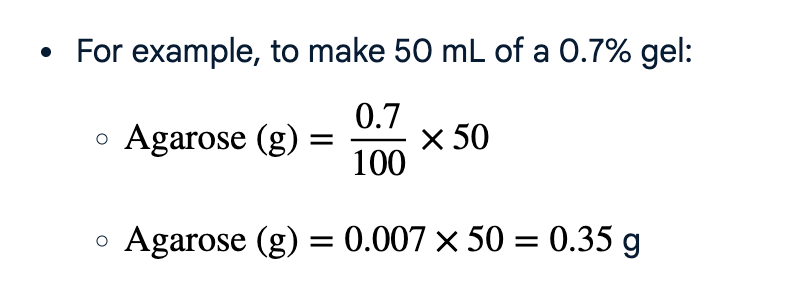Dynamic Genome Midterm 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
what are the SI Prefixes

Pipette Review
Dilution Equation
water= final working volume - initial stock volume

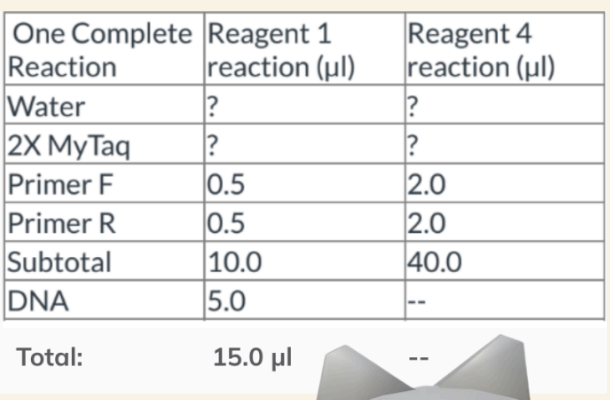
PCR Table calcuations
7.5µl of 2X MyTaq
1.5µl water
for 4 RXNS:
2x MyTaq → 30µl
H20 → 60µl
What is the purpose of PCR
amplify a certain part of DNA to be able to have a quantity of DNA that can be studied
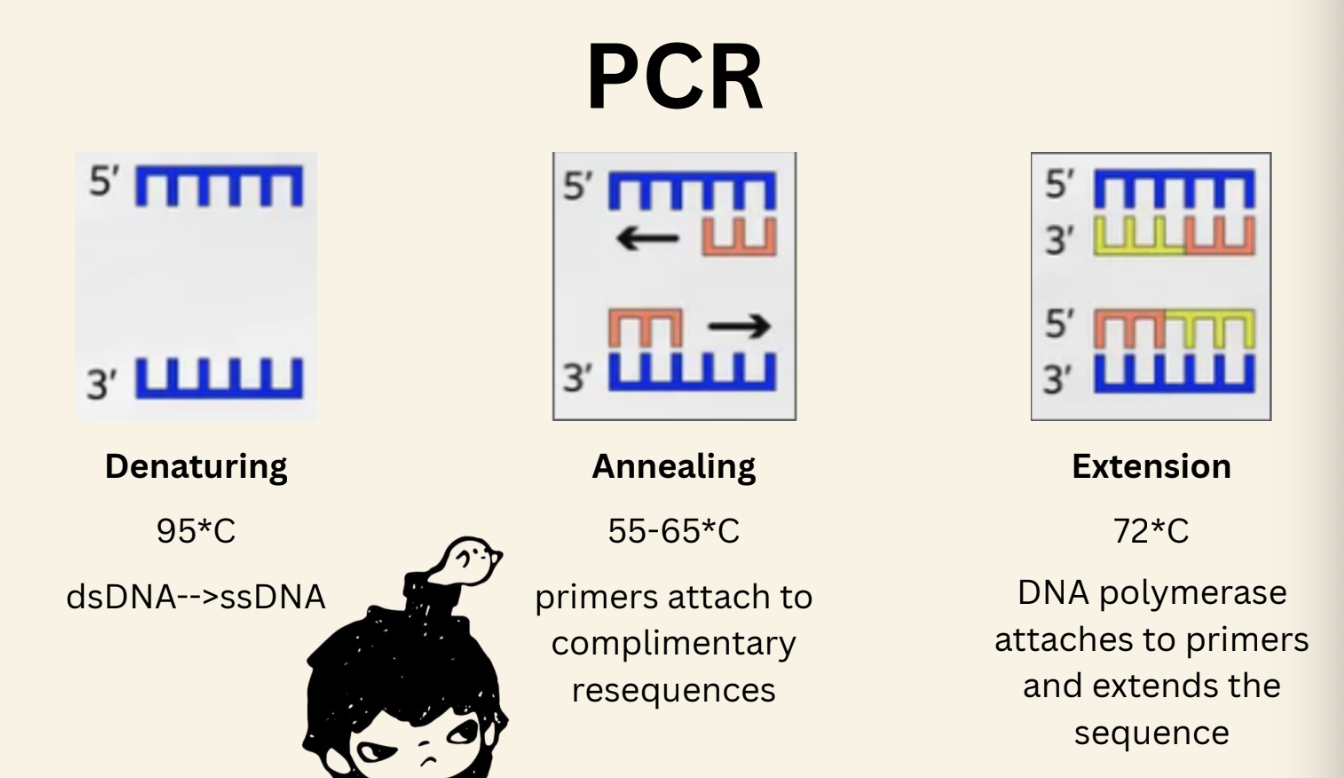
what are the stages if PCR?
