Motor and Social-Emotional Development in Early Childhood
1/442
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
443 Terms
What are the two main types of motor skills discussed in early childhood development?
Fine motor and gross motor skills.
What general changes occur in gross motor skills during early childhood?
Children develop a more adult-like center of gravity, increased strength and coordination, and improved endurance and metabolism for sustained physical activity.
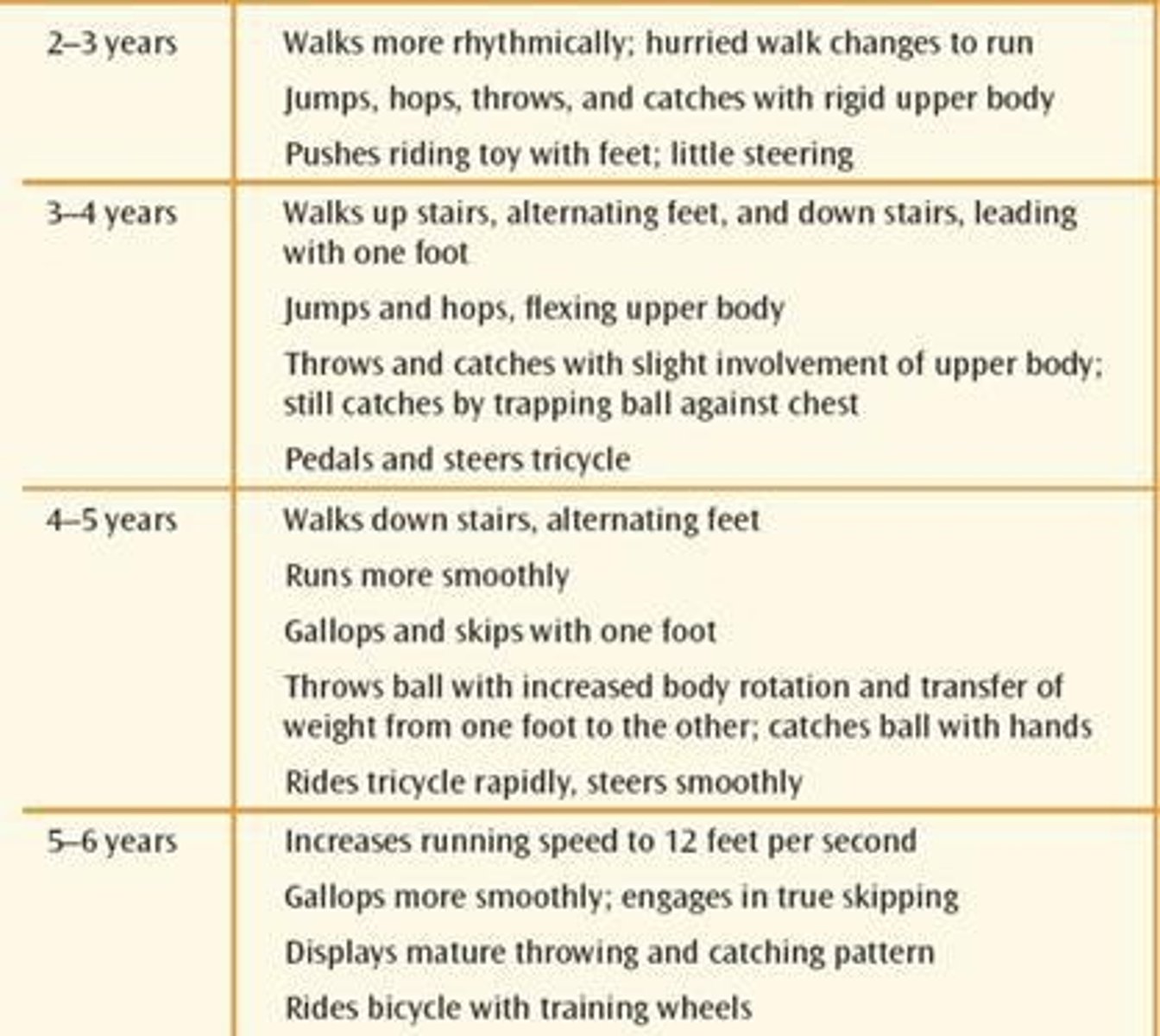
What is the significance of the center of gravity in early childhood motor development?
A more adult-like center of gravity contributes to increased balance.
