PSC 156 Chapter 3 Erikson Personality Mcadams generativity
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the five-factor
model of personality
traits?
The Essential Trait Approach : Which traits are the most important? Which
traits really matter?
Reducing the many to a few via Factor Analysis
Openness to
Experience
Curious, original, intellectual, creative, and open
to new ideas and experiences
Conscientiousness Organized, systematic, punctual, industrious,
dependable, responsible (Vs lack of direction)
Extraversion Outgoing, talkative, sociable, assertive, dominant,
active, excitement seeking
Agreeableness Warm, kind, cooperative, sensitive, trusting,
modesty (VS Antagonism)
Neuroticism Anxious, irritable, moody, tense (VS emotional stability)
OCEAN
Which of the following traits is NOT part of the Big Five
personality factors?
A) Openness
B) Conscientiousness
C) Intelligence
D) Agreeableness
C
Which Big Five personality trait is characterized by a tendency to
experience negative emotions such as anxiety, fear, and sadness?
A) Openness
B) Conscientiousness
C) Extraversion
D) Neuroticism
D
Which Big Five personality trait has been found to be the least
consistent across different cultures?
A) Openness
B) Conscientiousness
C) Extraversion
D) Neuroticism
A
What is rank-order-consistency is personality development?
Personality remains (
relatively stable over time)
Evidence for stability:
• Childhood personality predicts
adult behavior and life outcomes. Behaviors may
manifest
differently, but
the underlying
trait is the same
(e.g., shyness). For example as a kid may hide behind mom as adult may not go to parties. the stability of an individual's relative position or ranking within a group on a specific trait or measure over time
What are the 5 factors related to personality stability?
Temperament impacts behavioral & emotional tendencies, which then persist across the
lifespan
-Visible, physical factors (e.g., sex/gender, height, attractiveness)
-Environmental factors (e.g., SES, city/rural living, family size)
-Positive & Adverse experiences in childhood
Factors related
to nature AND
nurture =
relative
stability
Which of the following is NOT considered a factor that
contributes to personality stability across the lifespan?
A) Temperament influencing behavioral and emotional tendencies
B) Visible, physical factors such as sex/gender and attractiveness
C) Positive and adverse childhood experiences
D) Dramatic changes in social environment in adulthood
D
What are the 3 types of person-environment interactions? How do they affect personality traits over time?
They magnify personality traits.
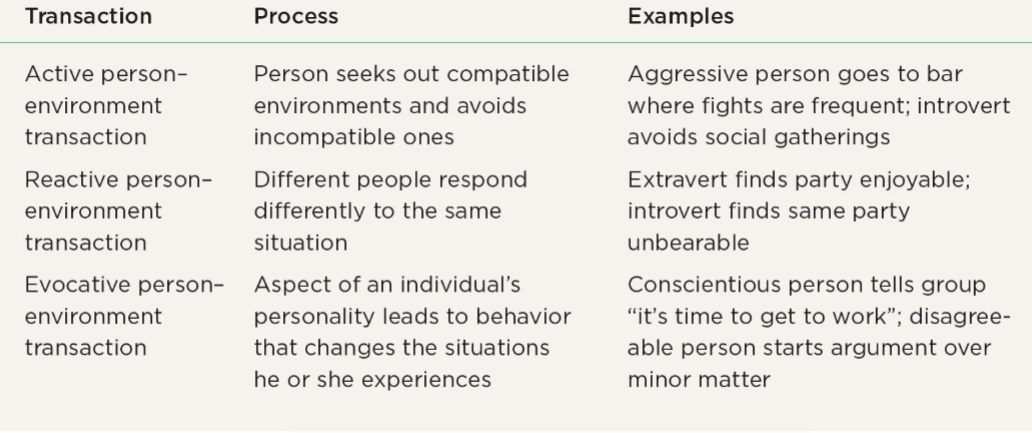
true or false: a cross sectional study found evidence for personality development by showing how traits change over time on average
True
cross-sectional
-Participants 10-65 years
-N=>1 mill, recruited via the internet
-Inclusion criteria: Must speak English
-Results: Age-related development in mean
levels of personality
True or false: personality stability and development cannot both exist at the same time
False. You could for example develop in terms of conscientiousness but the amount at which you develop conscientiousness is the same as the amount others develop conscientiousness, just different starting point
What are the main 5 causes of personality development? (as opposed to stability)
Physical development
Hormone-level changes
Increases in intelligence & linguistic abilities
Changes in social roles/responsibilities E.g., Erikson’s theory of development
Goals across the life span change
What are common personality changes that happen to people over time?
