Chem Unit 4: Bonding
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
its 5/7 do we think ill make it....I hate bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
IB definition of Ionic Bonds
The electrostatic attraction experienced between the electric charges of a cation and an anion
Ionic bonds usually consist of a…
Metal and nonmetal
What’s the overall charge of an ionic compound?
always ZERO
What are lattice structures
3-D repeating units of + and - ions
What’s the structure of an ionic compound? (IB)
Lattice AND repeating units of + and -
Ionic bonds are ….
Strong! because their attraction is equal in all directions
What is lattice Enthalpy
The energy required to overcome the electrostatic forces of attraction holding ions together in the lattice (section 16)
When the ionic charge is greater, the lattice enthalpy is…
greater
How are the melting/boiling points of ionic compounds? why?
HIGH because they are strong bonds.
Solubility of ionic compounds?
Soluble in water bc the partial charges in H2O are attracted to ions in the lattice.
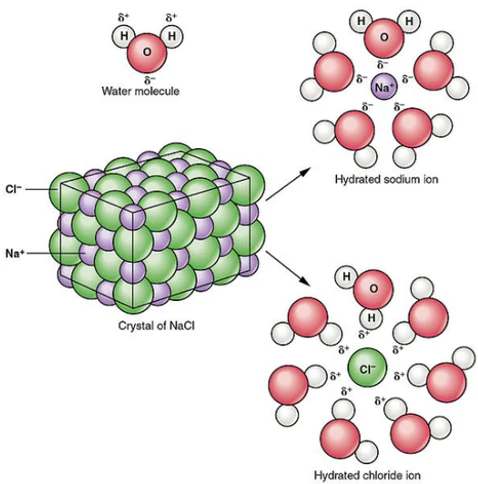
What is a “hydrated” ion
when ions get pulled out of the lattice and become surrounded by water molecules (in a solution with water)
Explain Conduction of ionic compounds
Cannot conduct as solids since particles stay in place.
Can conduct when in liquid/ dissolved in water because ions are free to move.
Electronegativity Difference
if its more than 1.8, its probably ionic. (Section 9)
When the electronegativity difference between 2 atoms is higher, then
it shows more ionic qualitiesand indicates that the bond formed is likely ionic.
The more polar it gets.
What are covalent bonds made of
two non-metals
What is a covalent bond, IB definition
The electrostatic attraction between a pair of e and positively charged nuclei
Covalently bonded compounds are also called…
MOLECULES
Which atom has a greater pulling of the electrons when covalently bonded?
the one with the larger electronegativity value
Diapoles
Atom with a higher electronegativity will be slightly negative
Atom with a smaller electronegativity will be slightly positive
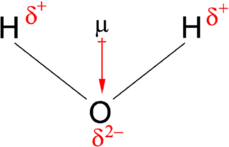
What are the types of covalent bonds?
Non-polar and Pure covalent
what are TRULY nonpolar bonds
the BrINClHOFs, bonding with the same atom.
Molecules of different atoms can be non-polar if
dipoles cancel OR Electron distribution is symmetrical
Bond enthalpy basically…
Bond strength
Longer bonds are weaker or stronger?
weaker
Who are the exceptions to the octet rule
Be and B are electron defficient
Electron Domains
e locations basically
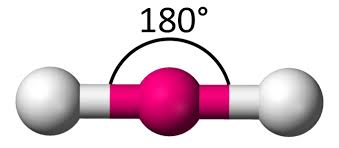
Linear shape for VSEPR.
180 degrees
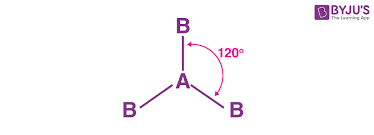
Trigonal Planar for VSEPR: degrees and domains, and what is the main element for the central?
