rutgers: macro exam 1
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
market
a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
trade-off
an alternative that we sacrifice when we make a decision
centrally planned economy
an economy in which the government decides how economic resources will be allocated
market economy
an economy in which the decisions of households and firms interacting in markets allocate economic resources
mixed economy
An economy in which most economic decisions result from the interaction of buyers and sellers in markets but in which the government plays a significant role in the allocation of resources.
productive efficiency
a situation in which a good or service is produced at the lowest possible cost
allocative efficiency
A state of the economy in which production is in accordance with consumer preferences; in particular, every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a marginal benefit to society equal to the marginal cost of producing it
voluntary exchange
a situation that occurs in markets when both the buyer and the seller of a product are made better off by the transaction
equity
the fair distribution of economic benefits
economic variable
something measurable that can have different values, such as the incomes of doctors
positive analysis
analysis concerned with what is
normative analysis
analysis concerned with what ought to be
micro
the study of how households and firms make choices, interact in markets, and how the government attempts to influence their choices
macro
the study of the economy as a whole
voluntary exchange
a situation that occurs in markets when both the buyer and the seller of a product are made better off by the transaction
scarcity
A situation in which unlimited wants exceed the limited resources available to fulfill those wants
Production possibility frontier
Curve showing maximum attainable combinations of two goods
Opportunity cost
Highest-valued alternative given up for an activity
Economic growth
Increase in production of goods and services
Absolute advantage
Ability to produce more than competitors with same resources
Comparative advantage
Ability to produce at lower opportunity cost than competitors
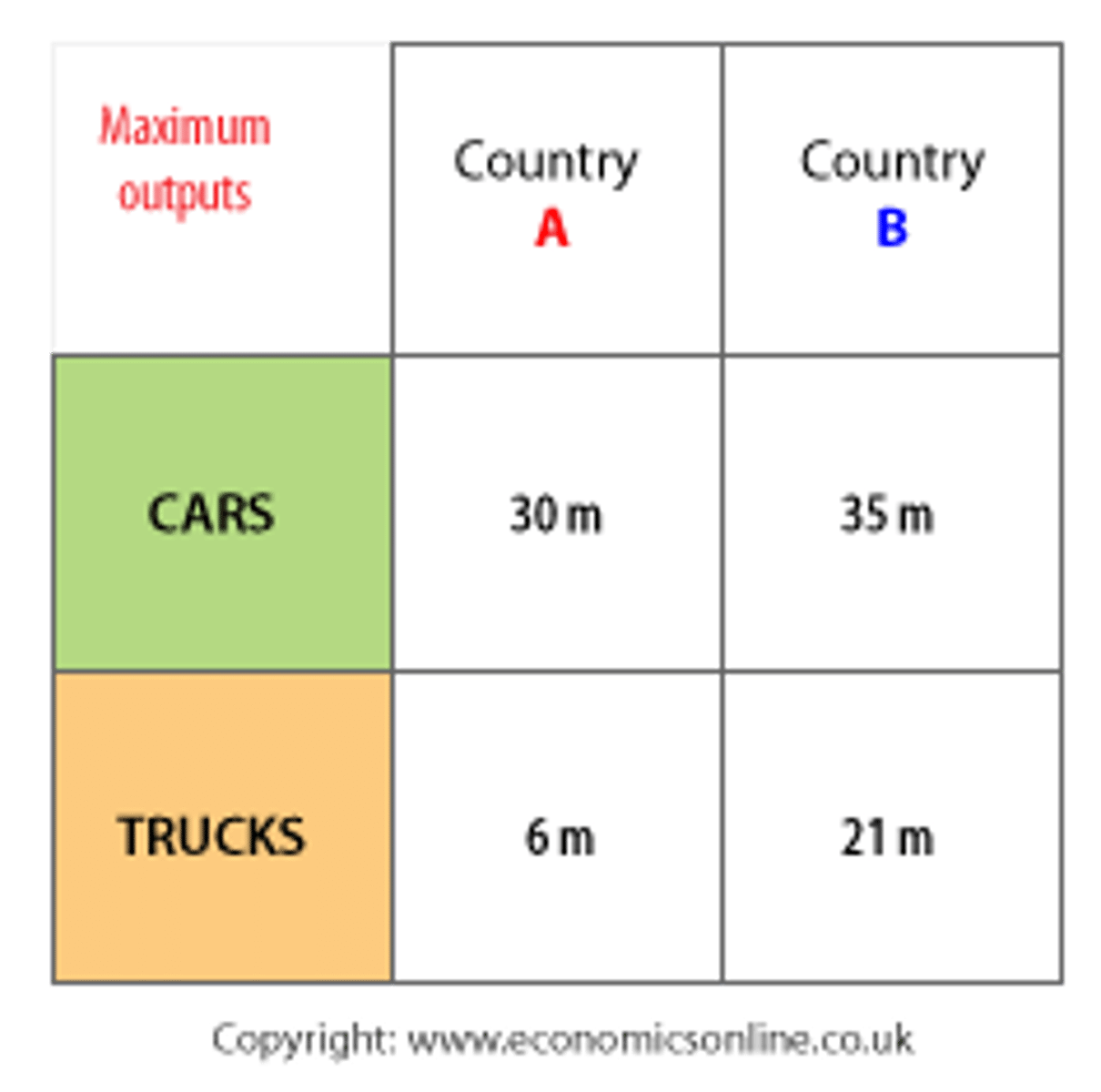
Trade
Act of buying and selling

Market
Group of buyers and sellers of a good or service
Households
Individuals providing factors of production
Factor markets
Markets where households sell factors of production
Firms
Supply goods and services to product markets
Labor
All types of work
Capital
Physical assets used to produce goods
Natural resources
Land, water, raw materials
Entrepreneur
Someone who operates a business
Entrepreneurial ability
Ability to bring factors of production together
Circular flow diagram
Model illustrating market participants and links
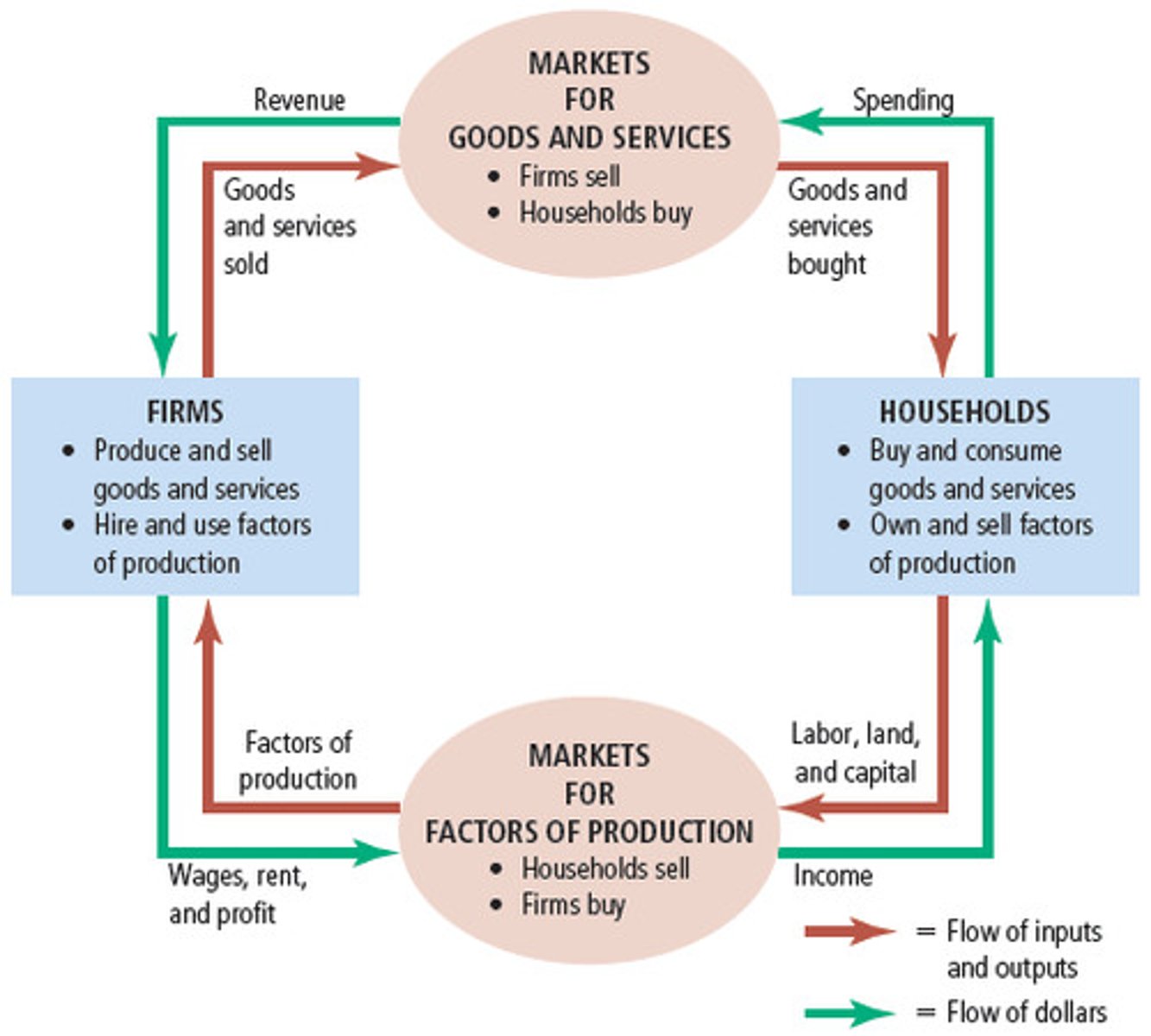
What do households provide to firms?
