BIO140: DNA RNA Proteins
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
DNA
Instructions for the structure and function of our cells and bodies
Made up of DNA nucleotides
Found and functions in the nucleus
Used to produce RNA through transcription, using the DNA to make a copy of the instructions in the form of RNA
→ Transcription
RNA
Copy of instructions
Made out of RNA nucleotides
Found in nucleus and cytoplasm
→ Translation
Proteins
_____: Serve as functional and structural molecules produced after reading the DNA instructions.
Made out of amino acids
Found in entire cell
Made in cytoplasm
Required by almost every cellular reaction
Fundamental to all traits and functions
DNA —> ___ —> Trait
DNA Structure & Function
Double helix, two strands of DNA nucleotides, twisted into helix
(P, Deoxyribose, [C,T,A,G])
Instructions for the structure and functions of our cells and body
Instructions for making proteins
RNA Name
Ribonucleic Acid
RNA Structure
Single strand of RNA nucleotides (P, Ribose, [A,U,C,G])
Shorter than a chromosome
length of the instruction needed to make protein
or length of a gene
Difference between DNA and RNA
DNA: Deoxyribose, Thymine, 2 strands, nucleus
RNA: Ribose, Uracil, 1 strand, Cytoplasm
RNA Function
Copy of instructions for a protein
RNA can leave the nucleus to move to a ribosome to make a protein
The 3 Kinds of RNA
Ribosomal RNA
Messenger RNA
Transfer RNA
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Found in ribosome
Structural
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
_____: Serves as a copy of instructions for making a protein. It can leave the nucleus to move to a ribosome to begin making a protein.
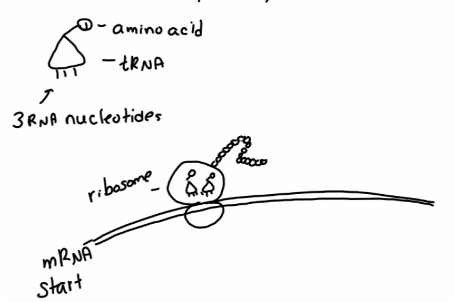
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
_____: transfers an amino acid to a ribosome. Helps ensure the correct amino acid is added to the protein.
Place for amino acids to bond at top
Place for 3 RNA nucleotides (anticodon) at bottom
There’s one ____ structure for each of the 20 kinds of amino acids

