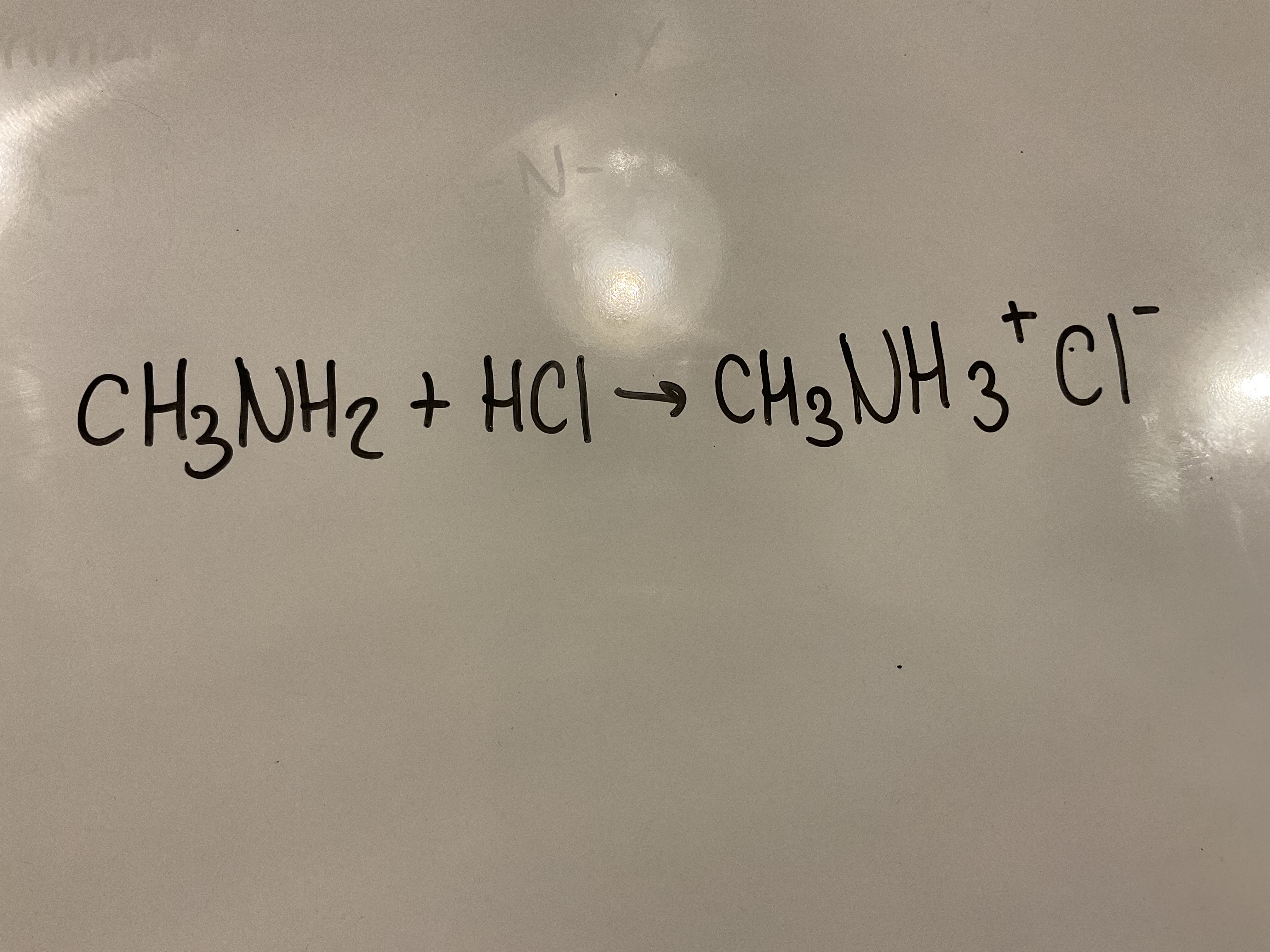
Soluble amines form alkaline solutions in water. Show the ionic equation for methylamine in water
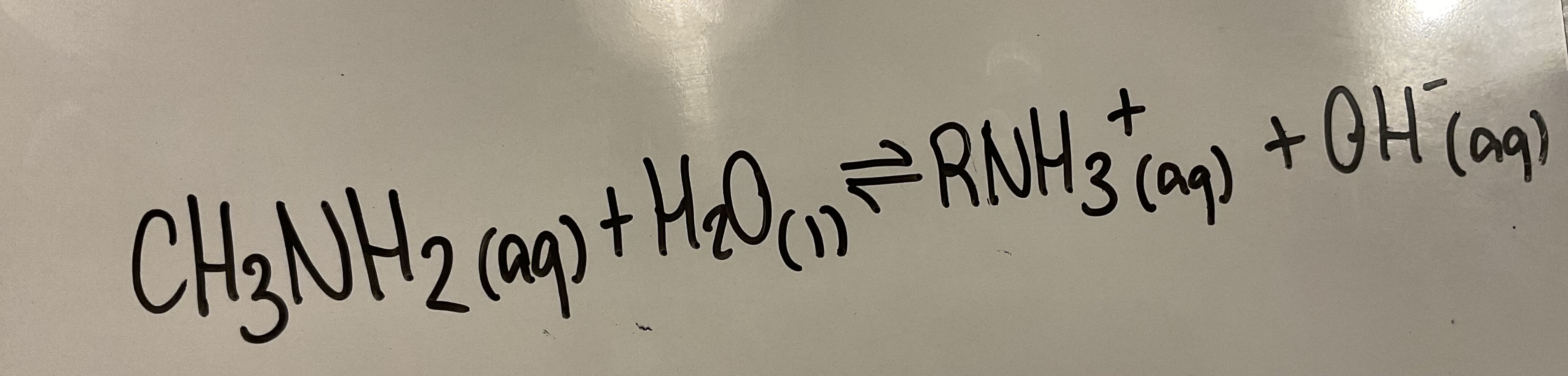
Amines can act as nucleophiles (like ammonia).
