ECO TEST 6: Ch 19&20
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Community Structure and Succession
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
distinct or gradual
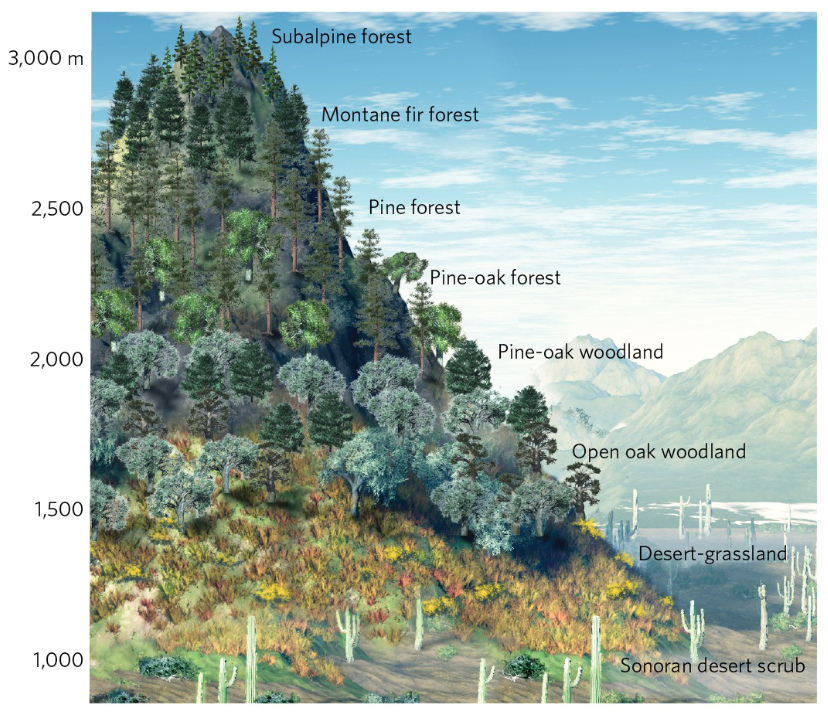
Communities can have ____ boundaries
Zonation of Terrestrial Communities
Boundaries caused by different abiotic conditions, competitions among species. Results in distinct zones of communities named for dominant or common species.
Ecotone
A boundary created by sharp changes in environmental conditions over a relatively short distance, accompanied by a major change in the composition of species
“the ecotone fallacy”
Many species are adapted to each of the habitats, but can also persist in the ecotone. Ecotones often support a high number of species: ____
Serpentine Soils
Derived from weathering rocks with high levels of nickel, chromium and other heavy metal.
several serpentine adapted species
Serpentine soils are toxic to many plant species, but home to
sharp ecotone
There is ____ between serpentine barrens and adjacent forest community

Interdependent communities
Communities in which species depend on each other to exist
Species interaction (mutualism, predator-prey, etc.) are ubiquitous
Species composition of communities should be predictable based on interactions
Communities resemble superorganisms
Independent communities
Communities in which species do not depend on each other to exist
Species presence/absence based on abiotic tolerances of each species
Species composition may be unpredictable
Can predict the pool of potential species, but not actual community
Independent species distribution
Line transect along a moisture gradient in the Great Smoky Mountains. Each species reaches peak abundance at a different point. This shows ____ between one another.
reduced competition
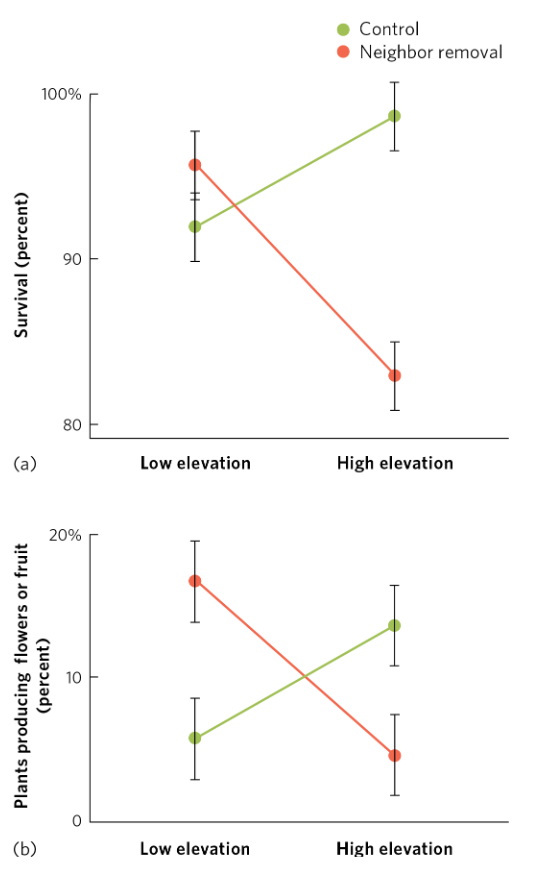
Neighbor removal experiment at high vs. low elevation sites.