The Six Types of Protein
Support
Enzymes
Transport
Defense
Hormones
Motion
Support Proteins
_____: Provide structure. Examples include collagen found in ligaments, tendons, and skin (the layer underneath the skin cells that holds the skin in place), as well as the Cytoskeleton and spindle fibers.
Enzyme Proteins
_____: Control chemical reactions by improving the rate of reaction, making them better and faster. An example is digestive Lactase, which digests lactose.
Transport Proteins
_____: Allow molecules to be moved or transported. Examples include Hemoglobin (which transports O2) and Plasma membrane channels (big protein tunnels that allow molecules like glucose to move from inside to outside the cell)
Defense Proteins
_____: Antibodies, which are part of the immune system. Antibodies are produced when an individual is exposed to something that does not belong in the body (an antigen, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi). Antibodies stay in the blood and recognize future infections from antigens, allowing the immune system to respond quickly and potentially result in less illness.
Hormone Proteins
_____: Function for communication between cells
Motion Proteins
_____: Found in muscle cells. They include contractile proteins that allow a muscle cell to get shorter and longer by sliding over each other to contract the muscle, which in turn allows the skeleton to move.
Amino Acid Structure
A carbon in the centre
A hydrogen on top
An amino group on one side
A weak acid group on the other side
A placeholder called the Reactive Group (R): different for each amino acid
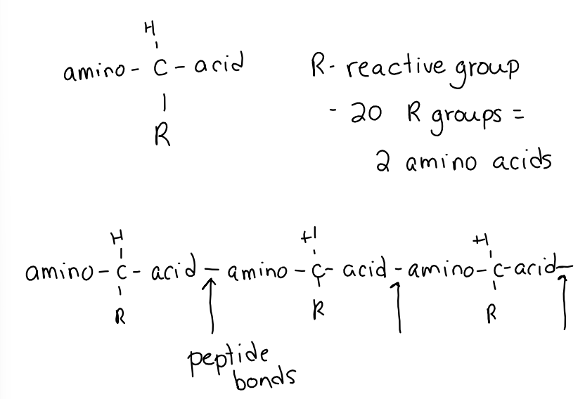
Peptide Bond
_____: The acid group of one amino acid bonds to the amino group of the next amino acid.
Polypeptide
_____: A chain of amino acids bonded together with peptide bonds. Once released and folded, it moves to the Golgi for processing and packaging.
Why do proteins need to have the correct structure or shape?
Protein function depends on it, they need the correct shape to be able to function. If the pieces are incorrect that function cannot be correct. For example, membrane proteins need a specific shape to be a part of the membrane. If a membrane protein has the wrong shape (like in Cystic Fibrosis) it cannot enter the membrane.
Interactions between amino acids
Attraction
Repulsion
Neutral
Attraction
Amino acid interaction
_____: Molecules are chemically attracted to each other, leading them to sit close to each other and form a chemical bond
Repulsion
Amino acid interaction
_____: Molecules are chemically repelled, causing them to move as far away as possible from each other, resulting in no bond.
Neutral
Amino acid interaction
_____: Molecules do not react to each other, leading to no change in physical position and no bond.
What happens to other amino acids during interactions?
The other molecules are dragged along, causing a shape change.
Four levels of protein structure
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Primary Structure
Level of protein structure
_____: The linear order of amino acids based on the order of nucleotides in the mRNA (which comes from the linear order of nucleotides in the DNA)
Secondary Structure
Level of protein structure
_____: The folding and swirling of the primary structure, based on the order of amino acids in the primary structure (attraction, repulsion, neutral)
Tertiary Structure
Levels of protein structure
_____: The further folding of the secondary structure, based on swirling and folding that brings amino acids into alignment, allowing them to interact with each other to form a complete 3D structure. All proteins have this level and most are ready to function at this point.
Quaternary Structure
Levels of protein structure
_____: When two or more tertiary proteins bond together to form a large, complete protein. Each tertiary structure must be correct in order to fit together with other tertiary structures are produce a functioning quaternary protein.
Importance of correct protein folding
Each level of protein structure depends on the previous one; an error in DNA can change the amino acid sequence, altering the protein’s shape and function.
Gene Expression
_____: The process by which the DNA instructions are translated into proteins. This flow of info can be summarized as:
DNA (transcription) → mRNA (translation) → Protein
Nucleotides
_____: Subunits of DNA
RNA nucleotides
_____: Subunits of mRNA
Amino acids
_____: Subunits of proteins
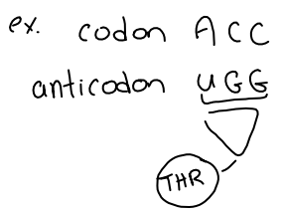
Codon
_____: A group of three nucleotides found in the strand of mRNA that correspond to an amino acid
Anticodon
_____: A structure consisting of three RNA nucleotides located at the bottom of the tRNA molecule, Its a part of the mechanism that ensures the correct amino acid is added to the protein through codon-_________ matching.
Redundancy
_____: The characteristic of the genetic code where there is more than one codon for most amino acids. It protects against some small changes in DNA because since multiple codons specify the same amino acid, a small change might still result in the insertion of the correct amino acid, meaning it doesn’t change to resulting protein.
Does a small change in DNA always change the protein?
No if there is redundancy
Sometimes
Transcription
_____: The process to build, create, or make a strand of mRNA based on a DNA template. The DNA serves as the original instructions, and the RNA is the copy of those instructions.
When does transcription start?
A cell initiates the process when it receives the signal to make a protein that is needed.
Transcription steps:
Enzyme finds genes on its chromosome and attaches to it
Breaks bonds between 2 DNA strands for the length of the gene, resulting in unbonded DNA nucleotides
Free RNA nucleotides are chemically attracted to exposed DNA nucleotides and sit beside them. If bonds form, the RNA nucleotide stays, if no bonds form, it leaves. Continues until instructions fully transcribed
P-S Backbone
Bonds holding mRNA to DNA are broken, the mRNA leaves the DNA, and it closes back up.
The mRNA is processed.
Exon Splicing
_____: Sections of mRNA that are not needed for a protein are removed and needed parts rejoining
Introns (interrupting instructions) are not needed and removed
Exons are needed
Result is processed mRNA
Translation
_____: The process of building the primary structure of a protein based on an mRNA template. It is the second stage of gene expression, where the mRNA copy is used to produce a protein (amino acids)
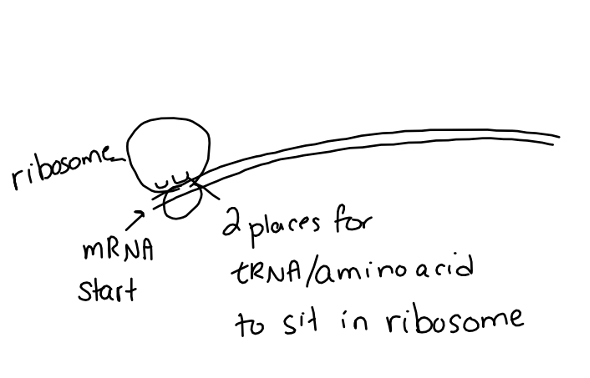
Structures and molecules needed to make a protein
Ribosome, tRNA, mRNA, amino acids
Codon-anticodon matching
_____: Ensures the correct amino acid is added to the polypeptide.
tRNA structure transfers an amino acid to a ribosome
tRNA has anticodon at the bottom
If the codon of the mRNA matches, the amino acid is added to the primary structure
What happens if the tRNA enters the ribosome and the codon and anticodon do not match up?
The tRNA and the amino acid leave the ribosome

Translation Steps
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation
Translation
_____: Begins when the mRNA leaves the nucleus, acting as a chemical signal for structures and molecules in the cytoplasm to be activated, including 2 parts of the ribosome. All parts come together (mRNA, ribosome subunits, first tRNA)
Elongation
Translation
_____: Adding amino acids to the growing chain, thereby putting together the primary structure of the protein. This involves the continual process of codon-anticodon matching, where matching tRNA’s deliver amino acids, which are then bonded into the chain.
Termination
Translation
_____: Triggered by the end of instructions, a stop codon. Its critical because it doesn’t code for any amino acid, meaning no more amino acids can be added.
The ribosome comes apart
The mRNA is released from the ribosome (returns to nucleus or to another ribosome)
The resulting polypeptide is released and folded, and moves to the Golgi for processing and packaging

What is one way a cell can make many copies of the same protein?
By having multiple ribosomes attach to and translate the same mRNA molecule at once (each ribosome reads mRNA codons and builds a separate copy of the protein)