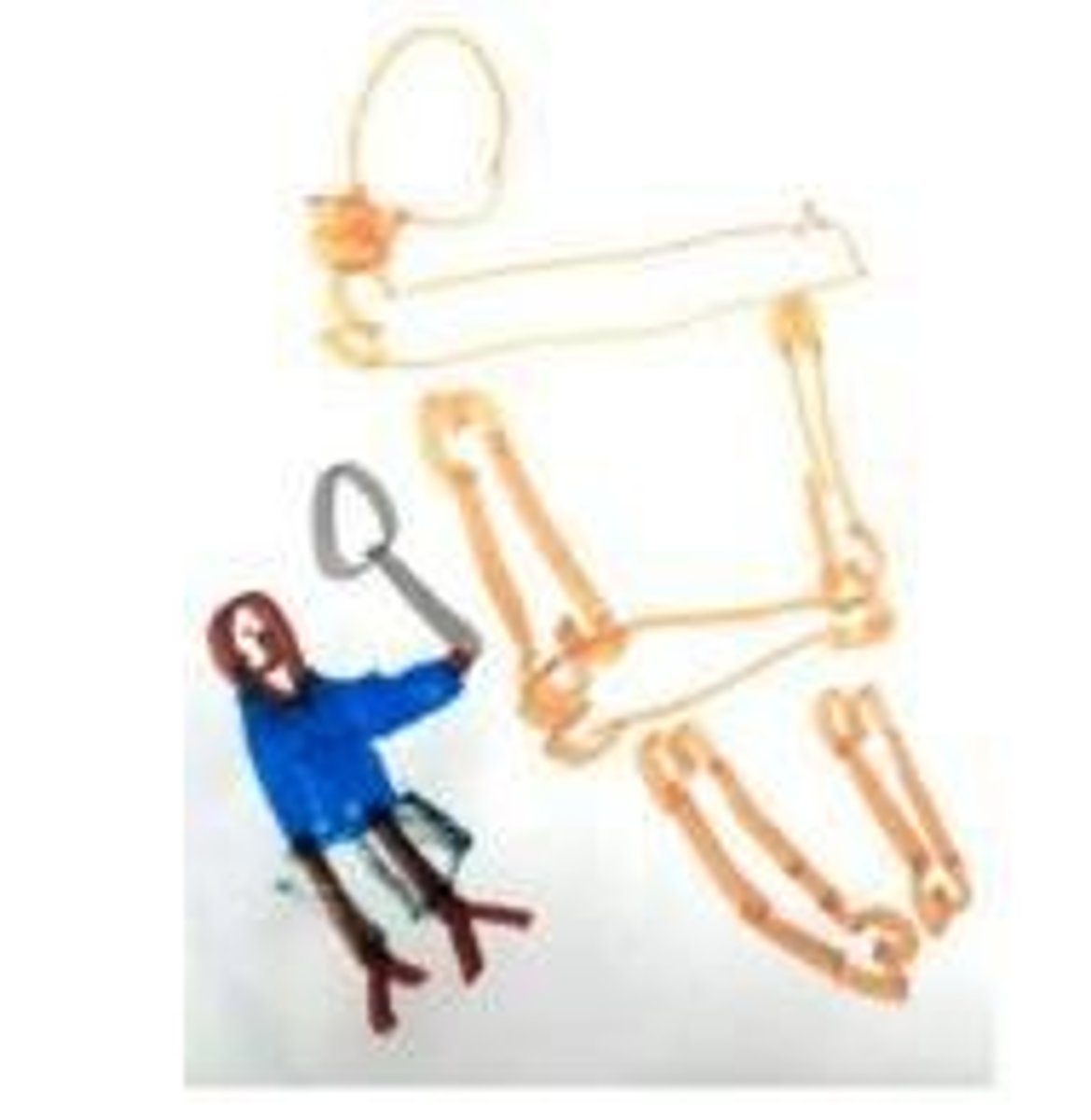
What are some fine motor milestones in early childhood?
Increased control and refined movements of fingers, hands, eyes, and face, enabling children to assist or complete self-help tasks and manipulate writing and drawing utensils.

At what age do children typically start to label their drawings?
Around age 3.
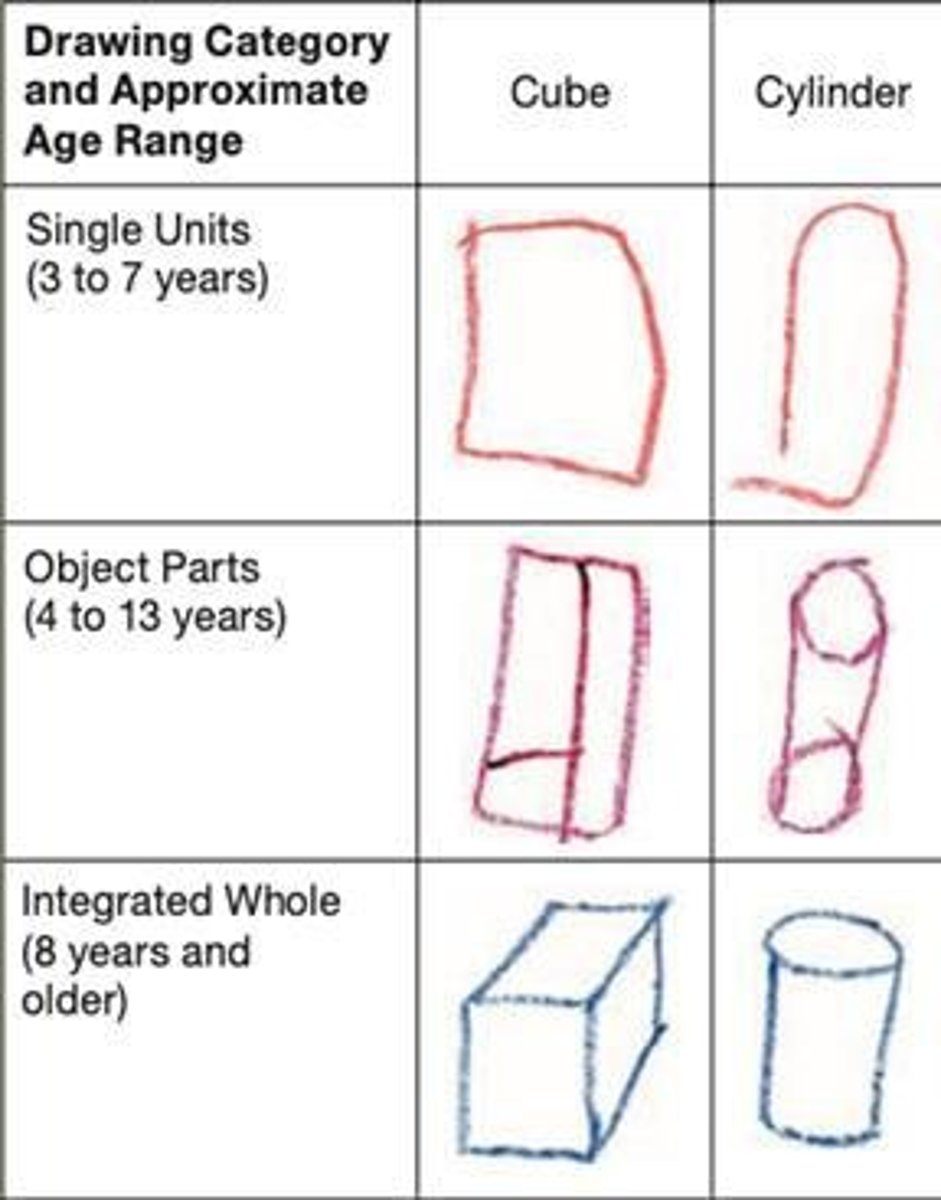
What progression in drawing skills occurs from age 3 to school age?