120 degrees. Three e domains. three domains must be bonding pairs. No lone pairs in the central atom, which is usually Boron (B) ( e difficient)
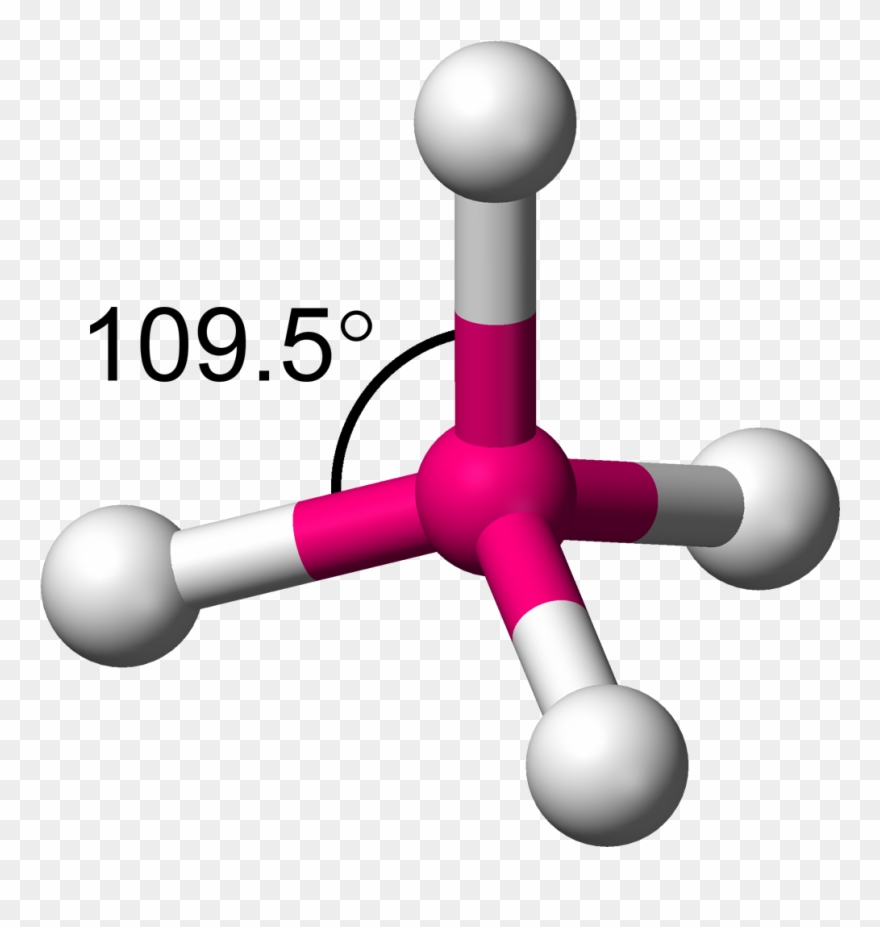
Tetrahedral for VSEPR: # of domains, and degrees
4 domains, 109.5 degrees
CHF3
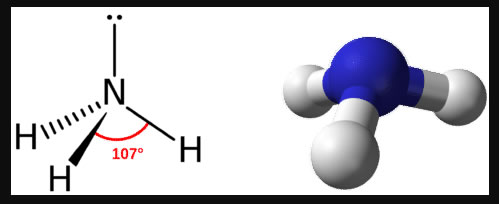
Trigonal Pyramidal for VSEPR, # of domains, # of lone pairs, degrees, usual central atom
four e domains, one lone pair, 107 degrees (adding a lone pair decreases by 2), central atom usually from Group 15
NH3
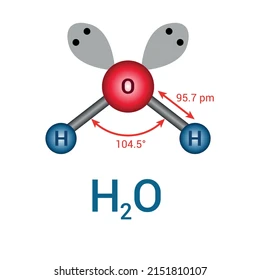
Bent / V-shaped for VSEPR, # of domains, # of lone pairs, degree, and usual central atom
4 domains, 2 lone pairs, 105 degrees (-2 for every lone pair), central atom usually from Group 16.
H2O
Whats a “trick” you use when drawing VSEPR shapes
calculate each atoms # of valence electron, add 1 e for each negative charge.
Divided the total of this by 2.
Draw this, and put [brackets] around it, with charge at top right
![<p>calculate each atoms # of valence electron, add 1 e for each negative charge.</p><p>Divided the total of this by 2.</p><p>Draw this, and put [brackets] around it, with charge at top right</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f5a24a3d-4650-4f12-9316-86af089c4cfd.jpg)
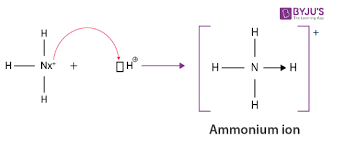
What are coordinate covalent bonds or “dative” covalent bonding
a covalent bond where the electrons in a shared pair originate from the same atom
represented by an arrow
Once formed, its no different than other covalent bonds
Giant Molecular / Macromolecular / Network Covalent Structures
Crystalline structures where atoms are linked by (usually) covalent bonds
Properties are VERY DIFFERENT compared to other covalent molecules: SUPER STRONG, HIGH BP, AND HARD
ex: Diamonds are carbons connected to carbons, and very very very strong

What are allotropes
Different forms of the same element, caused by the element forming different structures (diff properties)
Examples of allotropes of Carbon. why?
