A+P I Lec Exam (Ch 1-3)
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
anatomy
study of structure
oldest medical science
internal/external structures + physical relationships
physiology
study of function
medical terminology
language of A+P
derived from Latin/Greek
eponyms
names given to structures by ppl
mostly commemorative → we’re trying to transition away from that and use medically accurate terms
ex. fallopian tubes → uterine tubes
Gross Anatomy
surface anatomy
regional anatomy
systemic anatomy
clinical anatomy
developmental biology
embryology
clinical anatomy (gross anatomy)
pathological anatomy
radiographic anatomy
surgical anatomy
microscopic anatomy
cell biology
histology
physiology subspecialties
cell physiology
neurophysiology
immunology
pathophysiology
sign
OBJECTIVE disease indication
ex. blood pressure, fever
symptom
SUBJECTIVE disease indication
ex. tiredness, pain
levels of organization
chemical
cellular
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
human body systems
integumentary
skeletal
muscular
nervous
endocrine
cardiovascular
lymphatic
respiratory
digestive
urinary
reproductive
MURDERS LINK
most important life processes
metabolism
responsiveness
movement
growth
differentiation
reproduction
homeostasis
maintaining stable internal conditions despite continuous changes in environment
homeostatic regulation
adjusting physiological systems to maintain stable internal body system
nervous + endocrine systems work together
3 parts:
-receptor
-control center
-effector
variables
factors that can change homeostasis
ex. blood sugar, body temp, blood volume
receptor (homeostatic regulation)
send nerve impulses/chemical signals to control center
control center (homeostatic regulation)
receives input and sends those impulses/signals to effectors
effector (homeostatic regulation)
