3.1.11 - Biodiversity
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the definition of biodiversity
The variety of living organisms in an area
Why is biodiversity important?
It is important for the resilience of ecosystems, interdependence and to resist changes in the environment.
What is species richness?
the number of species in a community/given area
What is species diversity?
Species diversity looks at the number of different species in a community and the evenness of abundance across the different species present.
Why are ecosystems with a high species diversity more stable?
They are more resilient to environmental changes.
What are some reasons to maintain biodiversity?
Moral and ethics - humans have the ability to reduce their impact on the planet, ecological- biodiversity increases the stability of ecosystems, environmental - organisms provide essential environmental services, economic - range of organisms contribute to medicine, ecotourism, science and technology.
Why can species richness be a misleading factor for diversity?
It doesn't take into account the number of individuals of different species.
What do scientists use to calculate species diversity?
The index of diversity.
What is the formula for the index of diversity?
Where n = the total number of organisms for a single species and N = total number of organisms in the community.
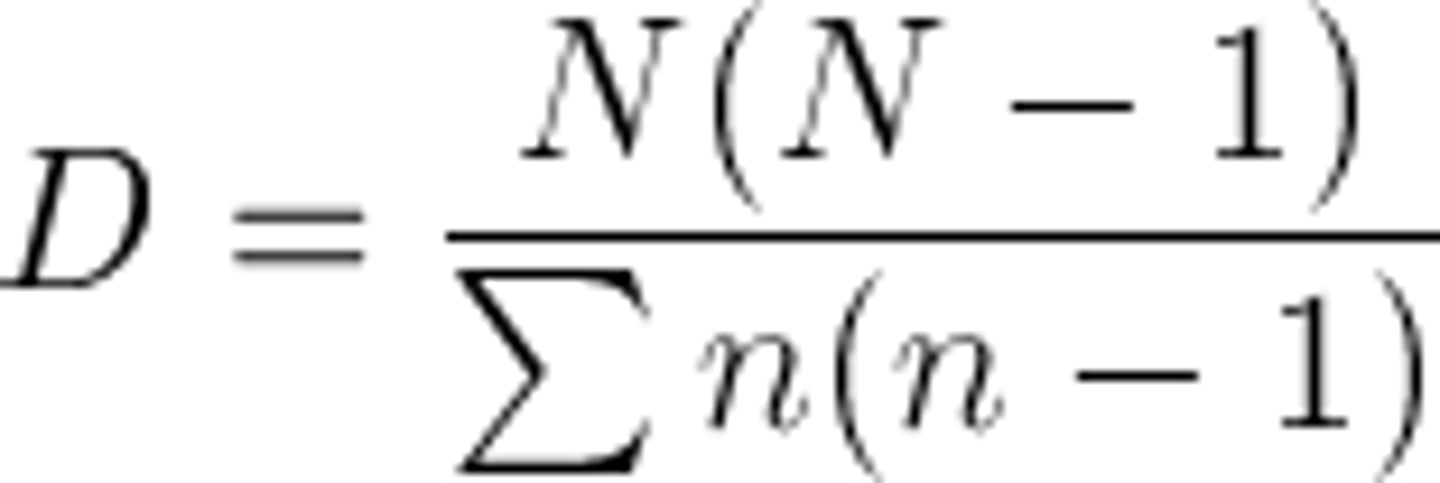
How is the species richness reduced by farming practices?
When farmers select a species for a particular quality, it reduces the gene pool and the genetic variety of alleles. When farmers deliberately fertilise and drain the land and sow the seeds of one or two plant species, it outcompetes the other species decreasing the species richness. This also decreases the variety of food sources and habitats for insects.
Farmers now have a smaller gap between harvesting and ploughing meaning there is less food available for birds, reducing the species richness. Monoculture ad pesticides are contributing to the decline of the bumblebee, which are essential pollinators.
What is genetic diversity?
The total number of different alleles of genes in a population
How can you measure the genetic diversity of a species?
Measurable characteristics, base sequence of DNA/mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins.
Why is measurable characteristics not a good indicator for genetic diversity?
It is not precise enough.
Which base sequence is easier to get mRNA or DNA?
mRNA as mRNA can be found in the cytoplasm but DNA is only in the nucleus.
Why is sampling used?
scientists rarely have access to entire groups of organisms, and most times it's impractical to try to gather data on an entire population. Also area may be too big.
What are the two types of sampling?
Random and systematic.
What is random sampling and why is it prefered?
The sampling points are completely random or due to change. This method is better than systematic as there is no bias.
What is systematic sampling?
The person carrying out the sampling decides the position of the sampling points. This might be bias.
What apparatus do we need to measure the biodiversity of an area?
Quadrat and random number generator.
What is the difference between species frequency and species density?
Species frequency is the probability that the species will be found within any quadrat in the sample area. Species density is the number of individuals of that species per unit area.
