Vision: from retina to cortex
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is the ‘problem’ with vision?
there is an inherent ambiguity in the visual signals our eyes receive
what is the pupil?
where light enters the eye
what is the iris?
adjustable aperture, constricts in bright light to make pupil smaller
what does the cornea and lens do?
focuses light on retina
what is accommodation?
when ciliary muscles change shape of lens to bring objects into focus at different distances
what are photoreceptors?
cells with light sensitive photopigments in outer segments
what are rods?
contain rhodopsin
respond in dim light
none in the fovea
what are cones?
three types with photopigments sensitive to different wavebands (long, medium, short)
daytime vision
what are the large parasol ganglion cells?
connects to the magnocellular system
what are the small midget ganglion cells?
connects to the parvocellular system
what are receptive fields?
the part of the retina from which the ganglion cells receive input
how does lateral inhibition affect the action potential of retinal ganglion cells?
centre-surround relationship (on-centre, off-surround)
light in the centre of the cell increases activity
light surrounding the cell decreases activity

features of retinal ganglion processing
poor at spotting change
good at picking out sharp edges
filters the input for useful info
what is the lateral geniculate nucleus?
contains pathways and cells that are responsive to vision??
in the thalamus
what do (parasol) magnocellular cells respond to?
movement and flicker
what do (midget) parvocellular cells respond to?
colour and detail
where are the koniocellular cells located?
in between the layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus
what do the koniocellular cells respond to?
blue-yellow colour??
what percentage of the cortex is dedicated to vision?
greater than 50%
other names for the primary visual cortex
V1
striate cortex
what are the cells in V1 sensitive to? (Hubel and Wiesel)
lines and specific orientations of lines
what does v1 contain?
a retinotopic map (not all parts of the visual system has this)
what are the streams of processing?
dorsal
ventral
what does the dorsal stream do?
‘where’ pathway
focuses on where things are in space
movement
runs along the top of the brain
what does the ventral stream do?
‘what’ pathway
focuses on object identification and recognition
runs along the bottom of the brain
what is a retinotopic map?
a representation of each point in the visual field arranged so that neighbouring parts of the retina are represented by neighbouring parts of V1
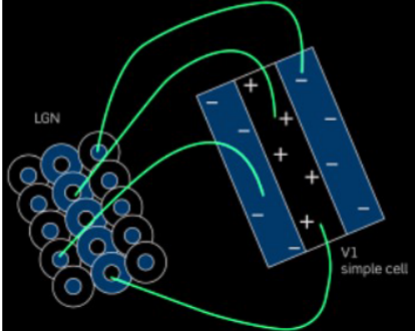
how do centre-surround receptive fields and v1 simple cells relate to each other?
if you take the outputs from the receptive fields and organise them in a specific way you can get a rectangular receptive field which is responsive to a certain orientation of line but not others