233 Unit 8 Lecture Exam (Part 2) - Sensory Pathways, Autonomic, Misc. Topics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
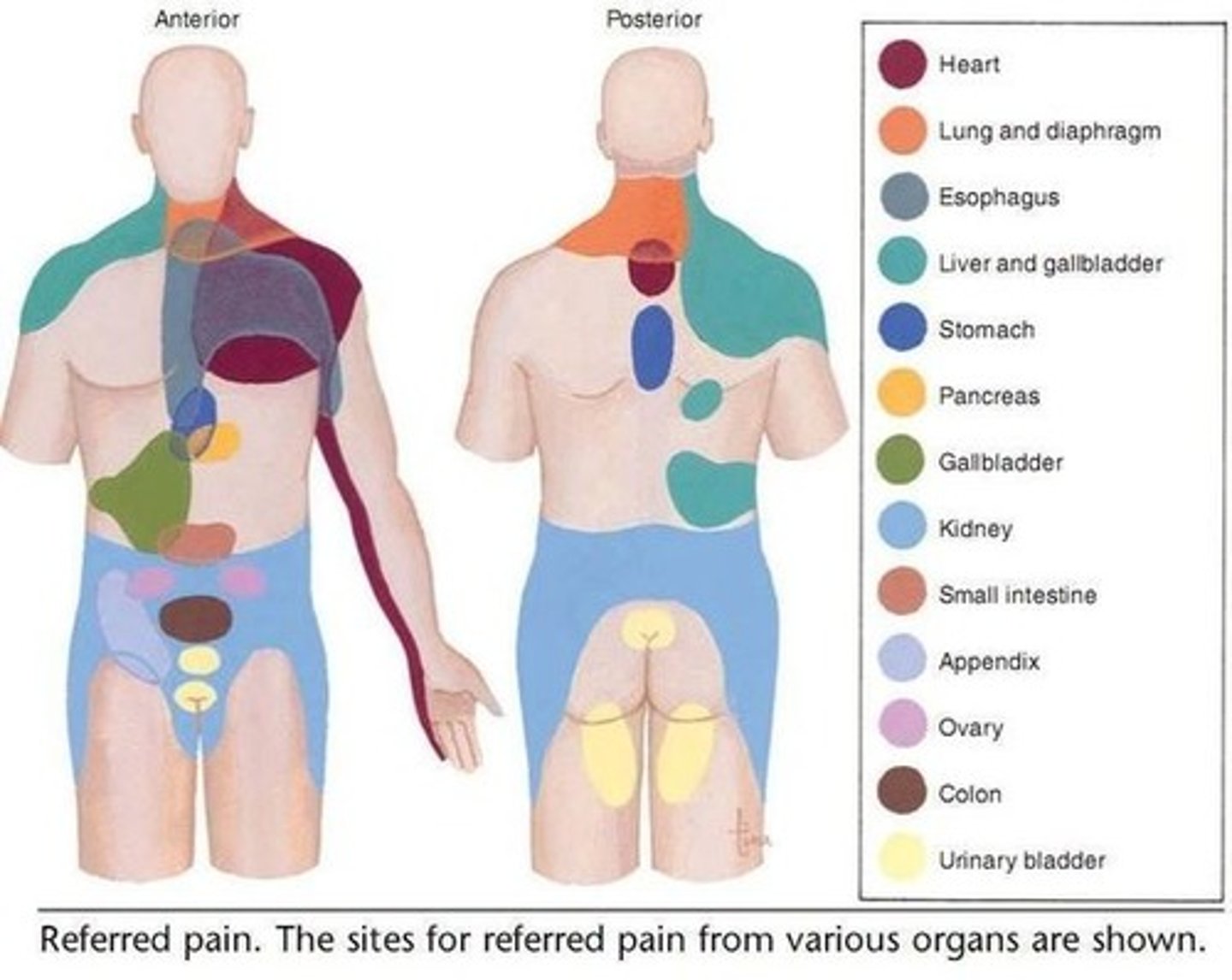
Referred pain is ________.
pain experienced in a part of the body other than the site of disease or injury
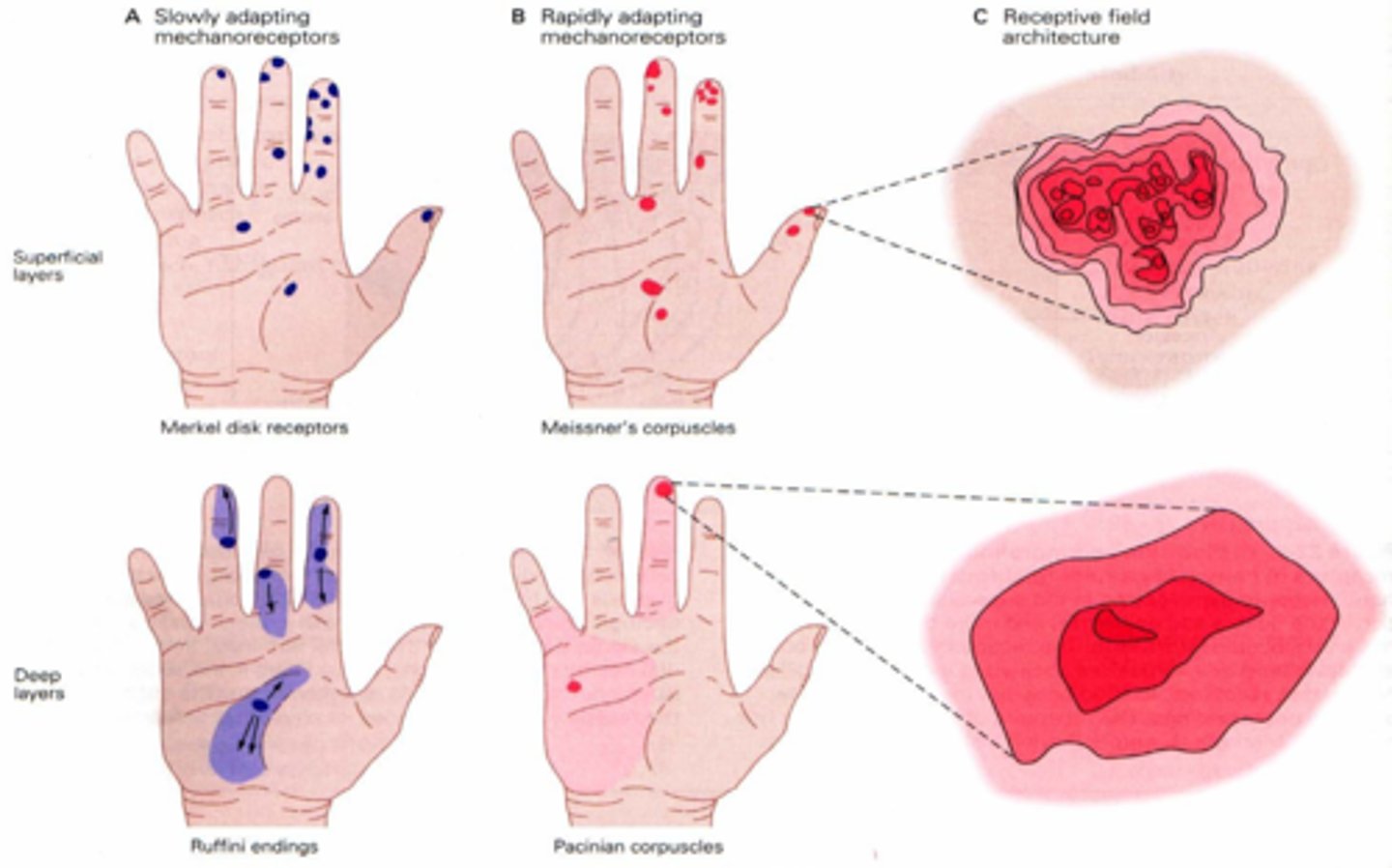
receptor fields
Using the two-point discrimination test you can fairly accurately determine whether you have been touched with one point or two because of the density of the receptor fields
Adaptation nervous system
A reduction in sensitivity in the presence of a constant stimulus

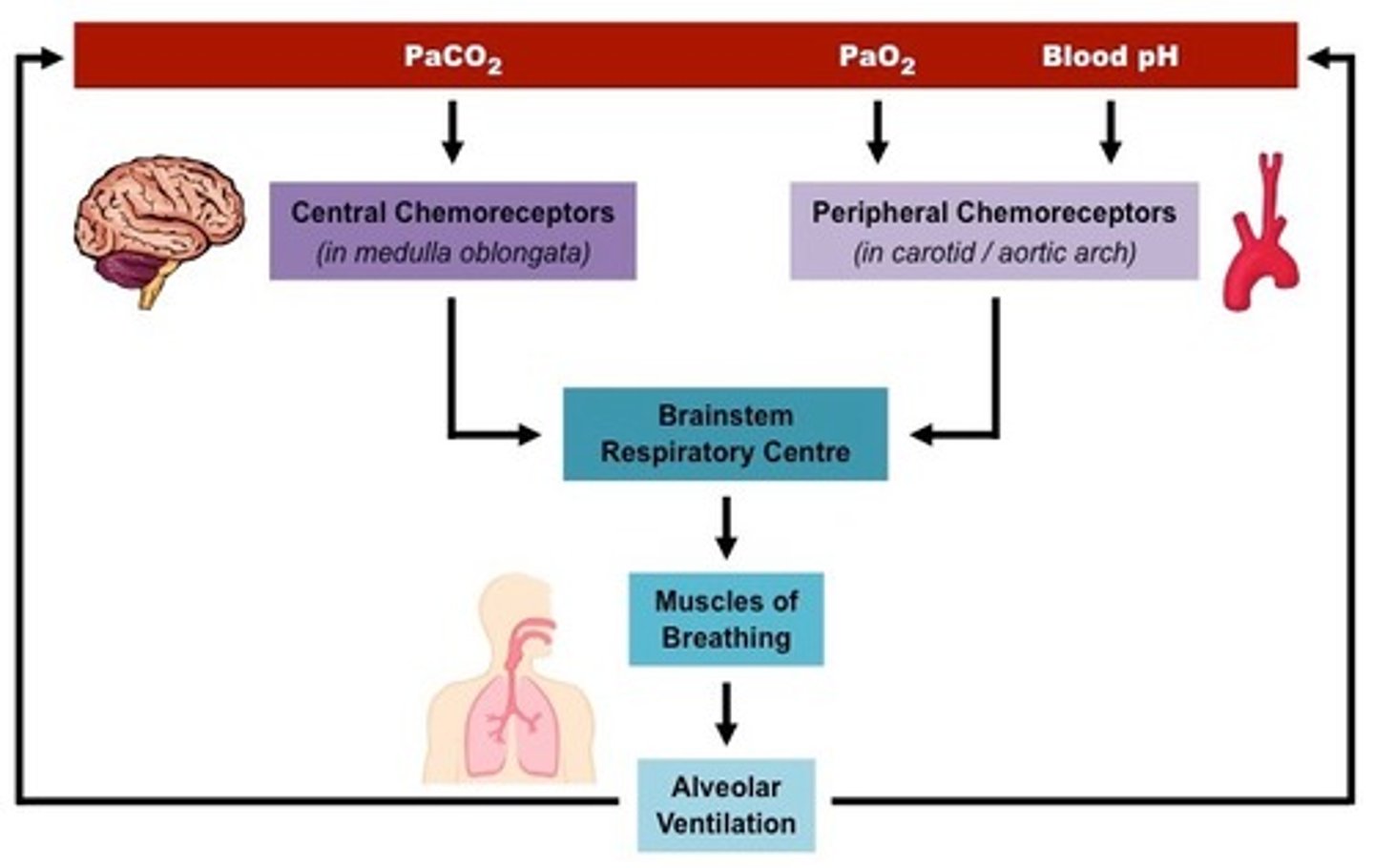
Chemoreceptors
chemical sensors in the brain and blood vessels that identify changing levels of pH, oxygen and carbon dioxide
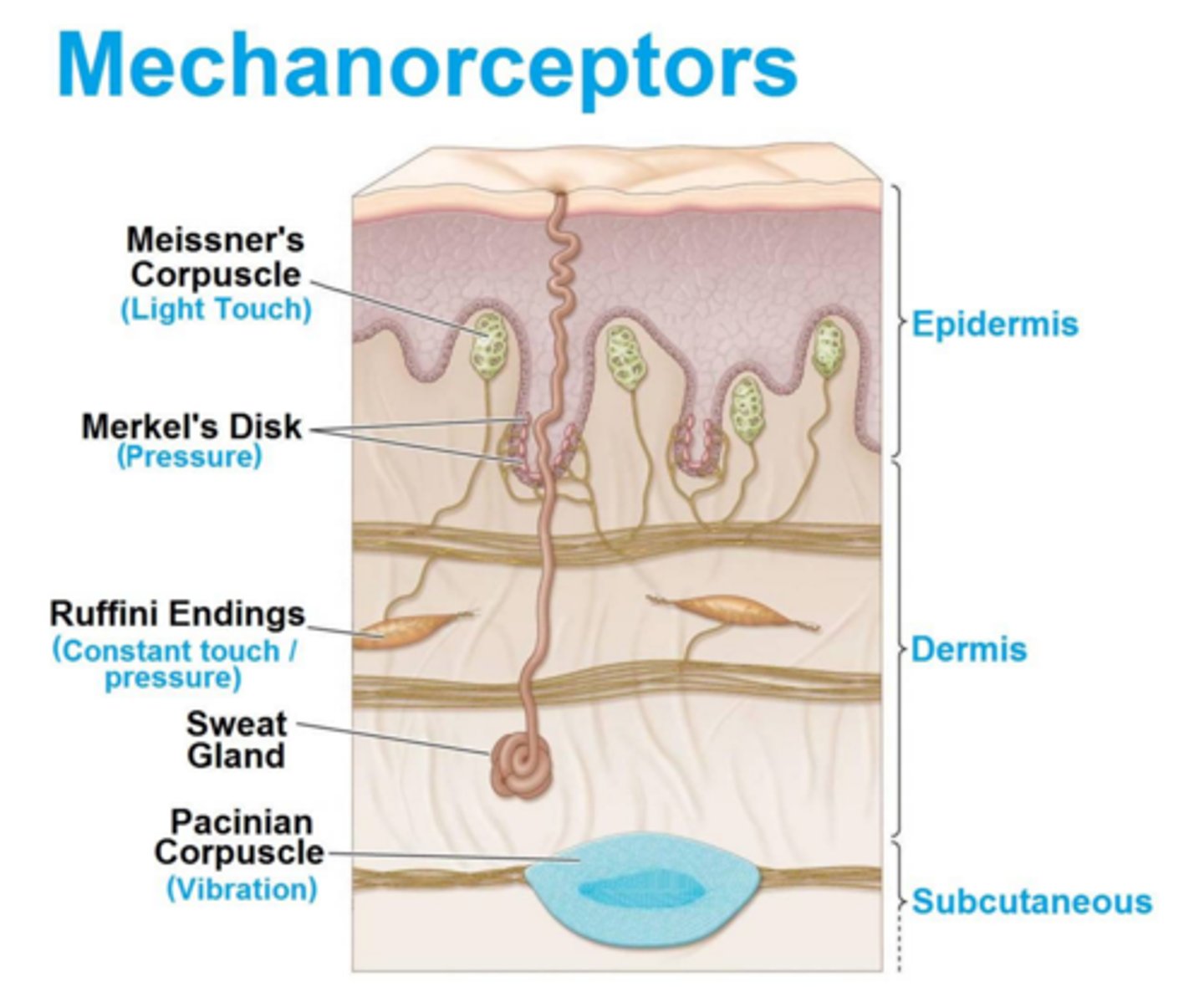