Factors of production
What do firms provide to households?
Goods and services
What do firms pay to households?
Money for factors of production
What do households pay to firms?
Money for goods and services
What is a free market?
A market with few government restrictions
What are property rights?
Rights to exclusive use of property
What is a demand schedule?
Table showing price and quantity demanded relationship
What is a demand curve?
Curve showing price and quantity demanded relationship
What does ceteris paribus mean?
All else equal
What is quantity demanded?
Amount of a good or service a consumer is willing and able to purchase at a given price
What is the law of demand?
As price falls, quantity demanded increases and vice versa
What are the two effects when the price of a good falls?
Substitution effect and increase in purchasing power
What is the substitution effect?
Change in quantity demanded due to price change relative to other goods
What is the income effect?
Change in quantity demanded due to change in purchasing power
What is the relationship between price and quantity demanded?
Inverse relationship
What is the law of supply?
As price rises, quantity supplied increases and vice versa
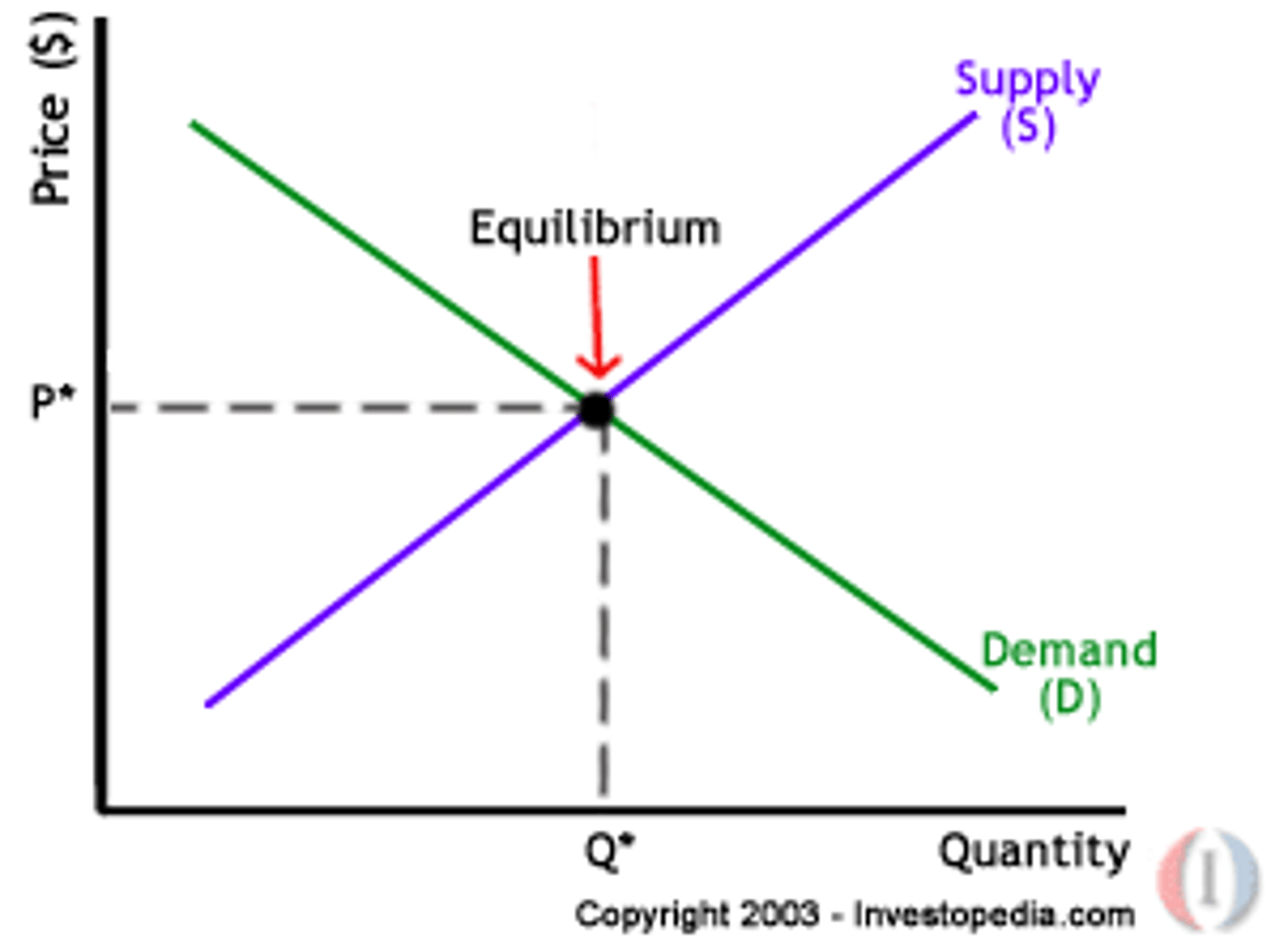
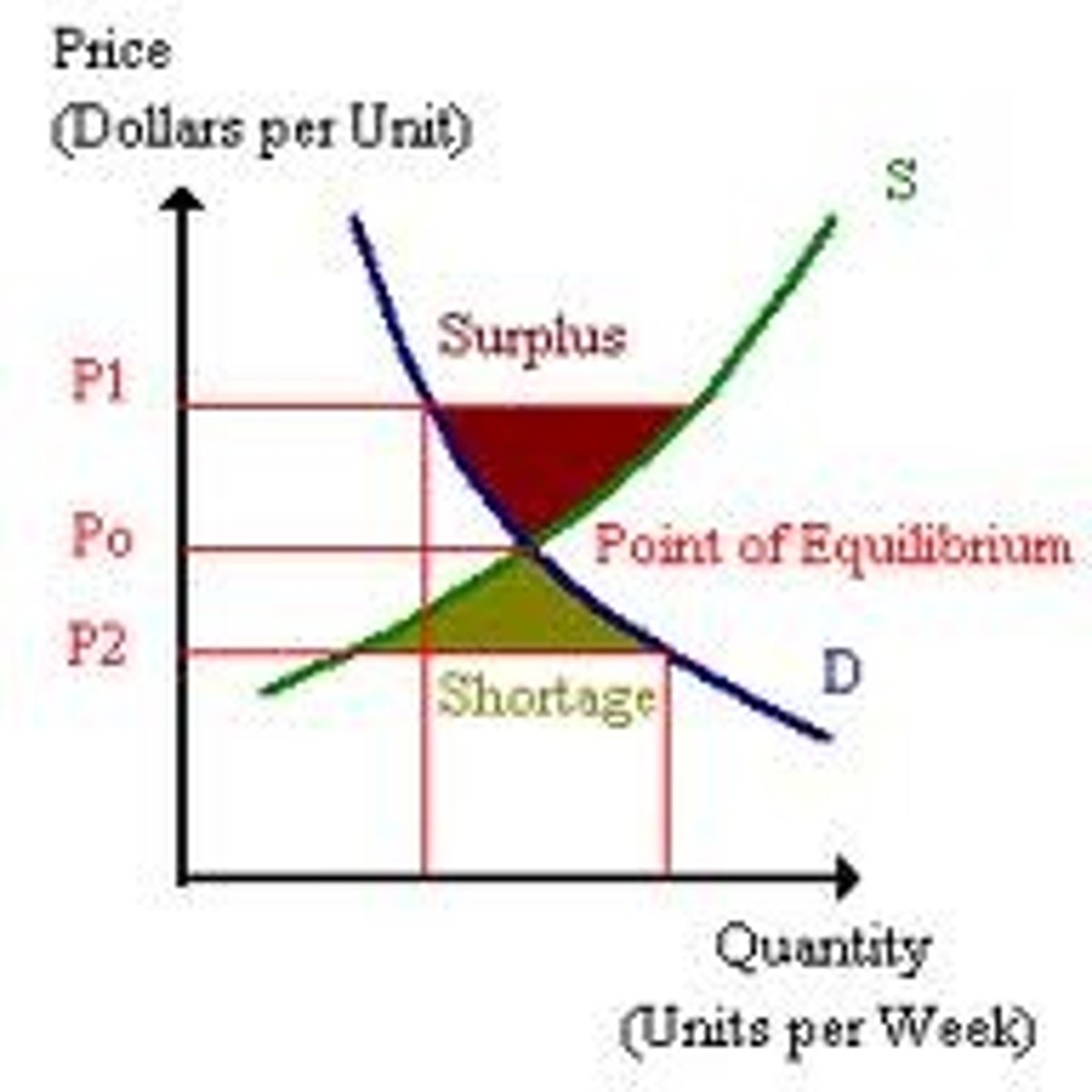
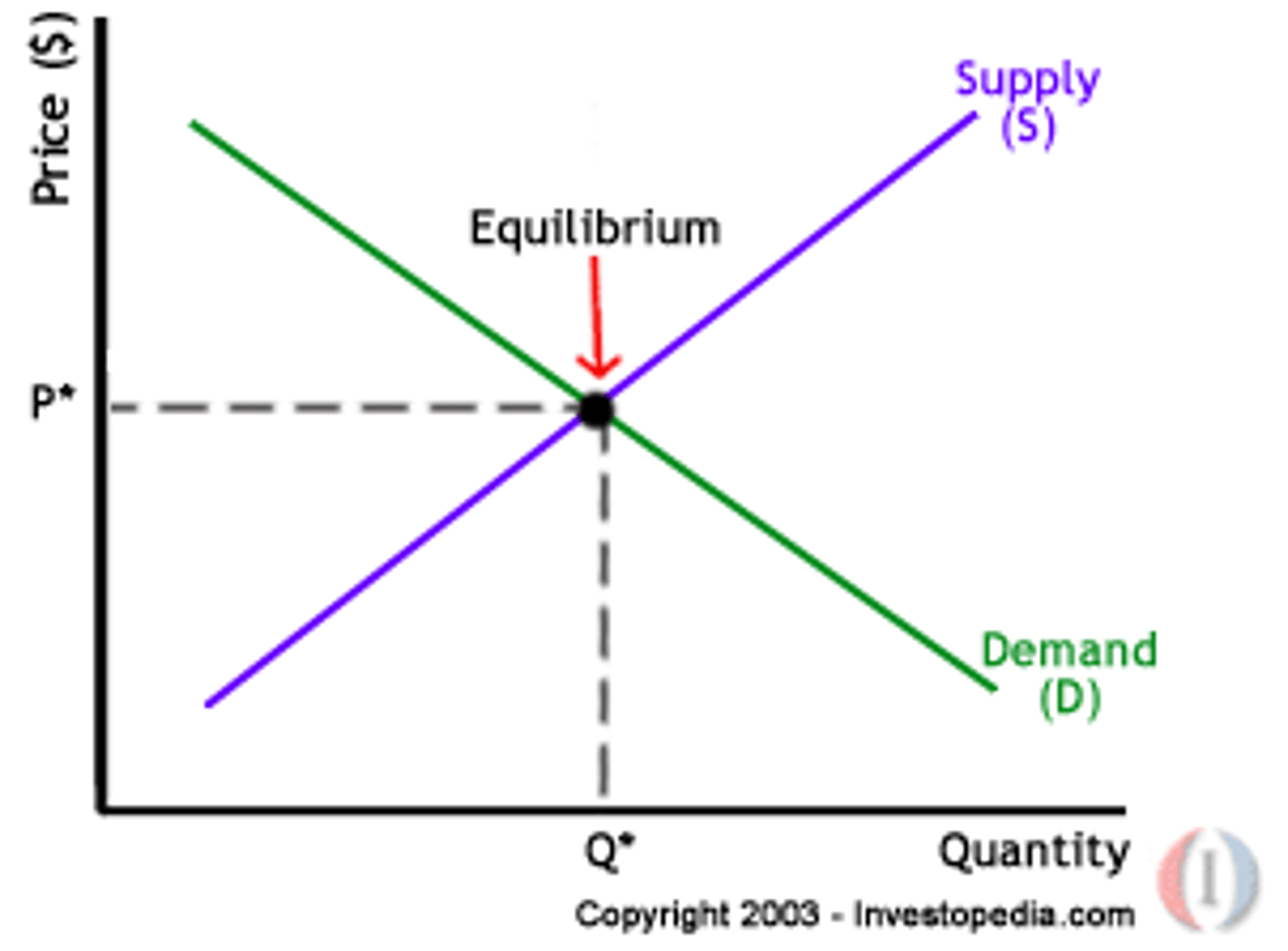
What is the equilibrium price?
Price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
What is a surplus?
Excess supply
What is a shortage?