Show how amines can react with haloalkanes to form secondary amines
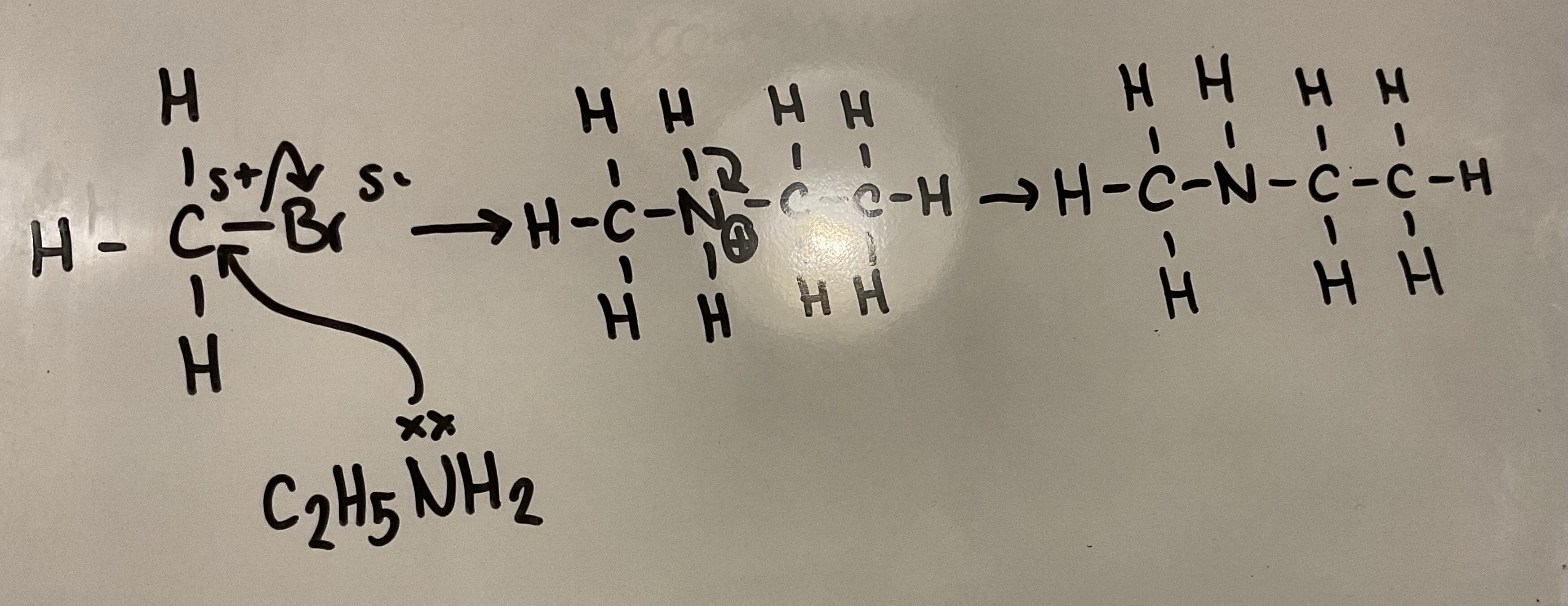
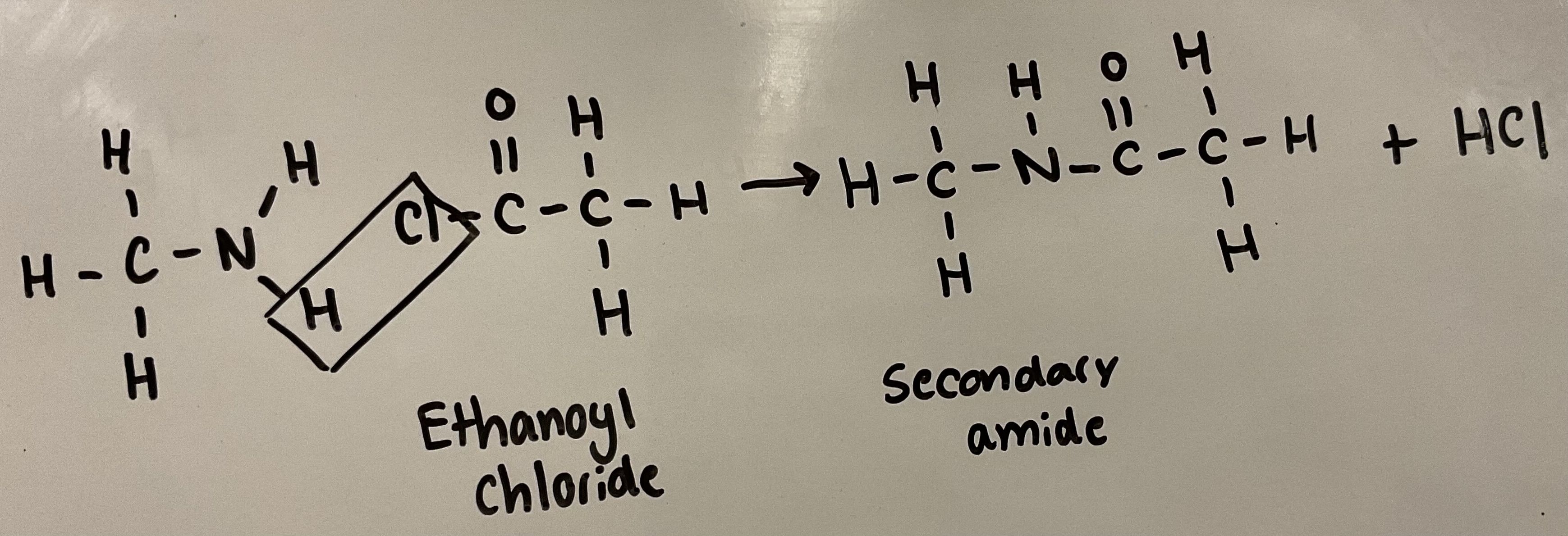
Amines can act as nucleophiles (like ammonia)
Show how amines can react with aceyl chlorides to form an amide
Use CH3COCl as your aceyl chloride
What are primary, secondary and tertiary amides
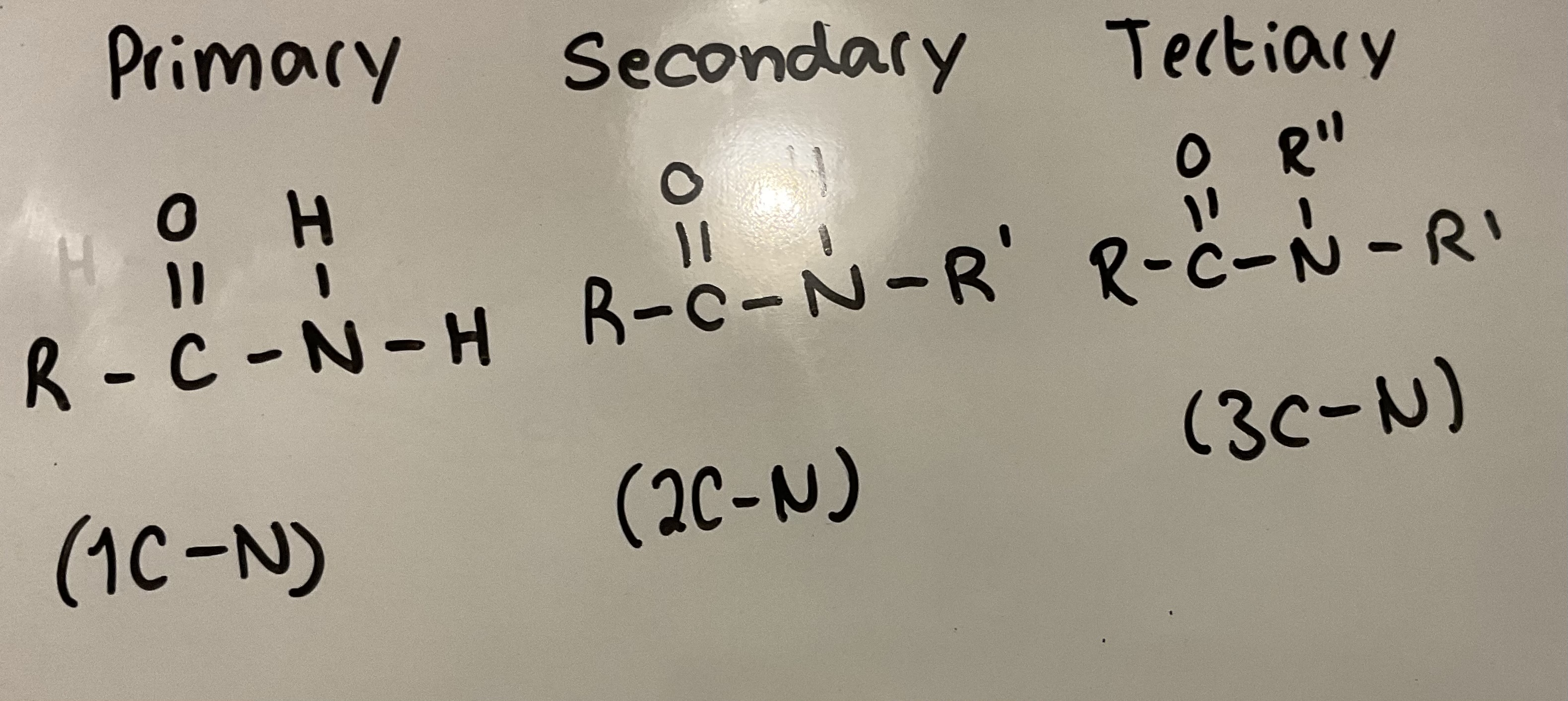
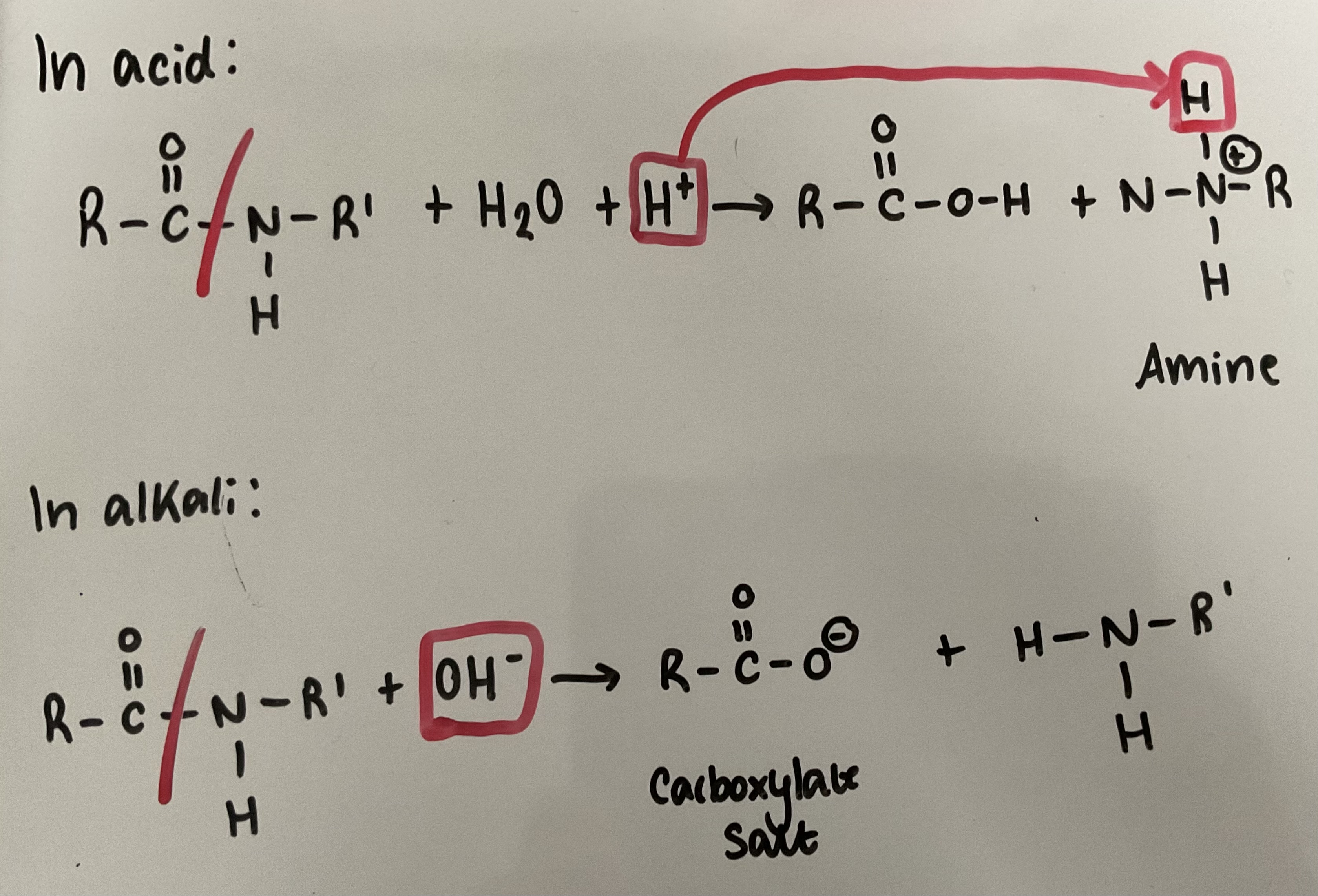
Show how amides can be hydrolysed in both acid and alkali conditions - give the conditions required
Heat under reflux
Define the term polymer