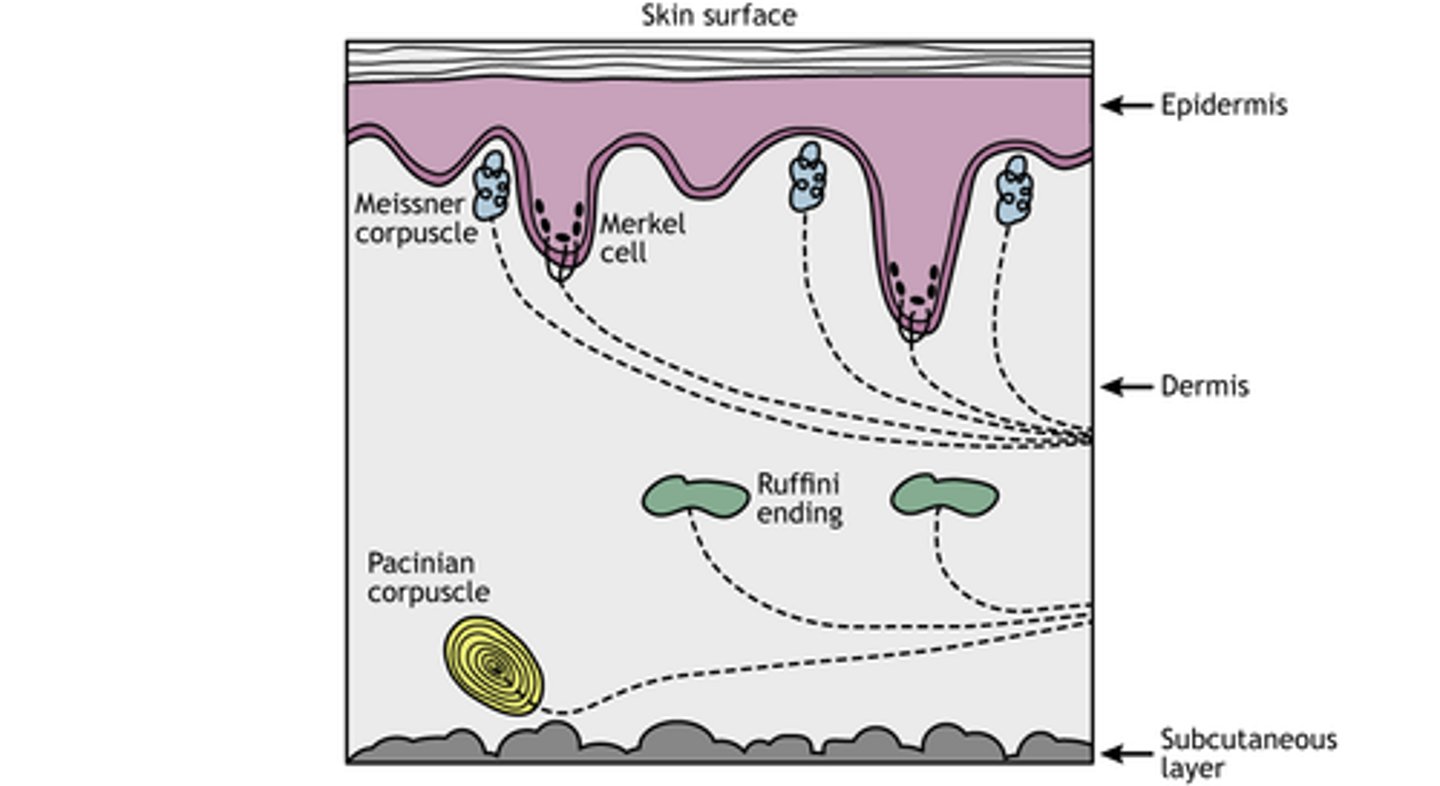
Meissner's corpuscles
sensitive touch receptors in the dermis (light touch)
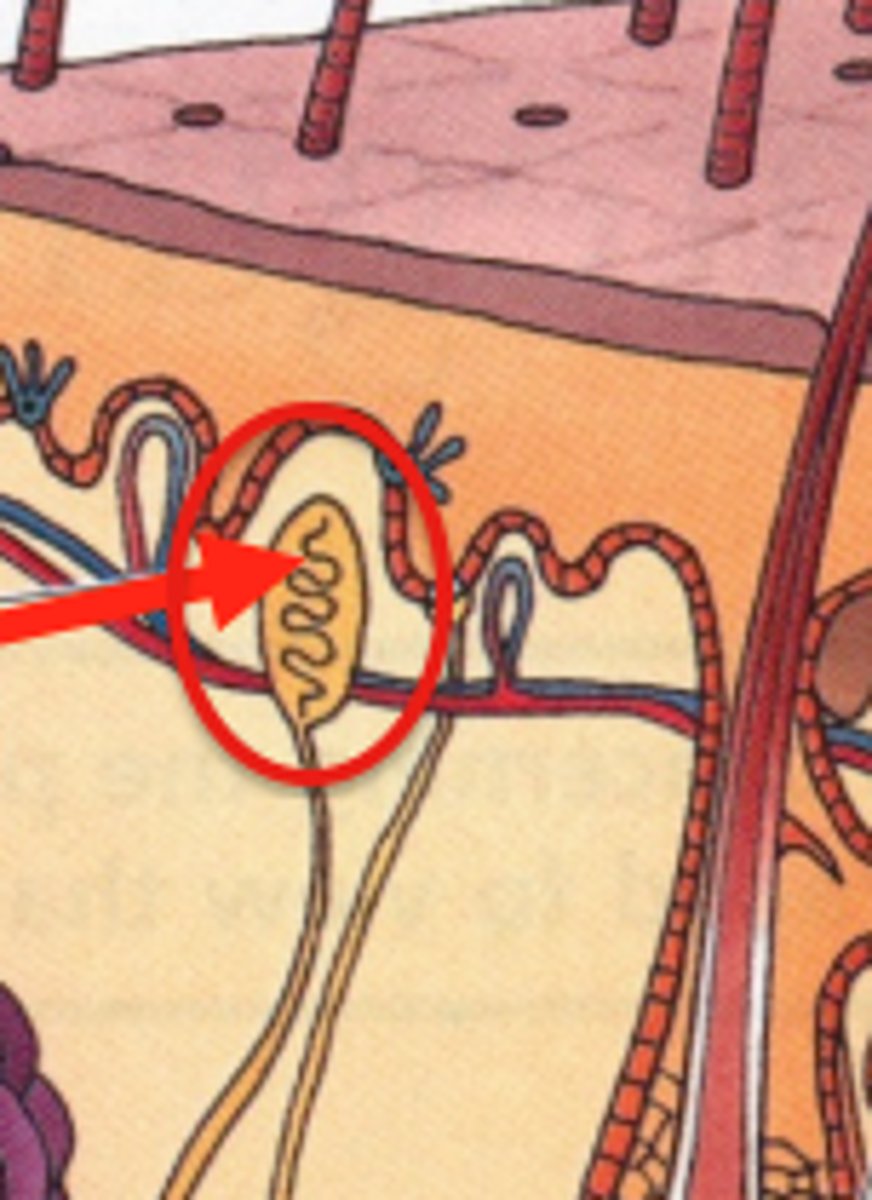
endorphines
"morphine within, runner's high"—natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters released during rigorous exercise. Reduces pain, enhances pleasure and improves mood.

Nociceptors
pain receptors--the pain can be lessened by release of endorphins
Bladder fullness is to ________ as blood pH is to ________.
baroreceptors (sensing fullness or pressure); chemoreceptors (sensing changes in pH)
Baroreceptors
monitor pressure. Baroreceptors in the aorta monitor blood pressure.
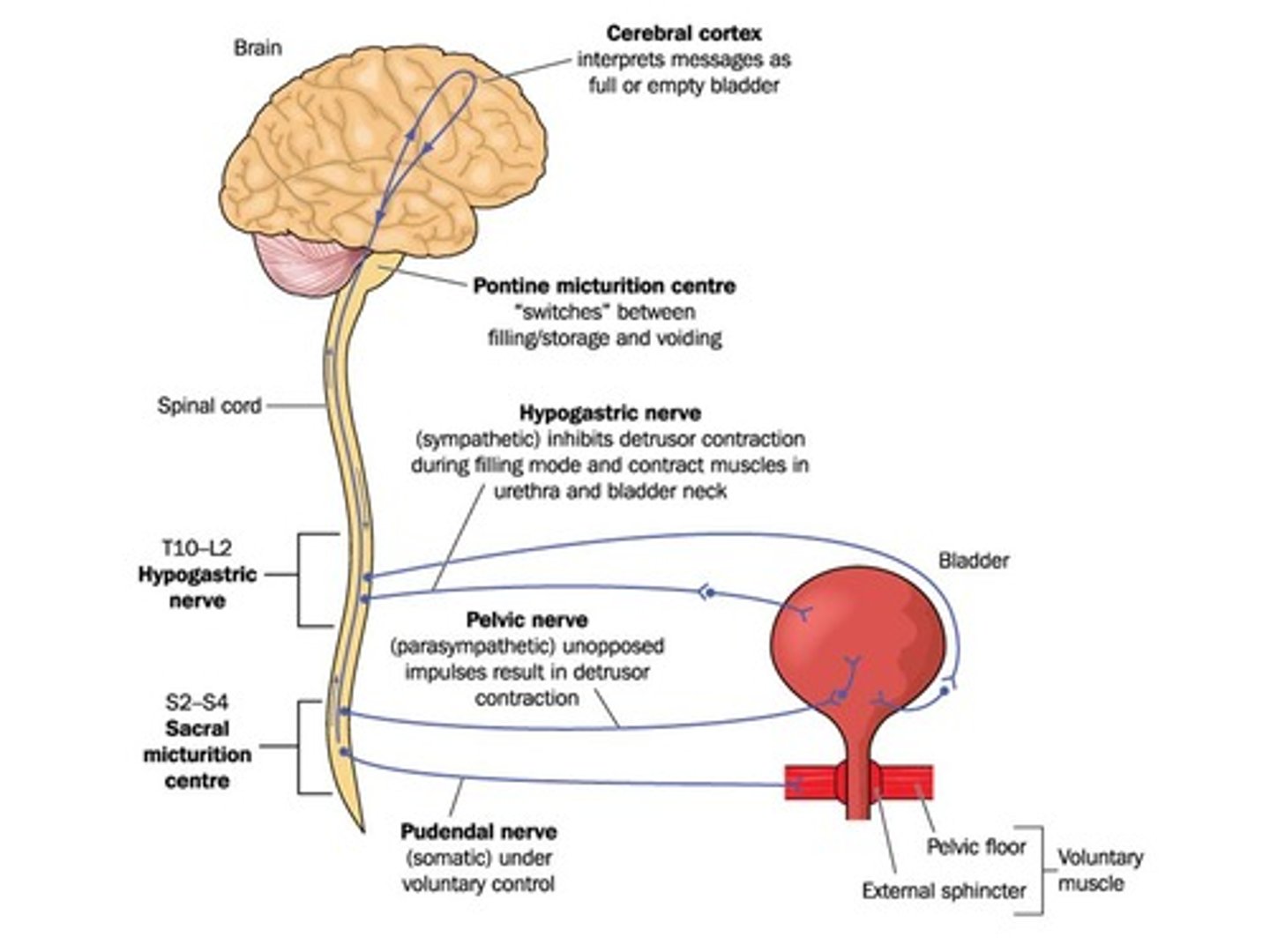
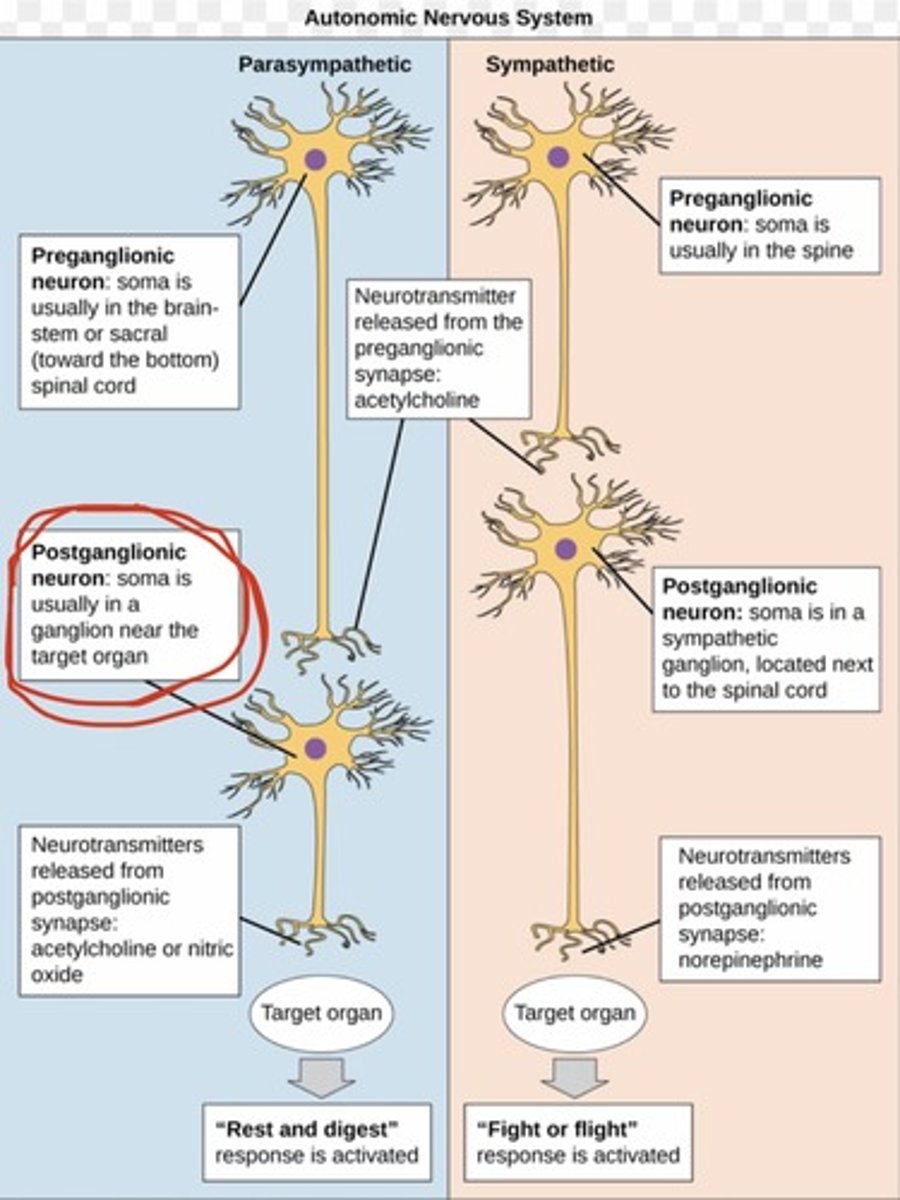
In which system are the ganglia in or near the target organ?