Excess demand
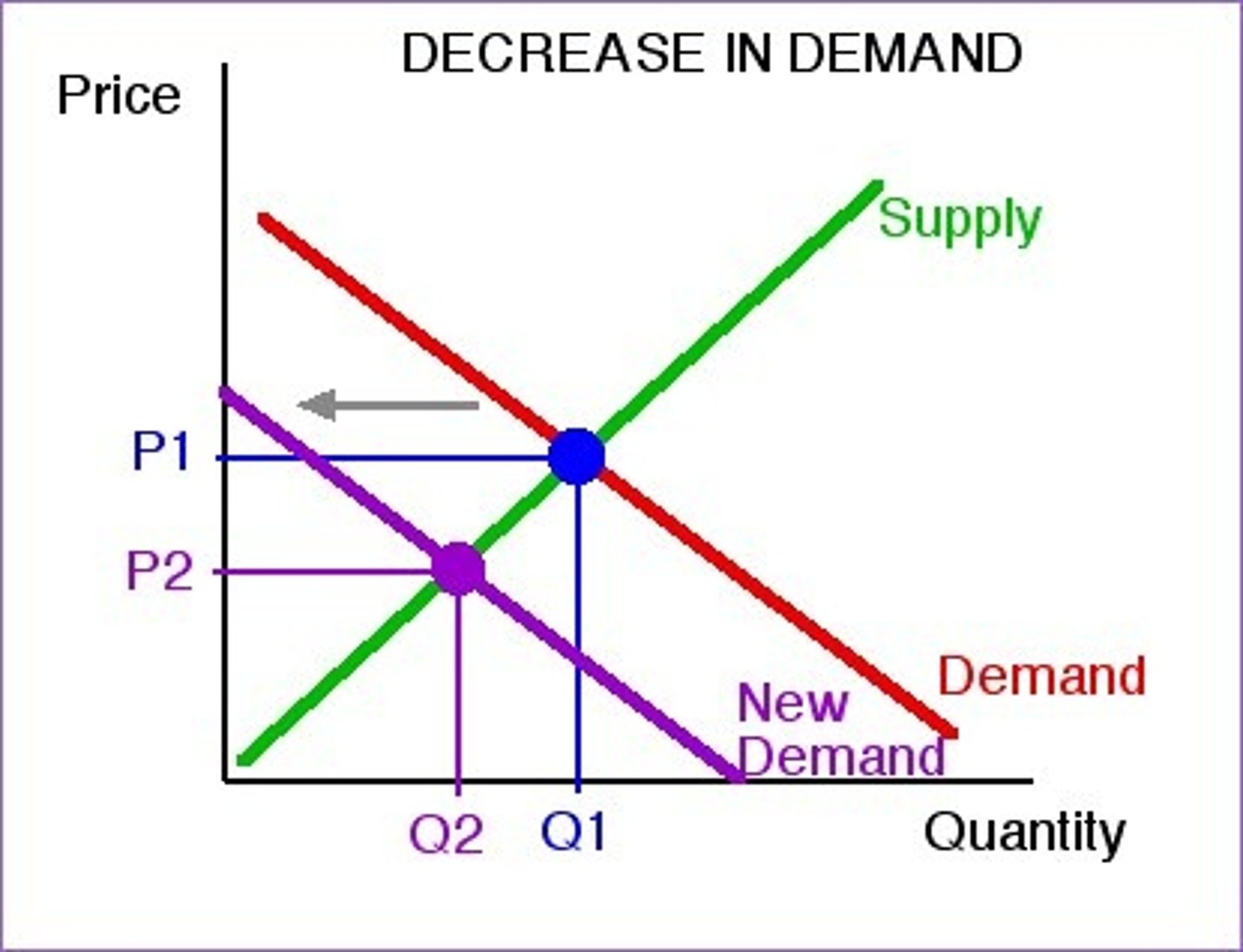
What is a shift to the left in demand?
DECREASE in demand
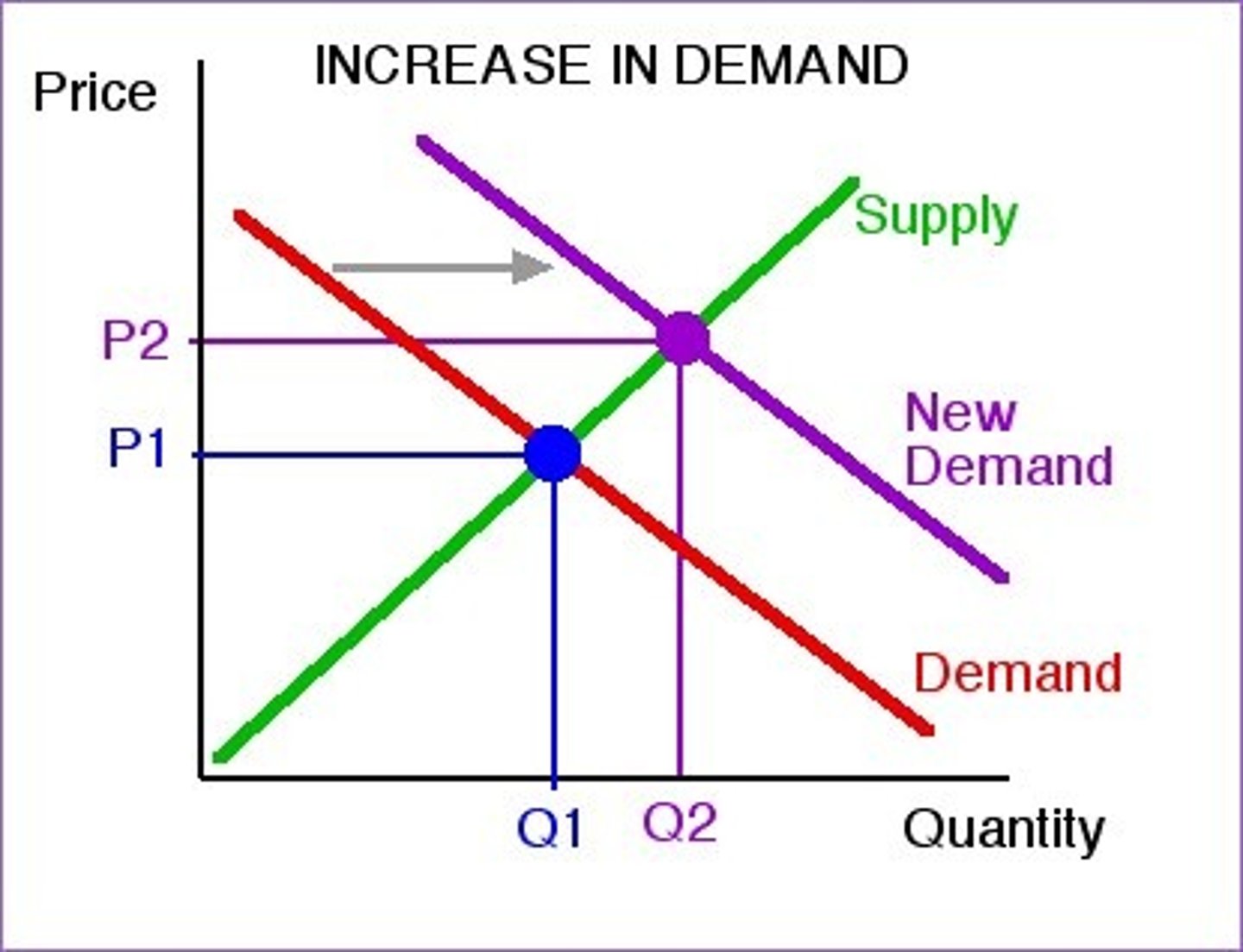
What is a shift to the right in demand?
INCREASE in demand
What are normal goods?
Goods for which demand increases as income rises and decreases as income falls
Give examples of normal goods.
Clothes, restaurant meals, vacations
What are inferior goods?
Goods for which demand increases as income falls and decreases as income rises
Give examples of inferior goods.
Second-hand clothes, ramen
What are substitutes?
Goods and services that can be used for the same purpose
Give examples of substitutes.
