Immunology Lim 5-10
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
What does vagina release to support commensals
Glycogen, which feeds the good bacteria
3 ways in which bacterial pathogens harm us
Release of endotoxins (such as tetanus)
Colonization of epithelium surface (streptococcus)
Tissue damage by colonizing in bulk or replicating intracellularly (like leprosy)
Most use something in between the above methods (Like Staphylococcus aureus)
List modes of actions of exotoxins
Pore formation
Enzymatic lysis
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Hyperactivation
Effect on nerve-muscle junctions
How does pore formation work when used by exotoxin
Released by Staph. aureus
Polymerizes on cell surface
Cell nutrients leak
How do exotoxins perform cell lysis
Alpha toxin (Phospholipase C) released by C. perfringens
Hydrolyzes phosphorylcholine causing cell lysis
How do exotoxins inhibit protein synthesis
Diphtheriae toxin enters cell
Blocks activity of elongation factor 2
Protein synthesis is blocked
Cell dies
How does exotoxin cause hyperactivation of cells
Cholera bacteria releases toxins
Toxin causes hyperactivation of adenylate cyclase
A lot of cAMP is made
Excess nutrients and electrolytes are released, causing diarrhea
How do exotoxins affect the nerves
Inhibitory, Botulism
Botulinum toxin stops release of acetylcholine
Muscles cannot be stimulated
Activator, tetanus
Tetanus toxin stops release of inhibitory signal
Constant neuron stimulating signals are sent
Typical structure and function of exotoxin
Two chain molecule, one chain is for entering the cell, the other chain is for performing toxic function
4 ways in which immune system kills bacteria
Complement mediated lysis
Chemotaxis
Phagocytosis
Killing using proteolytic enzymes or free radicals
What chemotaxis is found on microorganisms which facilitates immune system killing of them
FMLP-peptide on the N-terminal
5 ways in which phagocytosis can occur
Complement receptors binding to bound complements
Fc receptors binding to antibodies
PRRs recognizing PAMPs
LPS receptor binding to LPS
Receptors are CD18 and CD14
Lectins (Like macrophage mannose binding lectin)
Result of CD14 binding to LPS
Phagocytosis and TNF secretion by macrophage
Which cells express TLRs
Macrophage
Neutrophil
Dendritic cell
TLR5 detects what
Flagellin
TLR1/2 detects what
Triacyl lipopeptides
TLR3 detects what
dsDNA
TLR2/6 detects what
Diacyl lipopeptides
TLR2 detects what
Peptidoglycan lipoarabinomannan
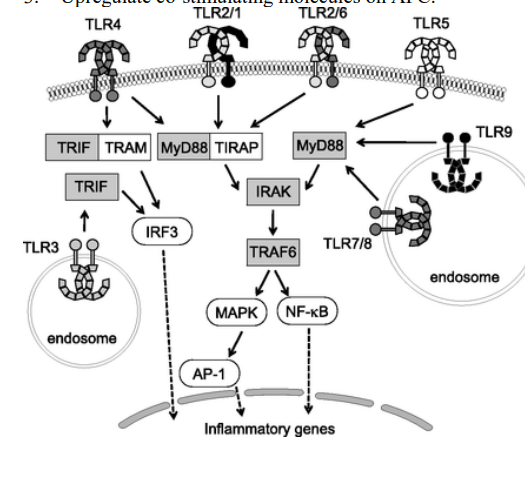
TLRs share a common intracellular pathway which leads to
Secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by macrophages (TNFs, IL-1)
ROS production by neutrophils
Upregulation of costimulatory molecules on APCs
TLRs intracellular pathway (Lim version)
How do oxygen metabolites participate in phagocytosis
Bacteria is in phagosome
NADPH oxidase pumps O2 into the phagosome
Creates ROCs like O2 → OH radical, H2O2, and O-
This is toxic to bacteria
If lysosomes fuse, they add myeloperoxidase, and peroxisomes add catalase
These, in presence of halides electron donors, create more toxic oxygen species like hypohalites
HIO
HClO
Nitric oxide pathway
Made is response to IFN-gamma signaling
Inducible nitric oxide synthetase is made as a result
i-NOS catalyzes a reaction between oxygen and guanidine side chain or arginine to yield nitric oxide