receives input to make changes happen and/or alter the controlled condition
negative feedback
response reduces/shuts off og stimulus
variable changes in opp direction of initial change
ex. blood pressure, body temp, blood sugar
positive feedback
response enhances/exaggerates the og stimulus
usually controls rare events that don’t need continuous adjustment
ex. uterine contractions during labor or platelet plug formation and clotting
causes of homeostatic imbalances
environment
own behavior
genetic makeup
the air you breathe
the food you eat
the thoughts you think
anatomical position
person stands erect
facing observer
hands at side
palms forward
feet together
supine
lying down
face up
prone
lying down
face down
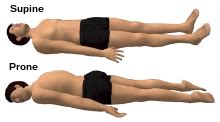
caudal/inferior (down/below)
cranial/cephalic/superior (up/above)
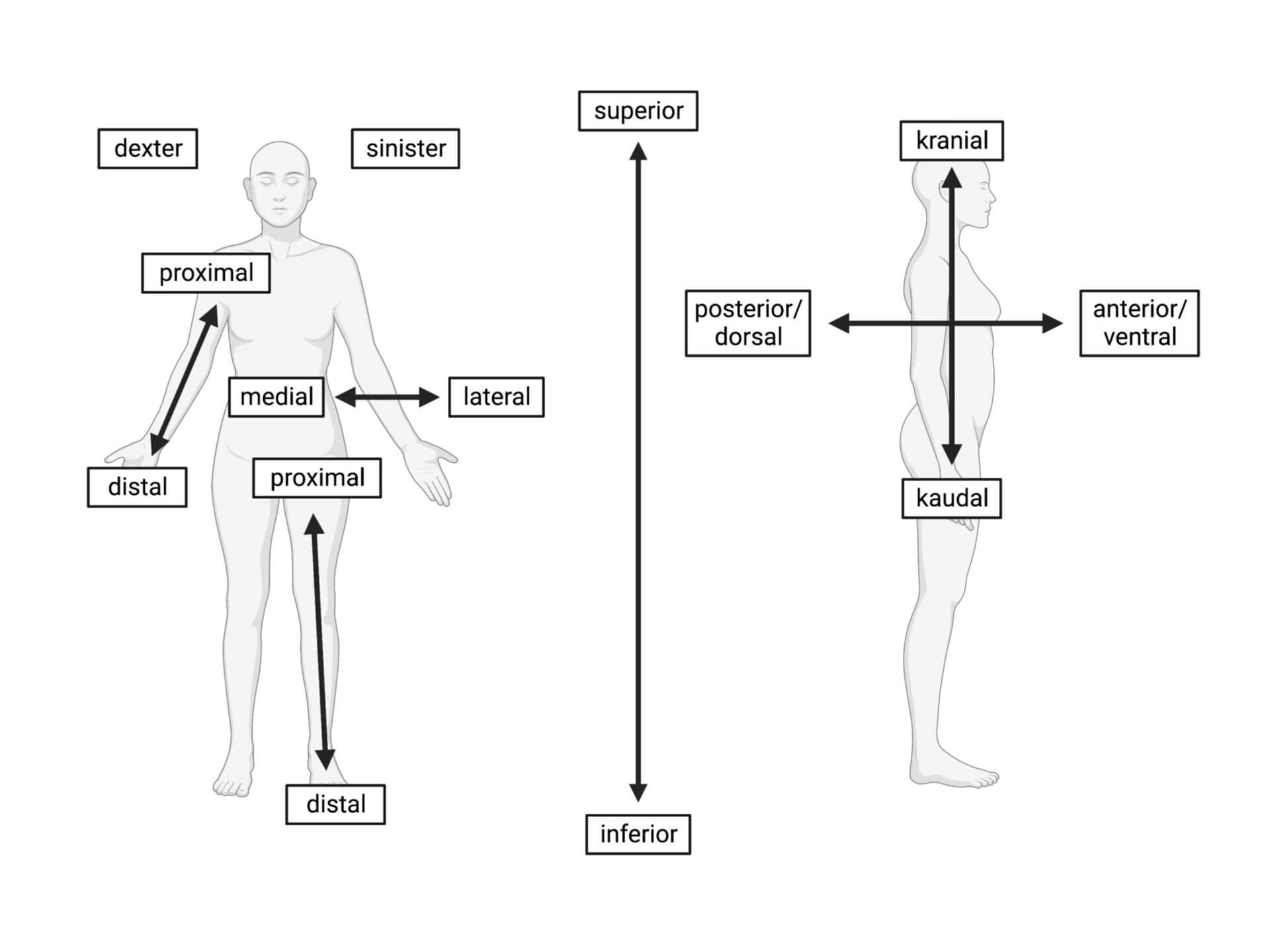
posterior/dorsal (back)
