Salivary Glands
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the salivary and lacrimal glands, their function, and innervation, based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
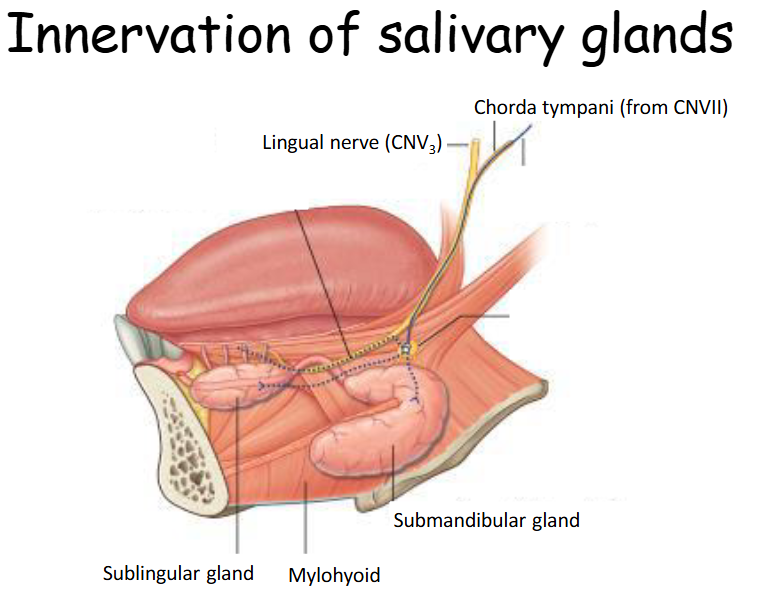
Sublingual Gland
Located under the tongue, lies in the floor of the oral cavity and found above the mylohyoid muscle.
Submandibular Gland
Located partially in the submandibular anterior triangle of the neck, and partially in the oral cavity proper by wrapping around the mylohyoid muscle.
Functions of Saliva
Lubricate food, Keep everything moist, Mouthwash, Digestion (contains amylase which digests starch).
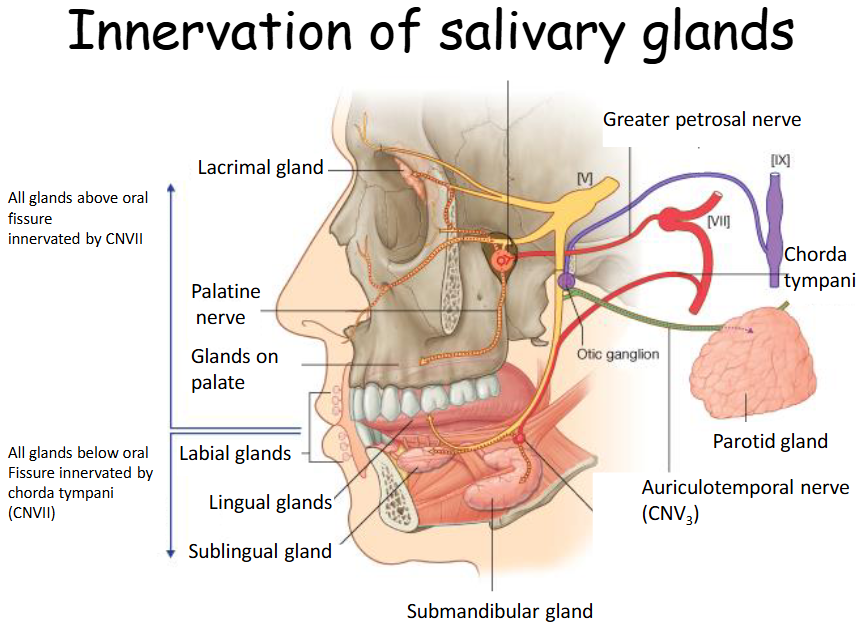
Chorda Tympani (from CNVII)
Innervates the sublingular and submandibular glands.
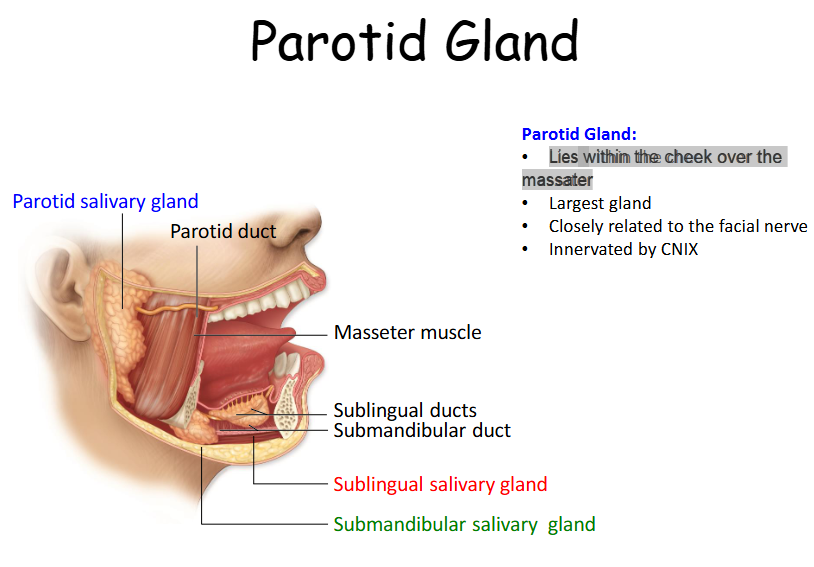
Parotid Gland
Largest gland, Lies within the cheek over the masseter, Closely associated with the facial nerve.