What is standard deviation?
Measure of the spread/dispersion of data around the mean. A large/high standard deviation suggests the results are more spread out.
What does an overlap between standard deviations suggest?
The results are not significantly different.
What does no overlap between standard deviations suggest?
The results are significantly different.
What is the meaning of gene pool?
Set of all genes in a particular species. A gene pool can be thought of as the sum of all the alleles at all of the loci within the genes of a population of a single species or a population
How can the gene pool change?
Natural selection
Genetic drift
The founder effect
Factors that influence genetic diversity
Selective breeding - reduces gene pool
The founder effect - Few individuals colonize a new region and they show less genetic diversity as they reproduce.
Genetic bottlenecks: Populations may face a dramatic drop of numbers due to a chance event. Few survivors will have a smaller variety of alleles.
How to dertemine if something requires the coefficent correlation or the t test?
cc - to find a correlation between two factors
t test - same variable in two different species.
What does biodiversity look at?
The variation that exists within and between all forms of life, biodiversity looks at the range and variety of genes, species and habitats within a particular region.
What are the three types of biodiversity?
genetic diversity, species diversity, ecosystem diversity
What is the difference between species diversity and species richness?
They both look at the number of species but species diversity also looks at the evenness of abundance.
What does a high index of diversity suggest?
Higher level of diversity.
How has farming practices changed recently?
Due to the higher yield, farms became more specialised so they only grew one crop ( monoculture.) There was a switch to cereal crops and fields were made bigger to accommodate more machinery. The land was made more arable by draining wetland and the use of pesticides and fertilizers massively increased.
How have conservationists attempted to maintain/improve biodiversity around farmlands?
Ways that conservationists have tried to maintain or improve biodiversity is by rewilding areas and removing all human interference (buffer strips around uncultivated areas allow native species to survive.) or by promoting organic farming. Additionally, governments are restricting the expansion of the area of agricultural land. Farmers can use hedgerows instead of fences, grow different crops and reduce the use of pesticides.
Why don't farmers want to make their practices more biodiversity - friendly?
Farming practices that maintain or increase biodiversity can be expensive, time intensive and labour intensive.
What are species?
group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Why is selective breeding used?
To produce resistance to disease, more product (such as meat or milk in cows), or even a gentle nature (in dogs)
What is the founder effect?
The founder effect is when a few individuals from a population colonise a new region. This population will only carry a small fraction of the alleles of the population as a whole. When two groups are isolated from each other, they become genetically isolated. This means they do not interchange genes with each other. The changes that happen in the alleles aren't shared so they evolve independently and they could grow into two different species.
What is a genetic bottleneck?
An event that causes a big reduction in a population. This causes a smaller gene pool which decreases the genetic diversity
How does obtaining the base sequence useful in determining how closely related organisms are?
The base sequence is obtained from DNA and is compared to other organisms to determine evolutionary relationships. The more similarities there are, the more closely related members of different species are.
What is the difference when comparing DNA and mitochondrial DNA?
Mitochondrial DNA has no crossing over since there's only maternal mitochondrial DNA present.
What do you have to make sure wen comparing mRNA?
make sure you are comparing the same mRNA samples.
Describe comparing amino acids
Proteins are easier to isolate. The sequence of amino acids of the same protein must be compared. The amino acid sequences are determined by mRNA sequencing. Amino acid sequences of proteins evolve slower than DNA therefore it will be likely that closely related species have the same amino acid sequences.
What is sampling?
investigating the abundance and distribution of species and populations
Describe random sampling
In random sampling, the positions of the sampling points are completely random or due to chance. This means there is no bias.
What does the distribution of a species mean?
The distribution of a species describes how it is spread throughout the ecosystem
What does the abundance of a species mean?
The abundance of a species is the number of individuals of that species
What would you use over a larger area?
Transects
What are the limitations of quadrats and transects?
The limitations of quadrats and transects are that they can only be used for slow and immobile species. Some species can be counted to find their abundance but others are too small or there are too many.
What is a more precise method of describing the distribution of a species?
Percentage cover is when the quadrat is divided into smaller squares. Percentage cover and frequency can give a good picture of the distribution of a species.
What is evolution?
Evolution is the formation of new species from pre-existing species over time, as a result of changes to gene pools from generation to generation
What is a null hypothesis?
Assumption that there will be no correlation or difference.
What is the critical value normally used?
0.05
What happens if p<0.05
If p<0.05, then the results are significant and the null hypothesis can be rejected.
When do you use correlation coefficent?
If you are looking for association then use correlation coefficent. - correlation between measurements of different variables from the same sample. E.g Leaf length and leaf width.
When do you use student t-test?
Students t-test is looking for differences between measurements of the same variable from different sample. E.g height of exposed plants compared to plants under a canopy.