anterior/ventral (front)
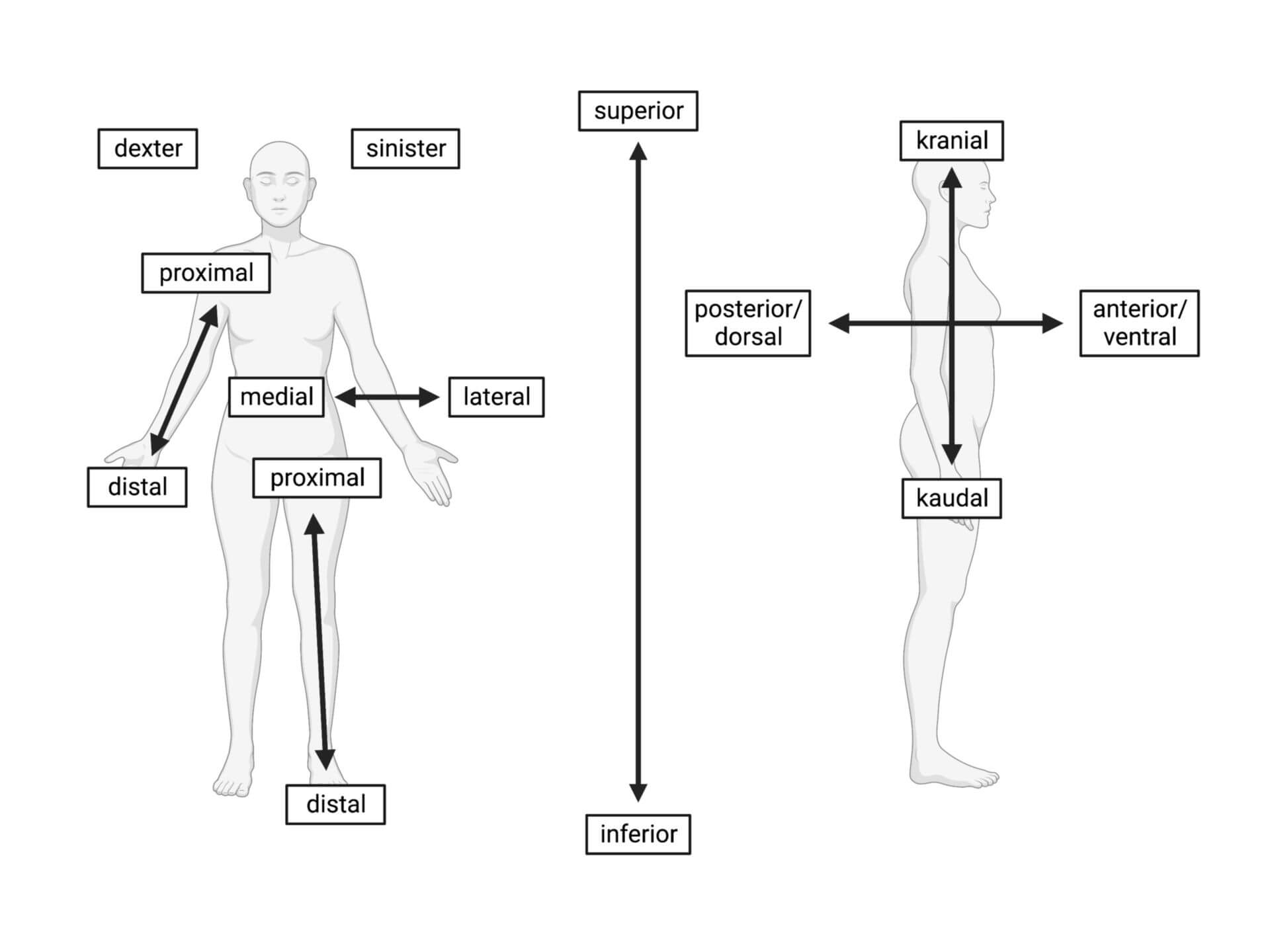
lateral (out/away from the body)
medial (in/towards the body)
proximal (up/close to the body)
distal (down/away from the body)
superficial (on the surface of the body)
deep (deep in the body)
cranial cavity
formed by cranial bones and has brain
vertebral cavity
formed by vertabrae and has spinal cord and spinal nerves
thoracic cavity
chest cavity
-pleural cavity
-pericardial cavity
-mediastinum
pleural cavity (thoracic cavity)
space bw layers of pleura that surround a lung
right and left each have a lung
pleural membranes
pericardial cavity (thoracic cavity)
space bw layers of pericardium that surrounds the heart
pericardial membranes
mediastinum (thoracic cavity)
central part of thoracic cavity bw lungs
connective tissue surrounds heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea, blood vessels
abdominopelvic cavity