At low elevation, removing neighbors increased survival and flowering (____)
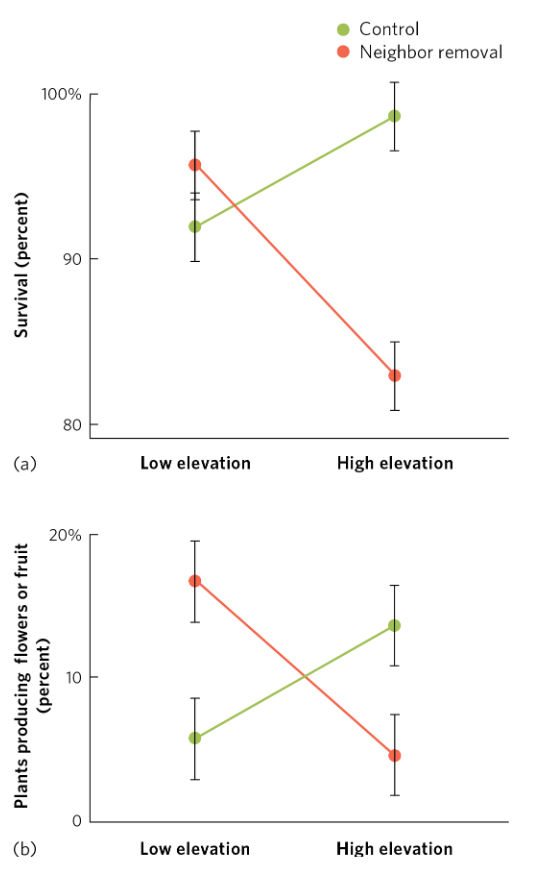
neighboring plants facilitate, interdependence of species
Neighbor removal experiment at high vs. low elevation sites.
At high elevation, removing neighboring plants reduced survival and flowering (____, ____)
number and relative abundance
Community diversity incorporates both the ____ of species.
Species richness
The number of different species in a community
Absolute abundance
The number of individuals of an individual species in a community
Relative abundance
The proportion of individuals in a community represented by each species
Species evenness
A comparison of the relative abundance of each species in a community
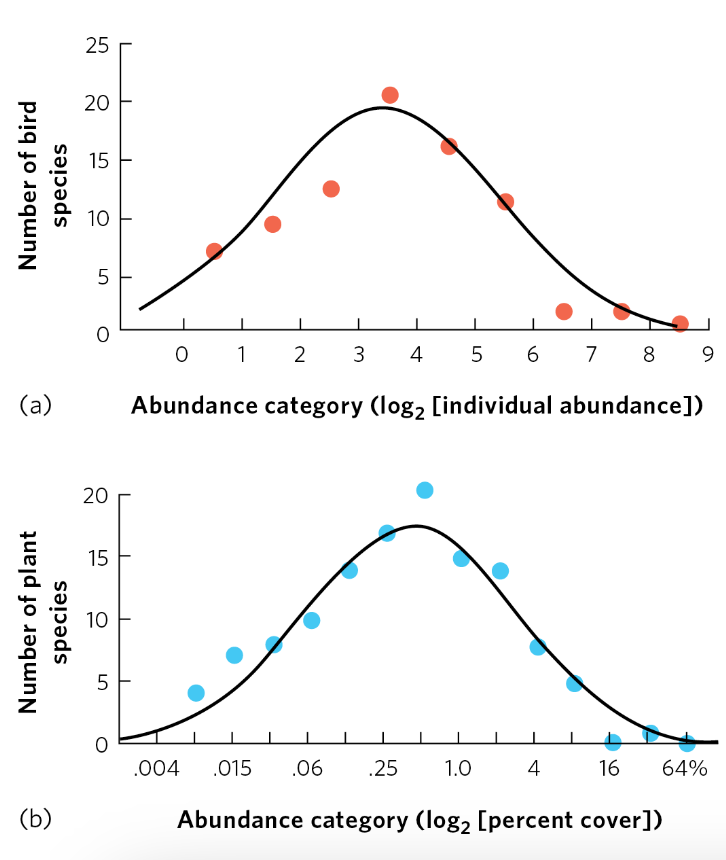
Log-normal distribution
Species frequently exhibit a ____ of abundance. Few very common & very rare species. Most species have intermediate abundance.
