Bisc 303: Chapter 2 Extensions to Mendelian Genetics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
How do geneticists limit the number of variables under investigation at one time?
By studying inbred populations of experimental organisms
A pure-breeding tall plant is crossed with a pure-breeding short plant. The hybrid offspring from this cross are all short. Which statement accurately summaries the relationship between the two height alleles?
The short allele is completely dominant to the tall allele
In pea plants, the production of starch in the seed is catalyzed by an enzyme that can be specified by two alleles: the allele R^1, which specifies a functional enzyme, and the allele R², which specifies a nonfunctional enzyme. If we consider the activity of this enzyme in plants with the genotype R^1R^1 to be 100%, plants with the genotype R^1R² exhibit 50% activity, while plants with genotype R²R² exhibit 0% activity. Plants with the genotype R^1R² genotypes). What is this an example of?
incomplete dominance
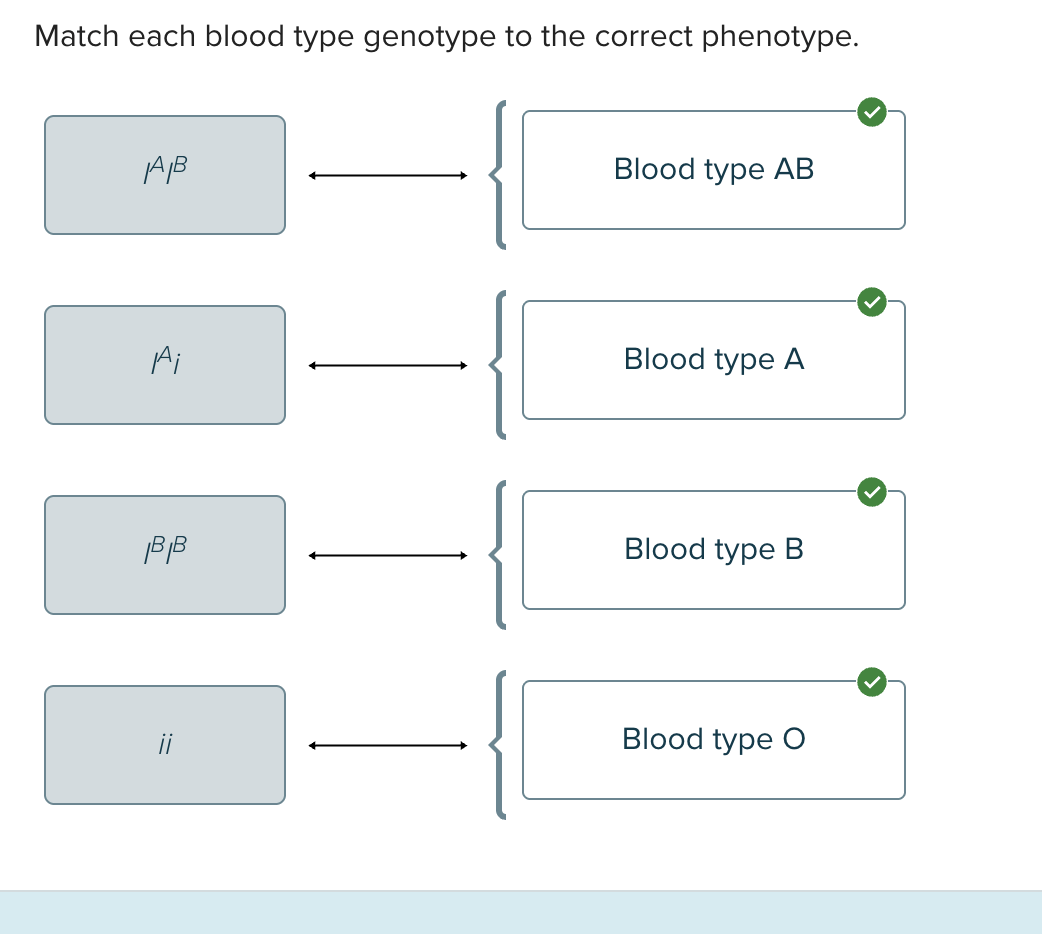
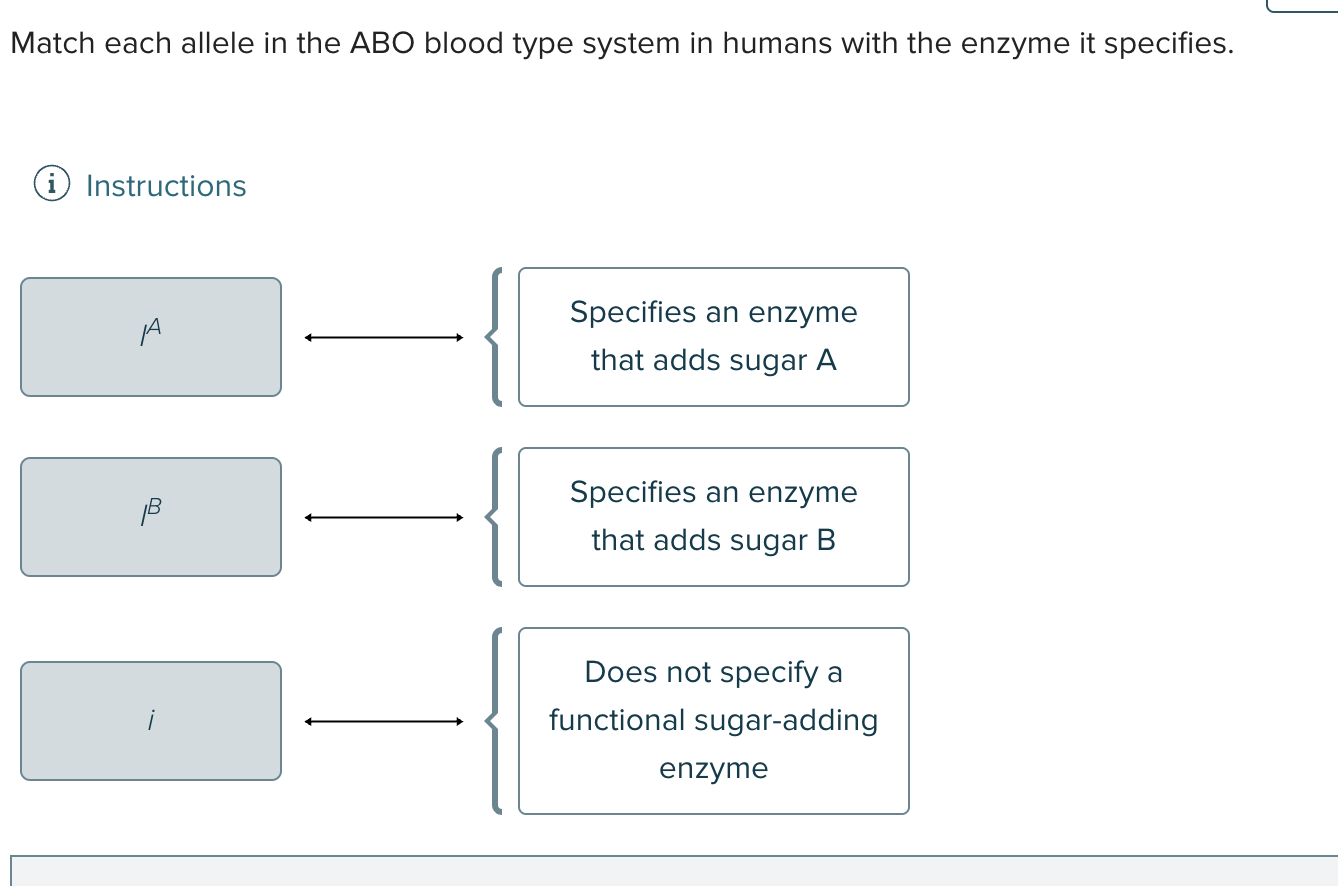
Choose the alleles that determine the ABO blood type in humans
I^A
I^B
i
An allele that is rare within a population is called _____ allele
mutant
Geneticists often study inbred populations of experimental organisms to analyze specific traits. The purpose of using inbred populations is to _____.
limit the number of variables being studied
The gene that determines the ABO blood group in humans has ___ alleles which can produce ____ genotype and ____ phenotype.