Polymers are long chain molecules made by joining many thousands of smaller molecules (monomers) together
Define the term addition polymer
Monomers added together forming a long chain in an addition reaction. Only 1 product with 100% atom economy. Monomers contain C=C
What is a condensation polymer and what are its properties
Small molecule (H2O or HCl) lost when monomer molecules join in condensation reaction to form long chain.
Monomers must contain 2 reactive functional groups (e.g. COOH and OH to form polyesters or COOH and NH2 to form polyamides)
Polyamides and polyesters are condensation polymers
Show how diamines and dicarboxylic acids react in a condensation reaction to form polyamides. Give the reagents and conditions
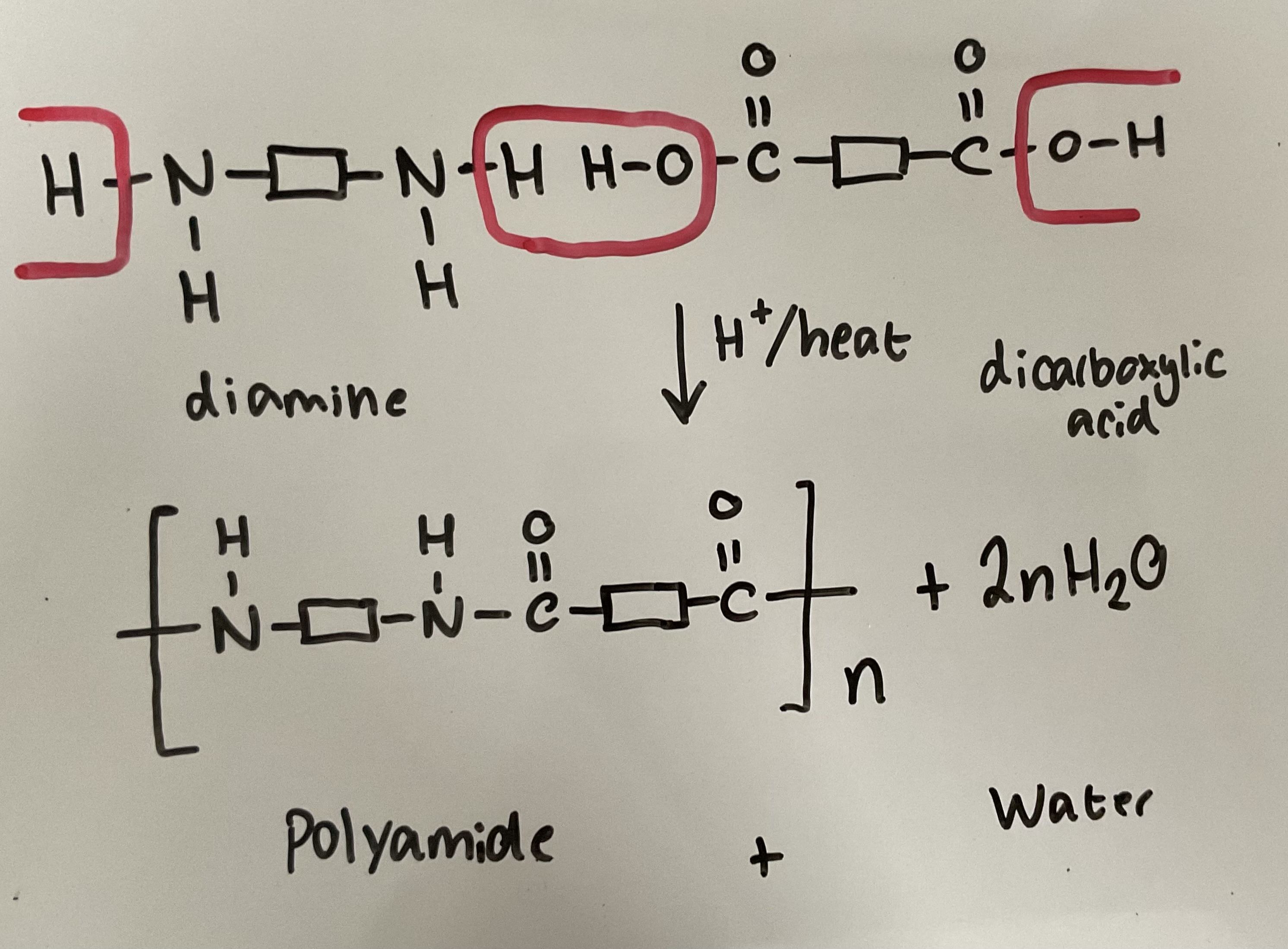
If a Nylon (Polyamide) is called Nylon 6,10 what do the numbers mean
First number - 6 carbons in diamine
Second number - 10 carbons in dicarboxylic acid
Show how a polyamide can be made from a single monomer containing both an amine and carboxylic acid
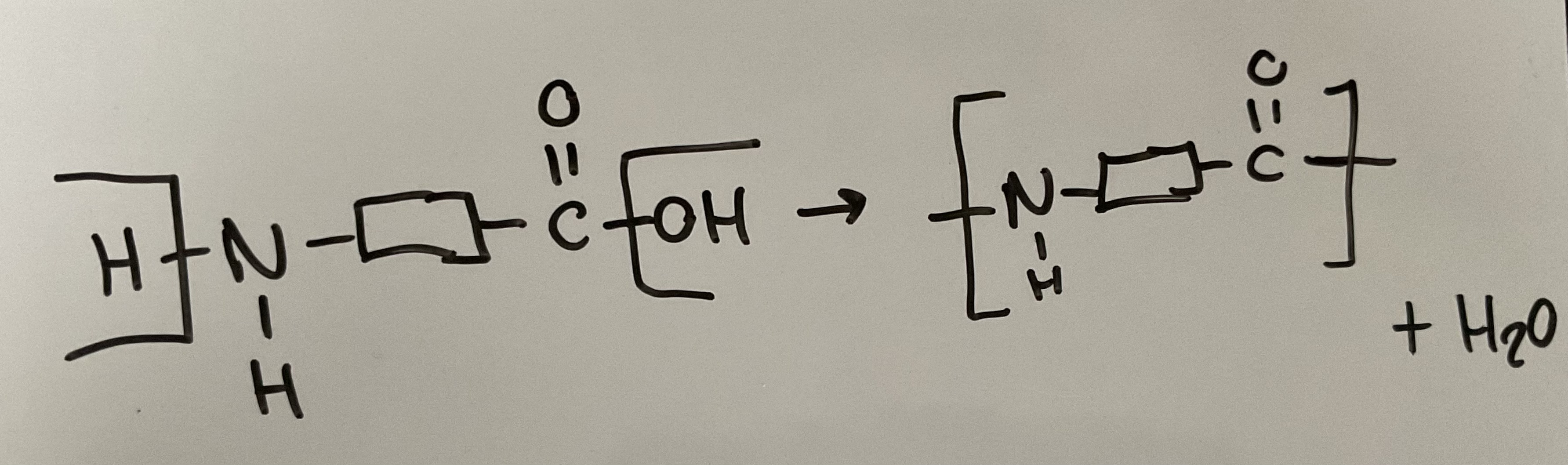
Show how diols and dicarboxylic acids react in a condensation reaction to form polyesters. Give the reagents and conditions
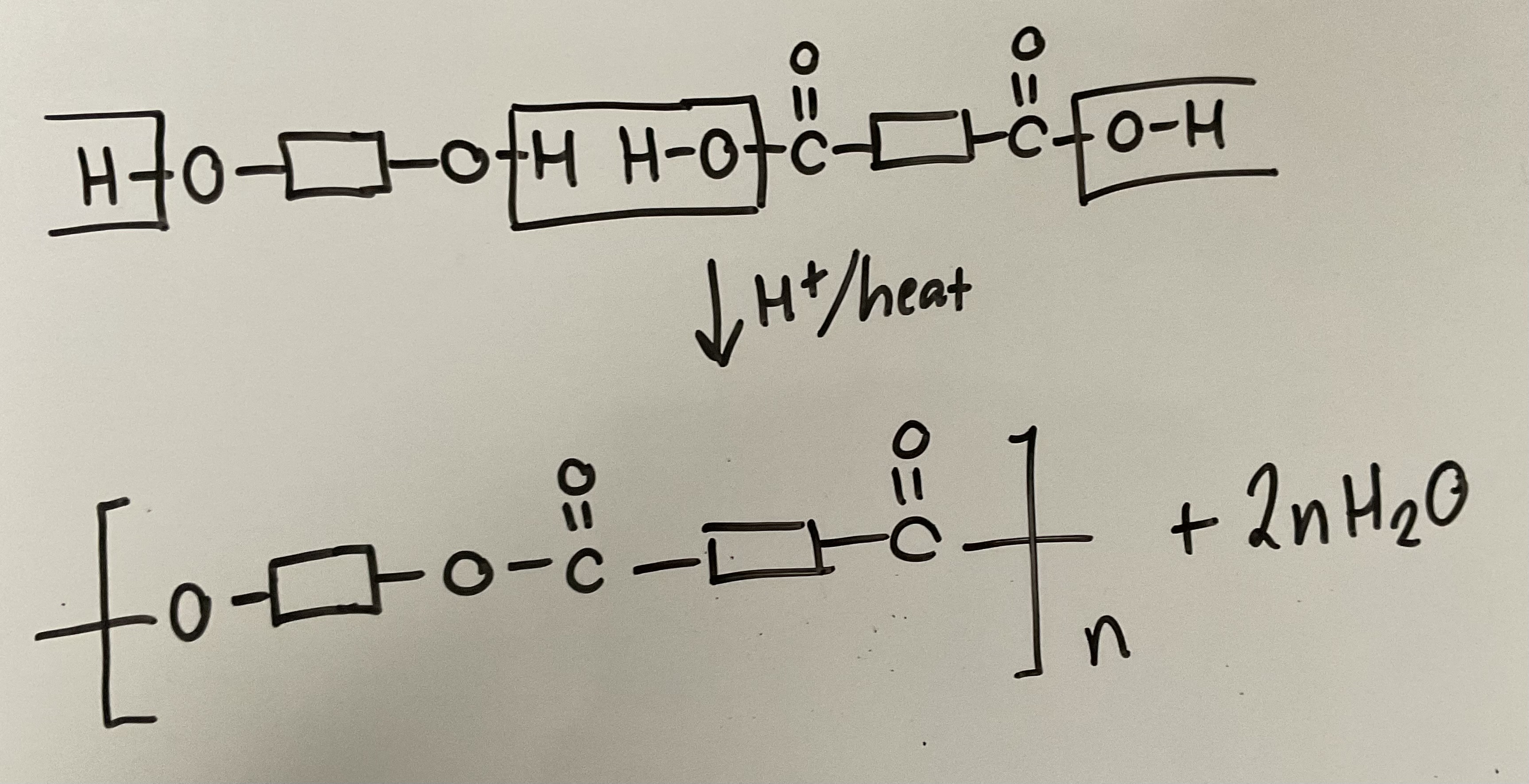