These can form peroxynitrites with ROCs
Made in response to TH2 signaling, IL-4/10/13
Arginase converts Arginine into urea and ornithine
Polyamines can be used for collagen synthesis and cell proliferation
Lysozyme role
Destroy proteoglycan
6 ways how microbes can fight off complement system
Send decoys which inhibit binding of complements
Made a capsule to block binding of complements
Express enzymes on surface to destroy complements
Express proteins to disrupt complement receptor binding to complements
Express proteins to divert complement binding
Membrane can resist insertions of lytic complex
Evasion mechanisms bacteria use to fight off antibodies
Release enzymes to cleave antibodies
Express fc-like receptors to stop opsonization
Roles of antibodies when fighting bacteria
Neutralize toxins
Complement activation
Opsonization
Neutralize immunorepellents
Block transport mechanisms and receptors of bacteria
Neutralize factors and enzymes released by bacteria
Evasion mechanisms of bacteria to escape phagocyte mediated killing (9+1)
Secrete toxins to kill phagocyte
Secrete toxins to neutralize chemotaxis
Special capsule to prevent complement formation and phagocytosis
Secrete molecules to prevent lysosome-phagosome fusion
Secrete catalase to destroy free radicals like H2O2
Special capsule to resist free radical damage
Stop antigen presentation
Escape phagosomes and multiply in cytoplasm
Prevent IFN-gamma responsiveness by macrophages
Inhibit H+ pump in phagosome to stop free radical damage
Three things that happen to tissue upon inflammation
Increased blood flow
Increased transduction of molecules into the tissue
Increased presence of white blood cells
Which complements trigger mast cells to release their granules
C3a and C5a
list 5 mediators of inflammatory response
C3a
C5a
Histamine
IL-8
PAF (Platelet activating factor)
2 ways virus spreads between cells
Release of virions
Cell to cell contact
Two ways to fight a virus infection
Prevent
Use interferons (innate immune system)
Antibodies to neutralize then (adaptive)
Kill virus
Kill infected cells via ADCC by NK cells
Induce apoptosis, by T cells
NK cell cytotoxicity
First line of defense against viruses
IgA and interferons
Two main strategies, and their sub strategies, which viruses use to survive in nature
Change of coating
Antigenic drift (mutation)
Antigenic shift (2 strains combine to form a new virus)
Latency
Sources of different interferons
Alpha and beta - made by all cells
Gamma - T cells and NK cells
Which interferon regulates macrophage action
Gamma
Effect of interferons on MHC upregulation
Alpha and beta upregulate MHC I
Gamma upregulates MHC I and II
What happens upon IFN signaling which aids in preventing the spread of viral infection
Synthesis of 2’5’ oligoadenylate synthetase
Degrades viral mRNA
PKR is synthesized, inhibiting elF-2 by phosphorylating it
Stops protein synthesis
Mx protein is synthesized and phosphorylated causing it to polymerize
Inhibits virus transcription and assembly
Gamma interferon activates which cells
Macrophage
NK cell
Effects of interferon gamma
Upregulation of MHC I and II
Activation of macrophages and NK cells
Blocking virus replication
Two types of parasites
Protozoa (unicellular)
Worms (multicellular)
How to fight two types of protozoans
Intracellular
Antibodies are ineffective
Cellular mechanisms are involved