Graphite, diamonds, fullerene, graphene.
This is bc carbon can take on different structures.
What types of attractions “hold” molecules together
Intermolecular forces
What are intermolecular forces
The forces that exist between molecules
What are intramolecular forces
Covalent bonds hold atoms together within molecules
London Dispersion Forces
Weak, between non-polar molecules and noble gasses
e are mobile, and they create temporary dipoles
Low mp and bp, bigger molecules have more strength
Greater # of e causes greater probability of the dipoles forming
Dipole Dipole attraction
Between polar molecules, as they have permanent dipoles
Stronger than LDF, so higher mp and bp than London Dispersion forces
Leads to polar solutes being soluble in polar solvents (H2O)

Van der Waals forces
Umbrella term for London dispersion forces and Dipole Dipole attraction
Hydrogen Bonding
strong intermolecular force.
Only H to [FON (holds the e more closely)] because of this, the H have a positive nucleus, therefore creating strong dipole-dipole attraction with lone pairs
(if the tests asks u for why something has a high mp/bp, check for Hydrogen bonding)
![<p>strong intermolecular force.</p><p>Only H to [FON (holds the e more closely)] because of this, the H have a positive nucleus, therefore creating strong dipole-dipole attraction with lone pairs</p><p>(if the tests asks u for why something has a high mp/bp, check for Hydrogen bonding)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a9cdd6c9-1494-4b9d-baf0-7e2e3dc4f7c9.png)
What is the relative strengths of intermolecular forces?
London Dispersion < dipole-dipole < Hydrogen Bonding
Metallic Bonding IB definition
between metals, happens due to loosely held e that are delocalized. e spread themselves through the metal structure.
IB Def: the electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalized electrons.
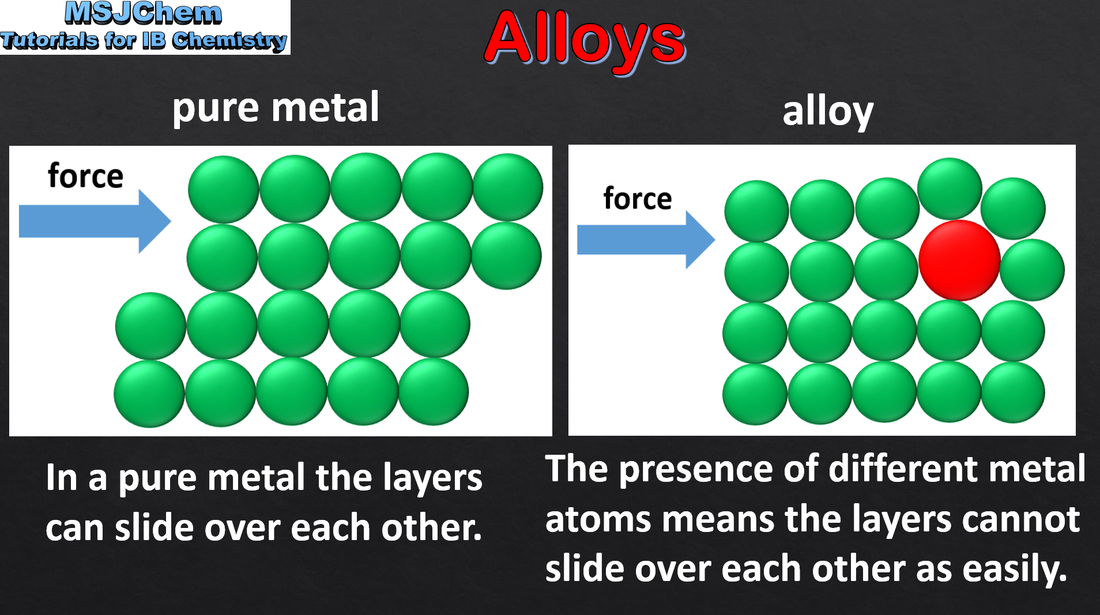
What are alloys and their properties
In molten state, two metals together, and the smaller atoms go in-between the bigger atoms in the lattice.
Stronger, harder, more durable, layers cannot slide over eachother as easily.
How to determine a substance’s ionic/covalent parameter
difference in electronegativity (1.8 or greater means IONIC)
What is the bonding continuum
Idea that Ionic, Covalent, and metallic bonding are not all separate, and it is a spectrum based on electronegativity values.