3
6
4
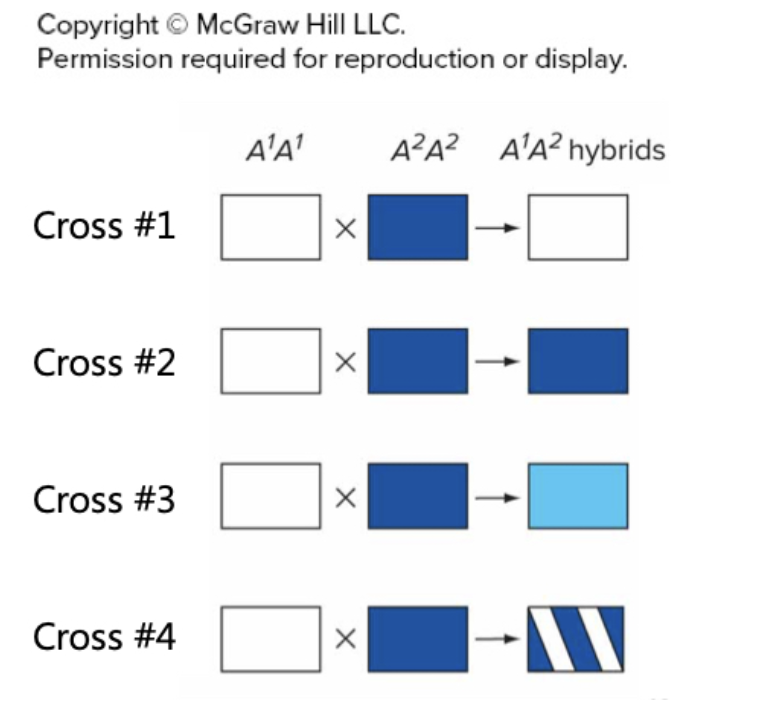
Two pure-breeding plants are crossed with one another. The first plant is homozygous for allele A^1 and has white flowers. The second plant is homozygous for allele A² and has blue flowers. The A^1A² hybrids all have blue flowers. Which allele is dominant?
The A² allele is dominant to A^1.
A mutation is defined as a ____
change in the genetic material
Which cross in this diagram represents the expected outcome if alleles A^1 and A² exhibit incomplete dominance?
Cross #3.
The proportion (or percentage) of an allele of a gene out of total number of copies of that gene in a population is called _____ _____
allele frequency
The gene that determines the ABO blood group in humans has ____ alleles which can produce _____ genotypes and ___ phenotypes
3,6,4
The most commonly occurring alleles in a population are called ____ alleles.
wild-type alleles
Which of the following genotypes will result in blood type A?
AA or AO
I^AI^A
I^Ai
A mutant allele is defined as an allele that ____
has an allele frequency that is less than 1%
Choose all correct statements about genes and their alleles.
A particular gene can have many different alleles and the different alleles can exhibit complex dominance relationships.
