Anticancer Agents/Drug Metabolism
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are some agents that inhibit DNA biosynthesis
Inhibitors for enzymes that catalyse the formation of thymine
5-fluorouracil
cycloserine
methotrexate
How does 5-fluorouracil work?
Prodrug - in vivo, it is activated by conversion to 2-deoxyfluorouridolate, then phosphorylated
Then binds to the enzyme active site irreversibly inhibiting it
How does methotrexate work?
It is a competitive inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase, it inhibits the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate
Tetrahydrofolate is a THF cofactor, which is essential for thymidylate, purine, and some amino acid synthesis
Therefore, methotrexate inhibits DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
Not useful as an antibacterial agent as it has low specificity for bacterial DHFR
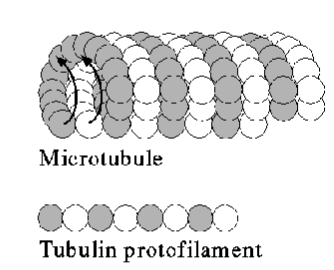
Describe the structure of a microtubule
Formed of tubulin heterodimers (alpha and beta subunit)
What are vinca alkaloids
Assembly inhibitors of microtubules
They bind to free tubulin dimers and form non biologically active aggregates
e.g. vinblastine + vincristine
What do spindle poisons do
Prevent the assembly or disassembly of microtubules
How do microtubule disassembly inhibitors work
Bind to the tubulin and prevent its disassembly back into free subunits
e.g. paclitaxol - for solid tumors
What are some requirements for a drug to be orally available
Must be able to be formulated as a tablet/syrup
Must be able to survive stomach acid (pH 2.0)
Must have an overall neutral ionisation state to be able to cross the cell membrane
Must have the correct hydrophilic/hydrophobic balance (LogP)
What are Lipinski’s rules
For a compound to be orally available and show good absorption/permeation of biological tissue, it must:
Have a molecular weight of less than or equal to 500
Have a clogP of no more than 5 (mlogP less than or equal to 4.15, XlogP less than or equal to 5.7)
Have no more than 5 hydrogen bond donors (-OH, -NH)
Have no more than 10 hydrogen bond acceptors (O, N)
Have no more than 5 fused rings
What are exceptions to Lipinski’s rules
In general if one rule is broken the compound could still be orally active but if two are then it wont be.
If the compounds have active biological transport systems the rules are not applicable
What are phase I reactions
In the liver, the body tries to start metabolising compounds by making them more soluble so they can be excreted
In phase I, the body tries to introduce or unmask polar groups.
These reactions are catalysed by flavin mono-oxygenase enzymes, esterases, proteases or epoxidases.
What are phase II reactions
Increasing the solubility of compounds formed in phase I reactions through conjugation reactions. All increase the polarity of the molecules for excretion.
e.g. addition of a sulfate by a sulfatase enzyme, addition of a glutathione tripeptide, addition of a sugar to an OH to form a glycoside.