2.1.3 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is a nucleotide?
A monomer of a nucleic acid
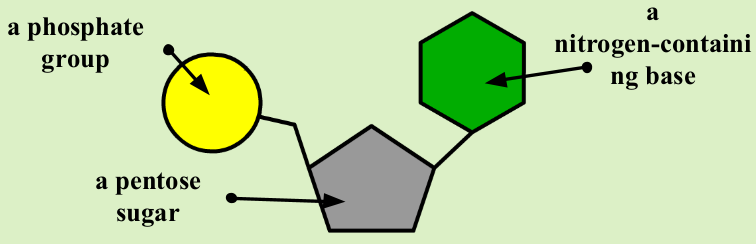
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
What is the difference between DNA and RNA nucleotides?
In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose
In RNA, the sugar is ribose
What is a purine base?
A double ring structure.
e.g. adenine (A) & guanine (G) are purine bases
What is a pyrimidine base?
A single ring strucutre.
e.g. thymine (T), cytosine (C) & uracile (U) are pyrimidine bases
What is the difference between DNA and RNA’s bases?
DNA contains: A, G, T & C
RNA contains: A, G, U & C
How are polynucleotides formed?
Pentose carbon 3 on one nucleotide bonds to a phosphate from another nucleotide, through condensation reactions→ nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds
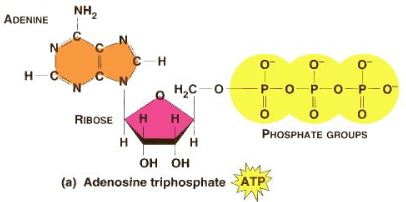
What is the structure of ATP?
It is a phosphorylated nucleotide:
Adenine (base)
Ribose (pentose sugar)
3 Phosphate groups
What is the structure of DNA?
Double helix composed of two polynucleotide strands, joined together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
Backbone is a sugar-phosphate arrangement
2nd polynucleotide chain runs in the opposite direction to this 1st (anti-parallel)
What happens during semi-conservative DNA replication?
Hydrogen bonds break (DNA helicase)
Double helix structure unwinds
Free activated DNA nucleotides join the unpaired bases (DNA polymerase)
Hydrogen bonds form
Phosphodiester bonds form between nucleotides
What are the features of the genetic code?
Triplet code
Degenerate
Non-overlapping
Widespread
What happens during transcription of DNA?
Hydrogen bonds between bases broken by DNA helicase - DNA unzips
Free activated RNA nucleotides diffuse into position with exposed bases on reference stand, using complementary base pairing
Condensation reactions catalysed by RNA polymerase creates mRNA
RNA molecule breaks free from DNA & leaves nucleus through a nuclear pore
Arrives in cytoplasm & moves to a ribosome
What happens during translation?
In the ribosome, there is complementary base pairing between codons & anti-codons
Another tRNA molecule approaches & joins
A condensation reaction forms a peptide bond between the 2 amino acids
mRNA moves, & the first tRNA leaves
Another amino acid is bought in
A chain of amino acids continues to be built up until a stop codon is reached on the mRNA
What is the role of tRNA?
tRNA is used in translation to transport specific amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome
What is the role of rRNA?
Forms part of the ribosome