has 4 quadrants and 9 regions
-abdominal cavity
-pelvic cavity
abdominal cavity (abdominopelvic cavity)
from the diaphragm → top of pelvis
has stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, SI, LI, and peritoneum surrounds organs
peritoneal cavity - space lined by peritoneal membranes
pelvic cavity (abdominopelvic cavity)
area within the pelvis
has urinary bladder, distal part of LI, and internal reproductive organs
serous membranes
cover viscera within thoracic + abdominal cavities
lines the walls of thorax + abdomen
2 layers: parietal + visceral
parietal (serous membrane)
covers internal surface of body wall/cavity
visceral (serous membrane)
covers organs
viscera
organs are partially or completely enclosed by cavities
there is fluid in the space bw these 2 membranes
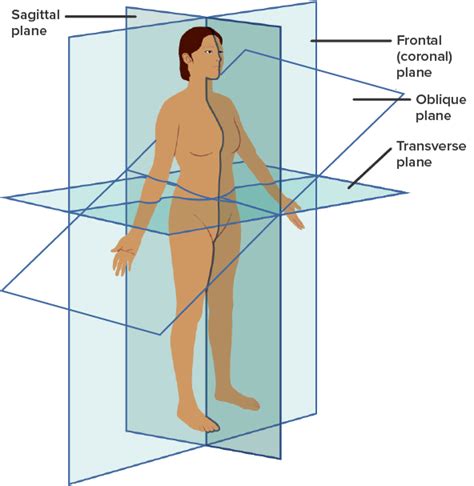
frontal/coronal plane
divides into anterior/ventral and posterior/dorsal
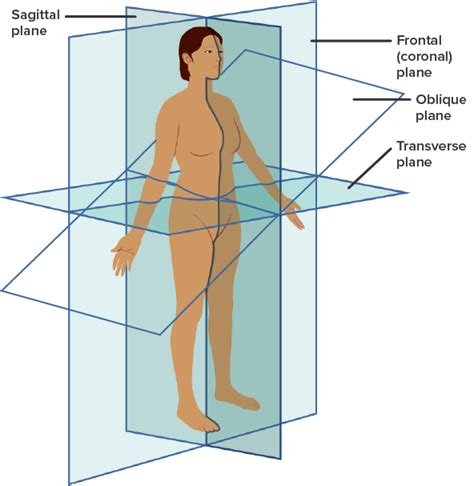
