AP World History - Unit 2: Networks of Trade
Height of the Middle Ages: Trading and Crusading
Merchants emerged in towns - referred to as Burghers, became politically powerful
Towns often formed alliances with each other
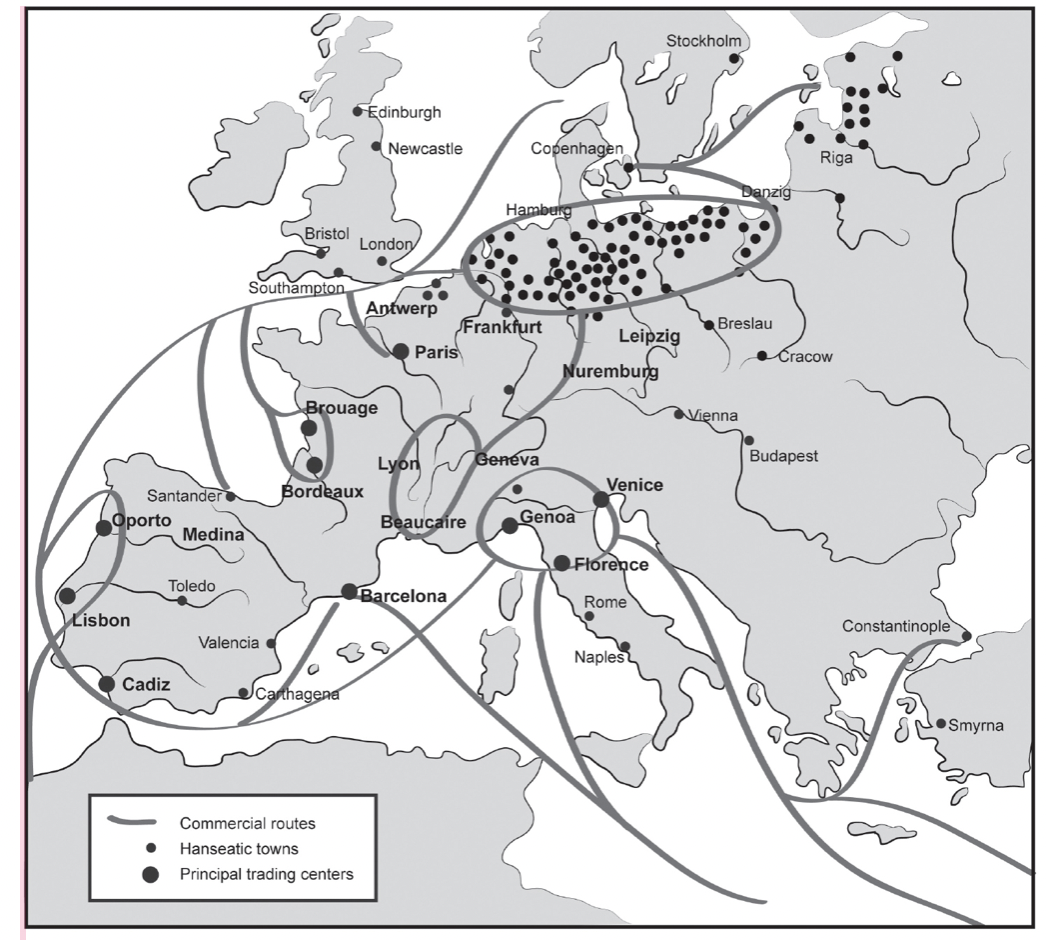
Hanseatic League (1358): trade alliance though northern Europe to drive toward nationhood, increase social mobility and flexibility
Architecture: Romanesque to Gothic - especially reflected in cathedrals
- Flying buttresses: tall windows and vaulted ceilings
- Often had art and sculpture, music
Scholasticism: growth of education and knowledge - founding of universities for men; philosophy, law, medicine study; ideas of Muslims and Greeks - came in conflict with religion
Crusades (11-14th century): military campaigns by European Christians to convert Muslims and non-Christians, combat religious questioning
- Combat Heresies: religious practices/beliefs not conforming to traditional church doctrine
- Pope Innocent III: issued strict decrees on church doctrine - frequently persecuted heretics and Jews, unsuccessful 4th crusade
- Pope Gregory IX: Inquisition (formal interrogation and prosecution of perceived heretics with punishments like excommunication, torture, execution) - church often referred to as Universal Church or Church Militant
- Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274): Christian theologian who made advancements in Christian thought - faith and reason aren’t in conflict
Urbanization
- Trade led to the growth of urban culture - cities usually were around trade routes
- Silk Route cities were the most populous - Baghdad, Merv, Chang’an
- Constantinople before 1400 and Paris and Italian city-states after 1400 were big European cities
The Rise and Fall of the Mongols
- Set of tribes and clans that were superb horseman and archers
- Genghis Kahn: unified the tribes in Mongolia in the early 1200s to expand their authority over other societies - first invaded China in 1234
- Mongol Empire: spanned from Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe - spit into hordes after death of Genghis Kahn, ruthless warriors destroying cities but remained peaceful after settling into cities
- Golden Horde: conquered modern-day Russia
- Kublai Khan: Genghis Kahn’s successor - ruled China
- Didn’t really have a set culture - didn’t enforce religion or way of life on conquered nations, but did make any cultural advancements
- Timur Lang: Mongol leader who took over India and destroyed everything - grew Islam in the nation
- If any residents of society the Mongols took over resisted, they would immediately kill them, so most had no choice but to give in - they were ruthless fighters, organized and mobile
- Impact:
- Great diffusers of culture
- Prevented Russia from culturally developing
- World trade, cultural diffusion, global awareness grew as they spread through Europe, the Middle East, and Asia
Mali and Songhai
- Mali had a lot of gold that Islamic traders were interested in
