Understanding Working Memory and Its Models
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What does the Multicomponent Model of working memory propose?
It proposes that working memory consists of multiple, functionally distinct components, including domain-specific subsystems (phonological and visuospatial) that operate independently.
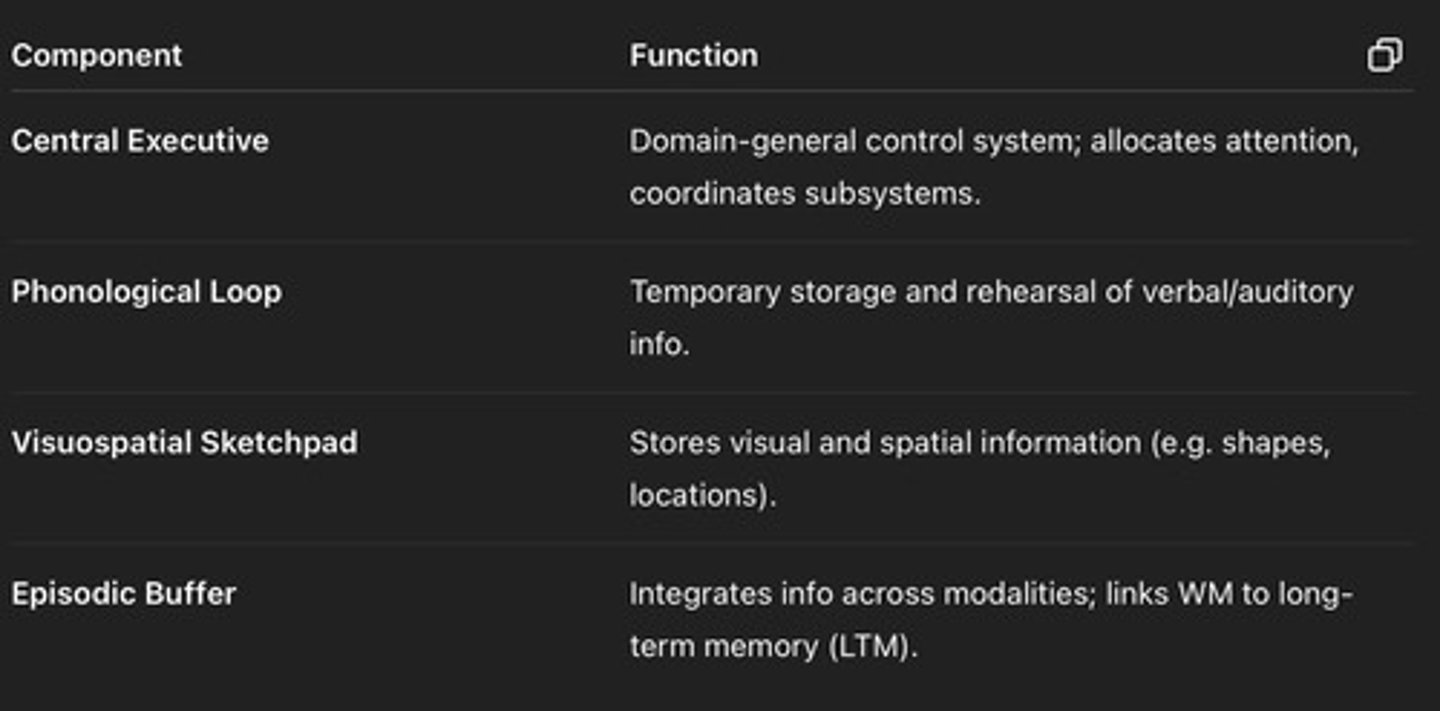
Central Executive
Domain-general control system
Allocates attention
Coordinates subsystems
Phonological loop
Temporary storage and rehearsal of verbal/auditory info
Visuospatial sketchpad
Stores visual and spatial information
Episodic buffer
Integrate info across modalities
Links WM to LTM
What is the role of the episodic buffer in the Multicomponent Model?
Provides a multimodal workspace and supports the binding of information into coherent episodes.
What is the Word Length Effect (WLE) in relation to the phonological loop?
Indicates that shorter words are recalled better than longer words, as shown in studies by Baddeley et al. (1975).
What evidence supports the phonological loop's function?
Word Length Effect
Cross-linguistic studies
Phonological similarity effect, which shows lower recall for phonologically similar words.
How does articulatory suppression affect the phonological loop?
Articulatory suppression, such as repeating irrelevant speech, impairs the phonological loop function and abolishes the Word Length Effect for visually presented words.
What does the phonological similarity effect demonstrate?
Recall is lower for phonologically similar words compared to semantically similar words, indicating distinct processing mechanisms.
What evidence supports the visuospatial sketchpad's distinct function?
Mental rotation tasks show that spatial processing uses a distinct store that is not affected by phonological interference.
What is the significance of the dissociation between verbal and visuospatial tasks?
It supports the idea of dual-modality storage in working memory, indicating that verbal and visuospatial information are processed separately.
What challenge does Vergauwe et al. (2022) present to the domain-specificity of working memory?
They found no performance difference between same-domain and different-domain combinations in working memory tasks, suggesting a single, domain-general resource may underlie WM processing.
What is Cowan's Embedded-Processes Model of working memory?
It posits that working memory is not a separate system but the activated portion of long-term memory, with components including long-term memory, activated LTM, and a narrow focus of attention.

How does Cowan's model define the focus of attention?
A narrow capacity (4±1 items) where active cognitive processing occurs.
What is an example of activation from long-term memory into working memory?
An example is temporarily activating your birth year from long-term memory into working memory for a task.
What is the primary function of the phonological loop?
Responsible for the temporary storage and manipulation of verbal and auditory information.
What is the role of the visuospatial sketchpad in working memory?
Responsible for the temporary storage and manipulation of visual and spatial information.
What does the executive attention hypothesis suggest?
It suggests that executive attention is a key component in managing and regulating working memory processes.
What is the binding hypothesis in relation to working memory?
Posits that working memory integrates information from different modalities into coherent episodes.
What are the three hypotheses explaining limits of working memory capacity?
Executive attention hypothesis
Binding hypothesis
Domain-specificity challenge.
How can variation in working memory be measured?
Through tasks that assess recall, manipulation of information, and the ability to manage interference.
What is the significance of activation-based models in understanding working memory?
Activation-based models relate working memory to long-term memory by suggesting that working memory is the activated portion of long-term memory.

What does the term 'activated LTM' refer to in Cowan's model?
The temporarily heightened accessibility of information stored in long-term memory.