log scale
Normal distribution when plotted on a ____
Rank-abundance curve
Plots the relative abundance of each species in a community in rank order from the most abundant species to the least abundant species
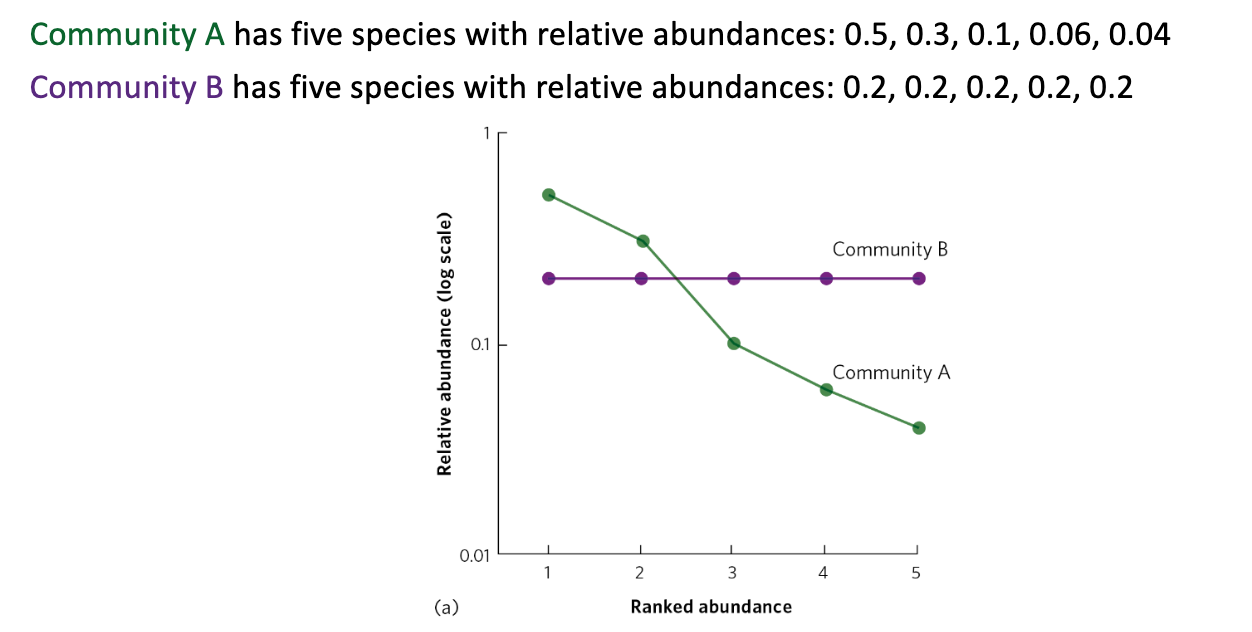
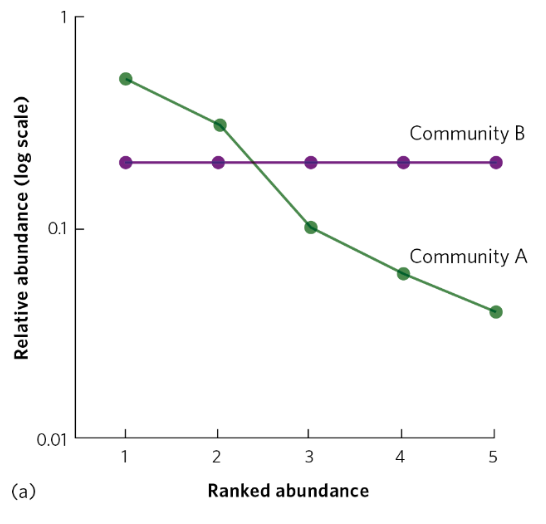
richness; evenness
Rank-abundance curves illustrate species richness and species evenness. Both communities have equal species richness. Community B has higher species evenness than Community A
Length along x-axis: ____
Slope of the line: ____
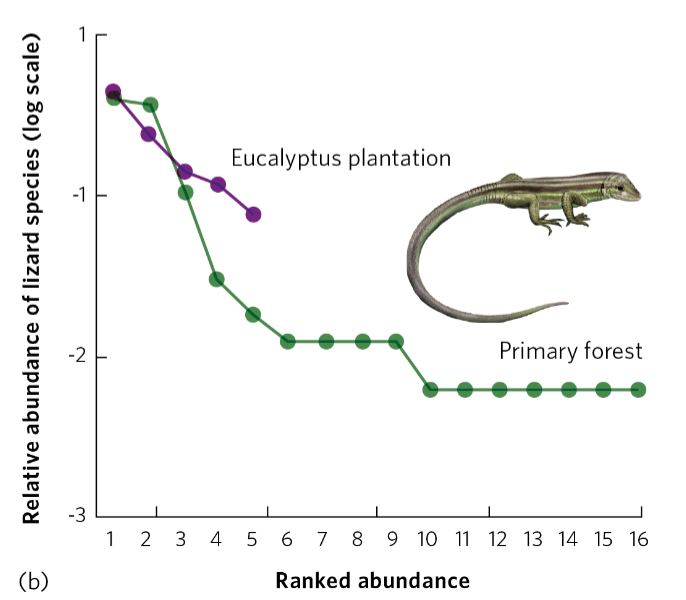
higher; slightly higher
Lizard communities in primary forests vs plantations in Brazil. Primary forest support ____ species richness, but ____ evenness in plantations
resources, habitat diversity, keystone species; disturbance
Species diversity is affected by____, ____, ____, and ____
intermediate productivity