sagittal plane
divides into left and right
SIDE view
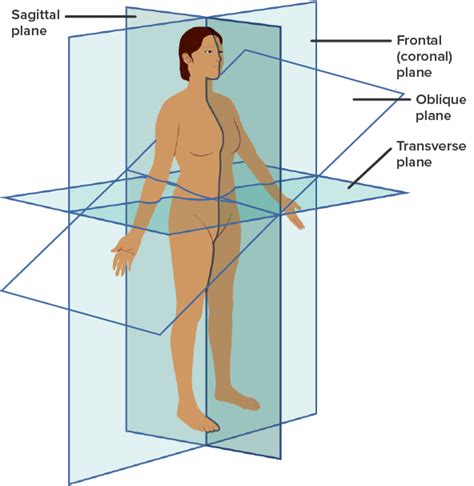
midsagittal plane
median
goes directly through the middle of the body like a hot dog
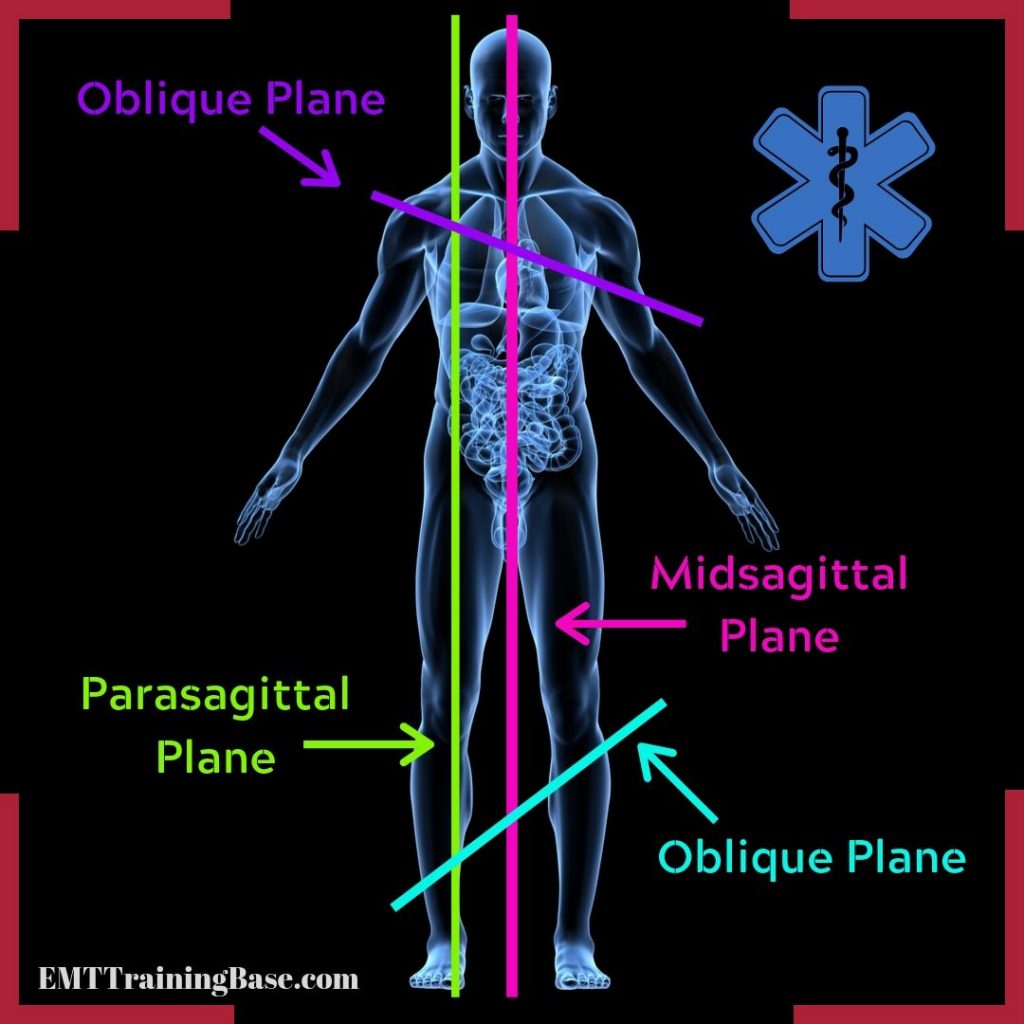
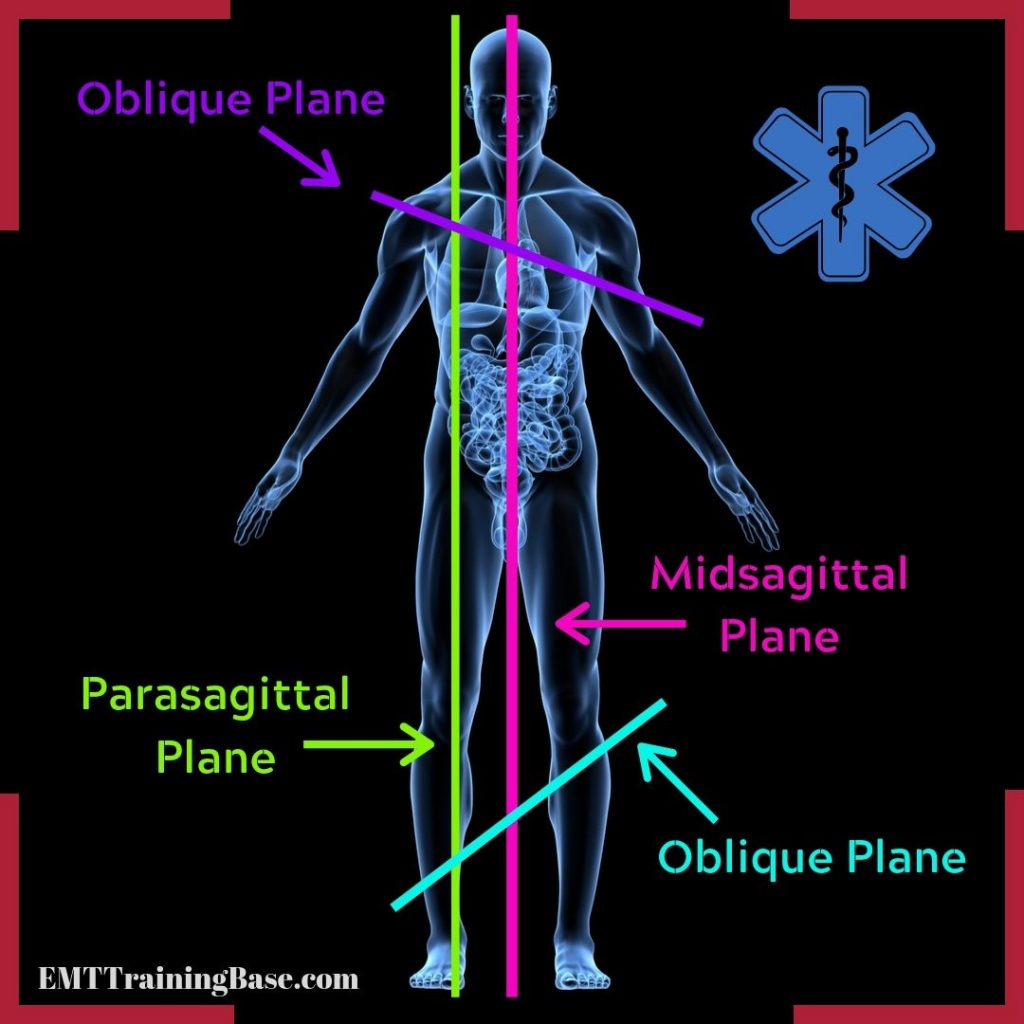
parasagittal plane
goes directly down the body but not in the exact middle
transverse plane
divides into superior/cranial and inferior/caudal
aka horizontal
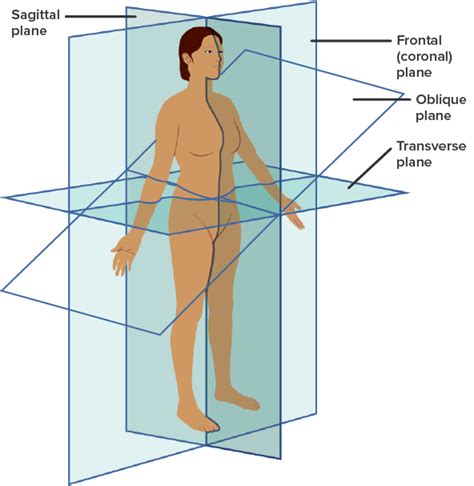
oblique plane
cuts into vertical plane at any angle other than 90 degrees
matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
solid-definite shape and volume
liquid-definite volume, takes the shape of the container
gas-no definite shape nor volume
elements
fundamental units of matter
96% of body is made of 4 elements
O, C, H, N
atoms
fundamental units of elements
neutron^0
proton^+
electron^-
how can we identify an element?