Big Mac and Whopper, Ford F-150 and Dodge Ram, Jeans and Khakis
What are compliments?
Goods and services that are used together
Give examples of compliments.
Big Mac and fries, Hot dogs and hot dog buns, Left shoes and right shoes
What are demographics?
Characteristics of the population with respect to age, race, and gender
What happens to demand during a natural disaster or pandemic?
Consumers buy less of most goods but more of few goods
Give an example of a natural disaster or pandemic affecting demand.
COVID-19 pandemic reduced the demand for goods that required people gathering (restaurants, concert tickets, etc.) but increased the demand for computing equipment to work from home
What is a supply schedule?
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied
What is a supply curve?
A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied
What is quantity supplied?
The amount of a good or service that a firm is willing and able to supply at a given price
What is the law of supply?
A rule that states that, holding everything else constant, increases in price cause increases in the quantity supplied, and decreases in price cause decreases in the quantity supplied
What are some variables that can shift market supply?
Prices of inputs, technological change, prices of related goods in production, number of firms in the market, expected future prices, natural disasters and pandemics
What is market equilibrium?
Quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
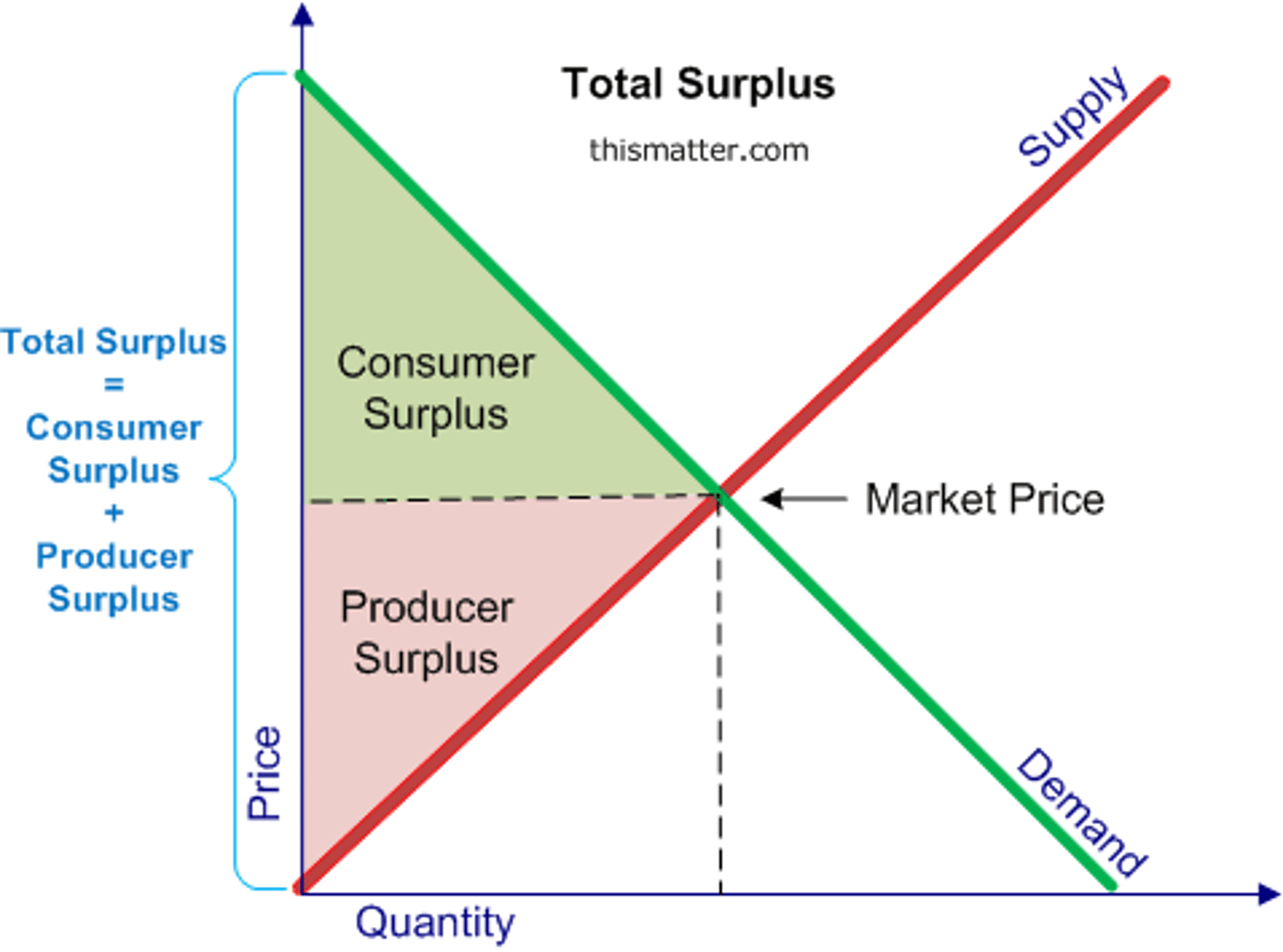
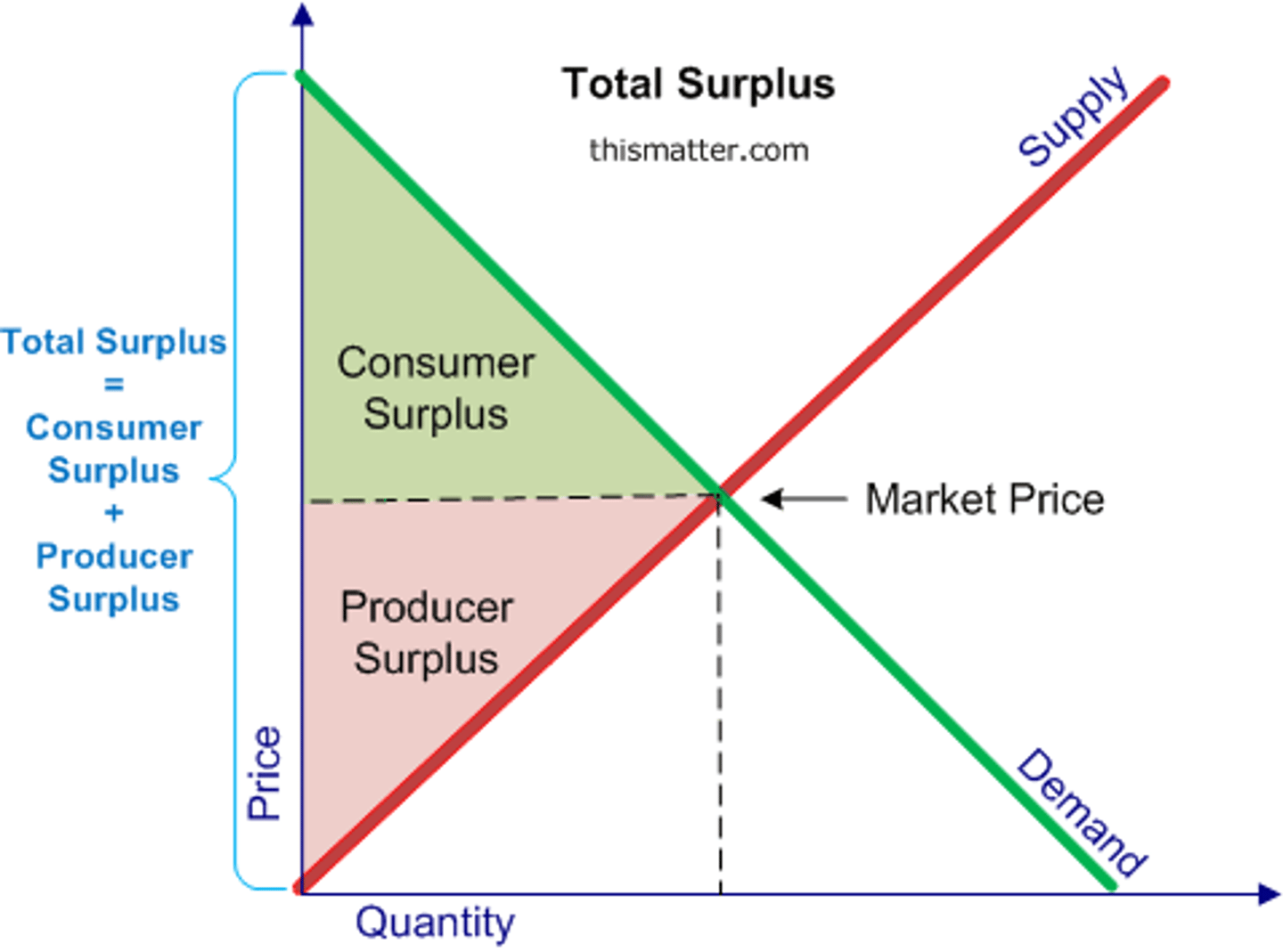
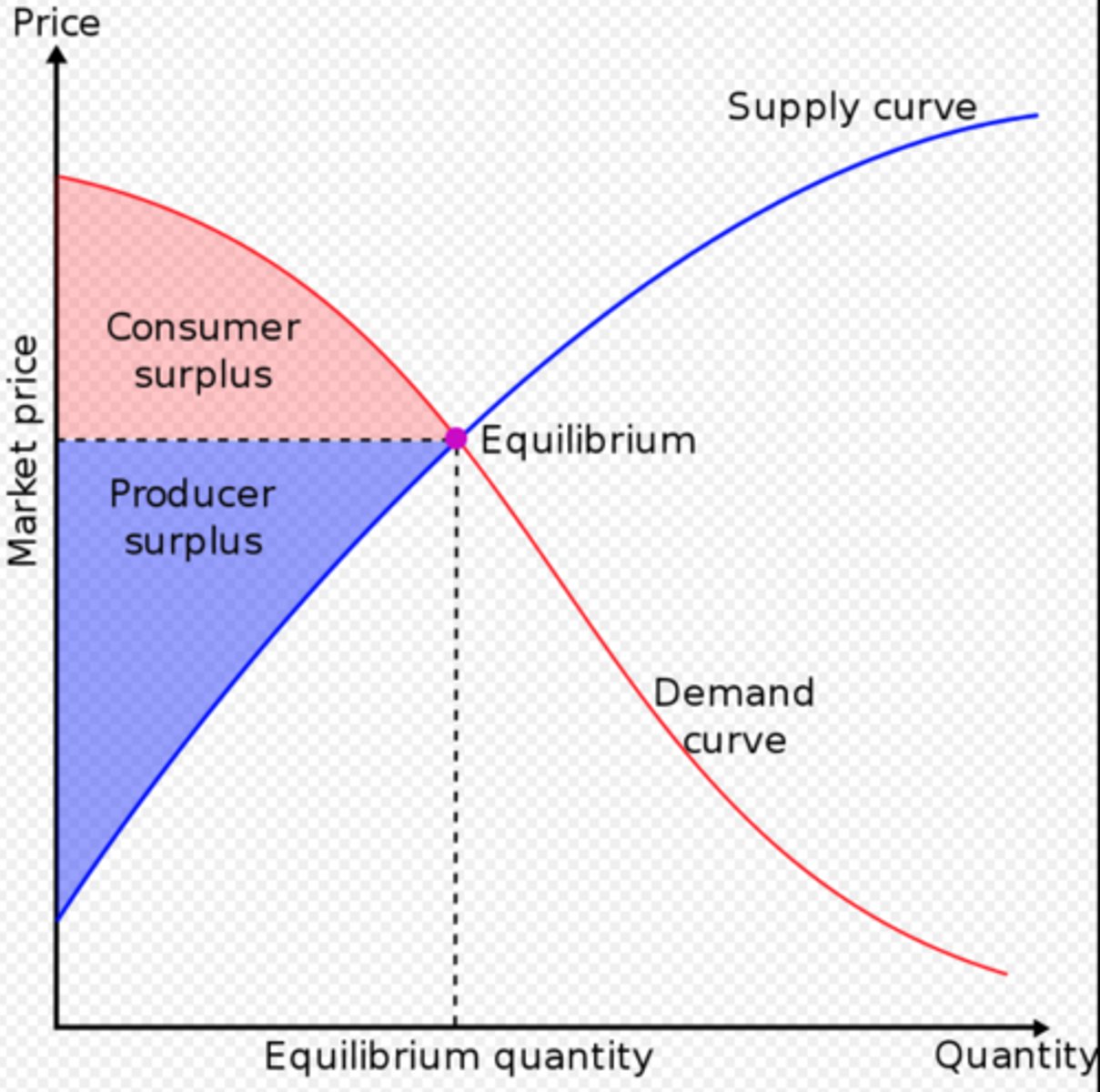
Define consumer surplus.
Difference between highest price consumer is willing to pay and actual price paid.
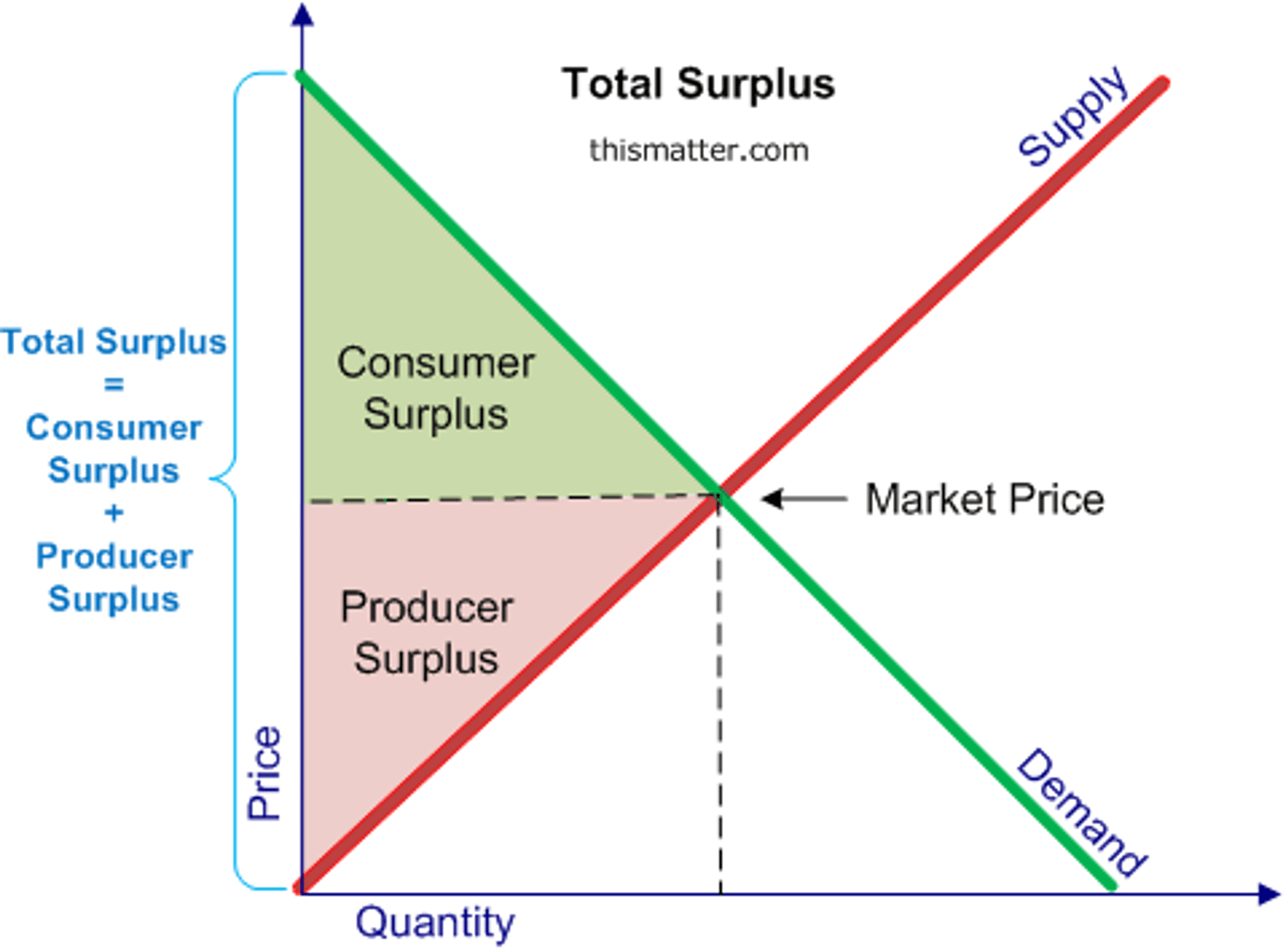
Define producer surplus.