Extracellular
Antibodies allow for ADCC, complement fixation and phagocytosis
How to fight worm infections
Antibodies mediate complement binding
Antibodies also mediate toxic granule release by eosinophils and IgE dependent mechanisms
How would macrophages fight intracellular pathogen
Making reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
How to boost the ability of macrophages to fight intracellular pathogens
Release cytokines which can increase the production of toxic metabolites
Roles of antibodies in fighting parasites
Direct damage via complement fixation
Enhance opsonization
Block the spread of pathogen by blocking the receptor they need to enter cells, such as plasmodium
ADCC
Which cells recruit eosinophils cells
Mast cells release mediators which recruit eosinophils
What do eosinophils use to attack worms
Release Major basic protein (MBP)
Reactive oxygen species
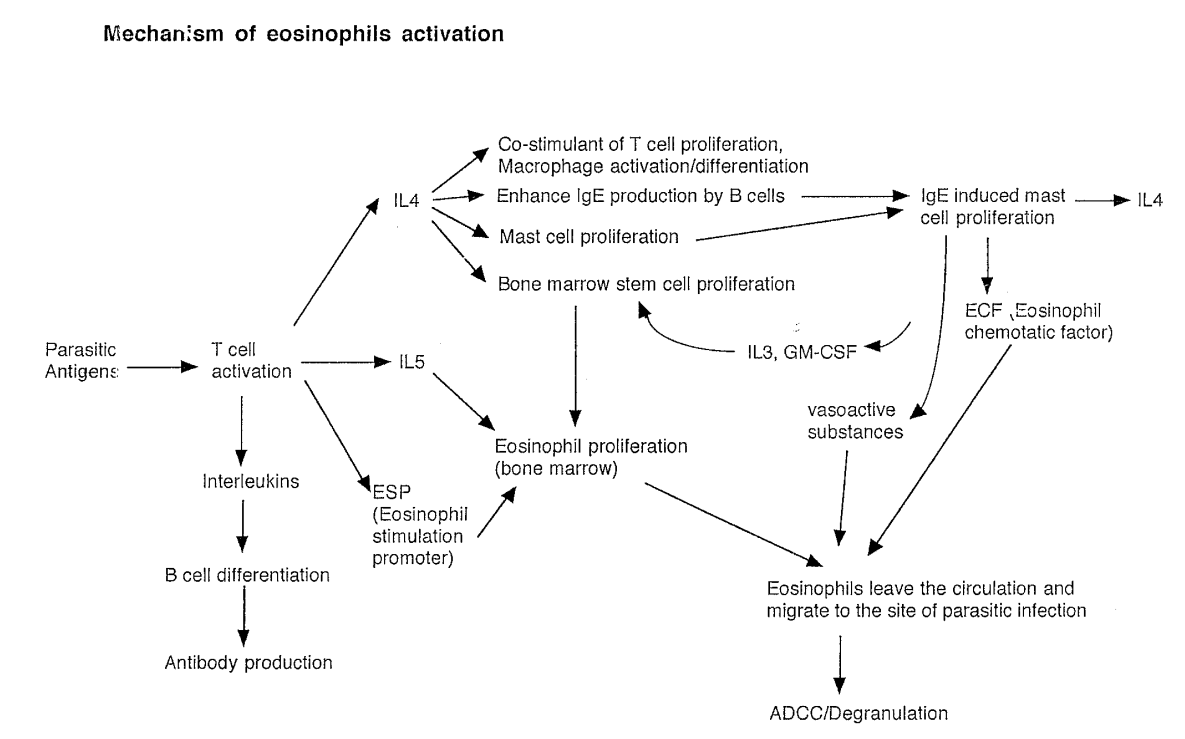
Factors needed to produce eosinophils (3)
All come from T cells
IL-5
Eosinophil stimulating promoter (ESP)
IL-4 → Bone marrow stem proliferation
Result is production of eosinophils
Mechanisms of eosinophils activation full diagram
List where HIV can be isolated from
Lymphocytes
Urine
Blood
Saliva
Semen
Female genital tract secretion
Tears
Breast milk
Modes of transmission of HIV
Sexual
Organ donation
Needle sharing
Mother to child
Three waves of aids transmission in the US
Homosexual
Drug abusers
Heterosexual
Describe structure of HIV virion
envelope glycoprotein
gp120 and gp41
Envelope derived from host cell
Matrix protein p17
Structural core protein p24, p17, p9, p7
Reverse transcriptase
ssRNA
List genes of in HIV genome and purpose
LTR - for genome integration
gag - virion core proteins and antigens
pol - reverse transcriptase and integrase
vif - virion infectivity factor
vpr - TF
nef - negative activator factor
tat - transactivator protein
ref - regulatory virion protein
vpu - efficient budding
env - envelope proteins
Two steps of how HIV infects cell
gp120 binds to CD4 (Also CCR5 and CXC4)
Found on helper T-cells, macrophages, monocytes, and FDCs
gp41 helps the virion fuse with the host cell membrane
T-cells usually get killed by viral replication, but other cells will continue to carry the virus
Stages of a typical HIV infection
Initial infection, symptomatic
Seeding of virus across lymphoid organs
Latency period
Asymptomatic
T-cell count becomes lower
Constitutional symptoms (plasma viremia starts increasing)
Opportunistic infections
Death
Some opportunistic infections and tumors indicative of AIDS
Tumor - Kaposi’s sarcoma
Bacteria - mycobacteria and salmonella
Fungi - Pneumocytes carinii
Disease stages of AIDS
Contact
Seroconversion - detection of HIV antibodies
Sickness
Stage 1 - Acute
Stage 2 - Asymptomatic
Stage 3 - persistent generalized lymphadenopathy (PGL) - enlarged lymph nodes
Stage 4 - Symptoms, persistent infections, neurological problems, tumors
Laboratory markers of stage IV AIDS
Decreased CD4+ T cells
Increased IgE, IgA and Beta2 microglobulins
Reduced anti-gp120, anti-p17 and anti-p24 antibodies
Raised CD8+ T cells
3 classes of anti-HIV drugs
Nucleoside analogs like AZT which block transcription
Protease inhibitors stop assembly of viral particles
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
How can HIV develop resistance to anti-HIV drugs? How to fix?
