Leadership - Ch. 7
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
power
The potential or ability to influence decisions and control resources.
legitimate power
The lawful right to make a decision and expect compliance.
personal power
Power derived from the person rather than from the organization.
prestige power
The power stemming from one’s status and reputation
reward power
The authority to give employees rewards for compliance.
Coercive power
The power to punish for noncompliance; power based on fear.
dependence perspective
The point of view that a person accrues power by being dependent on that person for things they value.
self-leadership
The idea that all organizational members are capable of leading themselves, at least to some extent.
moral identity
The extent to which an individual holds morality as part of the self-concept.
strategic contingency theory
An explanation of sources of power suggesting that units best able to cope with the firm’s critical problems and uncertainties acquire relatively large amounts of power.
delegation
The assignment of formal authority and responsibility for accomplishing a specific task to another person
empowerment
Passing decision-making authority and responsibility from managers to group members.
organizational politics
Informal approaches to gaining power through means other than merit or luck.
political skill
An interpersonal style that manifests itself in being socially astute and engaging in behaviors that lead to feelings of confidence trust, and sincerity.
Leader political support
Political acts and influence behaviors performed by leaders to provide followers with valuable resources to advance individual, group, or organizational objectives.
positive psychological capital
An individual’s positive psychological state of development, characterized by four psychological resources: self-efficacy, hope, optimism, and resilience.
territorial games
Also referred to as turf wars, political tactics that involve protecting and hoarding resources that give one power, such as information, relationships, and decision-making authority.
Old power
•is held by few, and once it is acquired, it is jealously guarded. Such power is inaccessible to most people, and it is leader driven.
New power
•is created by many people, is open, participatory, and peer driven, and is about processes such as empowerment and shared leadership.
•Sharing knowledge on social media is an example of the new power.
Sources and Types of Power
•Power can be derived from many sources.
•How people obtain power depends to a large extent on the type of power they seek.
•Important to understand what types of power exist.
Position power (stems from the organization)
Legitimate power, Reward power, Coercive power
Expert power
•is the ability to influence others through specialized knowledge, skills, abilities.
Referent power
is the ability to influence others through desirable traits and characteristics.
•Power Stemming from Ownership
•Executive leaders accrue power in their capacity as agents acting on behalf of shareholders.
•Leader’s ownership power also associated with personal investments in the firm.
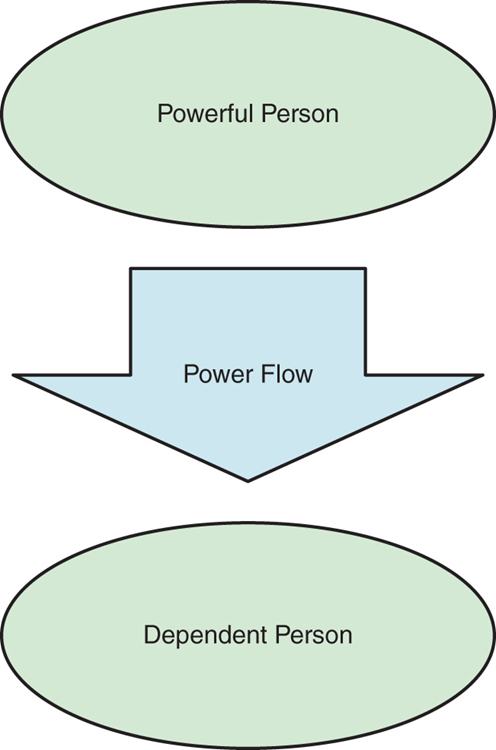
•Power Stemming from Dependencies
•According to the dependence perspective, people accrue power when others are dependent on them for things of value.
•Dependence power can be positional or personal.
Power resides implicitly in the other’s dependence
•Power Derived from Capitalizing on Opportunity
•Power can be derived from being in the right place at the right time and taking the appropriate action. (“It pays to be where the action is.”)
•Power Stemming from Managing Critical Problems
•The strategic contingency theory of power suggests that units best able to cope with the firm’s critical problems and uncertainties acquire relatively large amounts of power.
•Power Stemming from Being Close to Power
•The closer a person is to power, the more power the person exerts.
The Dependence Theory of Power
Meaning
•is fit between work and person’s belief, values, and behaviors.
Competence or self-efficacy
is belief in capability to perform task well.
Self-determination
is having a choice in initiating and regulating actions.
Organizational politics
•Informal approaches to gaining power through means other than merit or luck.
•Politics are played to achieve power, either directly or indirectly.
•Leaders need political skill to build alliances and gain resources.
•Leader political support:
•Political acts and influential behaviors performed by leaders to provide followers with valuable resources to advance individual, group, or organizational objectives.
•Organizational politics often regarded as emphasizing self-interest at the expense of others.
Pyramid-shaped organizational structure
•A pyramid concentrates power at the top.
•Only so much power is available to distribute among people who want more power.
Subjective standards of performance
•People often resort to organizational politics because they do not believe that the organization has an objective and fair way of judging their performance and suitability for promotion.
Environmental uncertainty and turbulence
•When people operate in an unstable and unpredictable environment, they tend to behave politically.
Emotional insecurity
•Some people resort to political maneuvers to ingratiate themselves with superiors because they lack confidence in their own talents and skills.
Machiavellian tendencies
Some people engage in political behavior because they want to manipulate others, sometimes for their own personal advantage
What are some of the sources that organizational power is derived from?
position power, personal power, ownership, dependencies, capitalizing on opportunity, managing critical problems, and being close to power
What are people with a strong moral identity less likely to use power for?
self-interest
What does full-fledged empowerment include?
•the dimensions of meaning, self-determination, competence, impact, and internal commitment.
What is an important part of empowerment?
delegation
What must a leader do to acquire and retain power?
skillfully use organizational politics
When carried to the extreme what can organizational politics do?
hurt an organization and its members
What may political tactics and strategies may be?
either ethical or unethical