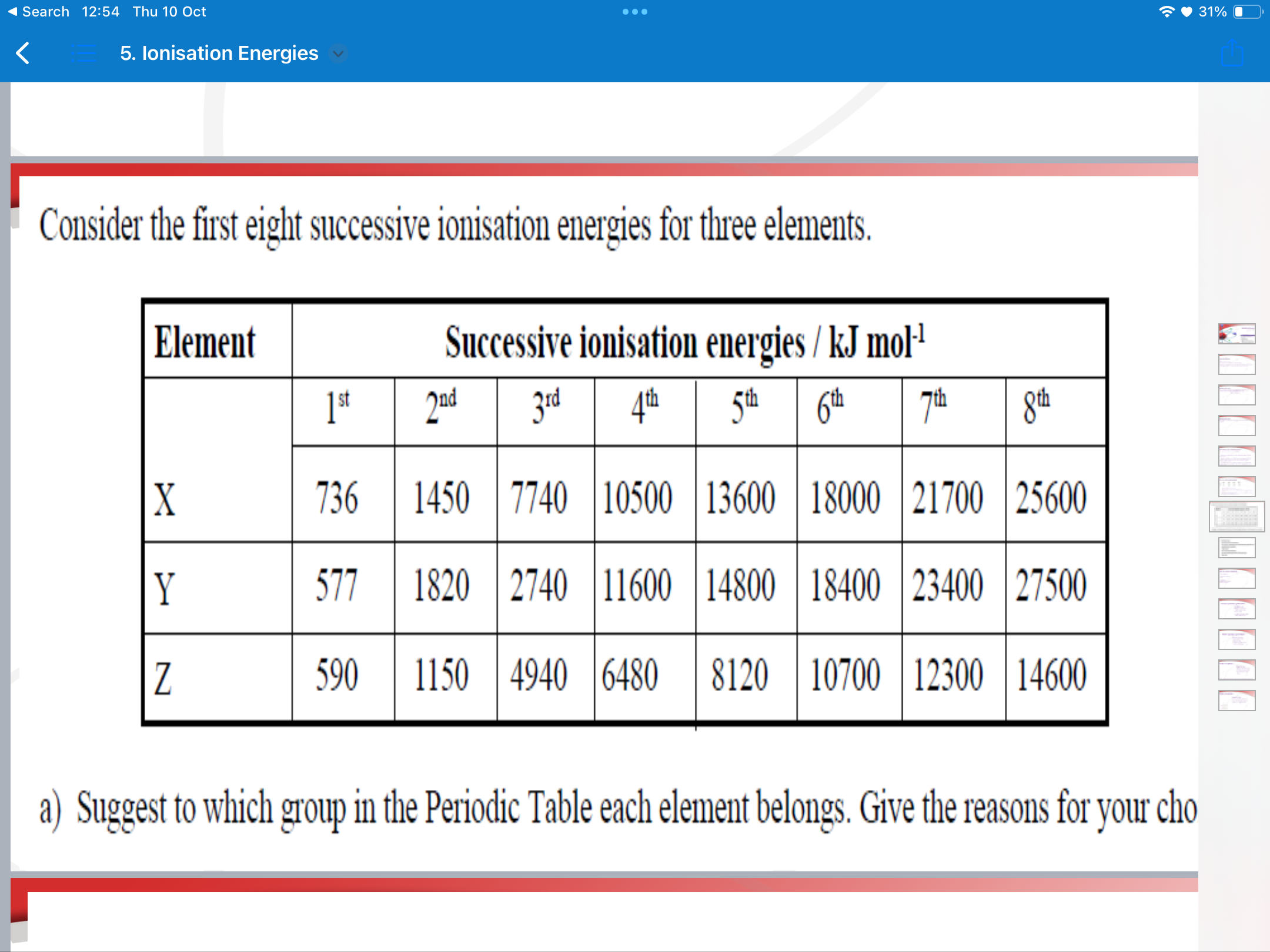
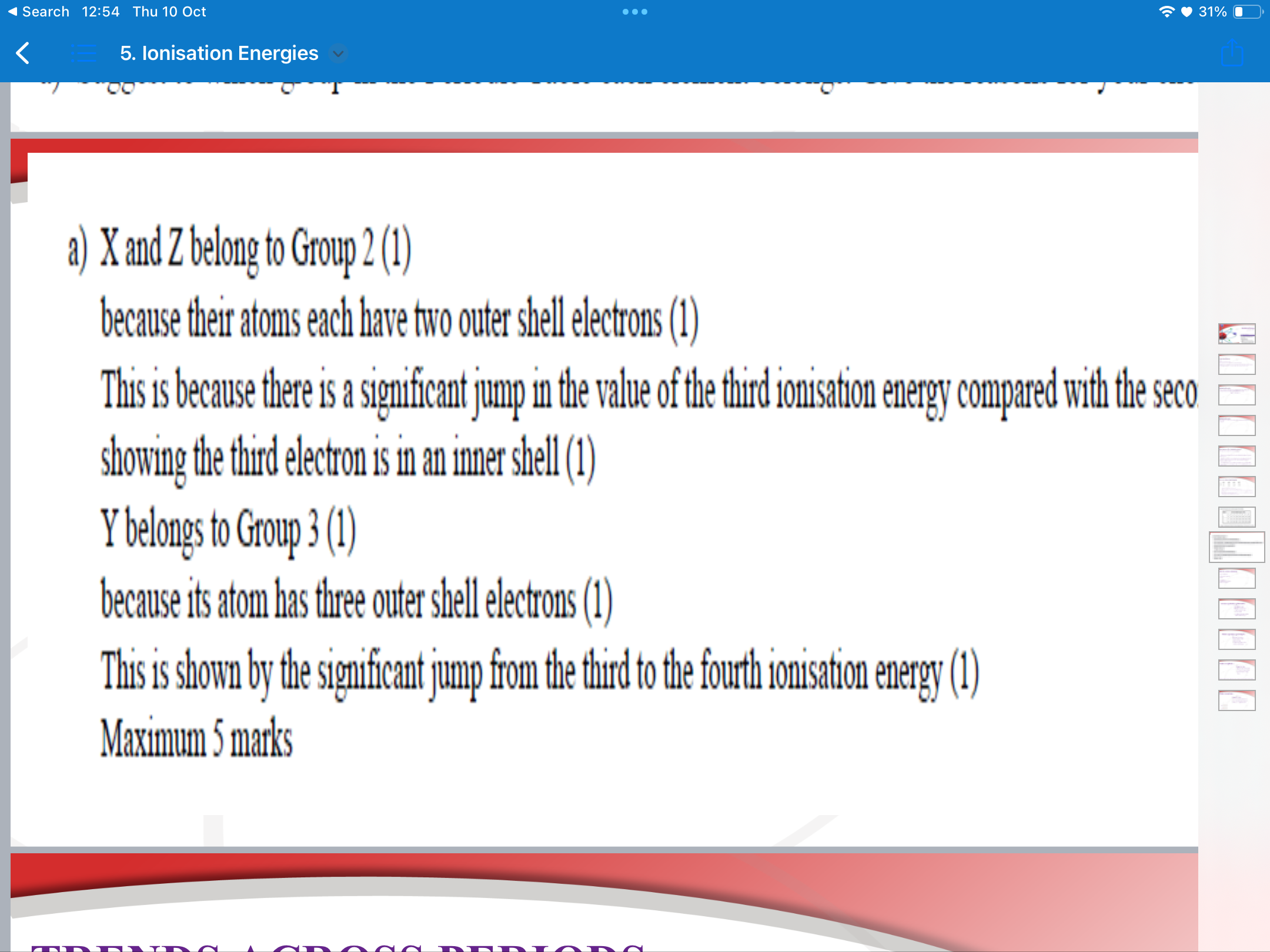
ionisation energy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
first ionisation energy
the energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms
formula to represent this
X(g) → X+(g) + e-
ionisation energy abbreviation
IE
units and what it is measured in?
kJ mol-1
removing electrons one by one- how it increases?
-the first electron needs the least energy to remove because it is being removed from the neutral atom.
-the second electron needs more energy than the first because it is being removed from a +1 ion.
-the third electron needs even more energy to remove because it is being removed from a +2 ion.
what are these increasing patterns called?
successive ionisation energies
second IE formula
Na+(g) → Na+2(g) +e-
term for formation of negative ion
electron iffinity
What does the successive ionisation energies of sodium suggest?
-it has one electron furthest away from nucleus (easy)
-eight electrons nearer into nucleus
-two electrons very close to nucleus (hard to remove because nearest to + charge of nucleus)
Why is 3p4 easier to loose than 3p3
because the repulsion between these paired electrons make it easier to remove one of them, despite the increase in nuclear charge
Factors that affect ionisation energy + why
-Nuclear charge (relate to protons, the same shielding)
-atomic radius (increase→ futher the outer electron is from the nucleus, so weaker force of attraction)
-shielding (less repulsion if less inner shells, strengthening force of attraction)
Why are the ionisation energies always positive?
as it is endothermic
energy is required to break the force of attraction between the electron and the positive nucleus
