Plant support and growth: Secondary Growth
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is secondary growth
it is woody growth, increased girth rather than length
Not all plants go through secondary growth
Annual plants, biennial plants, herbaceous perennials, tree ferns, and palms
Plants that do have secondary growth
all the seed plants except monocots
what is the function of Xylem
it is the main conducting tissue for water and minerals absorbed by roots
what is xylem composed of
parenchyma cells, fibers, vessels, tracheids, and ray cells
what are vessles
long tubes composed of vessel elements, which are open at each end
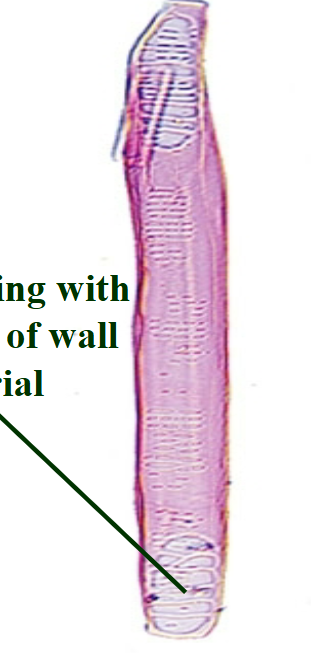
what are tracheids
tapered cells, not open at the end. often have pits in between them

Gymnosperm xylem has tracheids only
Anthophyte xylem has both tracheids and vessel elements
What is Phloem
it conducts photosynthates
what are photosynthates
dissolved foods, sugars, produce of photosynthesis
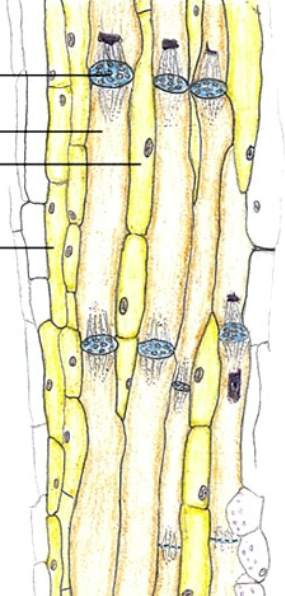
what are phloem composed of
sieve tube members and companion cells
what are sieve tube members
cylindrical cells, laid end-to-end
what is the epidermis
the outermost cell layer on all young plant organs, usually one cell thick, and forms a protective layer called the cuticle
what is the Axial system
vertically running cells (big vertical bunch of straws
what is the Radial system
Horizontally running cells (there are a few straws stuck horizontally through the big bunch)
what are the two secondary meristems
vascular cambium and cork cambium
What are rays
provide horizontal transport and storage in wood,
Phloem rays are triangular
what is the vascular cambium
the layer between the axial/radial systems and ?
what are the three parts of the Periderm
cork cambium, cork, phelloderm
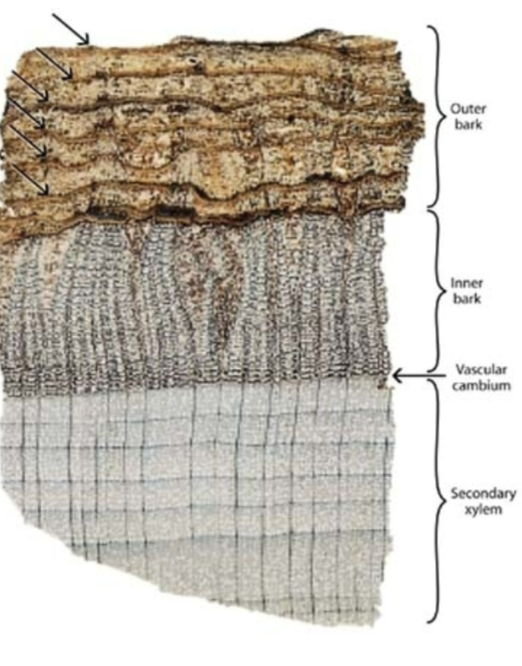
what is the outer bark
all tissues outside of the innermost cork cambium
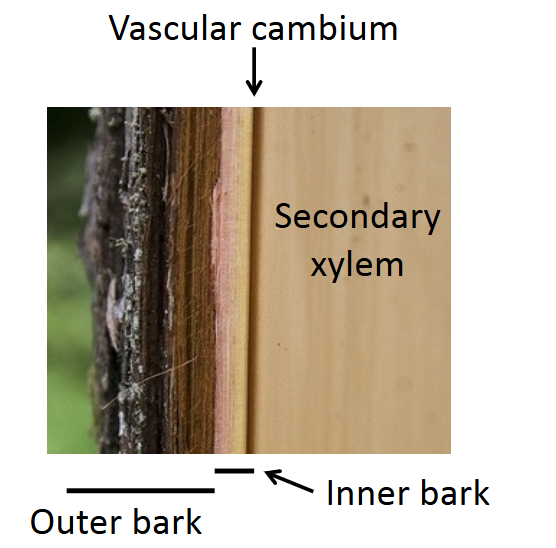
what is the inner bark
it is what is between the innermost cork cambium and vascular cambium
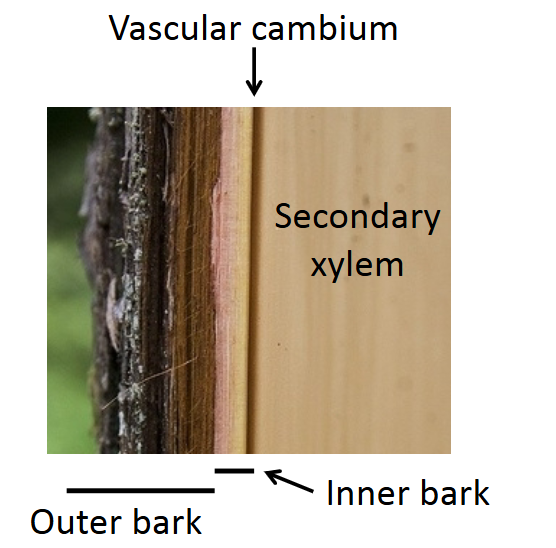
what is a result of continued secondary growth?
bark textures may seem to be flaking/peeling off
What are the characteristics of Heartwood
darker
non-conducting
no food reserve, all dead cells
what are the characteristics of Sapwood?
lighter
conducting
what are annual rings?
visible rings that mark the end of a year’s growth in species in seasonal environments