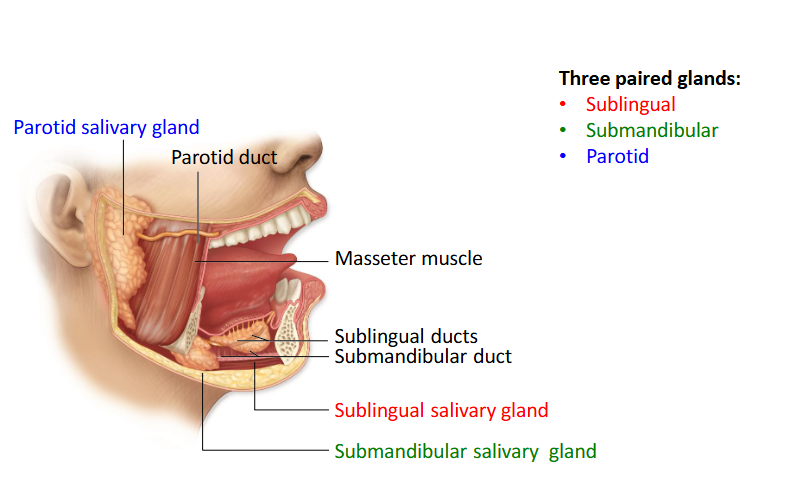
Parotid Duct
Takes saliva to the oral cavity by piercing the buccinator and enters the oral cavity via an opening that lies next to the 2nd molar tooth.
Chorda Tympani (CN VII)
Supplies the sublingual and submandibular glands.
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Supplies the parotid gland.
What are the 3 paired glands?
The three paired salivary glands are the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
What is the function of the glands?
• Lubricate food
• Keep everything most
• Mouthwash – chewing gum
• Digestion contains amylase
– digests starch
What is the innervation of the salivary gland?
Where is the parotid gland?
Lies within the cheek over the masseter
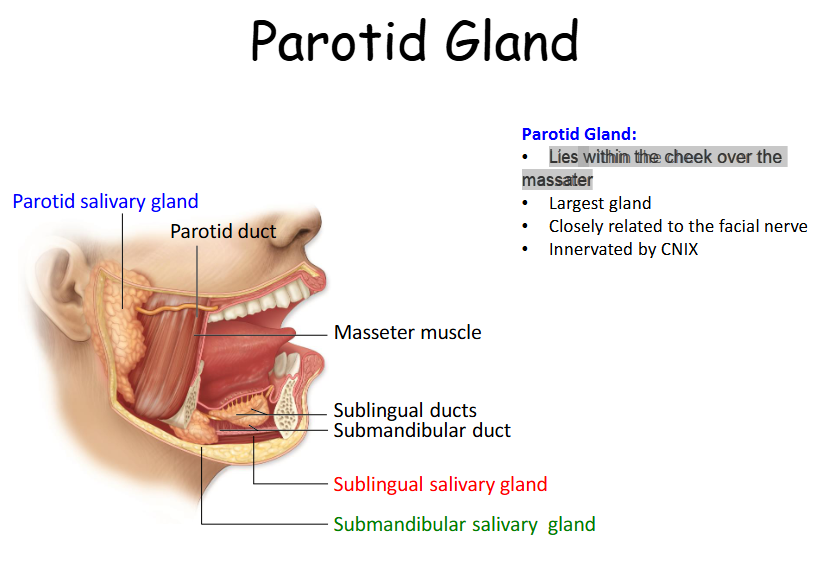
What innervates the parotid gland?
Innervated by CNIX
Is the parotid the largest gland?
Yes, it is the largest salivary gland.
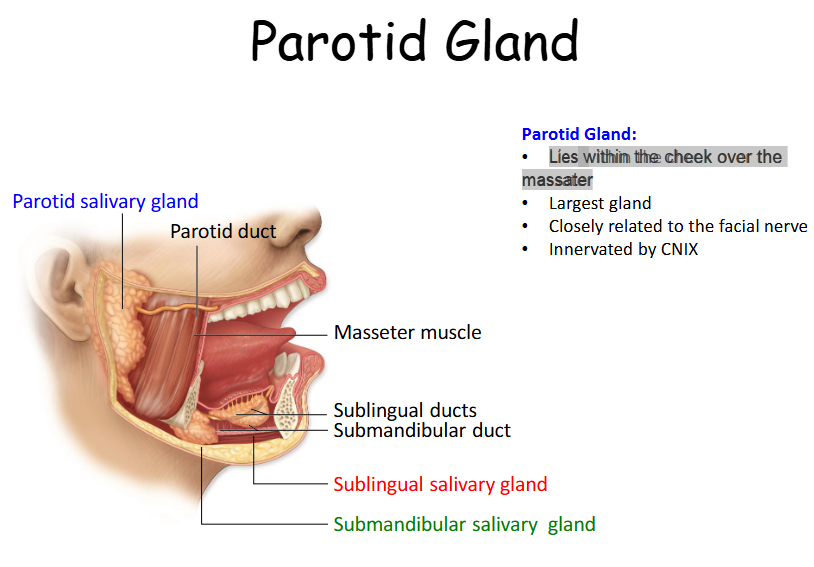
How does the parotid gland transfer saliva?
Not located within the oral cavity so it has a parotid duct that takes the saliva to the oral cavity by piecing the buccinator and enters the oral cavity via opening that lies next to the 2nd molar tooth
What is the innervation of the salivary glands?