parasympathetic division of the ANS
A large dog jumps out and scares you. The dog is actually friendly, but you notice that it takes a little while for your heart rate and respiratory rate to return to normal. This is likely because ____.
sympathetic activation of the adrenal medulla has released epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream; the effects take a while to wear off
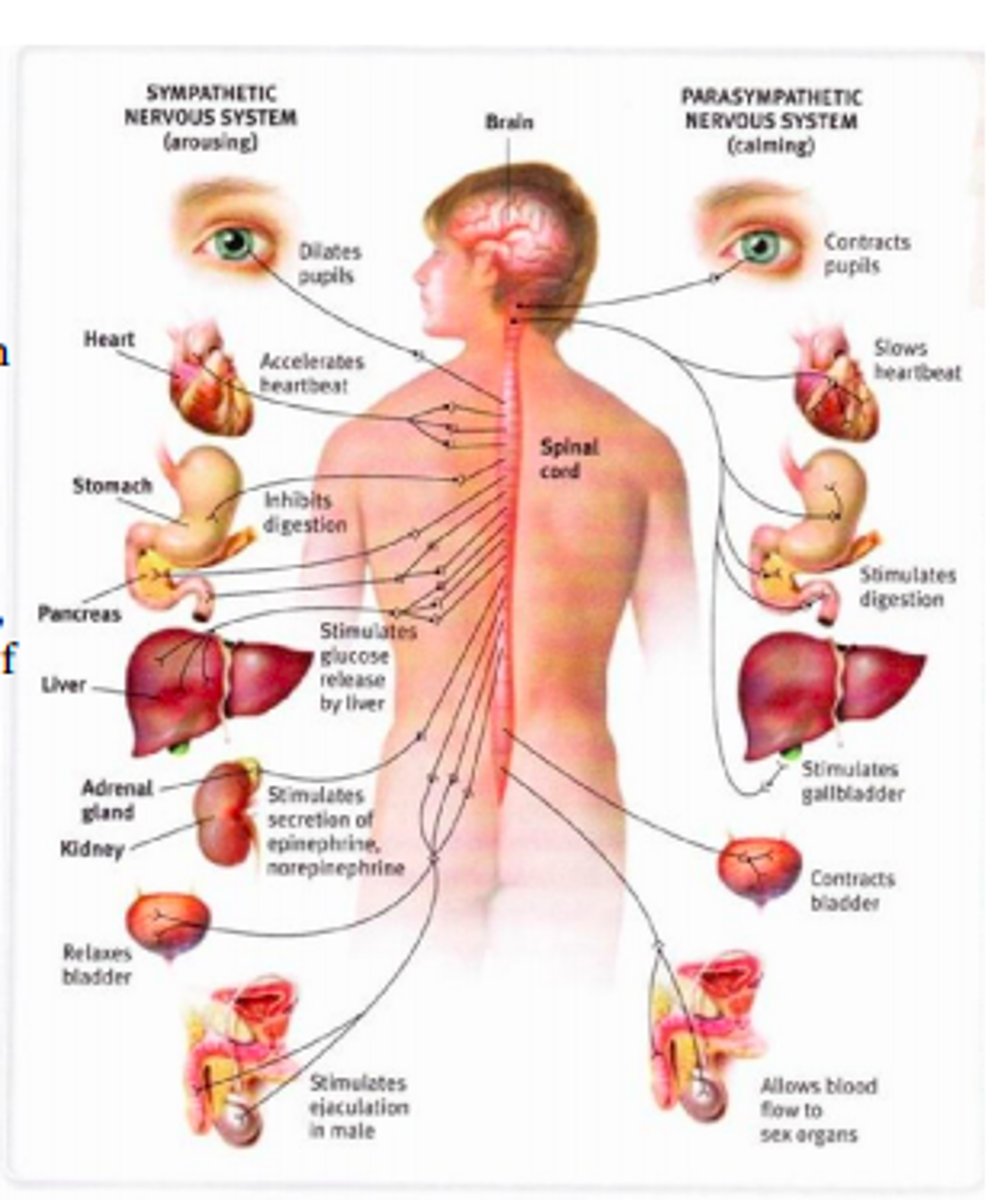
sympathetic chain ganglia
Clusters of ganglionic sympathetic neurons lying along either side of the spinal cord
sympathetic nerves
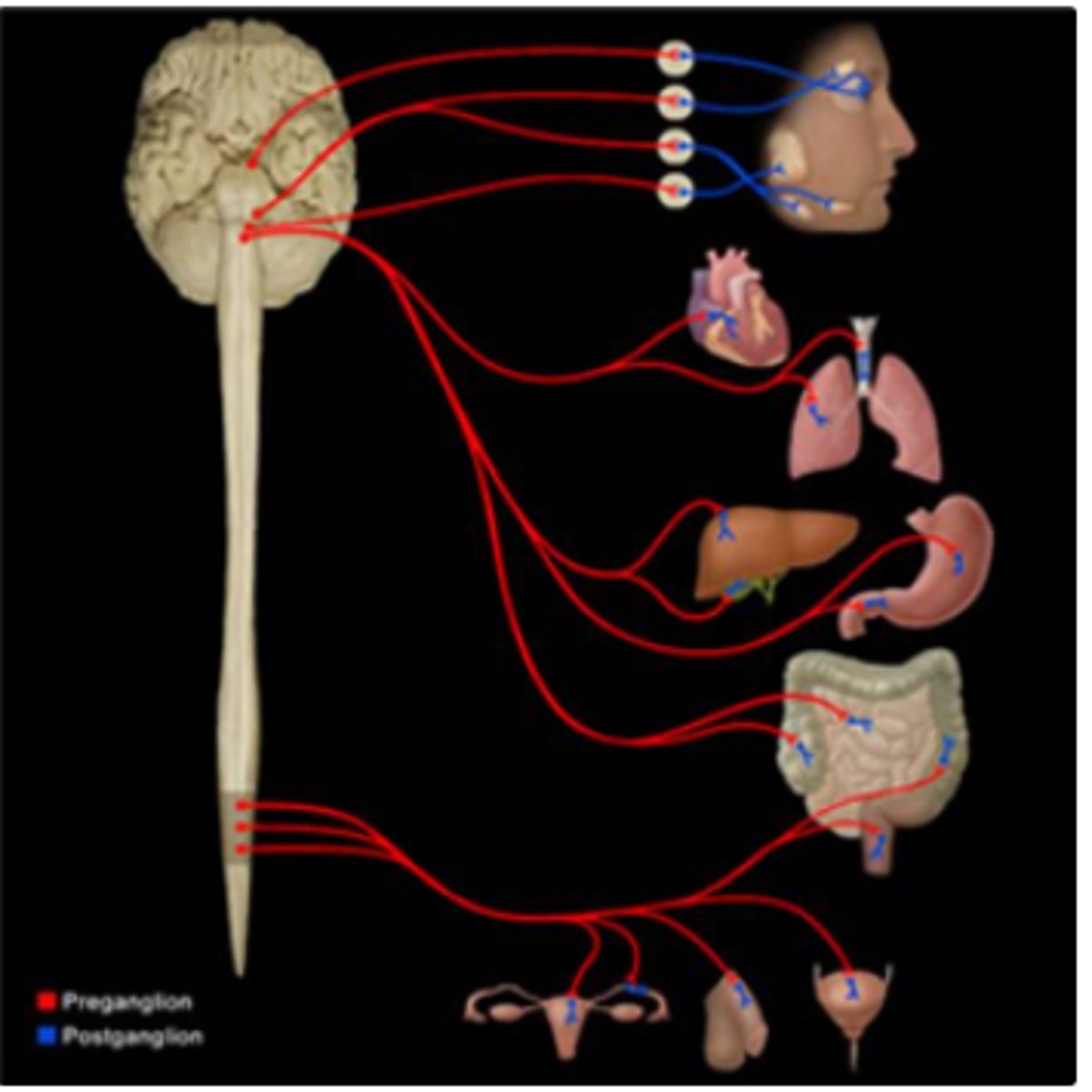
contains short preganglionic fibers and longer postganglionic fibers
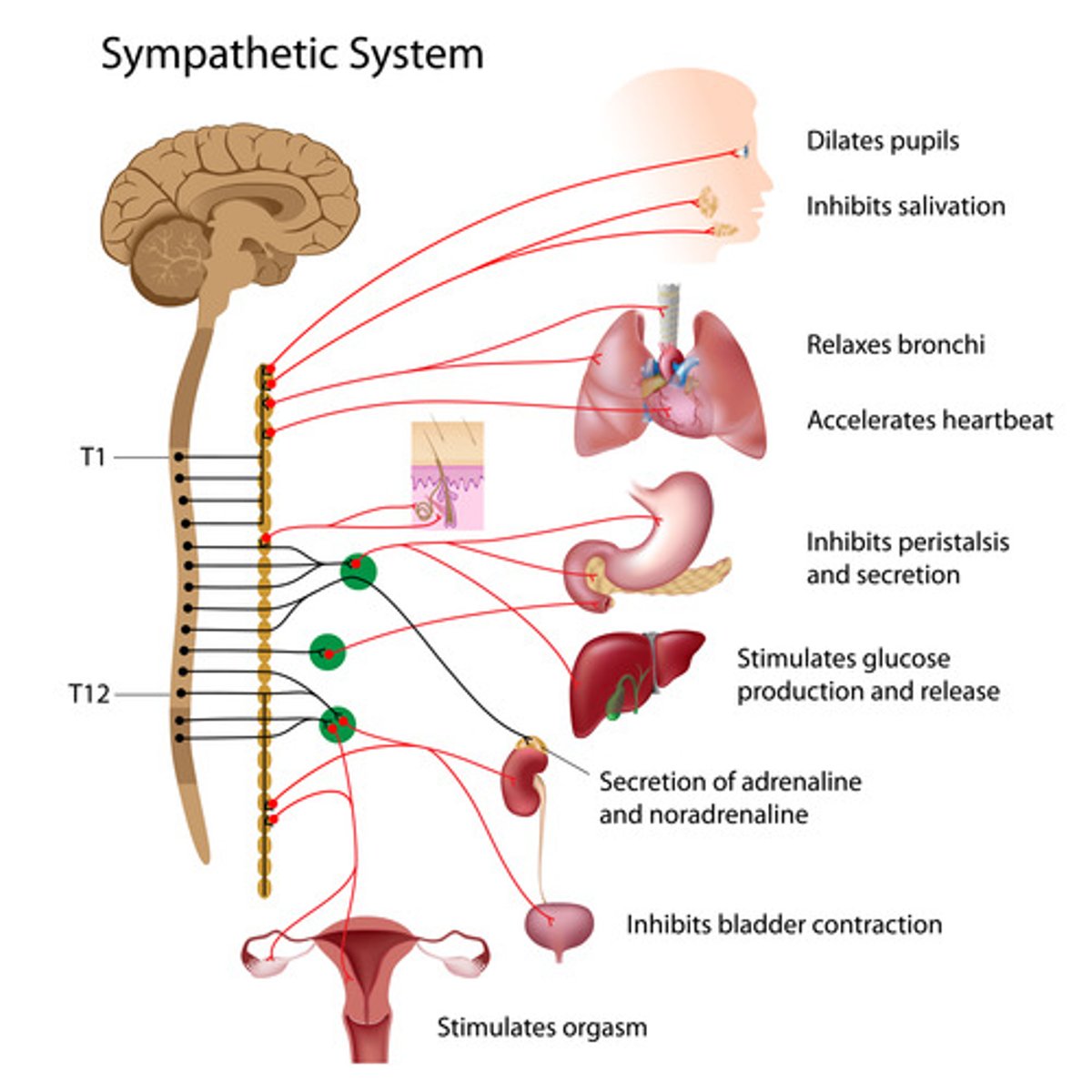
Effects associated with post-ganglionic sympathetic fibers include:
increased heart rate, reduced circulation to the skin, increased sweat secretion, dilation of the pupils
Drugs that have effects similar to those of sympathetic activation are called sympathomimetic drugs. Which of the following would you NOT expect to observe in a person who has taken a sympathomimetic drug?