Children move from labeling drawings to drawing boundaries and people, and eventually to more realistic drawings.

What is the Draw-a-Scientist Task used for?
To assess children's drawing skills and representation of scientists at different ages.
What concept describes operating at a skill level beyond what one can achieve alone, with help from a knowledgeable other?
Scaffolding or Zone of Proximal Development.
How do cross-cultural differences affect children's drawing skills?
Children in East Asian cultures often display advanced artistic skills due to direct instruction and a national art curriculum, while U.S. education emphasizes independence and self-expression.
What are some factors that influence individual differences in motor skill development?
Body build, culture and environment, and sex.
How does body build affect motor skill acquisition?
Taller and more muscular bodies tend to move more quickly and acquire skills faster.
What role does culture play in motor skill development?
Cultural values, adult support, and the available environment can significantly impact motor skill development.
What differences in motor skills are typically observed between boys and girls?
Boys tend to excel in power and force activities, while girls often perform better in fine-motor skills and balance.
What is the recommended amount of unstructured play for preschoolers each day?
At least 60 minutes.
What is the impact of formal lessons on motor skill mastery in young children?
Formal lessons have little impact; motor skills are primarily mastered through everyday play.
What are some ways to support motor development in children?
Provide appropriate play space and equipment, promote a fun attitude toward physical activity, and incorporate daily routines that support fine-motor development.
How can daily routines support fine-motor development?
Activities like brushing teeth and practicing using zippers can enhance fine-motor skills.
What is risky play?
Risky play is defined as 'thrilling and exciting forms of physical play that involve uncertainty and a risk of physical injury' (Sandseter, 2010).
How does risky play benefit children?
Risky play pushes the boundaries of a child's ability and is associated with improved self-esteem, confidence, physical activity, sustained attention, problem solving, and openness to new experiences.

What is the difference between risky play and harmful situations?
Risky play involves potential risks that can be thrilling, while harmful situations are hazardous and pose a danger to children.
What types of risks can risky play involve?
Risky play can involve physical risks as well as emotional and social risks, such as playing with someone new or introducing a new play idea.
What has been observed about unstructured play time in US preschools?
Unstructured play time in US preschools and kindergartens has significantly declined in recent decades due to shifting curricular expectations and standardized testing.
How does socioeconomic status affect access to play in preschools?
Higher-SES preschools tend to be play-based, while lower-SES preschools are often academically focused, which may lead to negative long-term outcomes for children.
What are 'affordances' in the context of children's play?
refer to the interactions with the physical environment that support children's play and development.
What impact does reduced play time have on low-income students?
Reduced play time primarily impacts low-income students, limiting their access to play-based learning experiences.
What is the significance of the research on risky play?
Most research on risky play has been conducted in European contexts, highlighting its importance for children's well-being across various developmental domains.
What are the potential negative outcomes of academically-focused preschools?
Academically-focused preschools may lead to negative long-term outcomes for children, particularly those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds.
What role do curricular expectations play in children's play opportunities?
Shifting curricular expectations and the emphasis on accountability and standardized testing have contributed to the decline of unstructured play time in early education.
What is the relationship between risky play and children's well-being?
Research indicates that there is a positive relationship between risky play and various aspects of children's well-being, including self-esteem and physical activity.
What is self-concept in early childhood?
The set of attributes, abilities, attitudes, and values that an individual believes defines who he or she is.
How do infants and toddlers develop body self-awareness?
They make strides in acquiring body self-awareness as they grow.
What are the observable characteristics that preschoolers use to describe themselves?
Physical appearance, possessions, and name.
At what age do children start to describe themselves in terms of emotions and attitudes?
By age 3 ½.
What personality traits do children recognize in themselves by age 5?
Traits such as timidity, agreeableness, and affect.
What is the difference between sex and gender?
Sex is assigned at birth based on biological factors, while gender is defined by sociocultural roles based on perceived traits.
Define gender identity.
An individual's perception of their own gender and congruence/incongruence with a defined gendered role.
What are some biological influences on gender identity?
Prenatal exposure to hormones can lead to more 'masculine' or 'feminine' traits.
How does the evolutionary psychology perspective explain gender differences?
It suggests that adaptations during human evolution produced psychological differences between males and females.