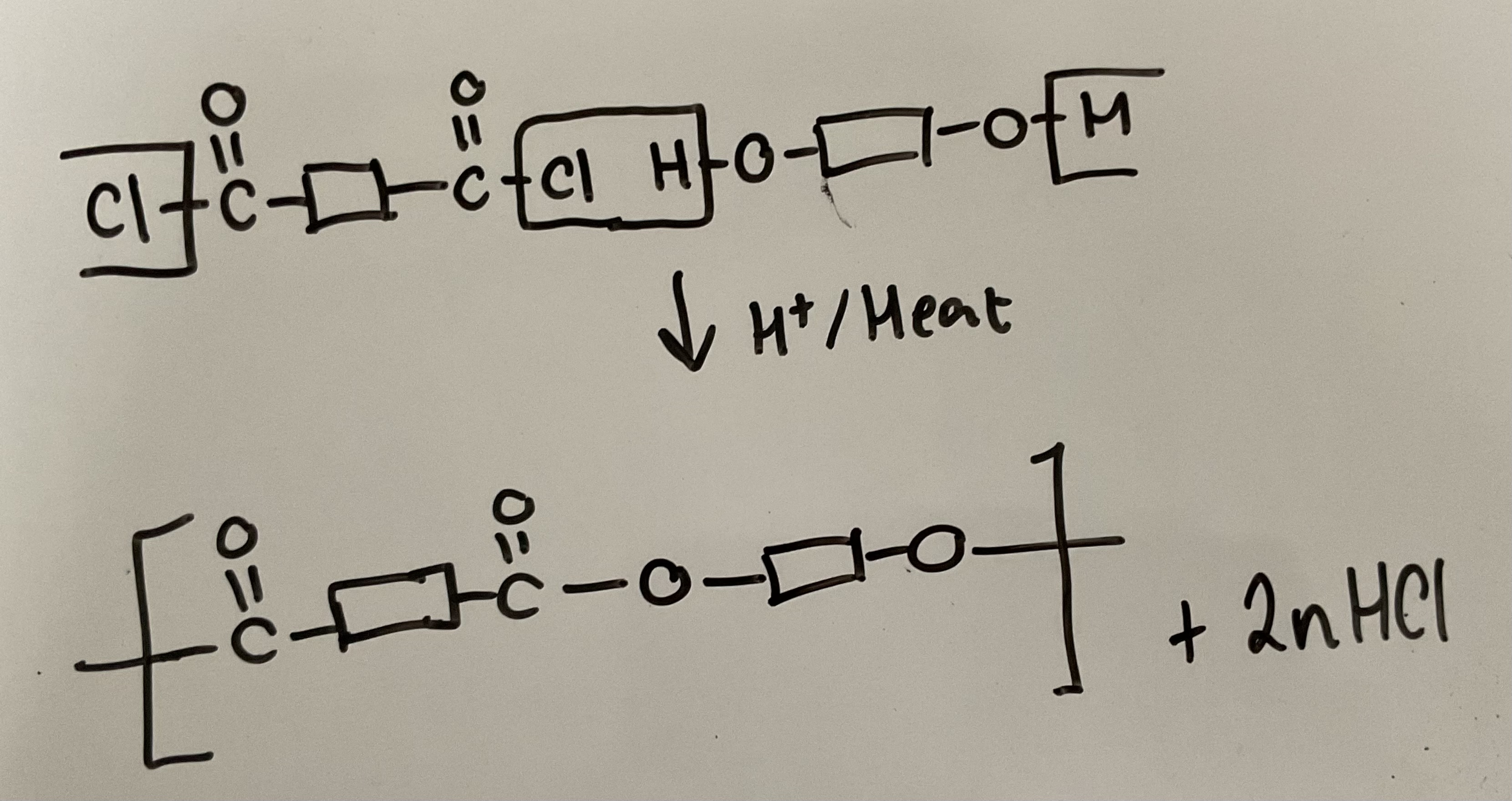
Show how diols and diacyl chlorides react in a condensation reaction to form polyesters. Give the reagents and conditions
Breaking down condensation polymers
Break all ____ and ___ bonds
Add water - put an OH on the C=O forming the ______ group and but a H on the -O/-N to make an _____/_____ group
Alkaline conditions - _____ groups form salts e.g. ____Na+
Acidic conditions - _____ groups form salts e.g. ____Cl-
Breaking down condensation polymers
Break all ester and amide bonds
Add water - put an OH on the C=O forming the carboxylic acid group and but a H on the -O/-N to make an alcohol/amine group group