any parasympathetic response--see diagram
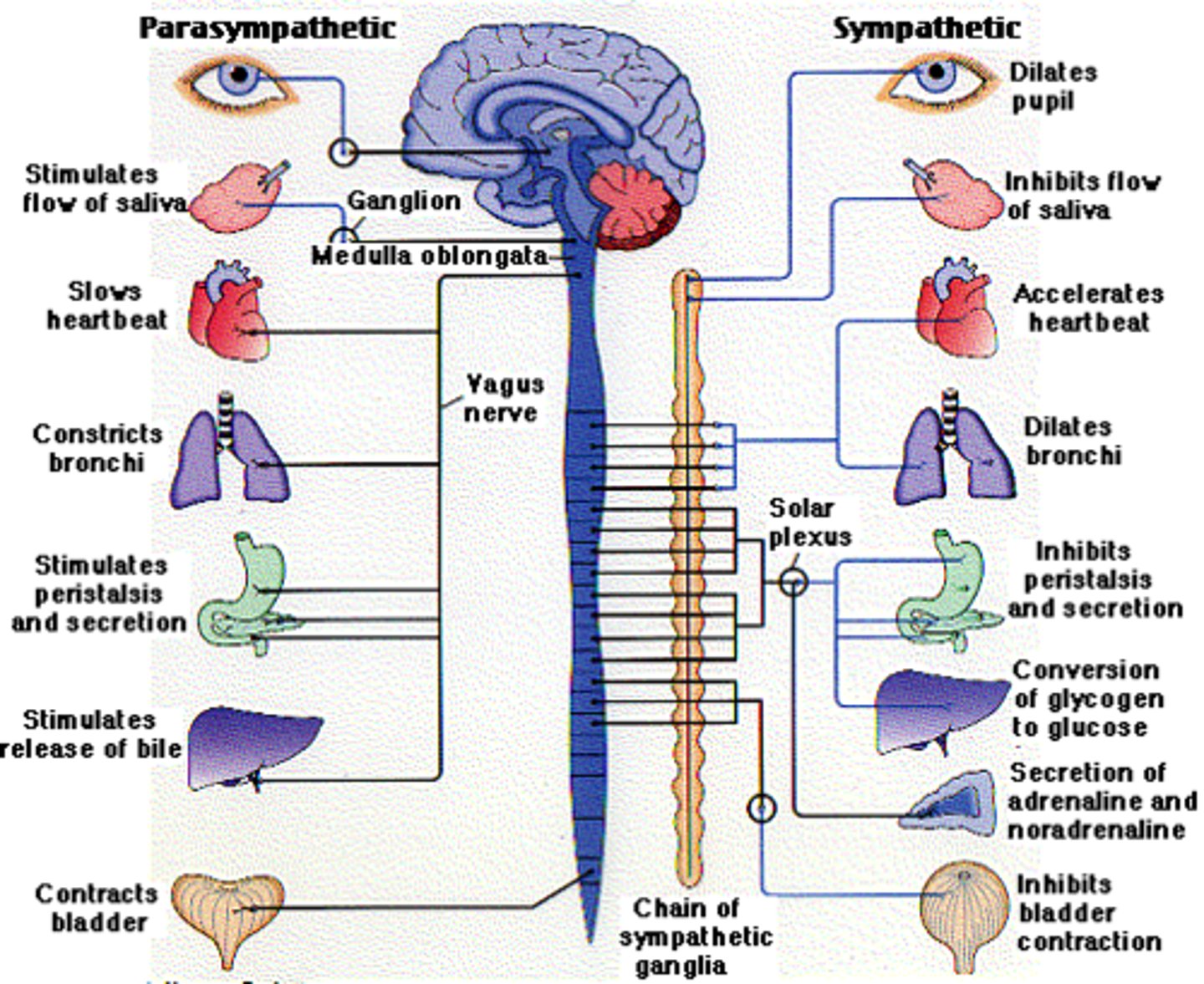
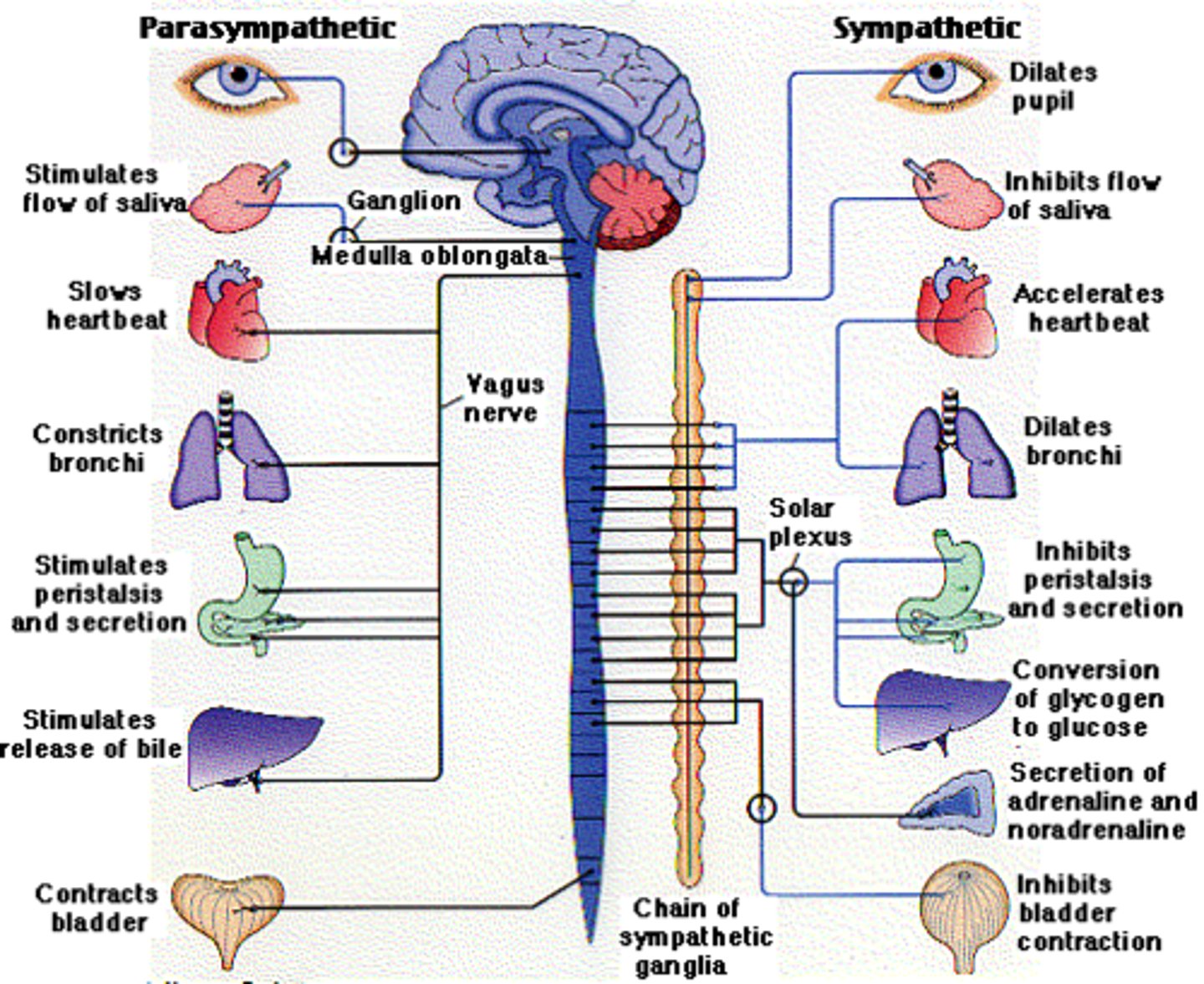
Almost 75 % of all parasympathetic outflow (effects of efferent signals) travels along the ________ nerve(s).
Vagus (CN 10)
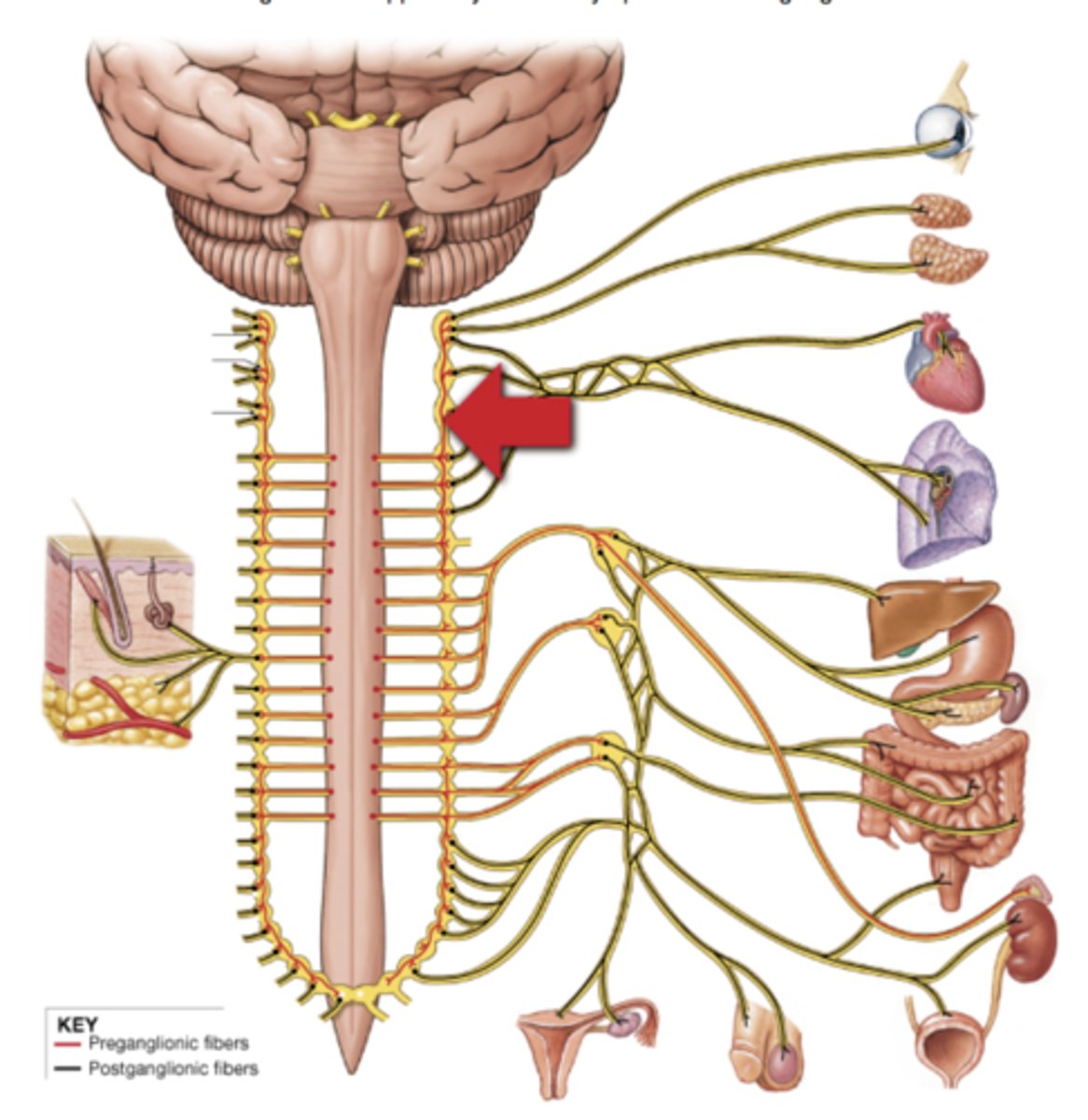
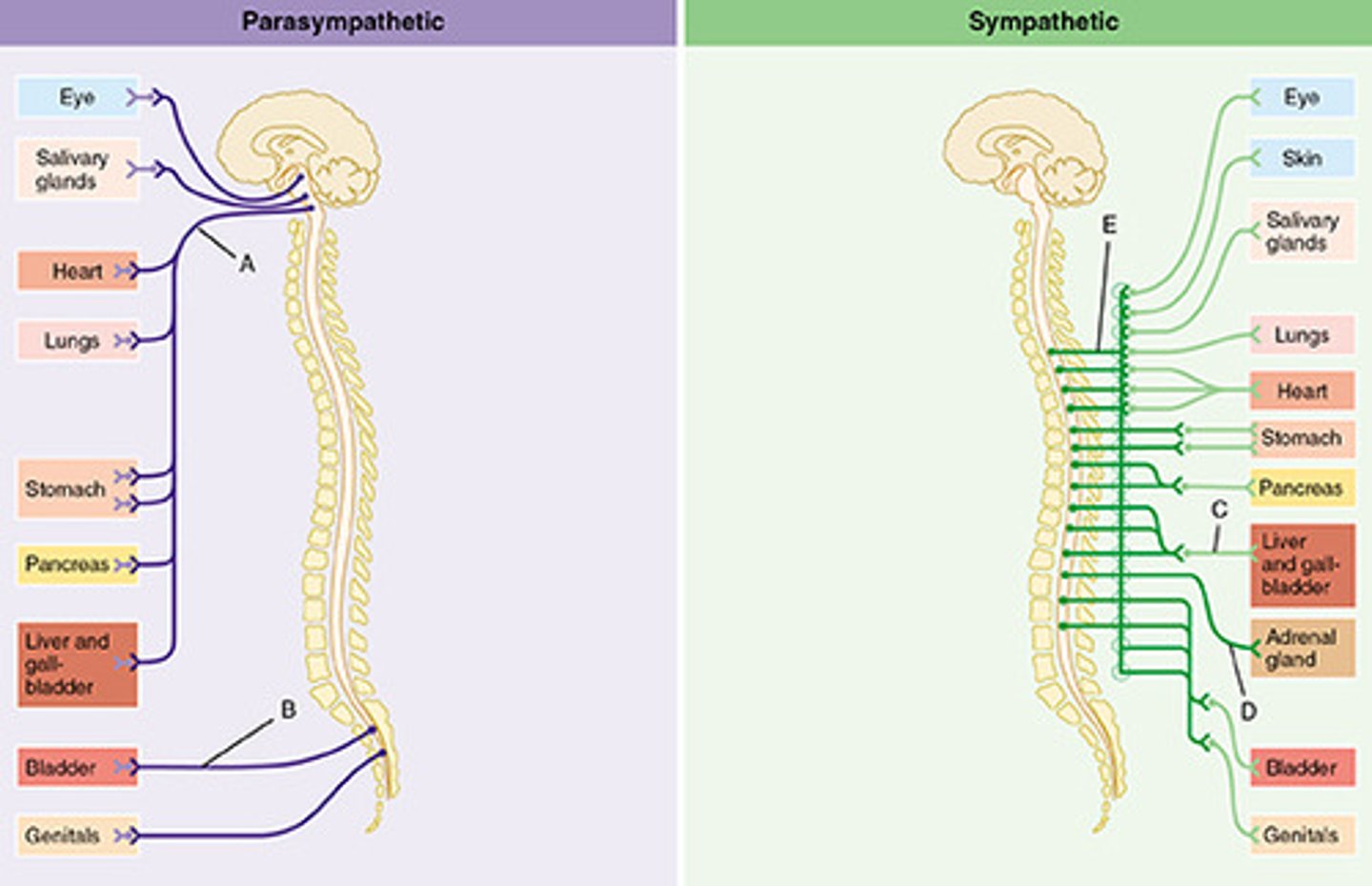
Sympathetic outflow from CNS
thoracic and lumbar - "thoracolumbar" outflow
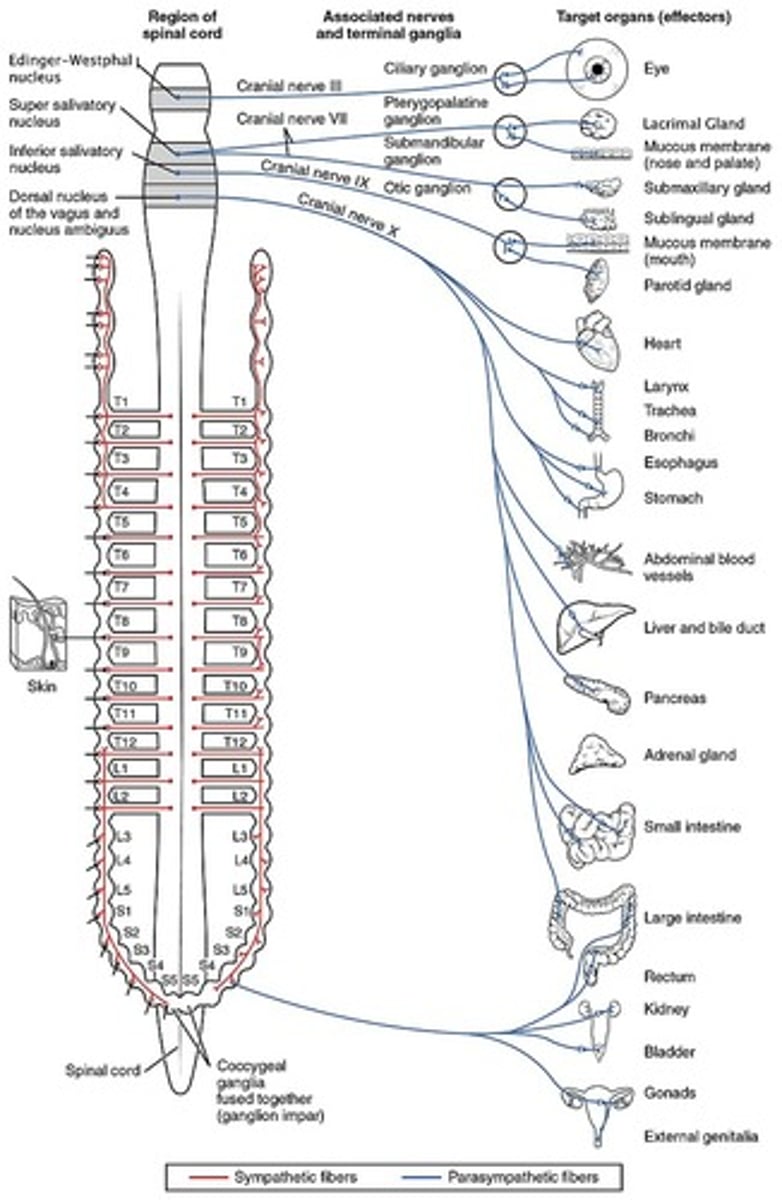
parasympathetic outflow
cranio-sacral outflow
Pre-ganglionic AND post-ganglionic axons in the ____________ division of the autonomic nervous system always use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter.