Hump-shaped distribution is the most common: highest diversity
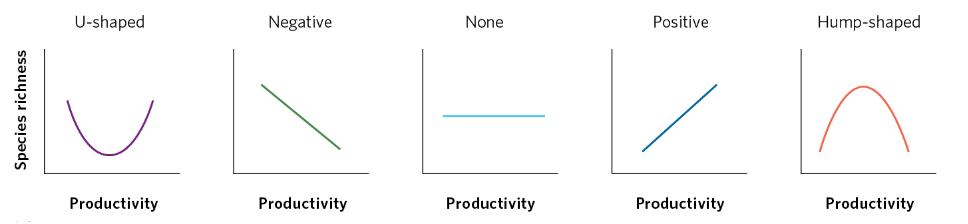
Low productivity
Only very tolerant species can persist (Effects of productivity and species richness)
High Productivty
Most competitive species outcompete other species (Effects of productivity and species richness)
places to feed and breed
Communities with a higher diversity of habitats should offer more potential niches (e.g., ____) and a higher diversity of species
bird species
Forests with more diverse foliage heights had greater diversity of ____.
Keystone species
A species that substantially affects the structure of communities despite the fact that individuals of the species might not be particularly numerous
keystone predator
Sea stars are a ____ in the intertidal zone. Predation keeps mussel species below K, limits interspecific competition.