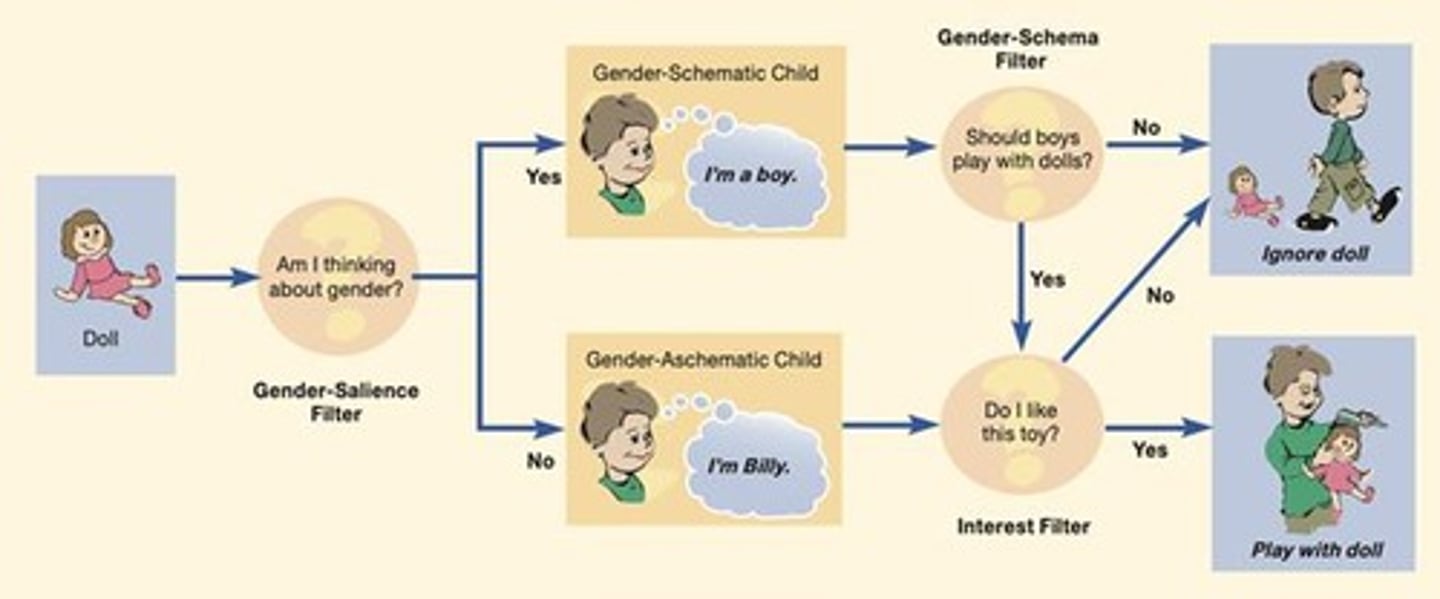
What is gender schema theory?
It explains how environmental pressures and children's cognitions shape gender development.
What is the definition of a friend in early childhood?
Someone who likes you, plays with you, and shares toys.

How do early childhood friendships differ from adult friendships?
Early childhood friendships are based on play and sharing, not the deeper emotional connections seen in adult friendships.

What characterizes nonsocial activity in early childhood?
Uninvolved observation or solitary play, emerging by 0 to 2 ½ years.
What is parallel play?
Playing near other children with similar toys without interacting, emerging by 2 to 3 years.
What is associative play?
Engaging in separate activities while exchanging toys and comments, starting around 3 years.
What defines cooperative play?
Playing together towards a common goal, emerging around 3 ½ to 4+ years.
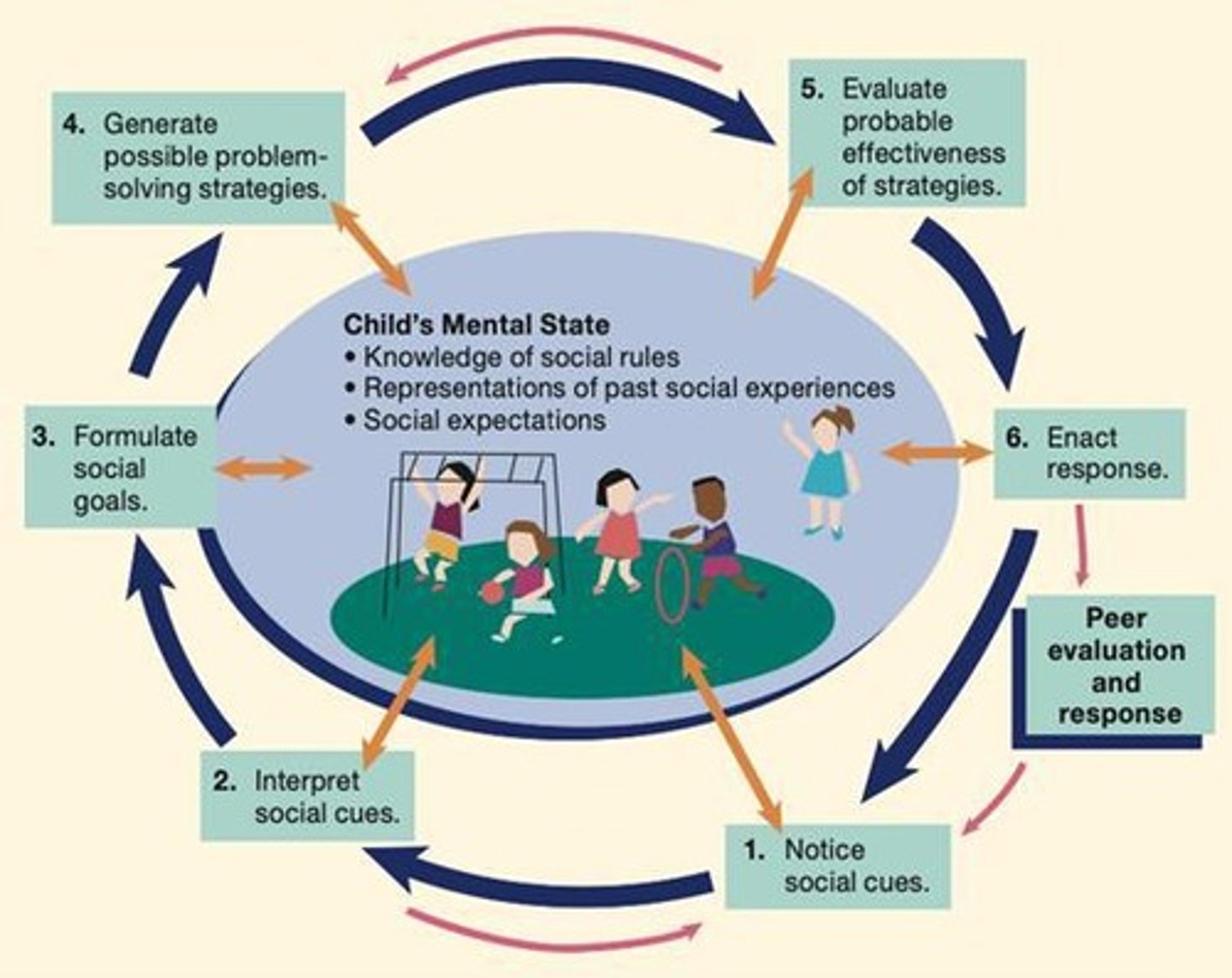
What is social problem solving in early childhood?