why is the second ionisation energy always bigger than first
when the first electron is removed a positive ion is formed, the ion increases the attraction between outer electron and so the energy required to remove the next electron is larger)
what happens to atomic radius across period
decreases (more protons) as higher nuclear charge
where are electrons easier to be removed from
electrons that are higher orbitals, than furthest from nucleus
describe the changes in bonding across the table?
mettalic bonding on left, changes to covalent bonding on right. Mettallic lattice at start, giant covalent in middle, simple molecular on right, monoatomic in group 0
Why in sodium is there a large gap between first and second electrons?
as the second electron is removed from an energy level closer to nucleus
why is there a general increase in energies?
increase in nuclear charge (increase photons to electrons)
Example of which elements belongs to group 4.
element X. Has a large increase in ionisation energy after fourth electron has been removed. This would suggest 4 electrons in outer energy level and fifth electron in energy level closer to nucleus. So X has 4 electrons in outer energy level so carbon
patterns for ionisation energy across and down
-down- decreases
-across-increases
Group 3 and 6 dip explained
Group 3 - has a s2p1 arrangement, outer p1 electron is furthest from nucleus, inner s2 electrons increase shielding so less energy is required to ionise p1 electron
Group 6- p4 arrangement -repulsion of two electrons in the same orbital means less energy is needed to ionise the outer electron
2 and 3 dip
4th has a p orbital, so further from nucleus, loose electron easier
5th and 6th orbital
4th has a spin pair repulsio, less energy