People become more socially dominant, agreeable, conscientious, emotionally
stable
• Decrease in openness to new experiences
• Honesty/humility and self-esteem (up to age 50) increase
• Risk-taking decreases
• Consistent with the maturity principle (individuals tend to become more socially dominant, agreeable, conscientious, and emotionally stable as they age. These positive, adaptive personality changes. Assumes linear progression fails to account for individual differences in development, overlooks short-term declines in mental health, and may not apply to all personality facets equally. ) & personality adjustment
Hormone-level changes are most likely to impact personality
development during which life stage?
A. Early childhood
B. Adolescence
C. Middle adulthood
D. Late adulthood
B
How do goals across the life span contribute to personality
development?
A. They remain constant and reinforce personality stability.
B. They are unrelated to physical or social development.
C. They adapt to changes in social roles and personal responsibilities
D. They only affect personality development during adolescence
C
How is differing cultures largely unaccounted for in personality research?
White people are 12% of the
world’s
population, but
80% of
psychology
research
participants
Culture and personality are inextricably linked,
mutually influencing one another
Culture as a social unconscious: should be
considered in ALL personality research
However, the vast majority of personality
research does not consider the importance of
race or ethnicity
The Epigenetic Principle (in terms Erikson)
Each struggle must be resolved to continue development.
What are all of Erikson’s stages?
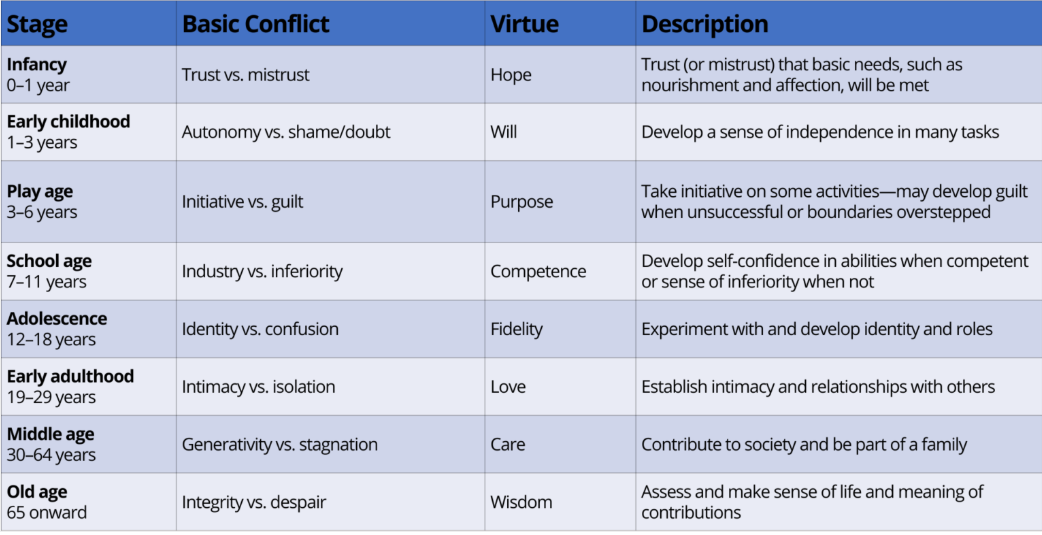
What Erikson age is considered old age 65+ and what does it entail?
Come to terms with a lifetime of choices
• Accept that life is drawing to a close
• Everyone can reach integrity, though not common
• Completing a life review can contribute to achieving integrity
Which of the following best describes Erikson’s stages of
development?
A. They are a series of quantitative changes in behavior and skills.
B. They focus exclusively on physical and cognitive development.
C. They are fixed stages that do not vary across individuals or cultures.
D. They represent qualitative stages centered on resolving psychosocial
conflicts.
D
In Erikson’s stage of Integrity vs. Despair, which of the following
is a key task for individuals?
A. Establishing long-term personal goals for the future
B. Coming to terms with a lifetime of choices
C. Developing independence from caregivers
D. Balancing work and personal relationships
B
Critiques of Erikson’s theory? how have Logan and Korte and McAdams tried to resolve them?
Poorly defined, untestable, incomplete
Logan: The stages as a cycle that repeats → developmental progression=trust,
achievement, and wholeness
Korte: Generativity as a set of impulses: Biological & parental; Technical;
Cultural; Agentic ; Communal → the perception of generativity (or not) is
continuous across adulthood
McAdams: Korte: Generativity as a set of impulses: Biological & parental; Technical;
Cultural; Agentic ; Communal → the perception of generativity (or not) is
continuous across adulthood. offering a more nuanced, lifelong, and multidimensional view, continuous! in other stages of life than middle adulthood
What are the two principles of McAdams model of generativity?
Concern: a general personality
tendency of interest in caring for
younger individuals
Action: the actual behaviors that
promote the well-being of the next
generation.
Middle-aged and older adults =
greater preoccupation with
generativity
Generativity definition → any type of
activity or intention to benefit others