Working together to resolve a problem or overcome an obstacle, which begins around 3-4 years.
How does social ability impact academic performance?
Social ability contributes positively to academic performance.
What role do peers play in early childhood development?
Peers influence social interactions and friendship development.
What are some environmental influences on gender identity?
Media, family, peers, and school.
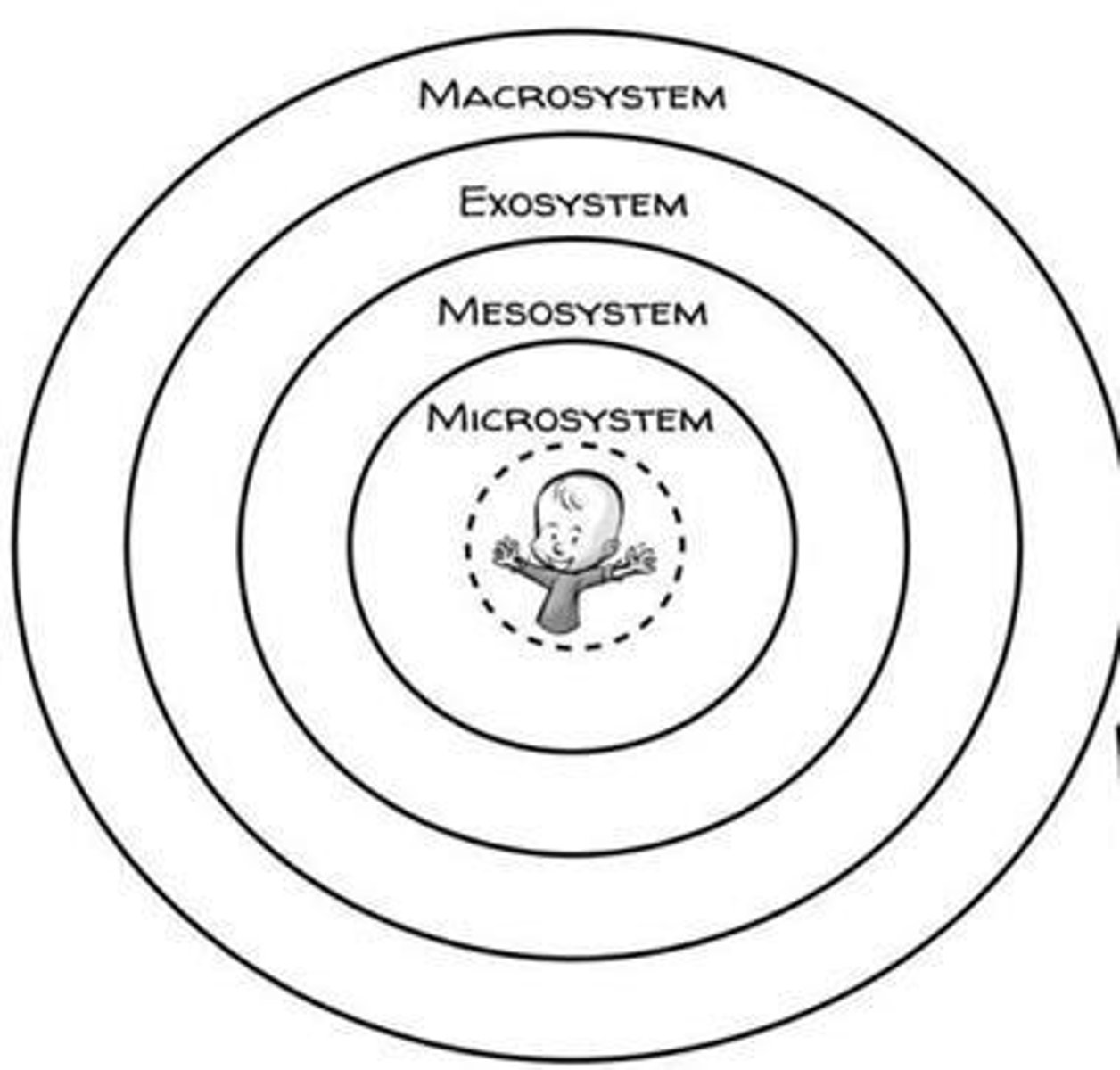
What is the significance of Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory in understanding gender identity?
It emphasizes the multiple environmental contexts that influence a child's development.
What are the cognitive categories of play and their age ranges?