Mutations
Use cocktail treatment
2 PrEP treatments
Truvada - for safety before intercourse and drug use
Cytidine analog and TDF
Both are RT inhibitors
Descovy - idk what he tried to say
Cytidine analogue and TAF
Both are RT inhibitors
TAF vs TDF as RT inhibitors
TAF is a newer version, absorbed faster
What to look for when diagnosing HIV?
Antibodies
Why not detect viral antigens when testing for HIV?
Because titre of virus is low in blood
What test is used to check for HIV antibodies? Basic steps
ELISA
Cover glass with HIV antigens
Add patient serum
Add anti-human IgGs with enzyme conjugated
Add ligand
If antigen is present, color will change
Confirmatory tests after ELISA
PCR
Western Blot
Difficulties in making HIV vaccine
Antigenic drift of gp120
Antibodies fail to protect the patient
Possibility of cell-cell transmission
Logic behind vaccines
Introduce antigens to activate T-cell response
T-cells form memory cells
They will activate faster when the infection occurs again
What does specificity mean in immunity
TCRs and BCRs are unique
An ideal vaccine should generate both
Humoral response (by B cells)
Innate response (by T cells, cytotoxic T cells)
5 ways to make vaccines
Attenuated live vaccine
Animal virus (like cowpox)
Non-virulent strain
Serially passage the virus to accumulate mutations till they lose virulence
Killed pathogen vaccine
Subunit (recombinant protein) vaccine
mRNA/DNA vaccine
Recombinant virus vaccine
How is Recombivax HB vaccine produced
Grow viral subunits is yeast cells
How is Engerix B vaccine made
How is polio inactivated
Using beta-propiolactone
Some methods of inactivating bacteria
Heat and formaldehyde
How do recombinant live virus vaccines work
Get vaccinia virus
Insert a gene of interests coding for antigen of a specific microorganism
Insert it into cells which will make virions
Collect virions for a vaccine
Inject into cells
Vaccinia proliferates and causes production of antigen
Body develops immunity against the antigen
How do conjugation vaccines work
Link a weak and strong antigen together
Body will react to strong antigen, and also remember the weaker antigen
Stronger antigen is called carrier protein
How does DNA vaccine work
Inject DNA
DNA codes for antigen
Antigen gets recognized and memorized
How mRNA vaccines work
mRNA uses lipids to enter the cell
Transcribed as antigen
Antigen gets presented on MHC I
If it enters another cell, it is presented on MHC II
Why not used killed virus vaccines?
Some organisms cannot be grown to sufficient quantity
Hep. B
Some won’t trigger an immune response
No mucosal immunity, i.e. pathogen can enter the body again
Example vaccine which shows why live attenuated may be better than dead vaccines
Polio vaccine is live attenuated virus
Orally administered
Triggers production of nasal and duodenal IgA, while dead vaccine does not
Therefore better immunity
Why is cholera vaccination not as effective as typhoid vaccination?