Difference between lowest price a firm would accept and actual price received.
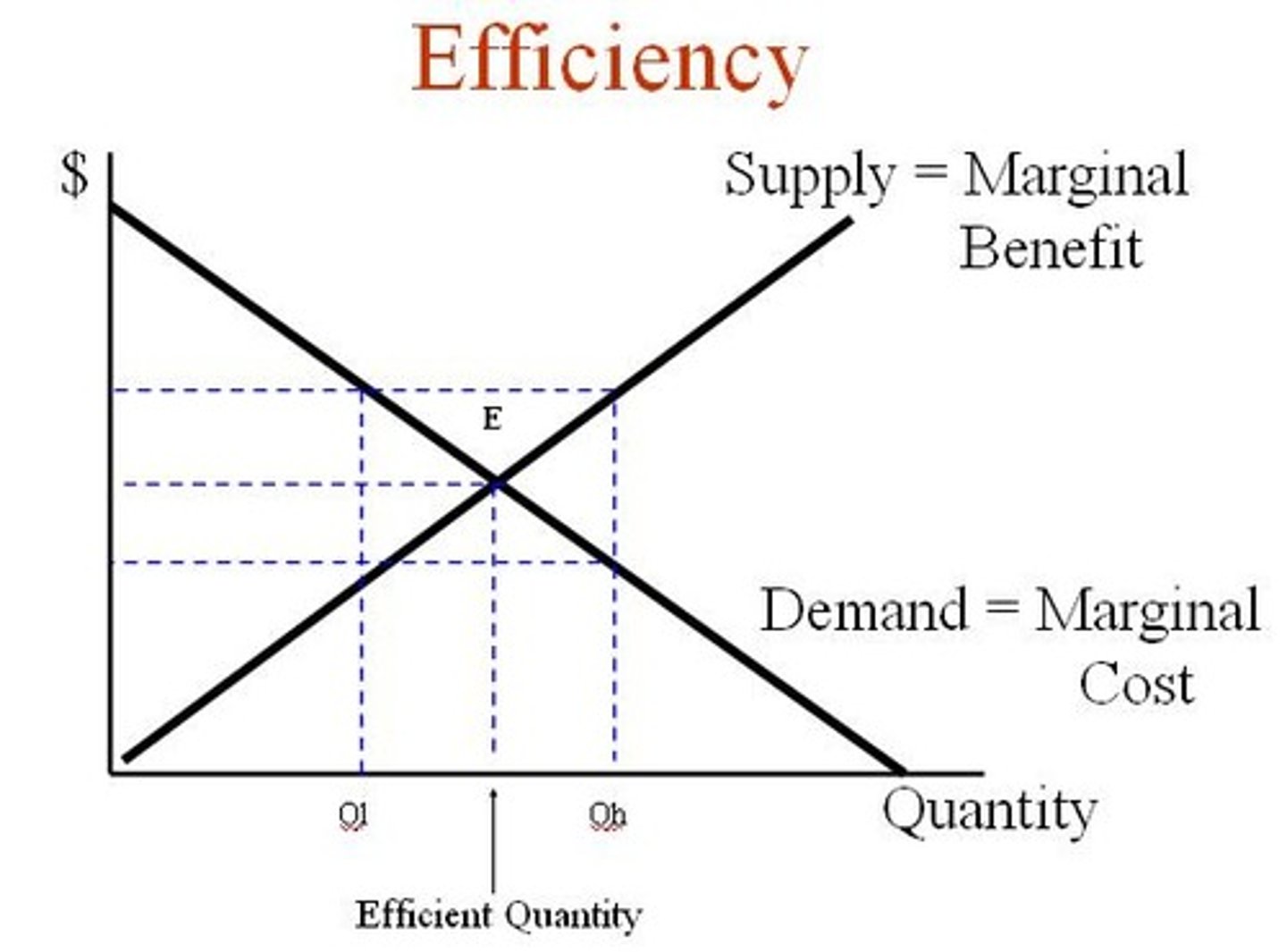
What is marginal benefit?
Additional benefit to a consumer from consuming one more unit.
How is consumer surplus measured?
By calculating the net benefit of consumers at a given price.
What is the effect of a price decrease on consumer surplus?
It increases consumer surplus.
What is the marginal cost?
Additional cost to a firm of producing one more unit.
What is the producer surplus for Heavenly Tea?
$0.75 on the first cup, $0.50 on the second cup, and $0.25 on the third cup.
How is total producer surplus calculated?
By adding up individual producer surplus on every unit sold.
What does consumer surplus measure?
Net benefit to consumers from participating in a market.
What does producer surplus measure?
Net benefit received by producers from participating in a market.
When is a market considered efficient?
When all trades have marginal benefit exceeding marginal cost.
What is economic surplus?
Sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
What is the net benefit for Theresa when the price of tea is $3.50?
$2.50
What is the net benefit for Tom when the price of tea is $3.50?
$1.50
What is the net benefit for Terri when the price of tea is $3.50?
$0.50
What happens to consumer surplus when the price of tea falls to $3.00?
Theresa, Tom, and Terri gain an additional $0.50 of consumer surplus.
What is the market price of tea for Heavenly Tea?
$2.00
What is the total producer surplus for Heavenly Tea?
The sum of the individual producer surplus on every cup sold.
What does the total producer surplus represent?
The area above the supply curve and below the market price.
What is economic efficiency?