Functional Play (0-2 years): Simple repetitive motor movements; Constructive Play (2-6 years): Creating or constructing something; Make-Believe Play (3-6 years): Acting out everyday and imaginative roles.
What is proactive aggression in early childhood?
When children act to fulfill a need or desire and unemotionally attack a person to achieve their goal.
What is reactive aggression in early childhood?
Defensive response to provocation or a blocked goal, meant to hurt another person.
What are the three forms of aggression in early childhood?
Physical Aggression (pushing, hitting, destroying property), Verbal Aggression (threats, name-calling, hostile teasing), Relational Aggression (social exclusion, malicious gossip, friendship manipulation).
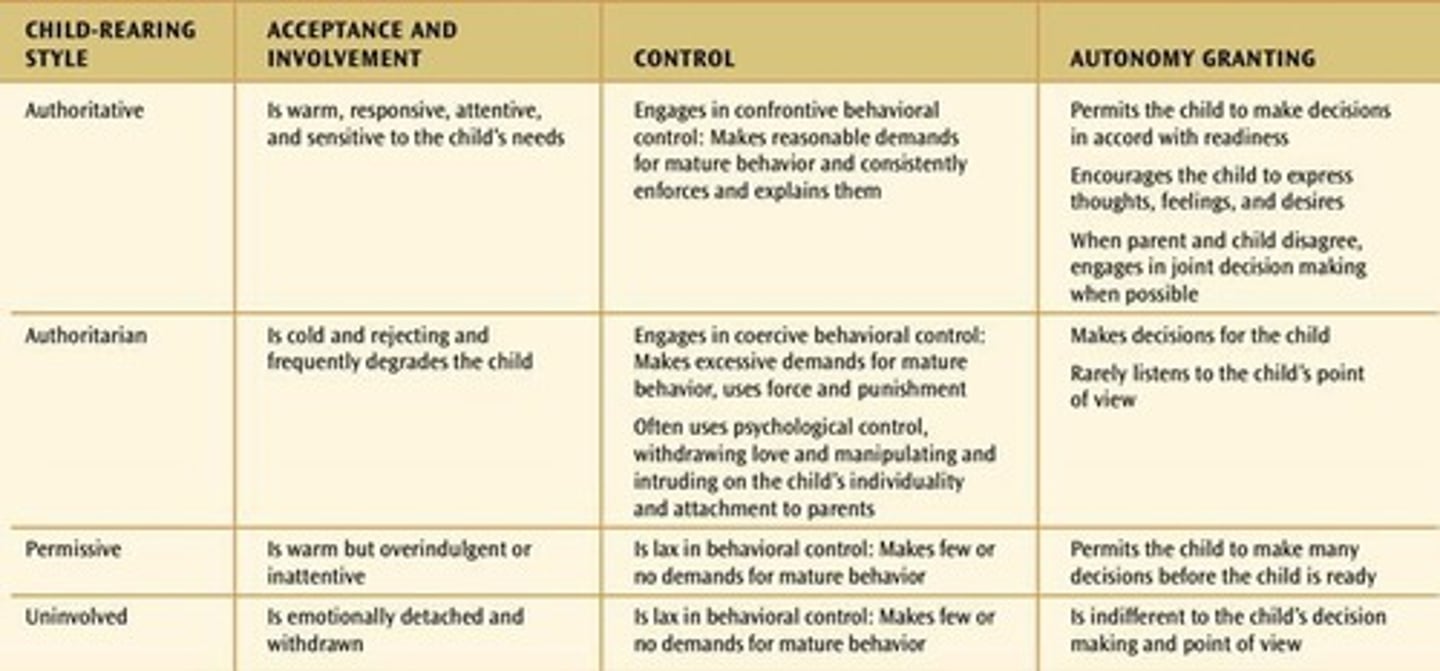
What are Baumrind's parenting styles?
Authoritative, Authoritarian, Permissive (Indulgent), and Neglectful.
What characterizes authoritative parenting?
Demanding yet warm and accepting, which can ameliorate negative traits of children's temperament.
What do children need from parents according to the notes?
Children need attention, acceptance, warmth, and involvement from parents.
What is the significance of 'contact comfort' in infant-parent attachment?
indicates that infant-parent attachment is based on more than just feeding.
How does vocabulary knowledge relate to early cognition?
Children's general vocabulary knowledge is positively linked to academic performance, executive function, and reasoning skills.
What predicts math skills in children years later?
A larger productive vocabulary size at age 2
How does knowledge of specific types of words affect children's performance?
Predicts performance on related tasks beyond general vocabulary.