Cholera resides in the gut
Typhoid enters organs
Vaccination causes production of circulating antibodies, which cannot reach the gut but can reach all organs
6 important criteria for a good vaccine
Safe
Effective long-term
Cost effective
Memory immunity
Duration of response
Stable (can be transferred)
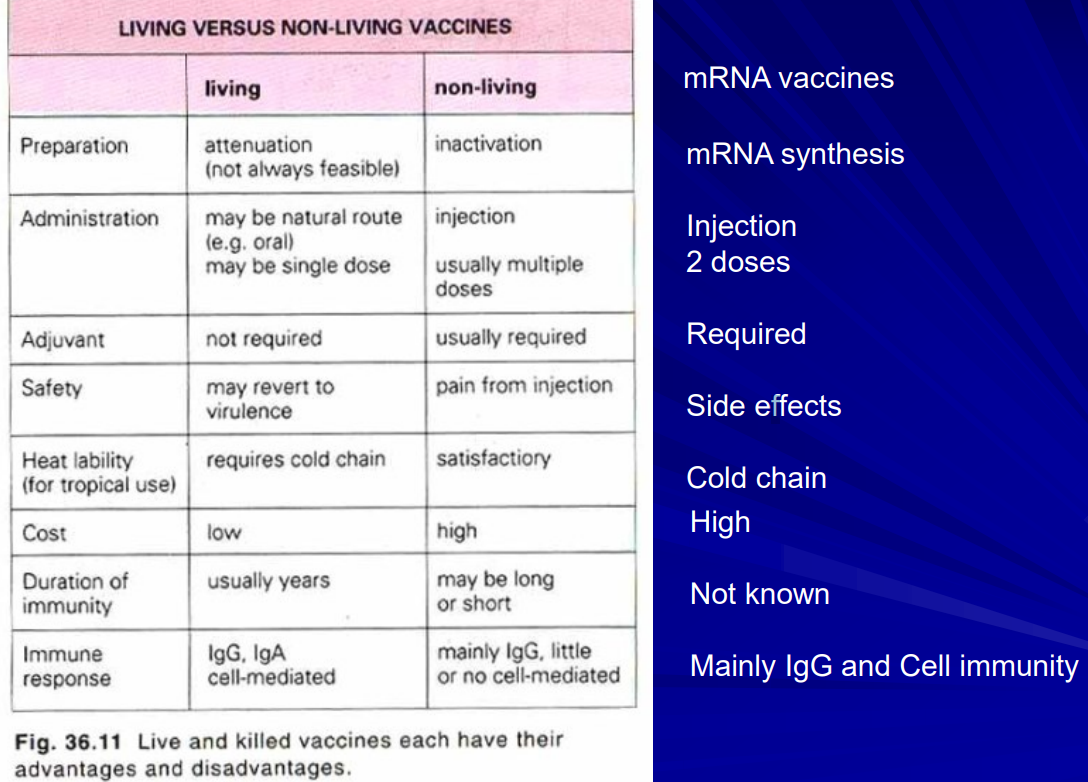
Table comparing inactivated, live and mRNA vaccines in following categories. Preparation, administration, Adjuvant, safety, heat liability, cost, duration of immunity, immune response
What characteristic of viral proteins causes antigenic shift
DNA/RNA polymerases lack proofreading ability
Serotype
A way of grouping pathogens according to whether they illicit an immune response. H1 influenza infection will not create antibodies for H2 influenza
Influenza virus has what two molecules on surface
Hemagglutinin (H)
Neuraminidase (N)
Formula for vaccine effectiveness
VE=100*(1-IRR)
where IRR=( Trial / Control )
mRNA vaccine delivery method
Lipid nanoparticles
What does mRNA vaccine LNP contain
uRNA
saRNA
modRNA
How do anti-S antigen antibodies work to stop COVID19 infection
They bind the spike protein, preventing the virus from infecting cells
Steps in production of inactivated vaccine
Produce virus using cells
Inactivate virus
Validate inactivation
Purification
Size exclusion chromatography
Filtration
Why is omicron a dangerous mutant
Because it can more effectively escape neutralization of antibodies produced in response to previous vaccines
IFN-alpha/Beta vs IFN-gamma in terms of Antiviral activity, and which cells secrete them,
IFN-alpha/beta are antivirals, IFN-gamma is pro-inflammatory
T cells produce IFN-gamma primarily, while all infected cells produce IFN-alpha/beta
Stems of IFN release during viral infection
Cell is infected, detects it with TLRs and releases type I interferons
Virus gets picked up by type I IFN-stimulated APCs, and its antigen is presented to T cells
T-cells release IFN-gamma to trigger macrophage and NK cell differentiation, as well as Th1 mediated response
Where can virus replication take place in infected cells
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
How fast do viruses replicate
Fucking fast