Ecosystem engineer
A type of keystone species that substantially affects communities by changing the structure of the landscape
community plants and animals present
Beavers convert flowing streams into standing ponds, changing the ____
Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
The hypothesis stating that more species are present in a community that occasionally experiences disturbances than in a community experiencing frequent or rare disturbances
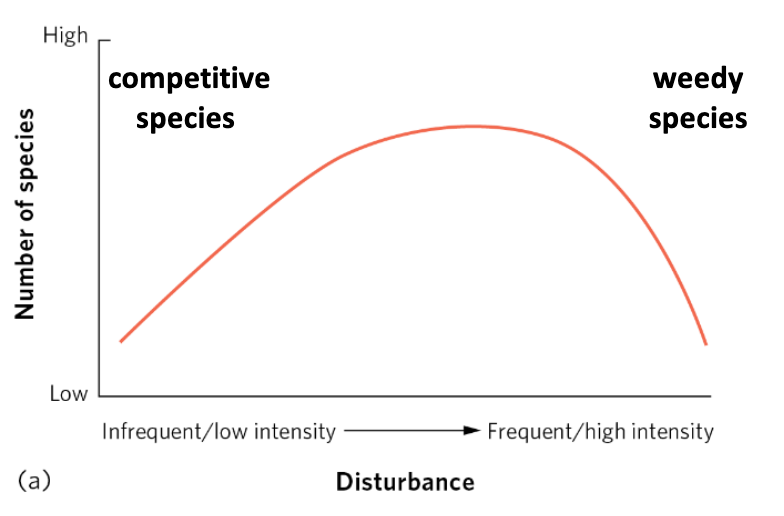
herbivory
Density of snails manipulated to vary intensity of disturbance through ____.
intermediate levels of disturbance
Algal species richness was highest at ____
food webs
Communities are organized into
Food web
A representation of how different species in a community feed on each other

direction of energy
Arrows indicate the ____ movement through the food web.
regulate the abundance
Predation and herbivory are key aspects that ____ of different species in communities
Direct effect
An interaction between two species that does not involve other species
Fish prey on larval dragonflies (-)
Dragonflies feed on bees (-)