Market outcome where marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
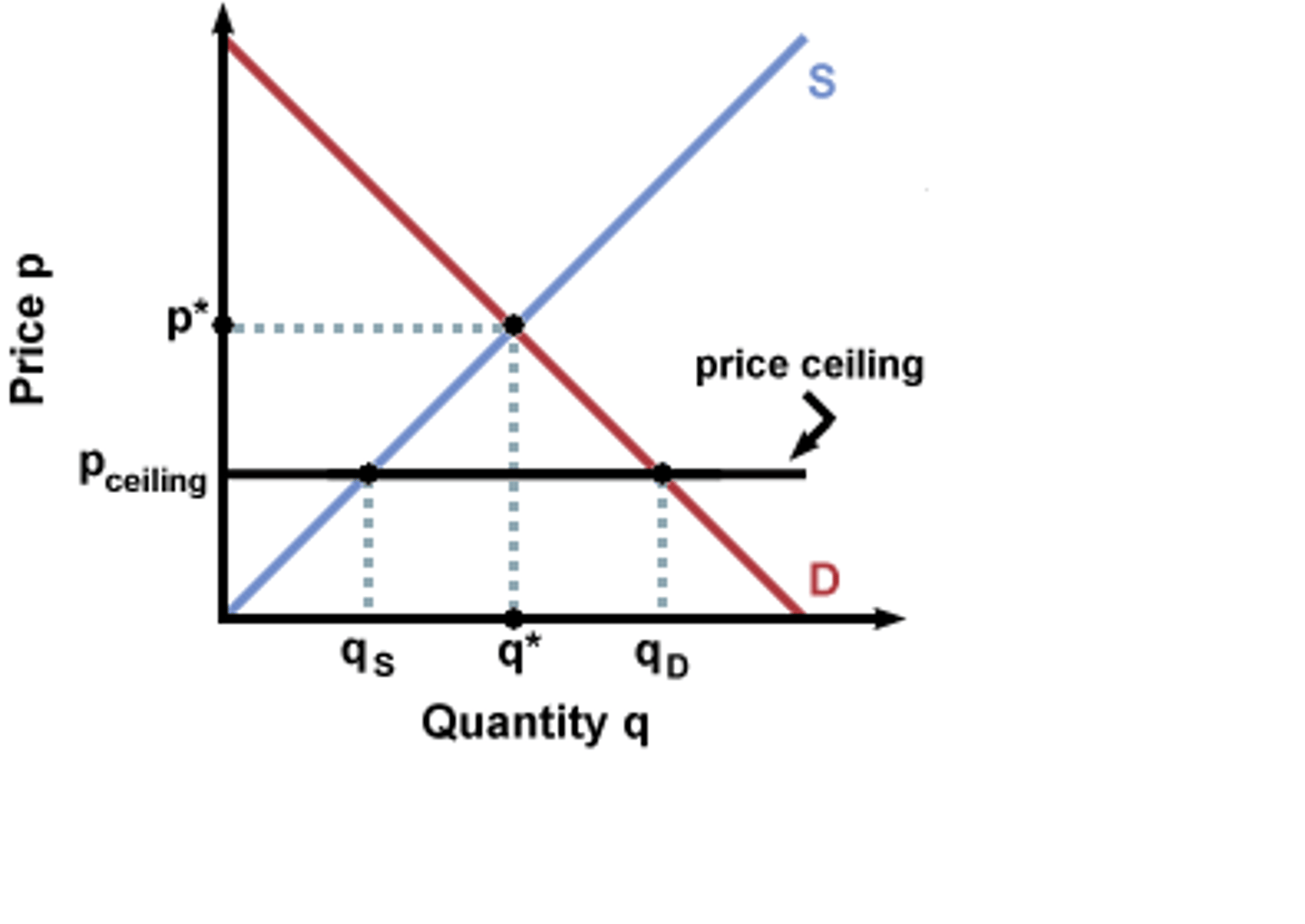
Define price ceiling.
Legally determined maximum price that sellers can charge.
What is a price floor?
Legally determined minimum price that sellers may receive.
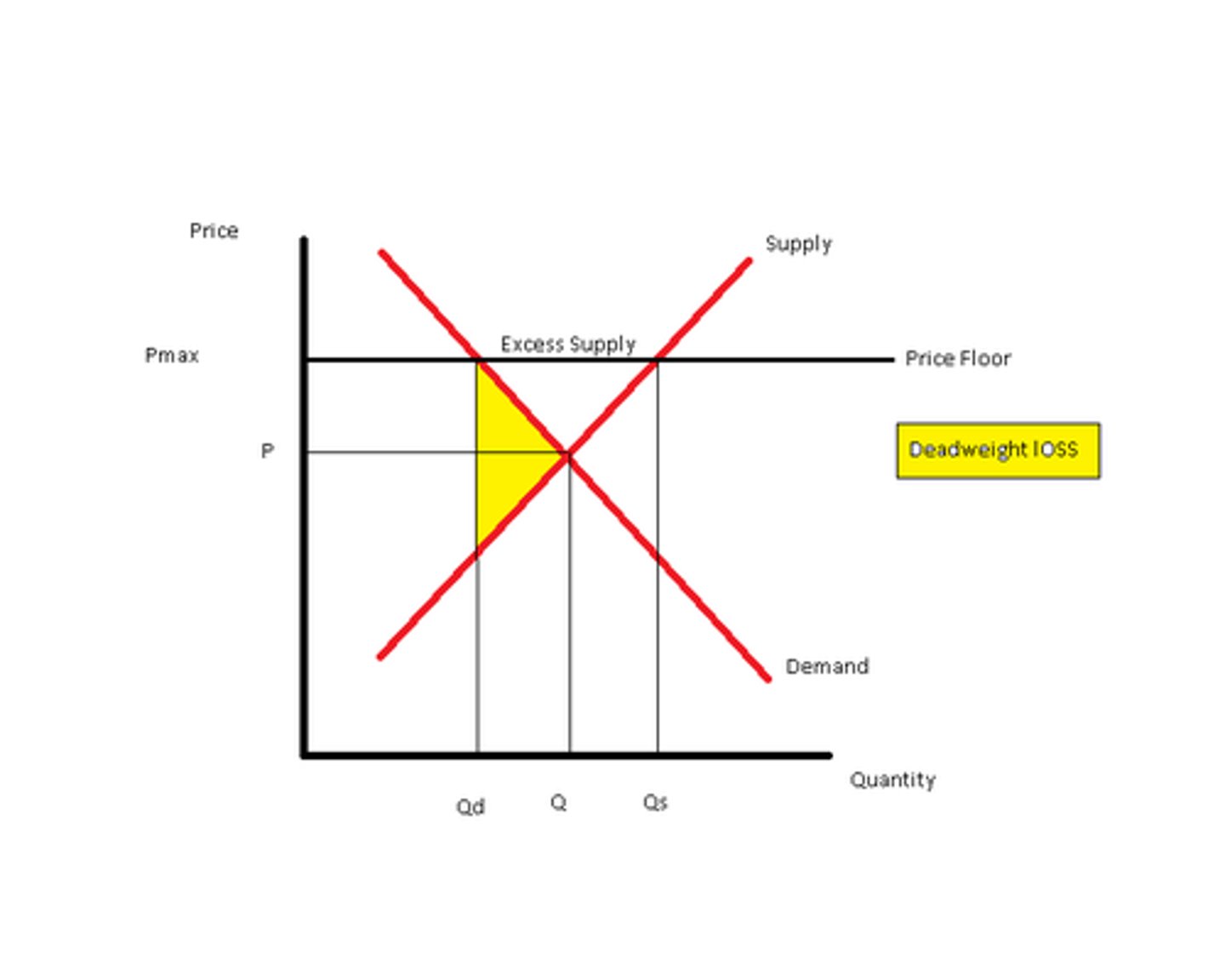
Give examples of price controls.
Minimum wage, rent controls, agricultural price controls.
What is a sole proprietorship?
A firm owned by one person and not organized as a corporation.
Define partnership.
A firm owned by two or more persons and not organized as a corporation.
What is a corporation?
A legal form of business that provides owners with limited liability.
Define asset.
Anything of value owned by a person or firm.
What is limited liability?
Legal provision that shields owners from losing more than their investment.
What is a tariff?
Tax imposed by a government on imports.
What are imports?
Goods and services bought domestically but produced in other countries.