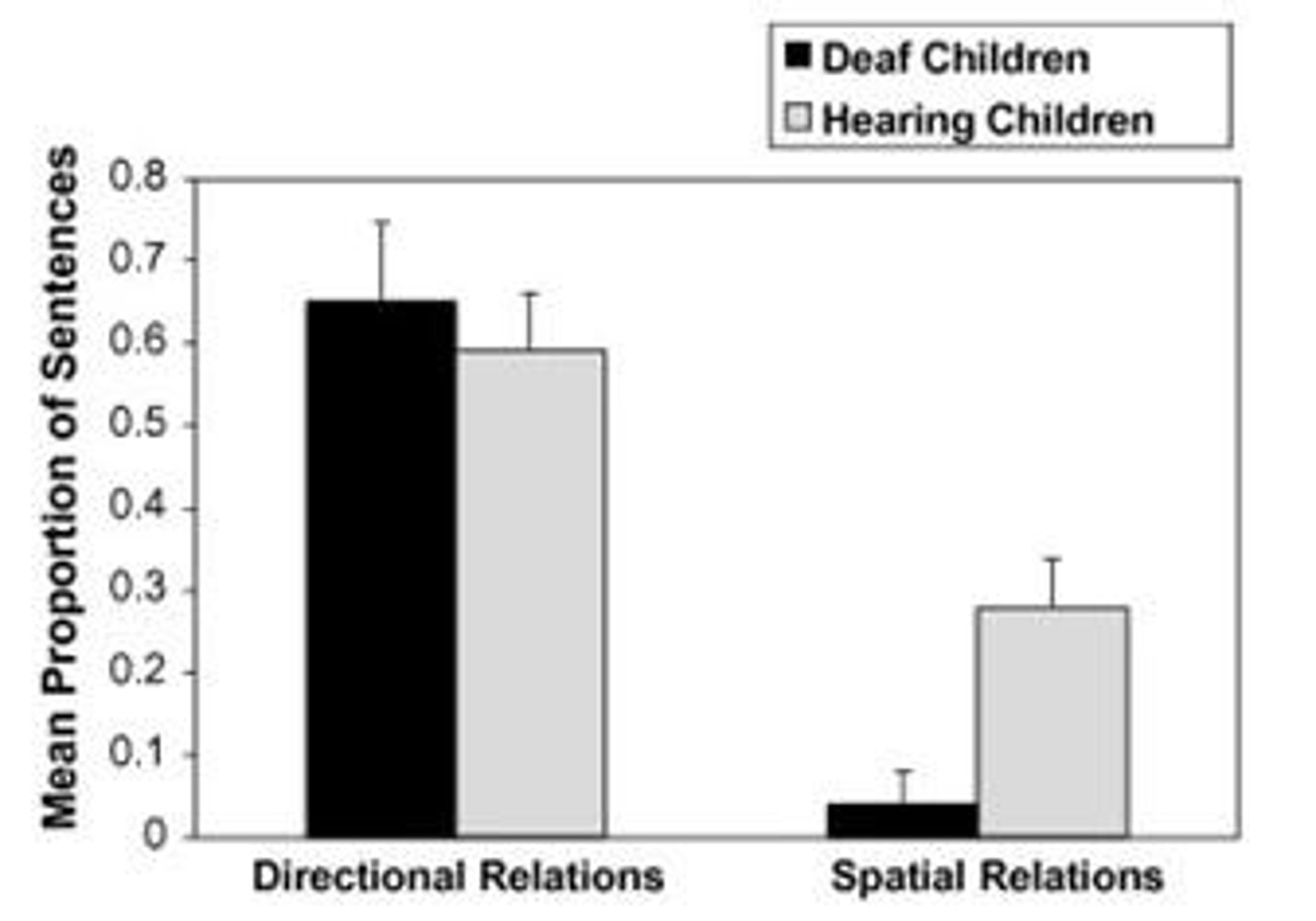
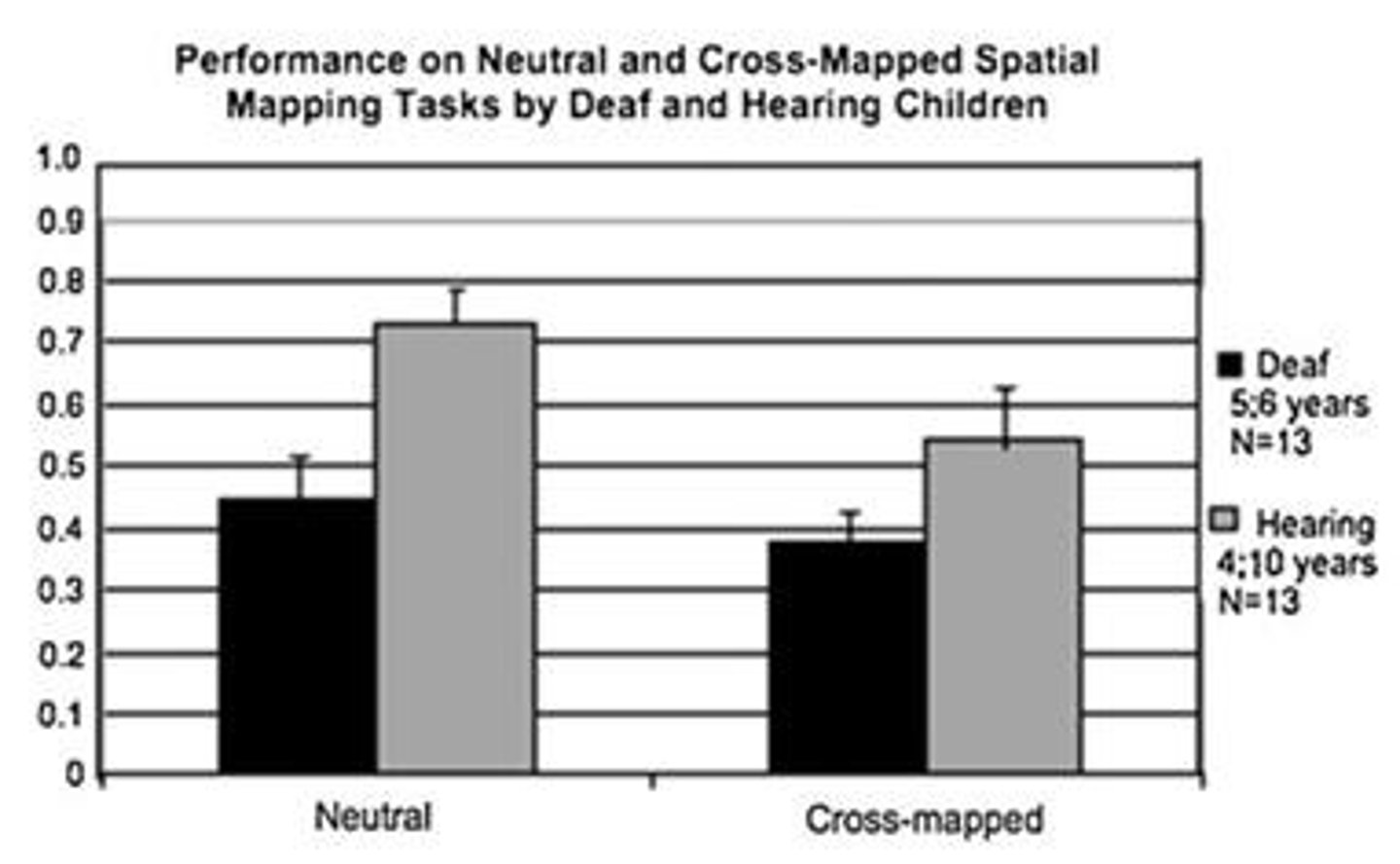
What is the role of language in understanding spatial relations?