Bees pollinate flowers (+)
Indirect effect
An interaction between two species that involves one or more intermediate species
indirectly
Fish reduce the population of dragonflies allowing higher population of pollinators. Fish ____ increase the pollination rate of flowers.
no direct effect
Low concentrations of the pesticide Malathion do not harm leopard frog tadpoles meaning there is ____
indirect
Other ____effects through the effects of Malathion on other species in the community include
Malathion reduced zooplankton (-)
Algal bloom of phytoplankton (+)
Shaded out Periphyton (-)
Decreased food for Leopard (-)
Density-mediated indirect effect
An indirect effect caused by changed in the density of an intermediate species
density
Sea stars reduce the ____ of mussels in the intertidal zone. This allows other species like snails to occupy limiting space on the rock
Trait-mediated indirect effect
An indirect effect caused by changes in the traits of an intermediate species
reintroduction of wolves
Trait-mediated indirect effects can be seen through the ____ into Yellowstone National Park
Change in behavior elk
Less browsing in some areas
rebound in tree population
increase in songbird diversity
Trophic cascade
Indirect effects in a community where effects from one trophic level have effects at multiple trophic levels above or below
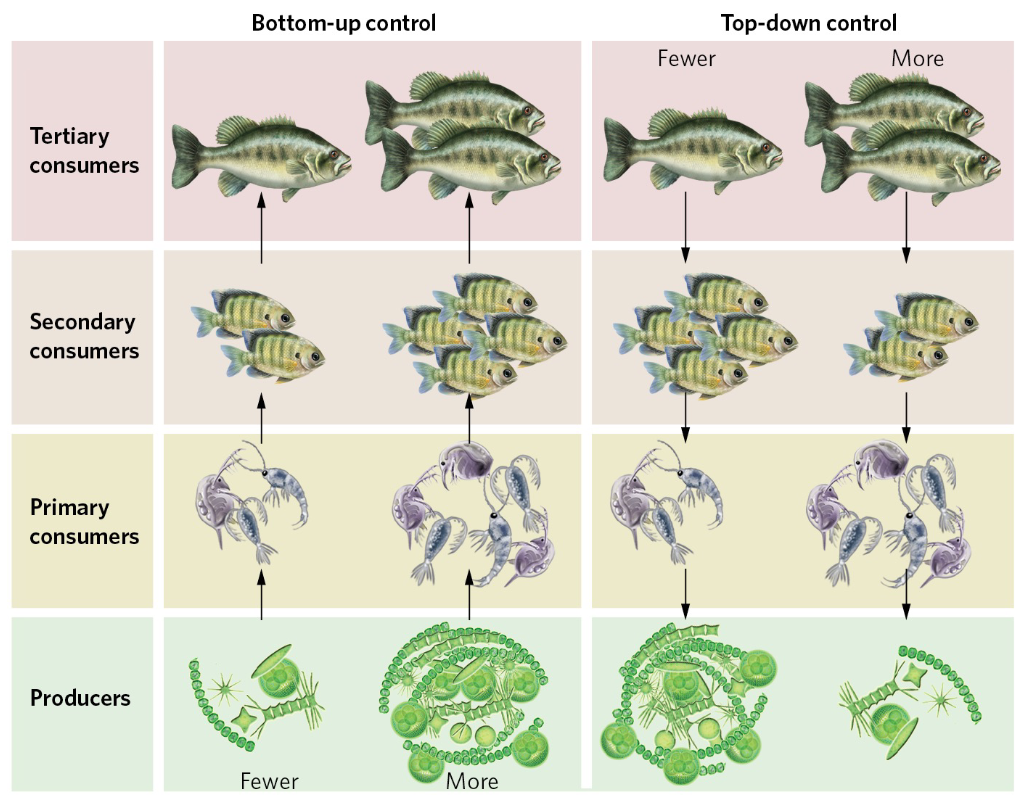
Bottom-up cascade
When the abundances within trophic groups are determined by the amount of energy available from the producers in a community
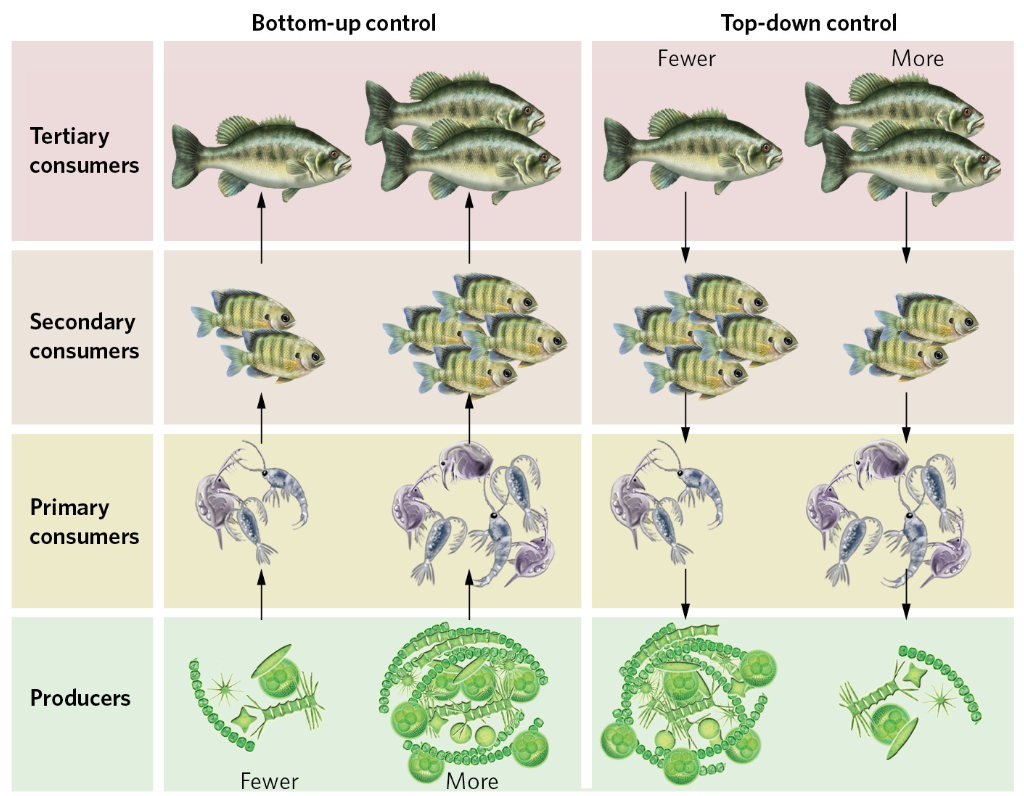
Top-down cascade
When the abundance within trophic groups is determined by the activity of predators at the top of the food web
replace each other over time
Succession occurs in a community when species ____
plant communities
This example of a direct observation of succession shows a diversity of ____
1794: Captain George Vancouver finds 32km wide glacier blocking bay
1879: John Muir finds open water
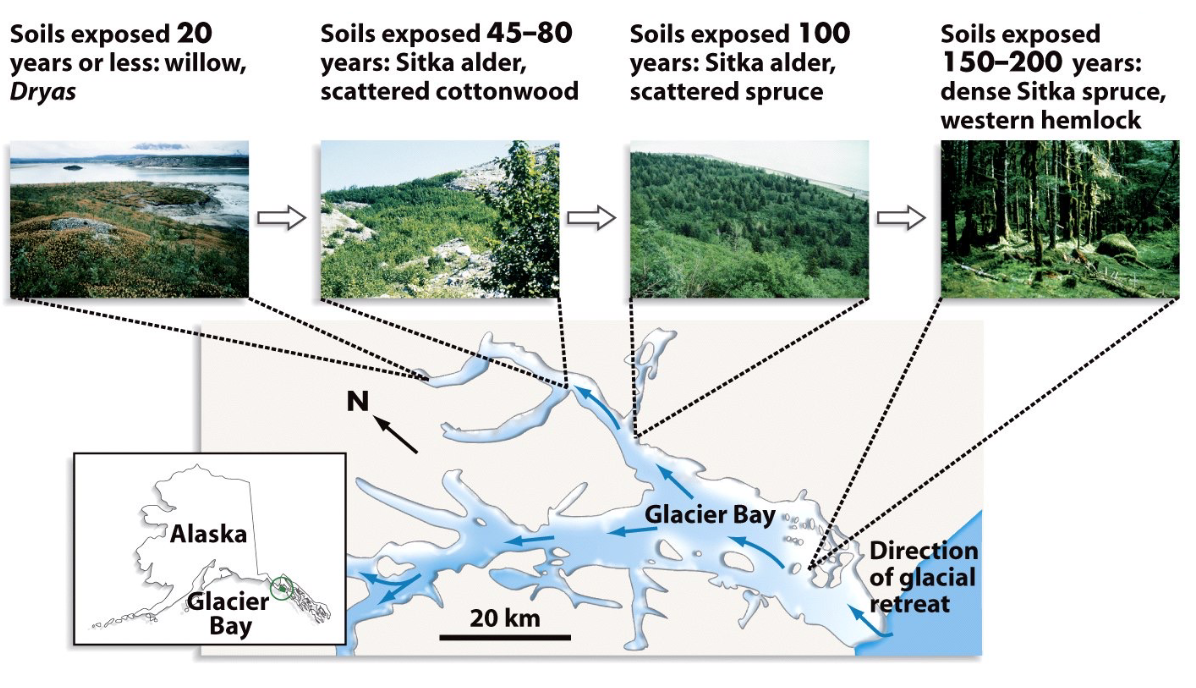
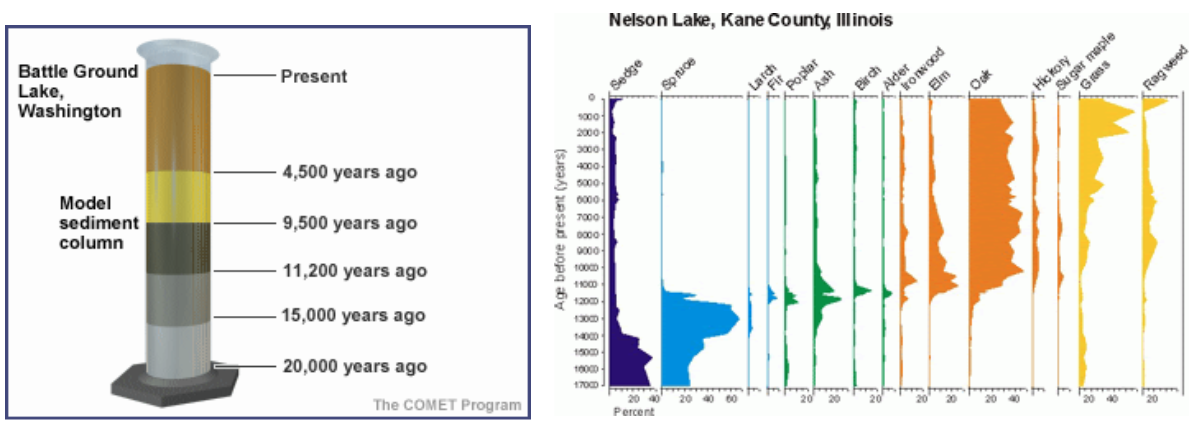
Chronosequence
A sequence of communities that exist over time at a given location
Chronosequence
Sediment cores from lakes:
Yearly accumulation
can identify pollen from specific species to identify past communities
This is an example of ____?