atomic number
mass number
atomic mass
atomic # (element)
no. of protons in an atom
mass # (element)
no. of p^+ and n^0 in an atom
ISOTOPE
atomic mass (element)
avg mass of all stable atoms in an element
isotope
same # of protons^+ and electrons^-
dif # of neutrons^0 → dif atomic masses
radioisotope
heavy isotope of certain atoms
unstable and decay
decomposes to more stable isotope by releasing E
ion
atom that has lost or gained e- to become stable
cation
anion
cation (ion)
atom loses e- → pos charged ion
ex. Na^+
anion (ion)
atom gains e- → neg charged ion
ex. Cl-
molecule
2+ atoms sharing e-
ex of a chemical reaction:
H (atom) + H (atom) → H2 (molecule)
“reactants” “product”
compound
has 2+ atoms of DIFFERENT elements
ex of a chemical reaction:
4H + C → CH4 (methane)
free radical
atom(s) w unpaired e- in outermost shell
unstable atoms that can damage cells, causing illness and aging
chemical bond
happens when atoms are held together by forces of attraction
they have E + can move
have stored chem energy that may be needed/released
ionic bond (chemical bond)
form when e- are TRANSFERRED from 1 atom to another → stability
attraction bw cation/anion
covalent bond (chemical bond)
form when e- are SHARED bw atoms → stability
nonpolar
polar
nonpolar (covalent bond)
e- are shared EQUALLY
electrically neutral
ex. carbon dioxide
polar (covalent bond)
e- are not shared equally
molecule has pos + neg poles
ex. water
hydrogen bond (chemical bond)
attraction of opp charged polar mols
extremely weak
H+ atom is attracted to neg part of polar mol (ex. N or O)
responsible for surface tension of water
help form intramolecular bonds (ex. protein structure)
chemical reaction
when new bonds are formed or old bonds are broken
reactant-starting substance
product-ending substance
-synthesis
-decomposition
-exchange
-reversible
-oxidation/reduction
activation energy
energy required for chem reaction to occur
catalyst
chem comps that speed up reaction by lowering the amt of activation E required
biochemistry
study of chem comp and reactions of living matter
inorganic compounds
water, salts, acids, bases
DON’T have carbon
(except CO2, CO)
organic compounds
carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
contain carbon, usually large, also have covalent bonds
water
really good solvent
has polar covalent bonds + bent shape, so each water mol can interact w many other mols
good in chem reactions
is added to break bonds in hydrolysis and is removed to make bonds in dehydration
high heat capacity + heat of vaporization
good lubricant + reduces friction
hydrophilic
water soluble
hydrophobic
water insoluble
pH
concentration of H+ solution
acidic < 7
basic > 7
neutral = 7
buffer system
maintain homeostasis by converting strong acids/bases → weak acids/bases to regulate pH
carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system
HCO3- (carbonic acid)
removes excess H+ in acids and adds more H+ in bases as needed
why is carbon useful?
-can combine in variety of shapes
-don’t dissolve easily in water
-good source of E
-has H and O
-larger than inorganic mols
carb
has C, H, O
H and O are in 2:1 ratio
provide E needed for life
lipid
has C, H, O but no ratio for H and O
sometimes has P
insoluble in water (hydrophobic)
phospholipid
modified triglycerides
glycerol + 2 fatty acids + Phosphate group
head is polar + hydrophilic
tail is nonpolar + hydrophobic
help cell membrane structure
steroid
has 4 ring structures
ex. cholesterol
made by liver and found in animal products
helps synthesize Vit D, steroids, bile salts
helps cell plasma membrane structure
protein
20-30% of cell mass
gives structure to body, regulates processes, provides protection, helps muscles move, transports substances, enzymes
has 4 structural levels
1+ polypeptides
peptide bond formation
amino acids are joined by peptide bonds (covalent) that connect amine group to carboxyl group
dipeptide
2 amino acids
polypeptide
many amino acids
primary structure (protein)
sequence of amino acids in polypeptide
secondary structure (protein)
alpha helixes, beta pleated sheets
tertiary structure (protein)
overall folding pattern → 3D shape
quaternary structure (protein)
2+ polypeptide chains relative to one another
enzyme
proteins that act as bio catalysts
high specific, efficient, subject to cellular controls
end in -ase
ex. hydrolase
nucleic acid
DNA makes genetic code in nucleus of cells
regulates most of cell’s activities
RNA guides protein formation
made of nucleotides:
nitrogen base, pentose sugar, phosphate group
ATP
primary E-storing mol in body
cells need this immediately
can be transferred to other comps that can use E in phosphate bond to do work
parts of a cell
cell membrane
cytoplasm
nucleus
cytoplasm (parts of a cell)
cytosol - gel like fluid component
organelles - structures that perform specific cell functions
all of these materials bw cell membrane and nucleus
inclusions - insoluble molecules