Biology IB SL C1.2
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Describe the structure of ATP.
ATP is composed of a nitrogen based adenine structure attached to ribose, a pentose sugar, which is then attached to a chain comprised of 3 phosphates.
Outline properties of ATP that make it suitable for the use as an energy currency within cells.
The third phosphate in ATP is very unstable, and can be easily transferred over to a protein or other molecule, with the release of energy.
Removing 1 phosphate from ATP converts it into ADP.
The ADP can later be "recharged" by phosphorylating it to ATP.
Outline example cellular processes that require use of ATP.
ATP is required for active transport (the movement of particles through a membrane with the help of proteins), anabolism (the building of polymers), and whole cell movements (involved the movement of the cytoskeleton which requires energy in the form of ATP in order to change its shape).
Describe the ATP-ADP cycle, including the relative amount of energy and the roles of hydrolysis and phosphorylation.
Once ATP has been hydrolyzed with the release of energy, the resulting ADP can be re-phosphorylated with the addition of energy. This cycle can be repeated indefinitely in the cell over its entire life.
State why heat is generated during the ATP-ADP cycle.
Because the breaking of the high-energy phosphate bond results in a release of energy due to the overall change in the chemical structure and stability of the molecules involved.
Define cellular respiration.
Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP.
List reasons why cellular respiration must be continuously performed by all cells.
Consider again the overall equation for cell respiration:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
As mentioned before, this is the same equation as burning glucose. It isn't safe to release that much energy all at once in the cell
List common substrates of cellular respiration.
Usually glucose or fats, but could also be amino acids, or sugars other than glucose.
Compare and contrast anaerobic and aerobic respiration.
Cell respiration can be aerobic (using oxygen) or anaerobic (without oxygen).
Aerobic respiration follows the equation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
With a high yield of ATP.
The mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration produces a low yield of ATP, but it doesn't require oxygen, and it's fast.
In humans:
glucose → lactate
In plants and yeast:
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
Identify the independent, dependent and controlled variation in experiments of variables affecting the rate of cell respiration.
Just like when investigating rate of enzyme activity, thinking carefully in terms of how the reactants and products change over time can help you design an investigation into cell respiration.
List two approaches for determining the rate of cellular respiration.
Cell respiration relies on enzymes, so possible independent variables include any factor that influences enzyme rate:
Glucose concentration
Temperature
pH
Type of sugar
Salinity
Oxygen concentration
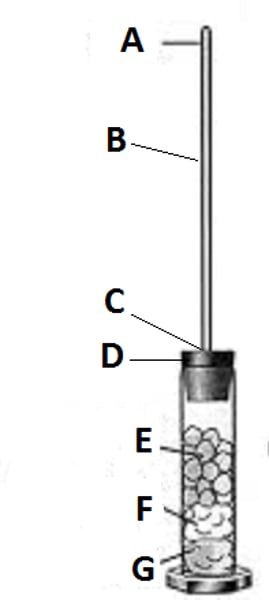
Describe an investigative technique for measuring the effect of a variable on the rate of cellular respiration.
Measuring the rate of cellular respiration can either rely on measuring the amount of oxygen taken in, or the amount of carbon dioxide being released. Respirometers are devices that measure these types of gas volume changes, and therefore provide information about the rate of cellular respiration.