parasympathetic
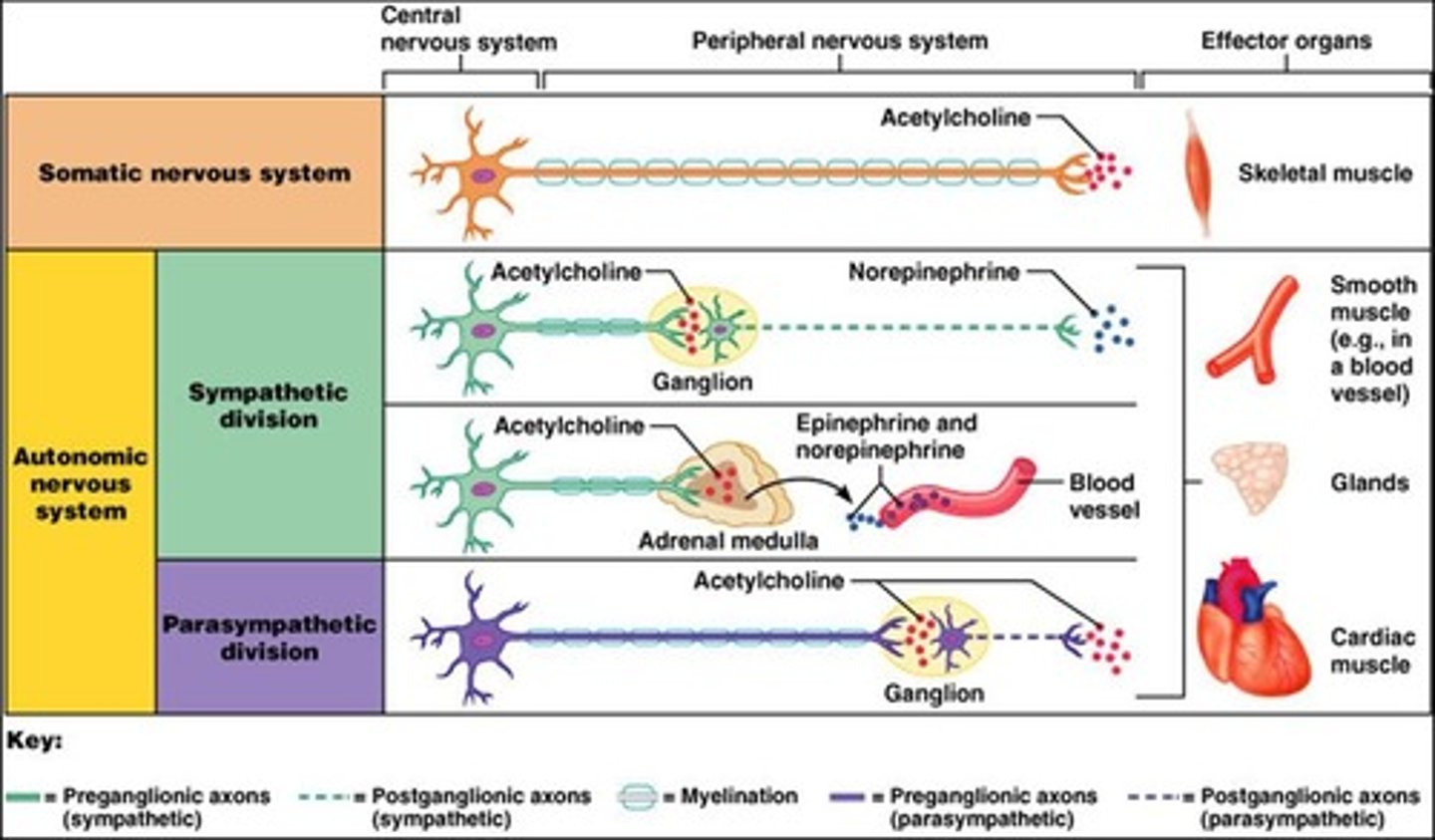
Compare preganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems
sympathetic has SHORT preganglionic fibers (they only go from spinal cord to Sympathetic chain ganglia) --parasympathetic has LONG preganglionic fibers (they extend to an area close to the target organ)
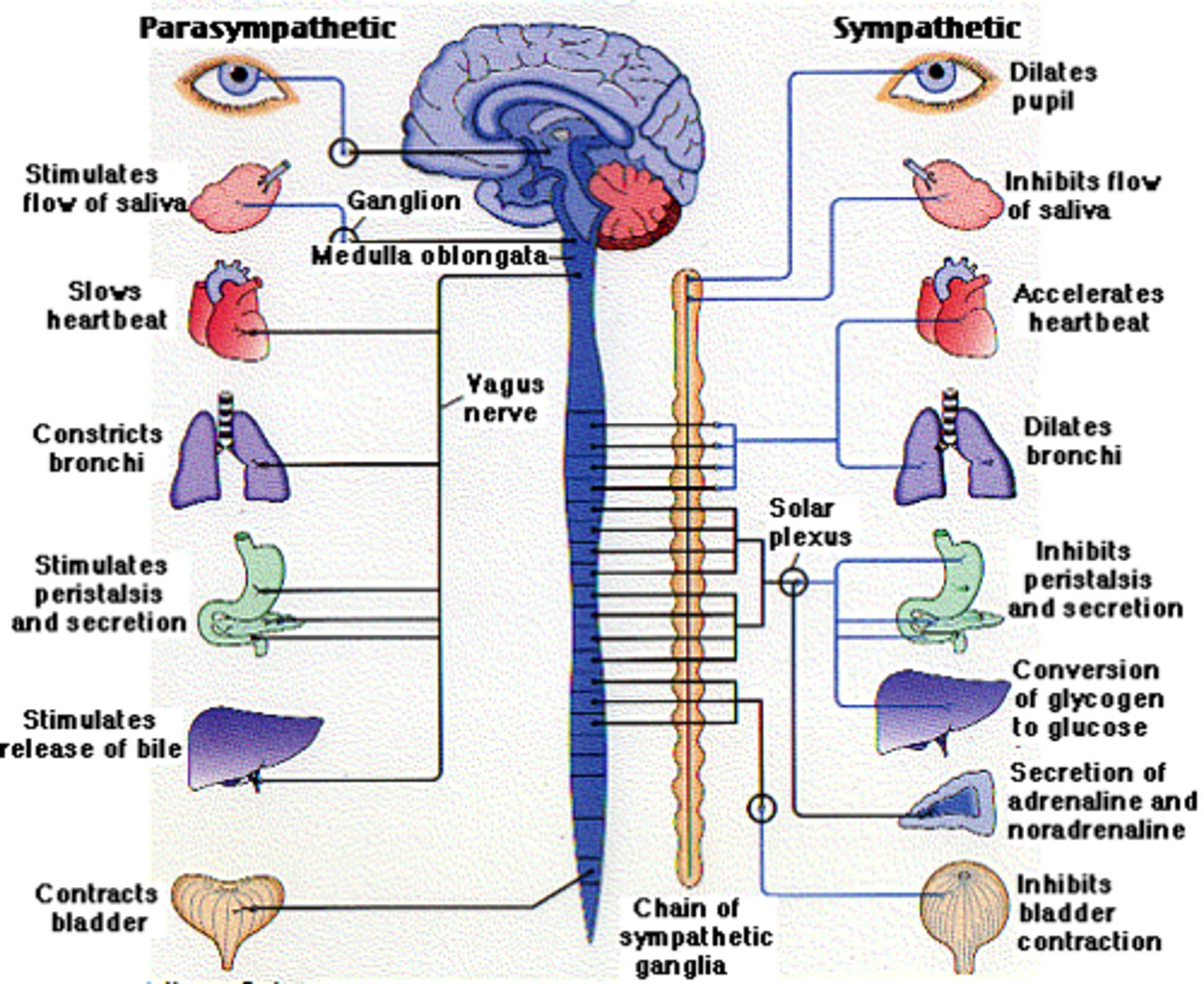
Which systems are controlled by the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
cardiovascular system, digestive system, urinary system, respiratory system, reproductive system
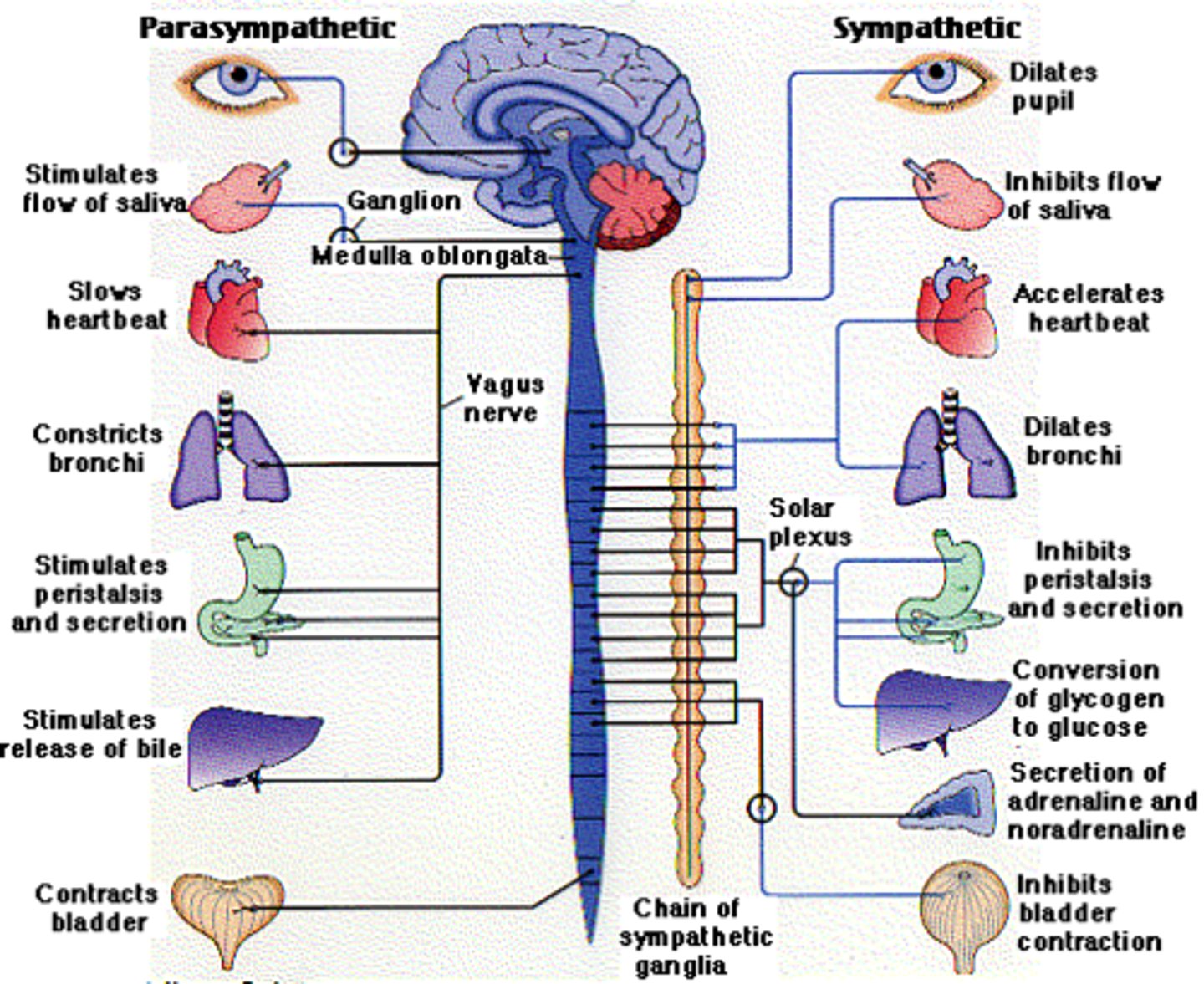
Parasympathetic effects are localized and short-lived because __________.