A diploid individual can only have two alleles of a particular gene
A change in the genetic material is called ____
mutation
The phenomenon in which one gene affects many traits is called ___
pleiotropy
Allele frequency is defined as the _____
proportion of a certain allele out of all of the copies of a gene in a population
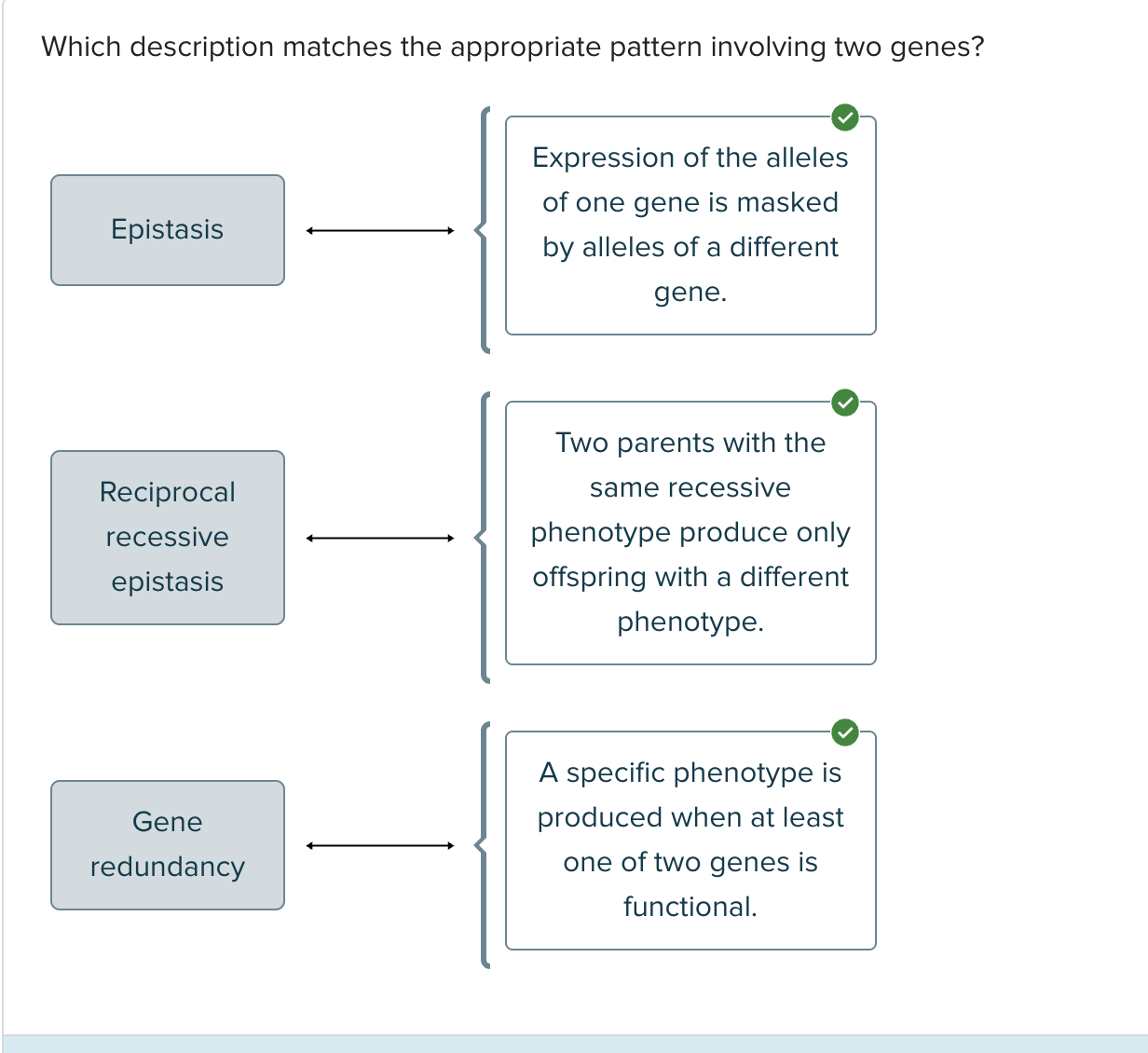
The type of genetic interaction in which the effect of an allele of one gene masks the effects of alleles of a second gene is called ____
epistasis
An allele of a gene is considered to be a wild-type allele if ____
most common allele in the natural population
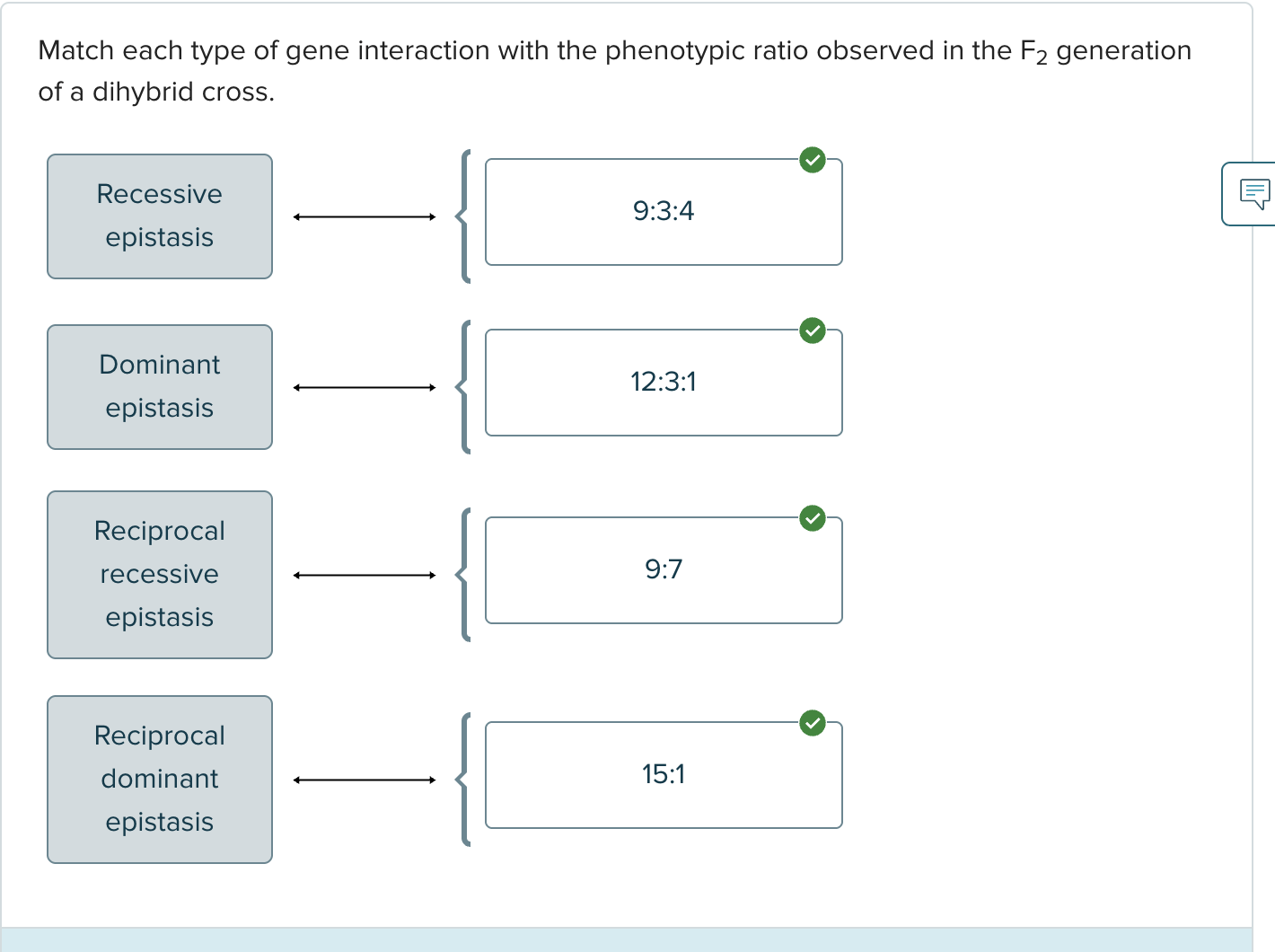
For Labrador retrievers the dominant allele B for gene 1 leads to black coat while the recessive allele b leads to brown coat. Alleles of gene2 can change this color, with the dominant allele E having no effect but genotype ee changing either black or brown to yellow color. This is an exmaple of ____
recessive epistasis
consider two genes (M and P) that exhibit recessive epistasis, such that the pp genotype masks the effects of any allele for the M gene. If F1 dihybrids (Mm Pp) are allowed to cross, the 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation will become____
9:3:4 because M-pp and mm pp individuals will have the same phenotype
Pleiotropy is a situation in which ____
one gene affects several different traits
A trait is controlled by two genes that work in succession, and a dominant allele of each gene is required to produce a certain phenotype. The interaction between the alleles of the two genes is referred to as ____ _____ epistasis
reciprocal recessive
What is epistasis?
A gene interaction in which the effects of an allele of one gene mask the effects of the alleles of a second gene
What genetic interaction is characterized by a 9:7 phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross (such as Aa Bb x Aa Bb)?
reciprocal recessive epistasis
Suppose that the covering on corn kernels can have a purple color due to the dominant allele P of gene. Alleles of gene 2 can mask this color, with the dominant allele C having no effect but genotype cc changing the purple color to colorless. This is an example of _____
recessive epistasis
In summer squash, fruit color is control by two genes: A determines whether plants will produce green or yellow pigment, while gene B determines___
whether or not pigment will be deposited (yields green or yellow squash) or not (yields white squash).