Providing more language cues helps children understand and remember spatial relations.
What is the relationship between general vocabulary and inductive reasoning skills?
Knowing more general words early on (e.g., 'animal' instead of 'dog') leads to faster vocabulary growth and better inductive reasoning skills.
What are the developmental outcomes associated with different parenting styles?
Different parenting styles influence children's behavior, emotional development, and social skills.
What is the impact of warm, involved parents on children?
Warm, involved parents can model caring concern and confident, self-controlled behavior, leading to better compliance from children.
What is the effect of authoritative parenting on children's behavior?
Children are more likely to comply with fair, reasonable control from authoritative parents.
What is the significance of the studies by Gentner et al. (2013) and Miller et al. (2016)?
These studies highlight how language shapes thought and understanding of spatial relations in children.
What does the term 'indulgent' refer to in Baumrind's parenting styles?
refers to a parenting style that is warm and accepting but undemanding and uncontrolling.
What are the implications of Harlow's monkeys study for parenting?
The study emphasizes the importance of contact comfort and emotional connection in infant-parent attachment.
How does authoritative parenting convey competence to children?
Authoritative parents convey to children that they are competent, fostering self-esteem and self-efficacy.
What are the characteristics of authoritarian parenting?
Authoritarian parenting is demanding and controlling but cold and rejecting.
What is the role of parenting in social emotional development?
Parenting plays a crucial role in shaping children's social emotional development and overall well-being.
What are the supportive aspects of the authoritative parenting style?
They serve as a powerful source of resilience, protecting children from the negative effects of family stress and poverty.
How can some aspects of the authoritarian parenting style be viewed positively in certain ethnic groups?
Research suggests that some aspects may be associated with positive developmental outcomes.
What is the distinction between 'tiger moms' and the authoritarian style?
The 'training parents' style is distinct from the controlling factor of the authoritarian style, despite similar emphasis on respect and obedience.
What is inductive discipline in the context of moral development?
Involves adults pointing out the effects of children's misbehavior on others, encouraging sympathy and concern.
What are the benefits of inductive discipline for children?
It provides information for future behavior, encourages prosocial behavior, gives reasons for behavior change, and helps form scripts to deter future misbehavior.
How do children learn moral behavior according to social learning theory?
Children learn largely through modeling by observing and imitating those who demonstrate appropriate behavior.
What characteristics of models affect children's willingness to imitate?
Warmth and responsiveness, competence and power, and consistency between words and behavior.
What are the undesirable side effects of corporal punishment?
It models aggression, causes fear and resentment, damages relationships with punitive parents, reinforces punitive behavior, and may transfer to the next generation.
What is the cognitive-developmental theory's view on children's moral judgments?
Children make moral judgments based on concepts of justice and fairness, distinguishing between social conventions and moral imperatives.
What are social conventions according to cognitive-developmental theory?
Customs determined solely by consensus, such as table manners or dress styles, where adults explain less and demand obedience.
What are moral imperatives?
Principles that protect people's rights and welfare, where adults explain the rights and feelings of victims.
How do young children differentiate between social conventions and moral imperatives?
They can distinguish between the two, but their understanding of accidental versus intentional actions is not fully developed.
What is the impact of positive parenting on child development?
Positive parenting fosters favorable self-esteem and cognitive and social maturity.
What is the relationship between parenting styles and resilience in children?
Supportive parenting styles, like authoritative, contribute to resilience against stress and poverty.
What is the significance of the phrase 'the best parenting style is subjective'?
It indicates that the effectiveness of parenting styles can vary based on cultural and individual factors.
What are the consequences of frequent corporal punishment?
It can lead to models of aggression, fear, anger, resentment, and poor relationships with parents.
What role does consistency between words and behavior play in moral development?
It enhances children's willingness to imitate moral behavior modeled by adults.
What are the implications of moral violations compared to social convention violations?
Moral violations are considered more wrong than violations of social conventions.
What are the key cognitive milestones in early childhood according to Vygotsky?
Attention, memory, inhibition, executive function, metacognition, and theory of mind.
What is sustained attention in early childhood?
Focused and extended engagement with an object, task, event, or other aspect of the environment, increasing sharply between ages 2½ and 3½.
What factors contribute to improvements in sustained attention?
Frontal lobe growth, gains in working memory, and adult scaffolding.
What is executive attention?
The ability to plan actions and allocate attention to goals.
What difficulties do preschoolers face regarding attention?
They struggle to prioritize salient features over relevant features and to use systematically organized plans.
How does memory improve in early childhood?
Recognition is better than recall, and children begin to use memory strategies such as organization and rehearsal.