acetylcholine is inactivated at the synapse by acetylcholinesterase
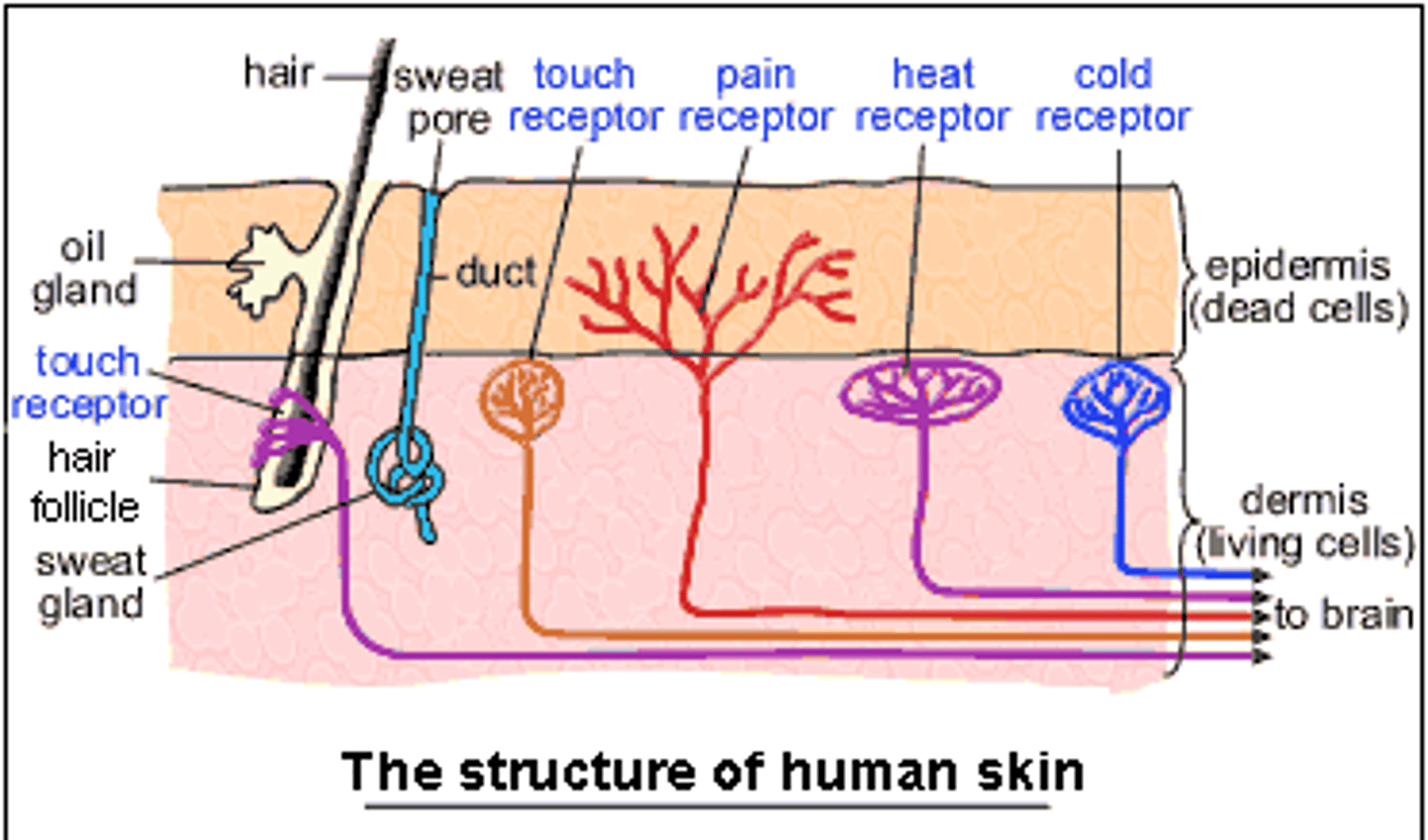
Mechanoreceptors
respond to touch, pressure, vibration, stretch, and itch (can be in ear or skin)
Photoreceptors
rods and cones, respond to visible light spectrum
Thermoreceptors
respond to changes in temperature
Proprioceptors
monitor posture and position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints

tactile receptors
provide sensations of touch, pressure, and vibration
Endorphins can reduce perception of pain sensations initiated by _____.
nociceptors
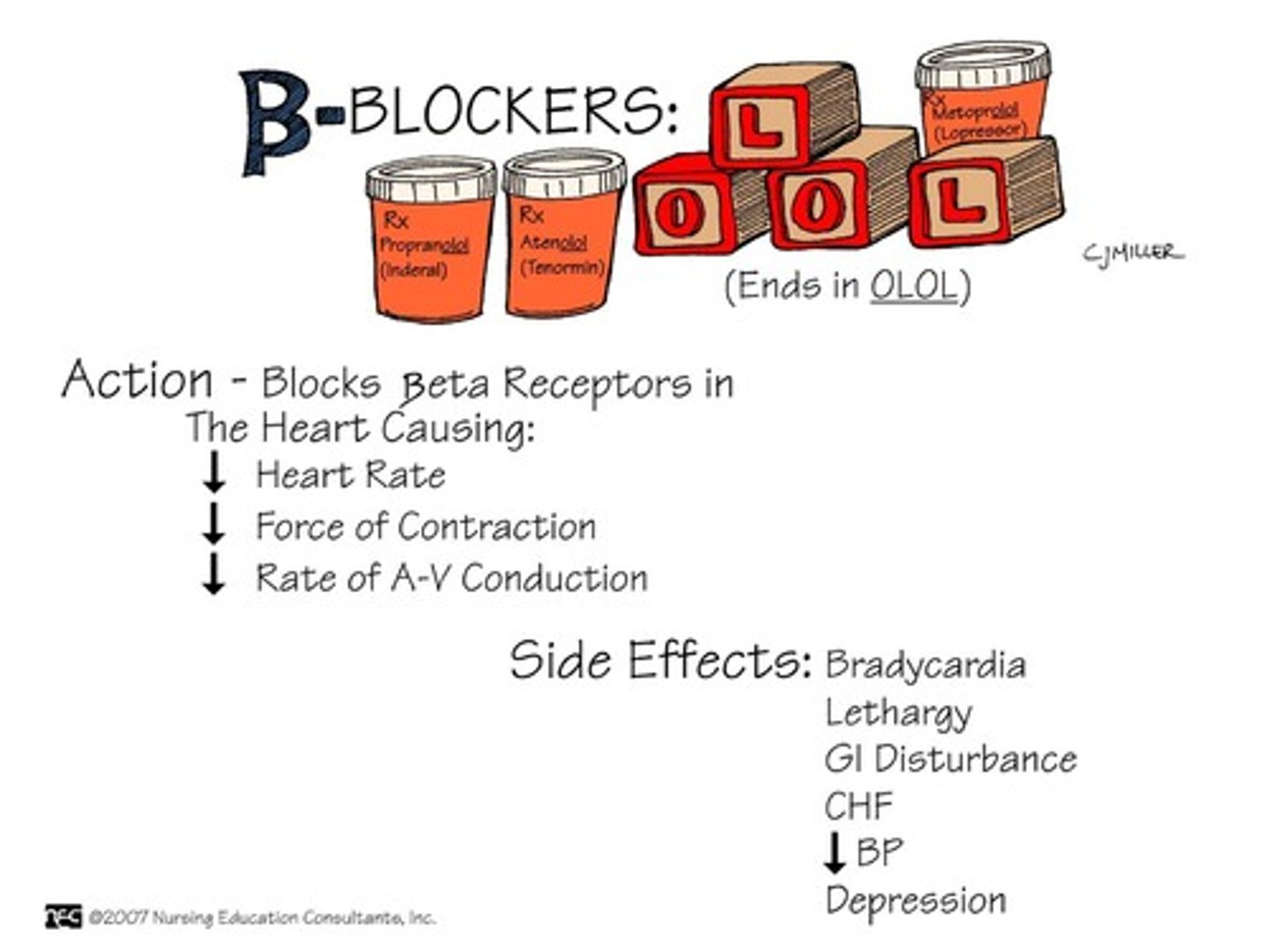
How do beta blockers affect the heart?
1) cause the heart to beat more slowly 2) decrease blood pressure 3) They help widen (vasodilate) blood vessels
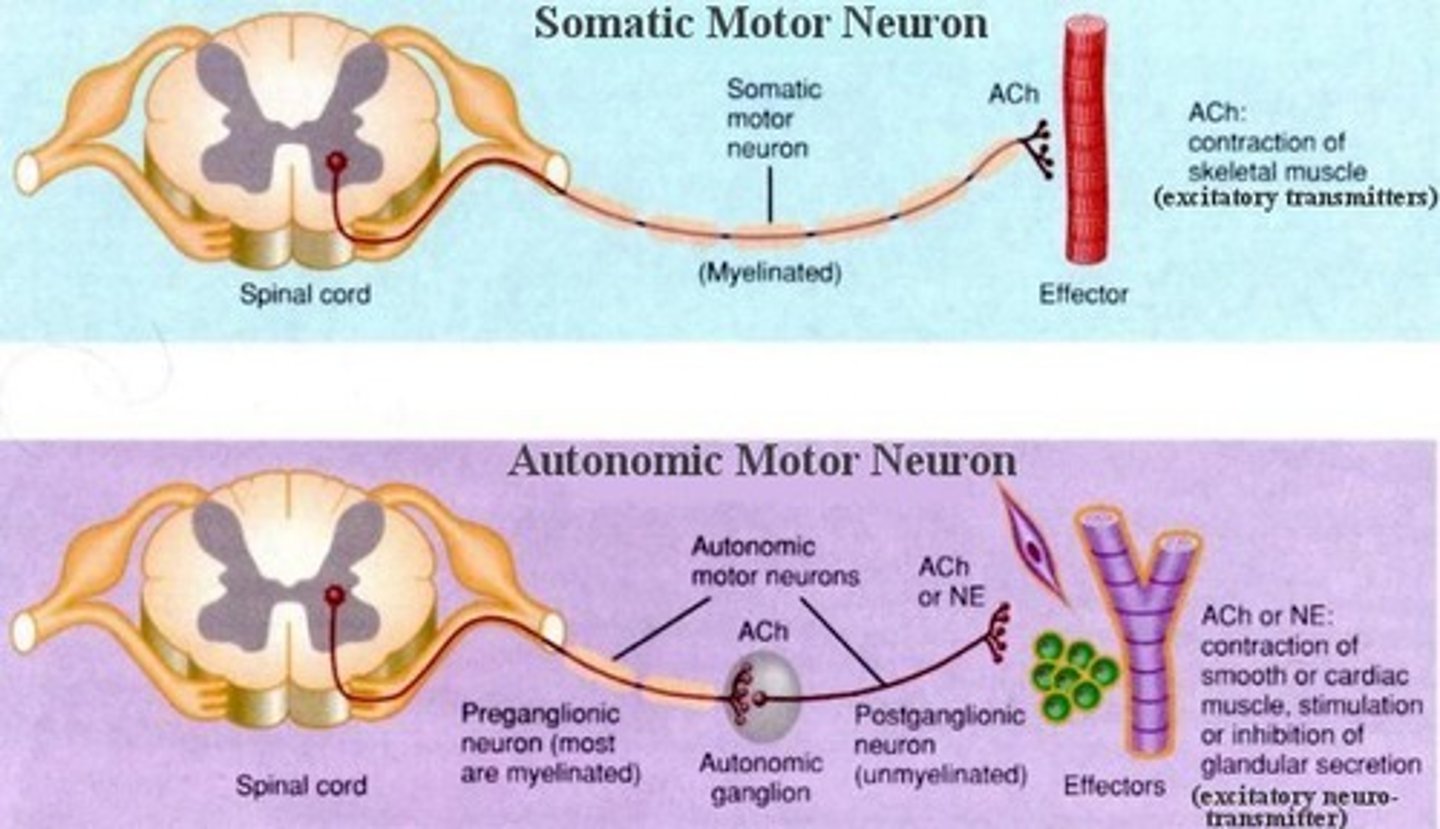
What type of effector is activated in a somatic reflex
skeletal muscle
Babinski reflex
Reflex in which a newborn fans out the toes when the sole of the foot is touched; adults will plantarflex
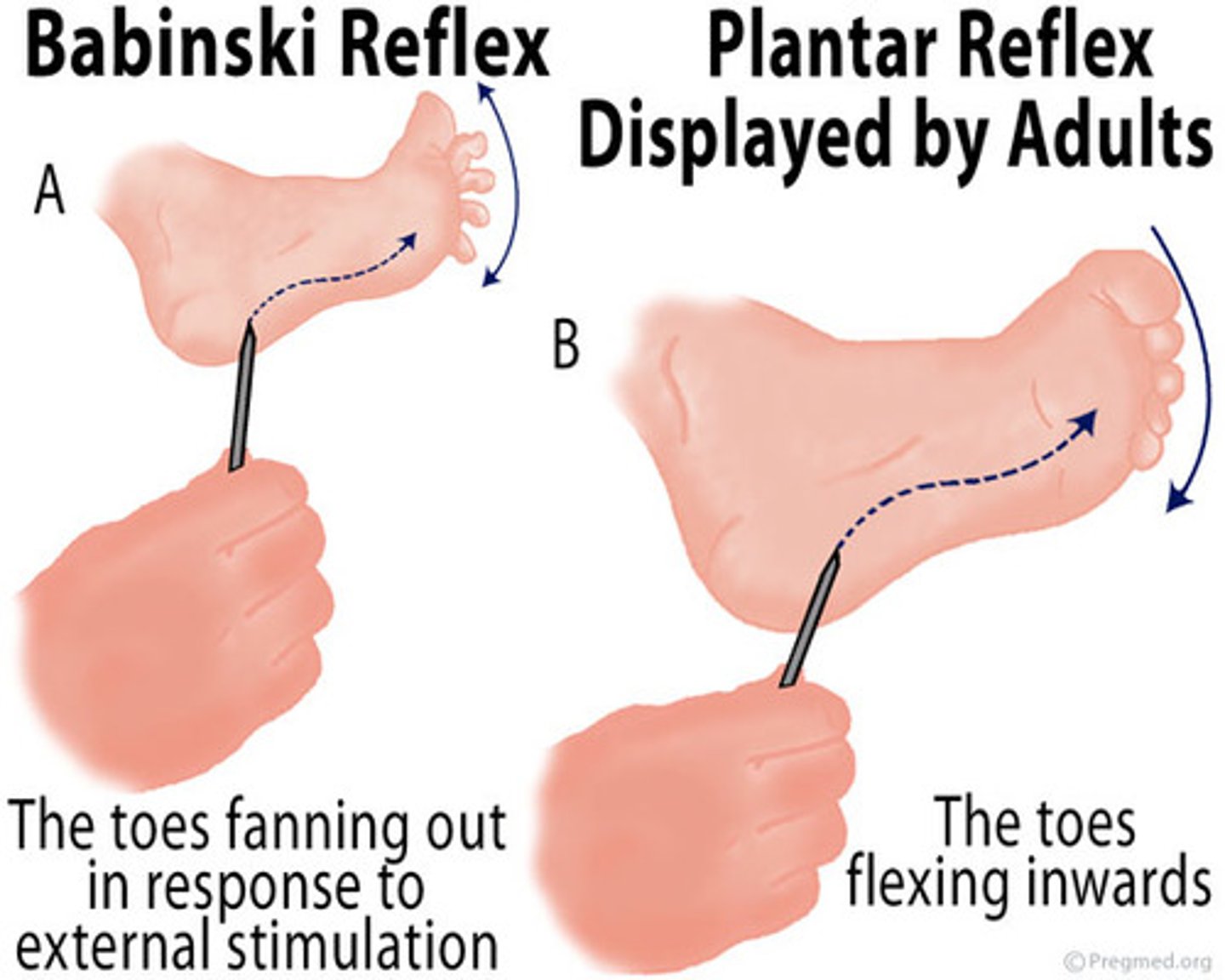
What is a normal response for an infant for Babinski reflex?