- Mansa Musa: Malian ruler who built the capital of Timbuktu and expended the kingdom beyond Ghana
- Sonni Ali: Songhai ruler that conquered region of west Africa in 15th century - became a major cultural centre until 1600
Chinese Technology
- Song Dynasty: bureaucratic system built on merit and civil service examination creating a lot of loyal government workers, improved transportation and communication and business practices
- Concentrated on creating an industrial society - improved literacy with printed books which increased productivity and growth
Review of Interactions Among Cultures
Trade Networks and Cultural Diffusion
Trade exploded from 1200-1450
Improved with better transportation and monetary systems
Main Global Trade Routes:
- The Hanseatic League
- The Silk Road
- The land routes of the Mongols
- Trade between China and Japan
- Trade between India and Persia
- The Trans-Saharan trade routes between west Africa and the Islamic Empire
Cultural diffusion - spread religions, languages, literature, art, idea, disease, plague
Bubonic Plague: started in Asia in the 14th century and carried by merchants - killed about 1/3 people
Indian Ocean Trade
- Dominated by Persians and Arabs - western India to Persian Gulf to eastern Africa
- Great Zimbabwe: trading empire in Africa from 11th to 15th centuries
Vibrant Indian Ocean Communities
- Sailors marrying local women created cultural intermixing
Silk Road
- China to Mediterranean cultures in early days of Roman Empire and from 1200 to 1600
- Cultural exchange through travellers stopping at trade towns - Kashgar, Samarkand
- Silk, porcelain, paper, religion, food, military technologies
Hanseatic League
- Made up of over 100 cities
- Created substantial middle class in northern Europe
- Set precedent for large, European trading operations
Expansion of Religion and Empire: Cultural Clash
- Both natural spread of religion through contact over trade and intentional diffusion through missionary work or religious war
Other Reasons People Were on the Move
- Ran out of room in certain places, but cities were always increasing in size as opportunities grew in them
- New cities and empires drew people in
- Muslim pilgrimages
Notable Global Travellers
- Xuanzang: Chinese Buddhist monk - through T’ang Dynasty to India to explore Buddhism
- Marco Polo: merchant from Venice, to China and Europe
- Ibn Battuta: Islamic traveler, through Islamic world to India to China
- Margery Kempe: English Christian, through Europe and Holy Land
Technology and Innovations
| Islamic World | China |
|---|---|
| paper mills | gunpowder cannons |
| universities | movable type |
| astrolabe and sextant | paper currency |
| algebra | porcelain |
| chess | terrace farming |
| modern soap formula | water-powered mills |
| guns and cannons | cotton sails |
| mechanical pendulum clock | water clock |
| distilled alcohol | magnetic compass |
| surgical instruments | state-run factories |