Alkaline conditions - COOH groups form salts e.g. COO-Na+
Acidic conditions - NH2 groups form salts e.g. NH3+Cl-
Mr is given to how many decimal places on a high resolution mass spectrum
4d.p.
NMR Spectrum is used to find
The number of different hydrogen ______ in a molecule
The number of hydrogen atoms in each _________
The type of chemical environment
The number of hydrogen atoms attached to the _______ carbon atoms
The number of different hydrogen environments in a molecule
The number of hydrogen atoms in each environment
The type of chemical environment
The number of hydrogen atoms attached to the adjacent carbon atoms
What is CDCl3 used for in NMR
Acts as a solvent for sample
Causes no peak due to having no hydrogen environments
What is TMS used for in NMR
Used as a reference peak as it gives a strong peak, furthest to the RHS
How is an H NMR spectrum interpreted
Relative peak area =
Chemical shift =
Splitting pattern =
Relative peak area = number of hydrogen in environment
Chemical shift = position of peak, chemical environment/group
Splitting pattern = n-1 = number of adjacent carbons on adjacent carbon
How is C NMR interpreted
Number of peaks =
Chemical shift =
Number of peaks = number of carbon environments
Chemical shift = indicates type of carbon environment
How many different carbon enviroment are there in a benzene ring
1 environment
How many different carbon environments are in a phenol
4 environments
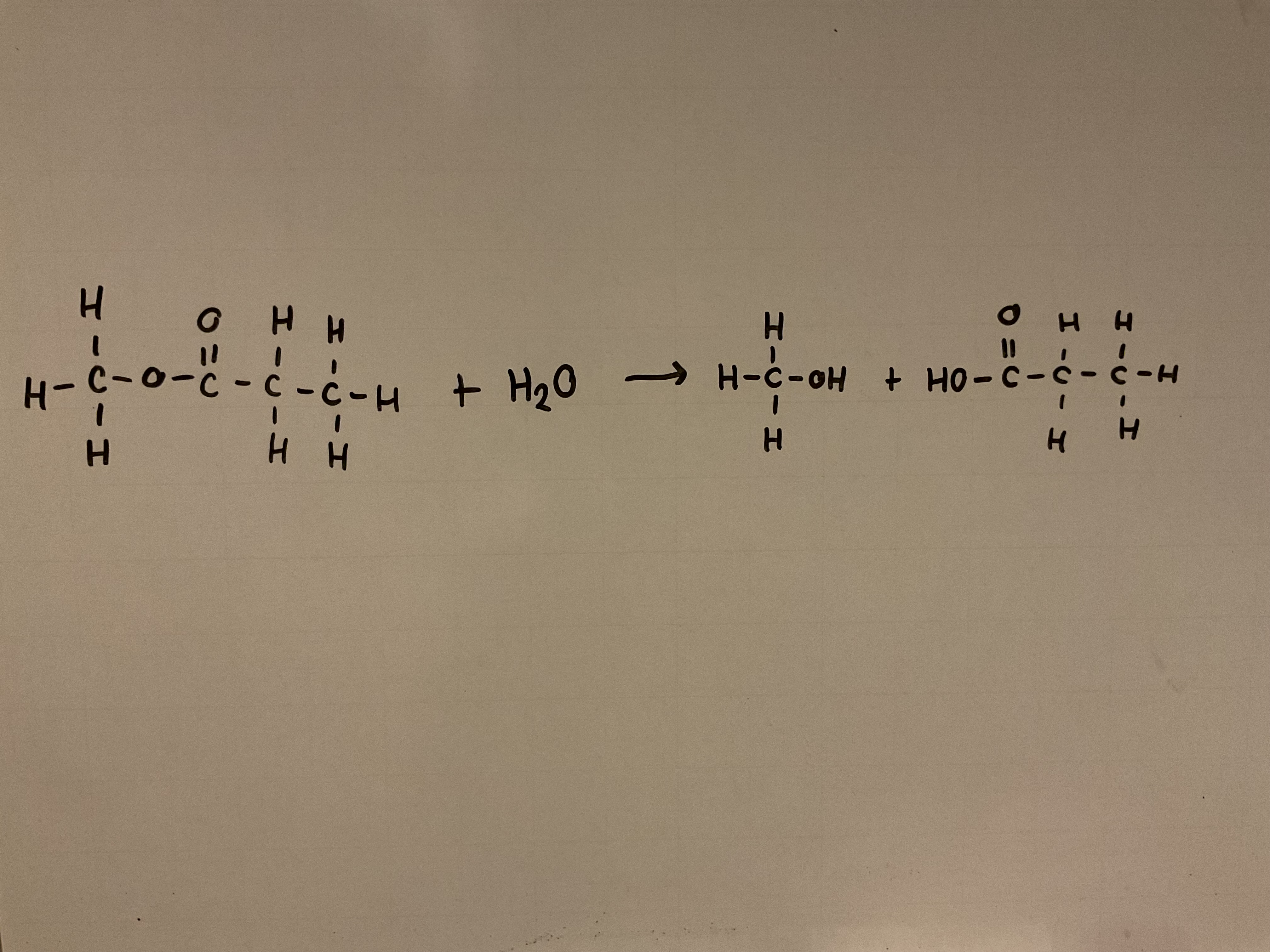
Show the hydrolysis of an ester (e.g. methyl propanoate) with an acid (e.g. HCl)
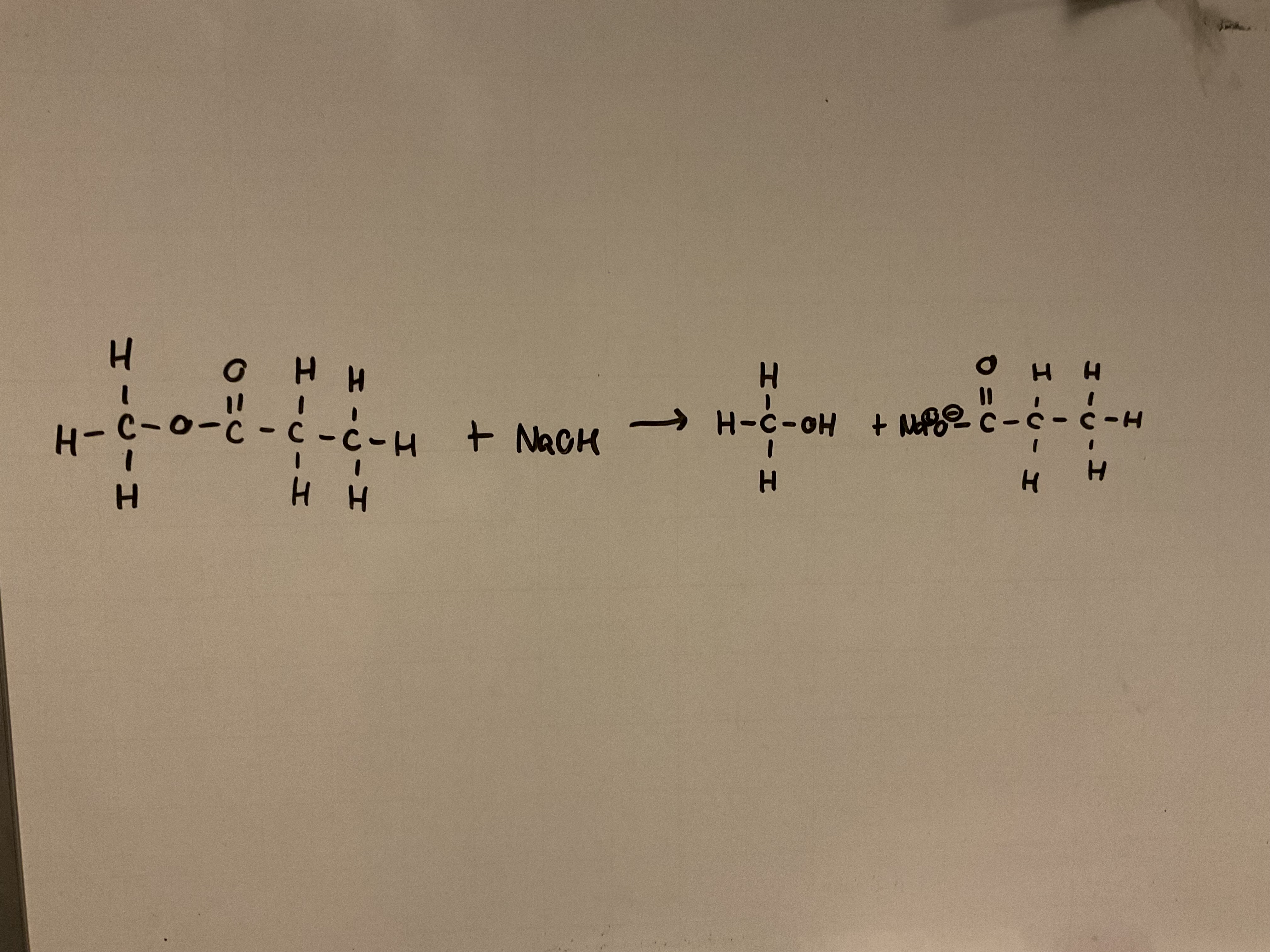
Show the hydrolysis of an ester (e.g. methyl propanoate) with an alkali (e.g. NaOH)
Show how an amide can be formed from an amine and an acid anhydride