A mutant allele is defined as an allele that ____
has an allele frequency that is less than 1%
For harebell plants, dominant alleles for two separate genes are needed to produce blue petal color. For snapdragon plants, the presence of a dominant allele for either of two genes leads to red petal color. Which one is an example of redundant gene action?
snapdragon plants
For a dihybrid cross involving recessive epistasis, what phenotypic ratio is expected in the F2 generation?
9:3:4
which of the following statements about reciprocal epistasis, involving two genes that affect pigment production, is correct?
at least one dominant allele of each gene must be present to produce the pigment
Suppose that eye pigment in an insect is produced by a metabolic pathway that requires two enzymes encoded by gene M (has two alleles: M encodes a functional enzyme and m encodes a non-function enzyme) and N encodes a functional enzyme and n encodes a non-functional enzyme), respectively. If Mm Nn individuals are crossed. What is the expected ratio of offspring with pigmented and nonpigmented eyes?
9 (pigmented eyes): 7 (nonpigmented eyes).
In summer squash, gene A controls the production of green (aa) or yellow (A-) pigment, while gene B determines whether pigment is deposited (bb) or not (B-). In this examples of dominant epistasis, what phenotypic ratio will be observed when Aa Bb plants are crossed?
12:3:1
For snapdragon flowers, the presence of a dominant allele for gene A or a dominant allele for gene B leads to red petals. Only the aa bb genotype leads to white petals. This is an example of ____
redundant gene action
When the dominant alleles of two gene have redundant functions, the alleles are most likely to exhibit ____
reciprocal dominant epistasis
Redundant genes are genes that ____
may specify nearly identical proteins with the same function
A scientist performs a dihybrid cross between two pure-breeding parents producing purple of white flowers. To the scientist’s surprise, the F2 generation exhibits 10 different phenotypes in a ratio of 1:2:2:1:4:1:2:2:1. The most likely explanation for this observation is that ____
Which of the following F2 phenotypic ratios in dihybrid cross is consistent with dominance epistasis between the alleles of two genes?
12:3:1
What is hetergeneous trait?
A trait that can result from a mutation in one of a number of different genes
For harebell plants, dominant alleles for two separate genes are needed to produce blue petal color. For snapdragon plants, the presence of a dominant allele for either of two genes leads to red petal color. Which one is an example of redundant gene action?
snapdragon plants
The term penetrance describes the ____
proportion of individuals with a particular genotype who exhibit the exptected phenotype
When dominant epistasis occurs between alleles of two genes, it often indicates that their functions are ____
antagonistic
The degree or intensity with which a particular genotype is expressed in a phenotype is refered to as ___
expressivity
Which of the following phenomena expand (i.e,. increase) the number phenotypic classes among the F2 offspring of a cross?
incomplete dominance, condominance
A phenocopy is a phenotype that results from _____
exposure to environmental agents
because deafness can results from a mutation in one of many different genes, it considered an ____ trait
heterogeneous
What term describes how many members of a population who have a particular genotype exhibit the expected phenotype?
penetrance
A trait for which the phenotypes fall into clear-cut categories, such as green peas or yellow peas, is an example of a _____ trait
discrete
When the dominant alleles of two genes have redundant functions, the alleles are most likely to exhibit ____
reciprocal dominant epistasis
Expressively is best defined as the ____
degree to which a genotype is expressed in a phenotype
The phenotypic values of a continuous trait _____
vary over a range of values
A change in phenotype that arises due to exposure to an environmental agent, such as a chemical, and resembles a phenotype caused by mutant alleles of specific gene is called ___
phenocopy
what is a heterogeneous trait?
a trait that can result from a mutation in one of a number of different genes
A discontinuous trait is a trait whose phenotypes ____
fall into discrete categories
When dominant epistasis occurs between alleles of two genes, it often indicates that their functions are _____
antagonistic
A trait that varies over a range of values that produce a bell curve when charted on a graph is called an ___ trait
continuous/ quantitative