Newborns dorsiflex and fan out toes

polysynaptic reflex
involves multiple synapses and at least one interneuron
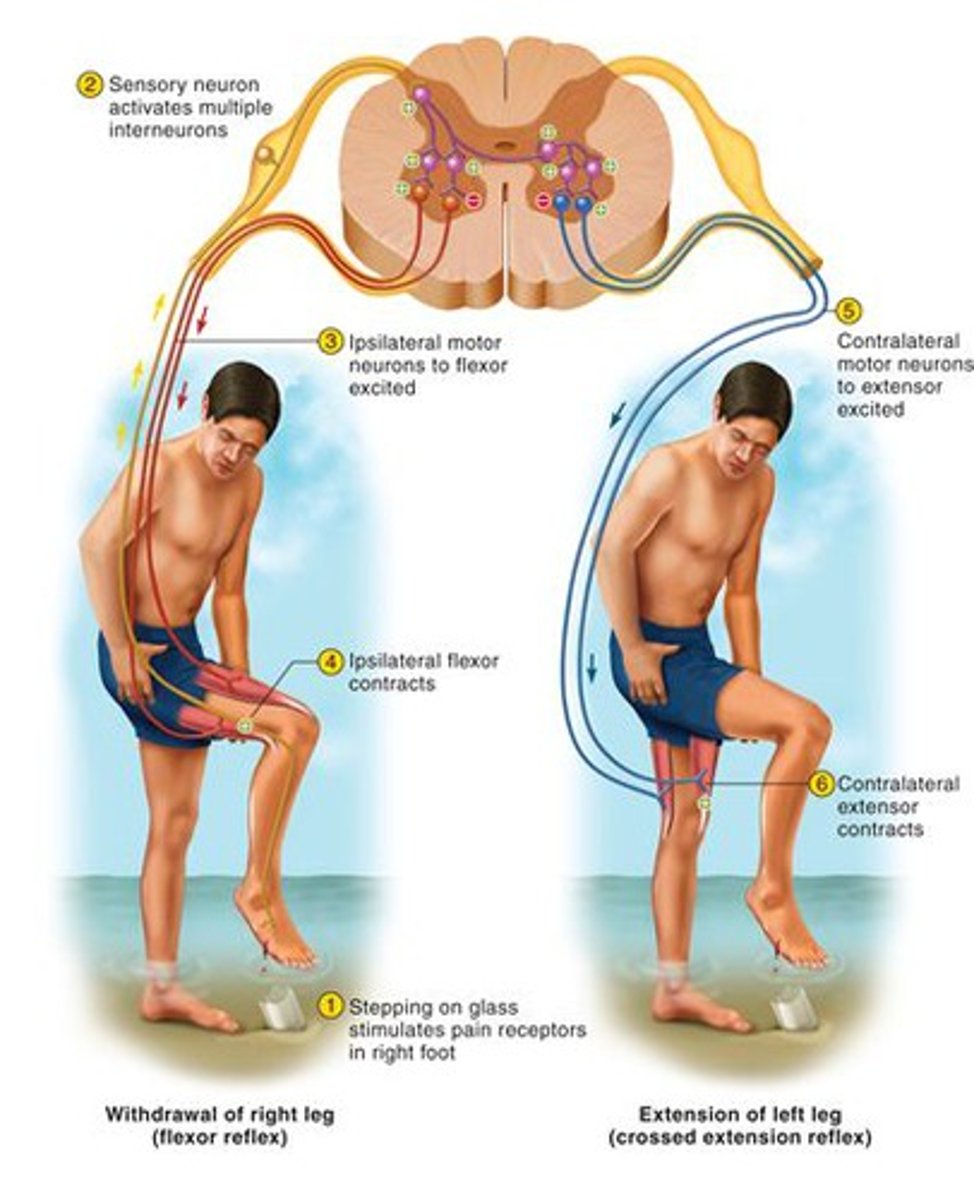
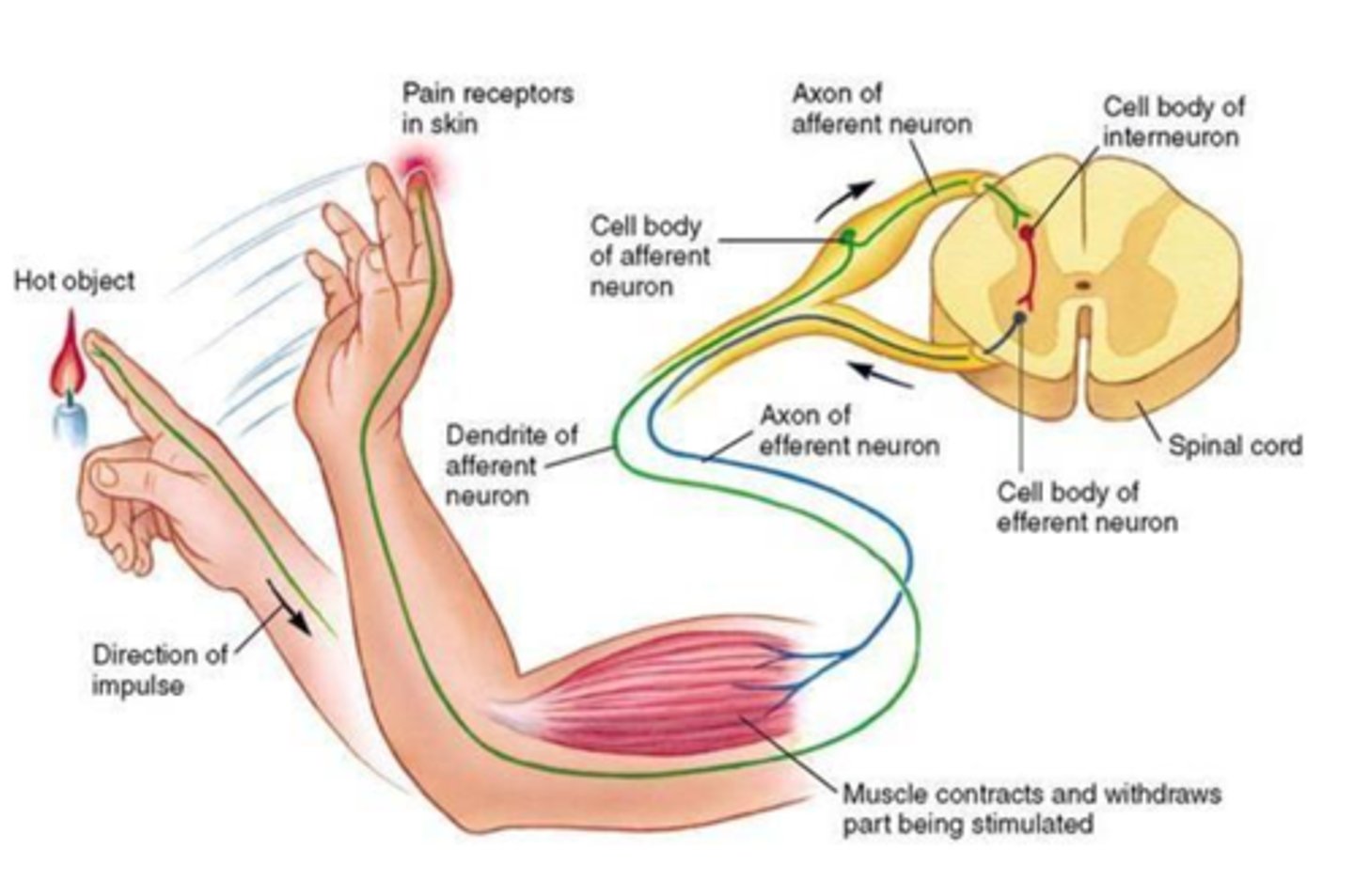
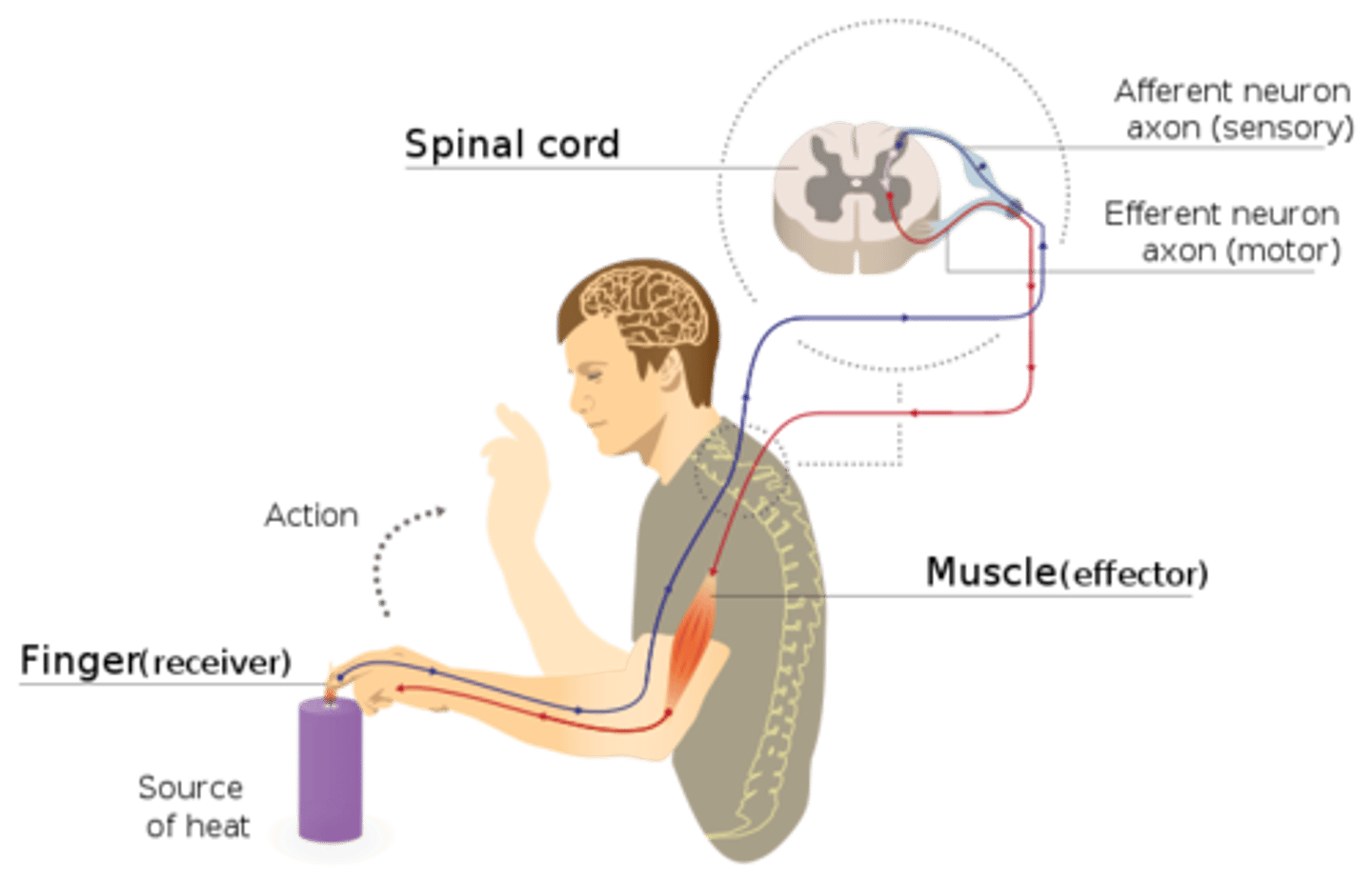
withdrawal reflex
a spinal reflex that pulls a body part away from a source of pain
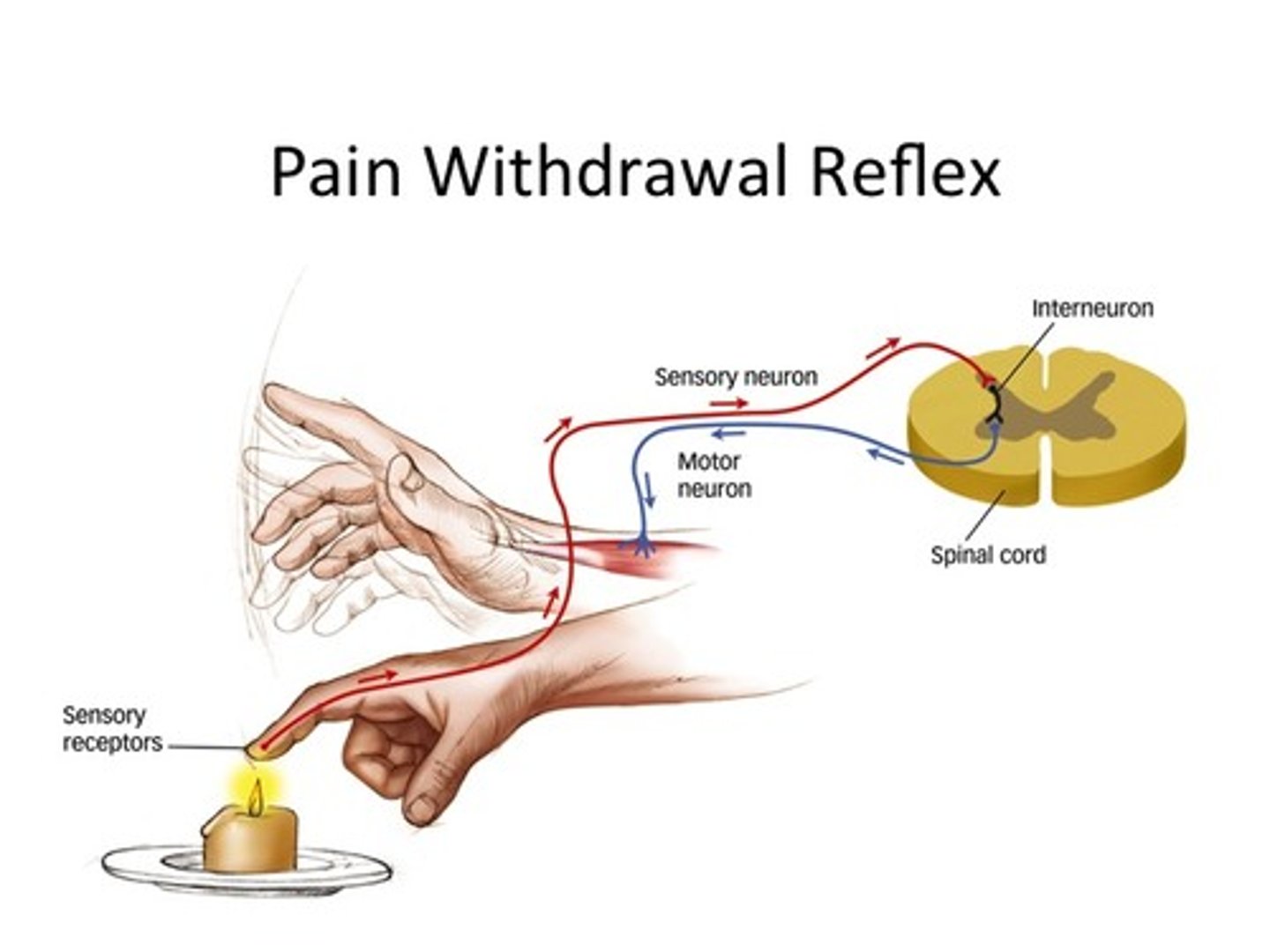
What triggers the withdrawal reflex?