Primary succession
The development of communities in habitats that are initially devoid of plants and organic soil, such as sand dunes, lava flows, and bare rock
mossess, lichens, drought-tolerant grasses
Examples of primary succession include ____. Accumulation of organic material allows further succession
Secondary succession
The development of communities in habitats that have been distributed and include no plants but still contain organic soil
abandoned for various length of times
An example of secondary succession includes former agricultural fields. Duke forest contains farms that were ____

animal communities
Succession is usually described in terms of changes in plant communities. However, changes in plants are typically mirrored by changes in ____
mechanisms
Succession can occur through different ____
Facilitation
A mechanism of succession in which the presence of one species increases the probability that a second species can become stablished
colonize
Early successional species can change the environment in ways that make it easier for later successional species to ____
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Earlier successional plants add organic material to the soil, provide shade etc. One specific example Alder trees host ____ in their roots
Inhibtion
A mechanism of succession in which one species decreases the probability that a second species will become established
further change
Intense competition in climax communities prevents ____ in community structure
Prior effect
When the arrival of one species at a site affects the subsequent colonization of other species
colonization
Ex. of Priority effect: When Bryozoans colonize ocean rocks, they can prevent further ____ by sponges, tunicates, etc.
Tolerance
A mechanism of succession in which the probability that a species can become established depends on its dispersal ability and its ability to persist under the physical conditions of the environments
low nutrients, and intense sunlight
Early successional plant species are tolerant of ____
shade and competition
Late successional plant species are tolerant of ____
tolerance; inhibition
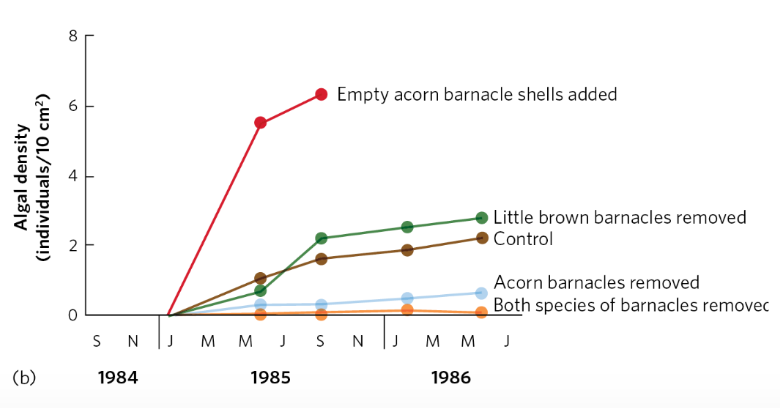
Scrape intertidal zone rocks clean and document pattern of succession
Little brown barnacles initially colonize (____)
Eventually outcompeted by acorn barnacles (____)
facilitate
(Test of succession results)
removing little brown barnacles had little effect
removing acorn barnacles resulted in much less algal growth
providing acorn barnacle shells increased algal growth
Acorn barnacles ____ the growth of algae by providing structure for algae to grow
permanent single climax
Succession does not always produce a ____ community
frequency + density + basal area
Old growth forest in PA. Understory (younger) tree community predicts what the canopy will look like in the future. Oak, Hickory, tulip poplar being replaced by species tolerant of shade and deer browsing like beech.
Importance value: ____

Transient climax community
A climax community that is not persistent
permanent establishment
Frequent disturbance may prevent ____ of a climax community
Vernal ponds dry up for part of the year. Succession restarts each spring when water returns