painful stimuli
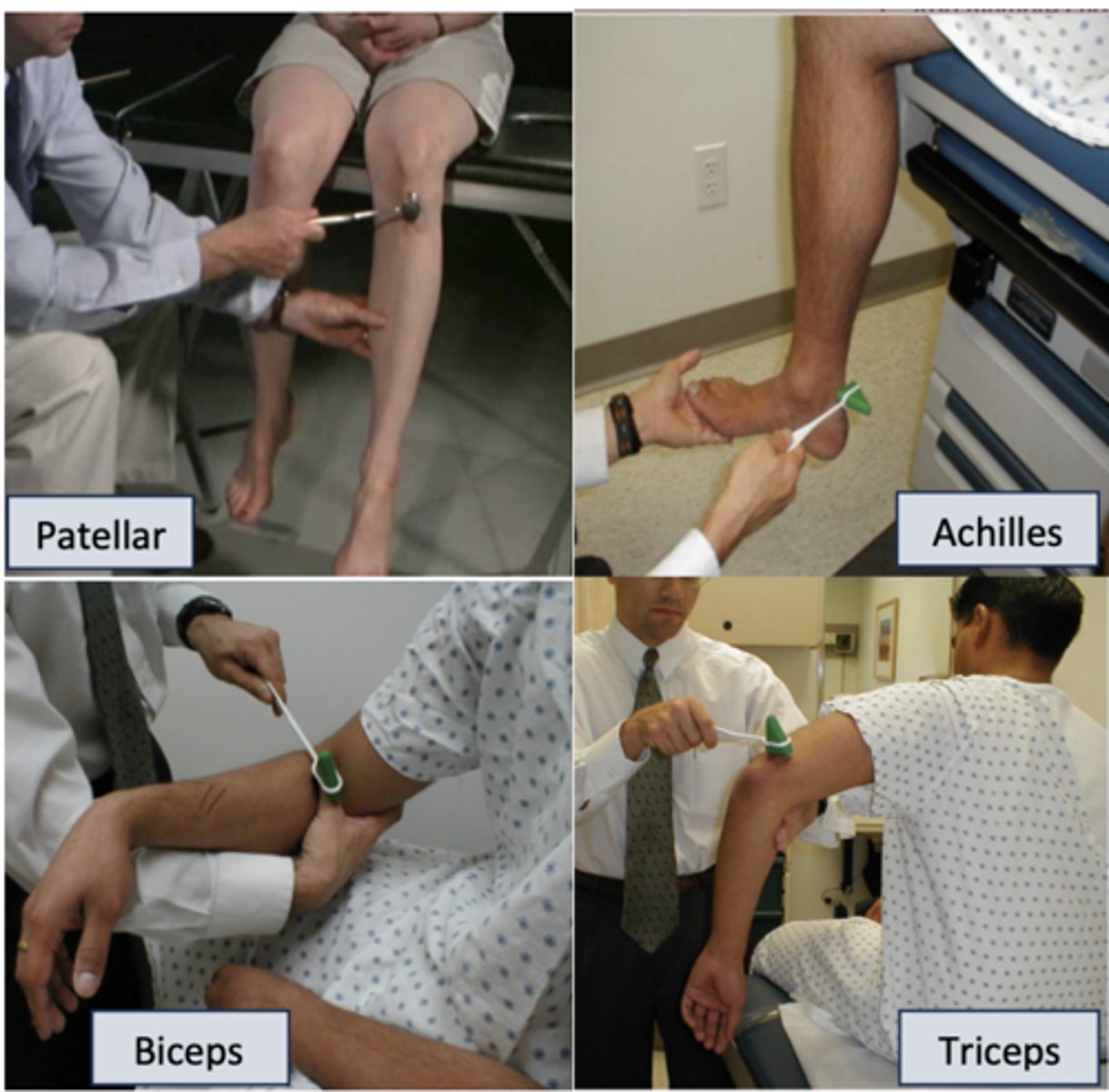
monosynaptic reflex examples
patellar reflex, biceps reflex, triceps reflex
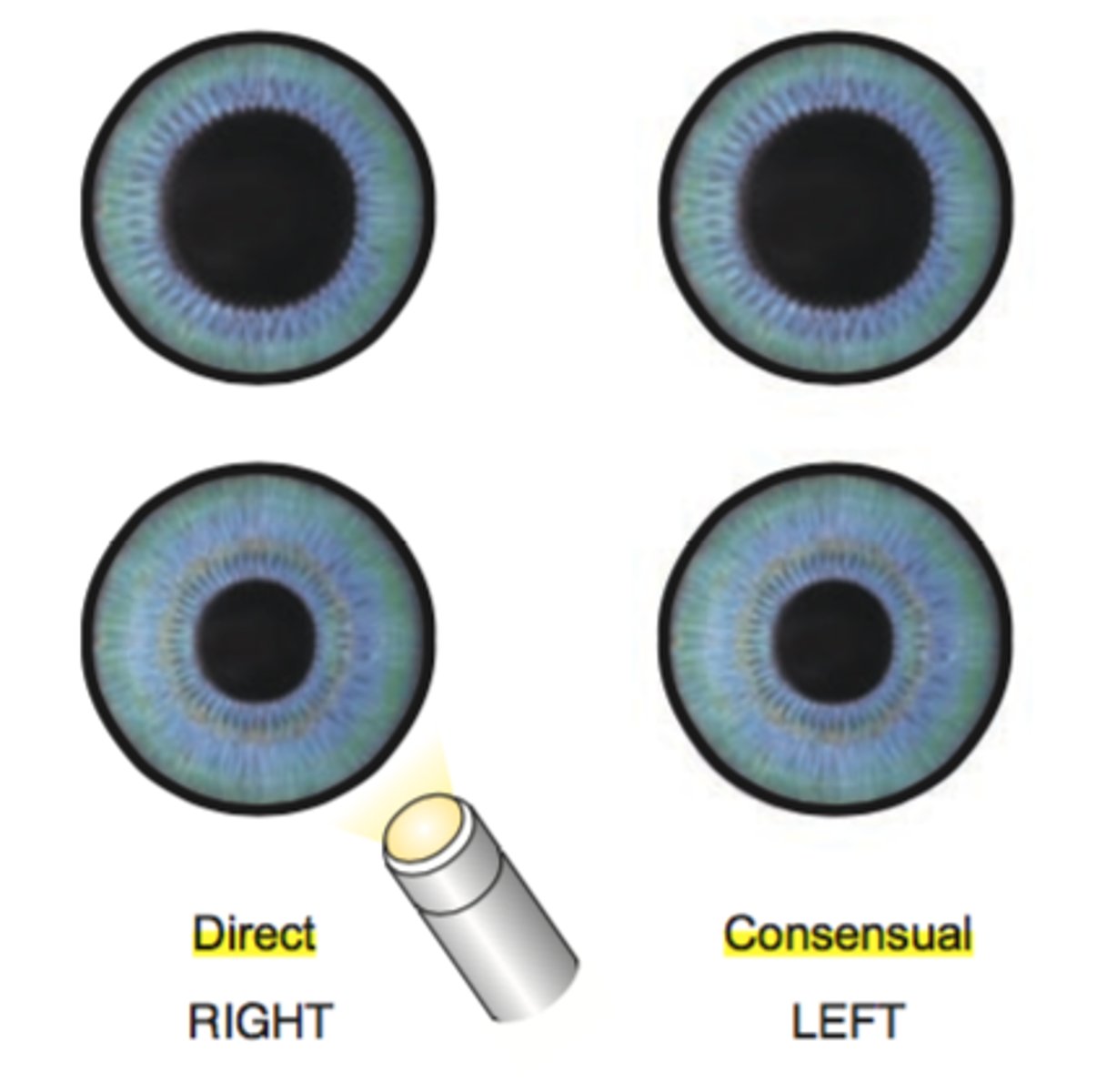
pupillary reflex
both pupils constrict when light is directed at one eye
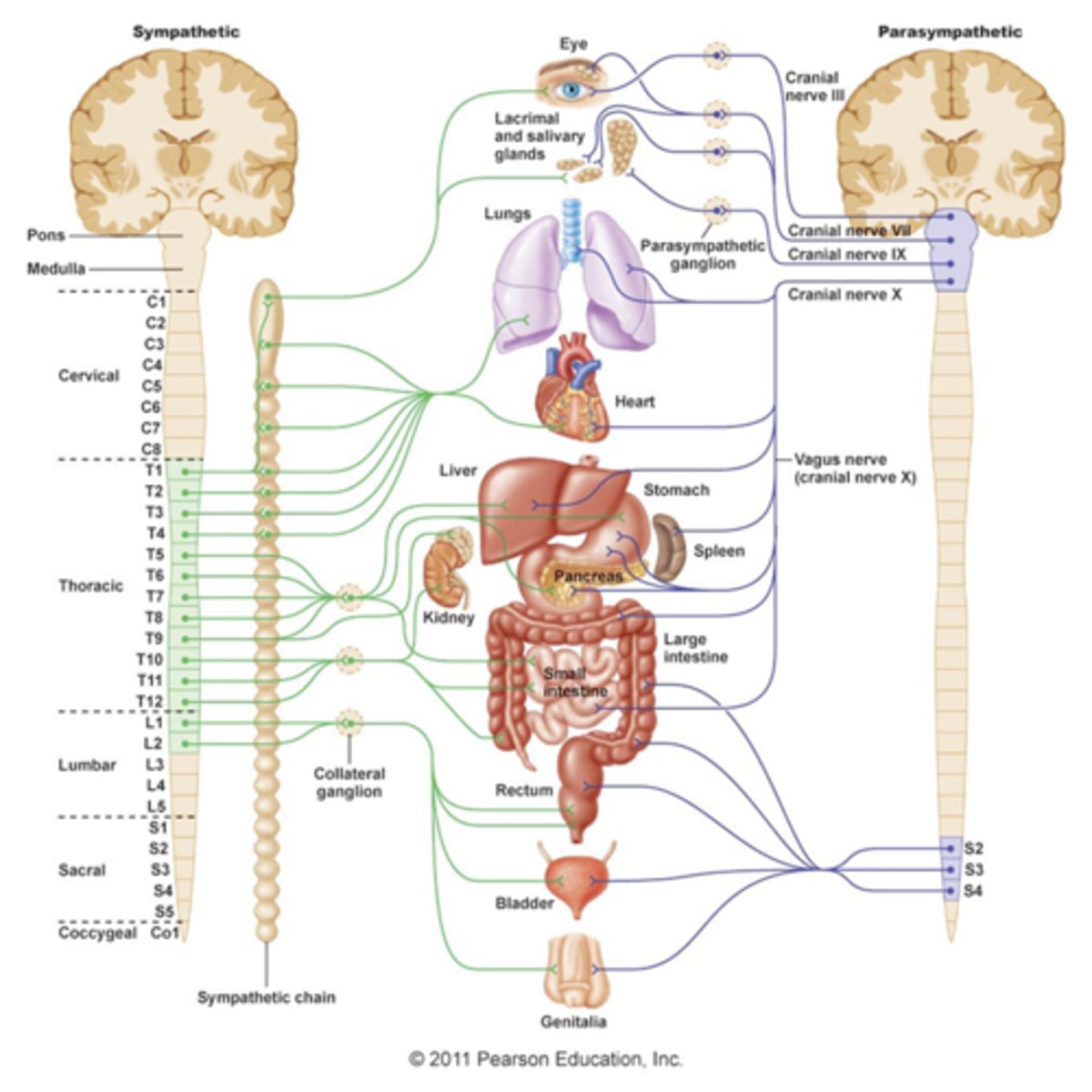
dual innervation
most viscera receive nerve fibers from both parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions
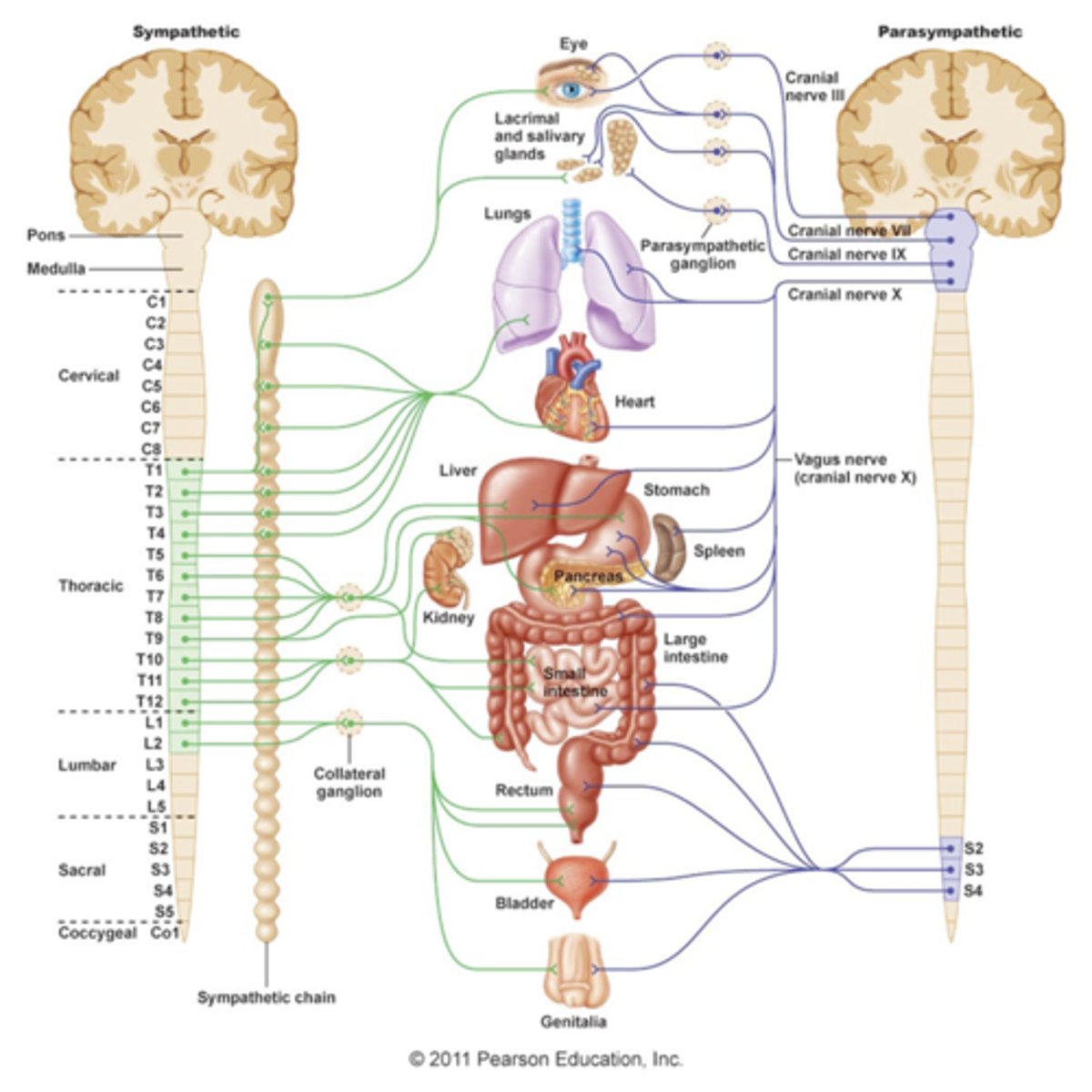
Interactions of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of same organ
antagonistic
Is it normal for one pupil to be dilated while the other is constricted?
No--this should be evaluated by doctor as can indicate serious injury or illness