denaturing: heat breaks hydrogen bonds within the double stranded DNA base pairs, seperating into 2 single DNA strands
annealing: temp is lowered to let DNA primers bind to their complementary sequence, thus they are attached ready for extension
extension: temp is raised again to a optimal working temp for the Taq polymerase, the DNA polymerase binds to a primer and starts synthesising a complementary DNA sequnce in the 5’→3’ direction
this will happen for as many cycles as needed where the DNA is doubled each cycle
What materials are needed for PCR
2x MyTaq
Forward & reverse primers →short, single stranded DNA sequences that primes ssDNA so DNA polymerase knows where to bind and start elongating for annealing
ddH2O
Positive and negative control. Positive control is used to verify the PCR is working using a well known sample and negative control verify that the mastermix is not contaminated w/DNA
What does MyTaq Contain?
Taq polymerase (DNA polymerase of extension)
Nucleotides for the polymerase to use during extension
Buffer to provide good environment for DNA polymerase to work effectively
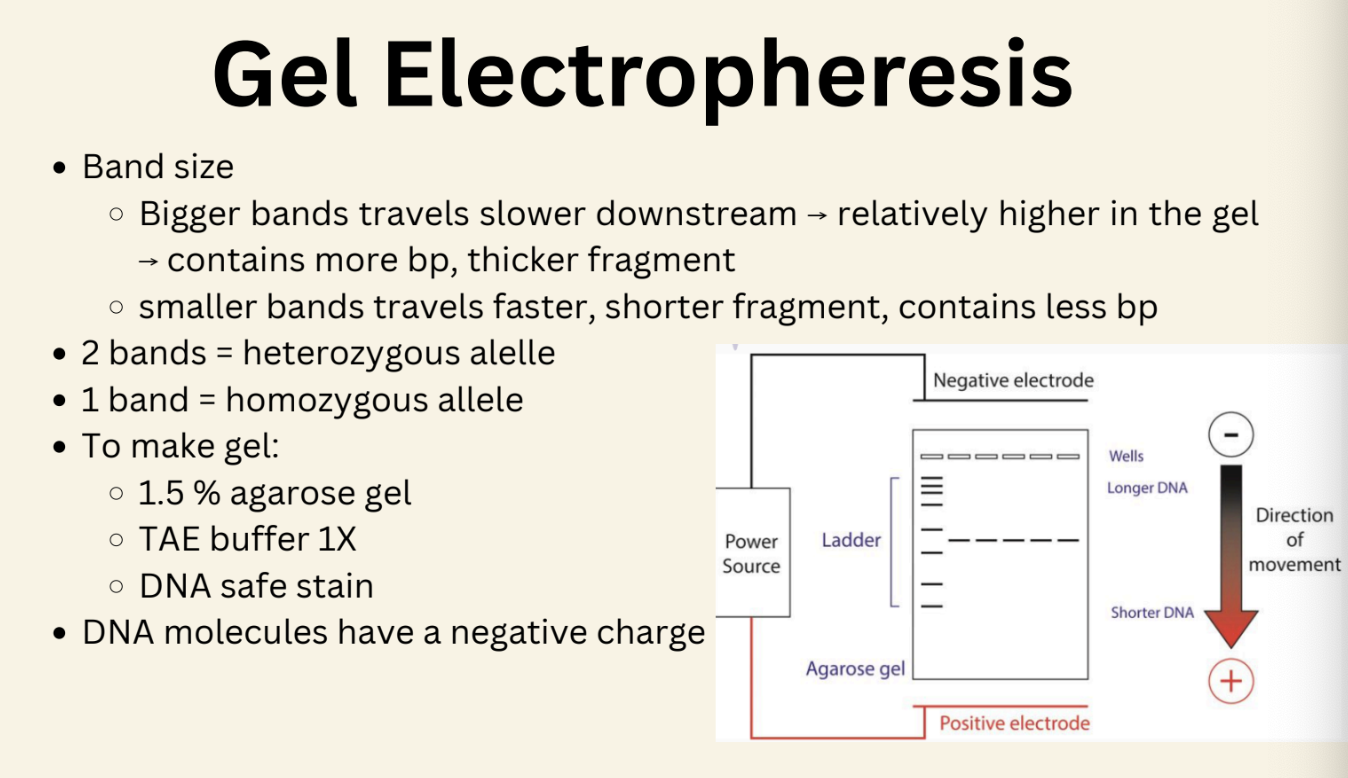
Gel Electropheresis
DNA polymorphism
variation of specific DNA sequences
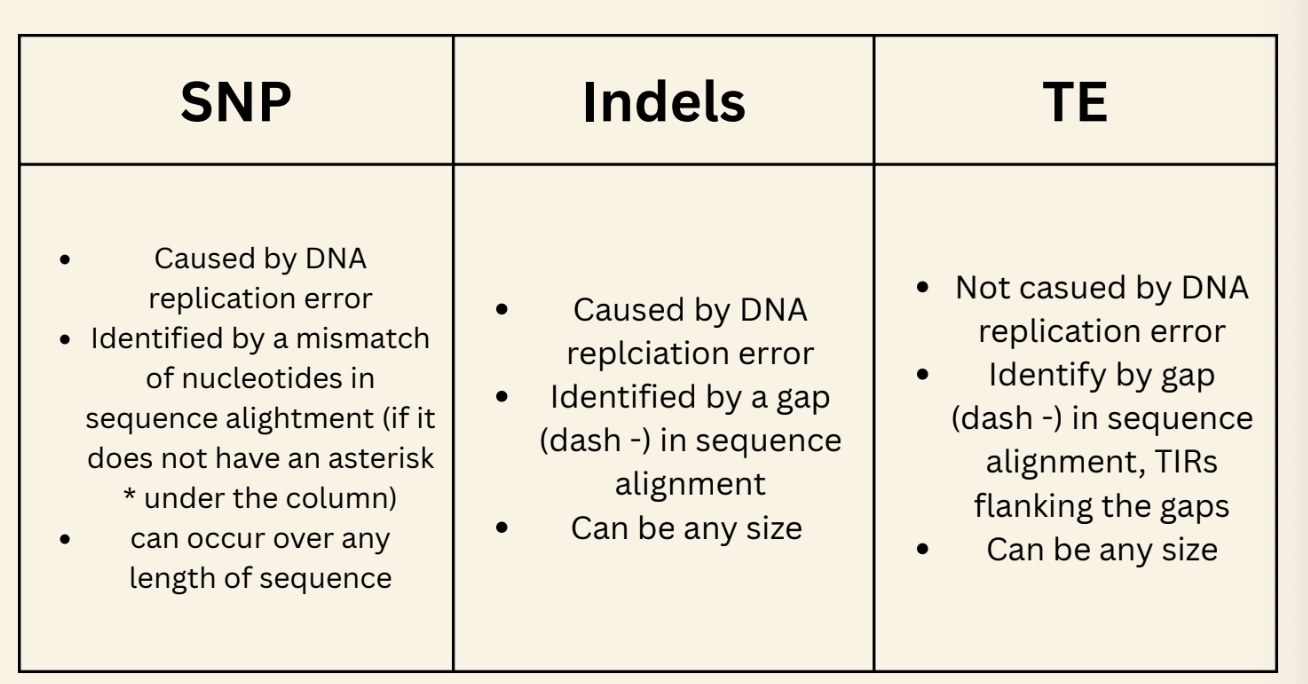
SNPs
A single nucleotide polymorphism: a difference in 1 nucleotide
sickle cell anemia is bc of a SNP
error during DNA replication
2 types of SNPs:
Synonymous: silent (doesnt change the amino acid that was coded for in the codon)
Nonsynonymous SNP: Missense/nonsense(most severe mutation) mutations that does change amino acid sequence
Indels
insertion/deletion of 1 or more nucleotides of DNA
can cause frameshift mutations if the number of necletides inde;ed is not a multiple of 3
“-” gaps
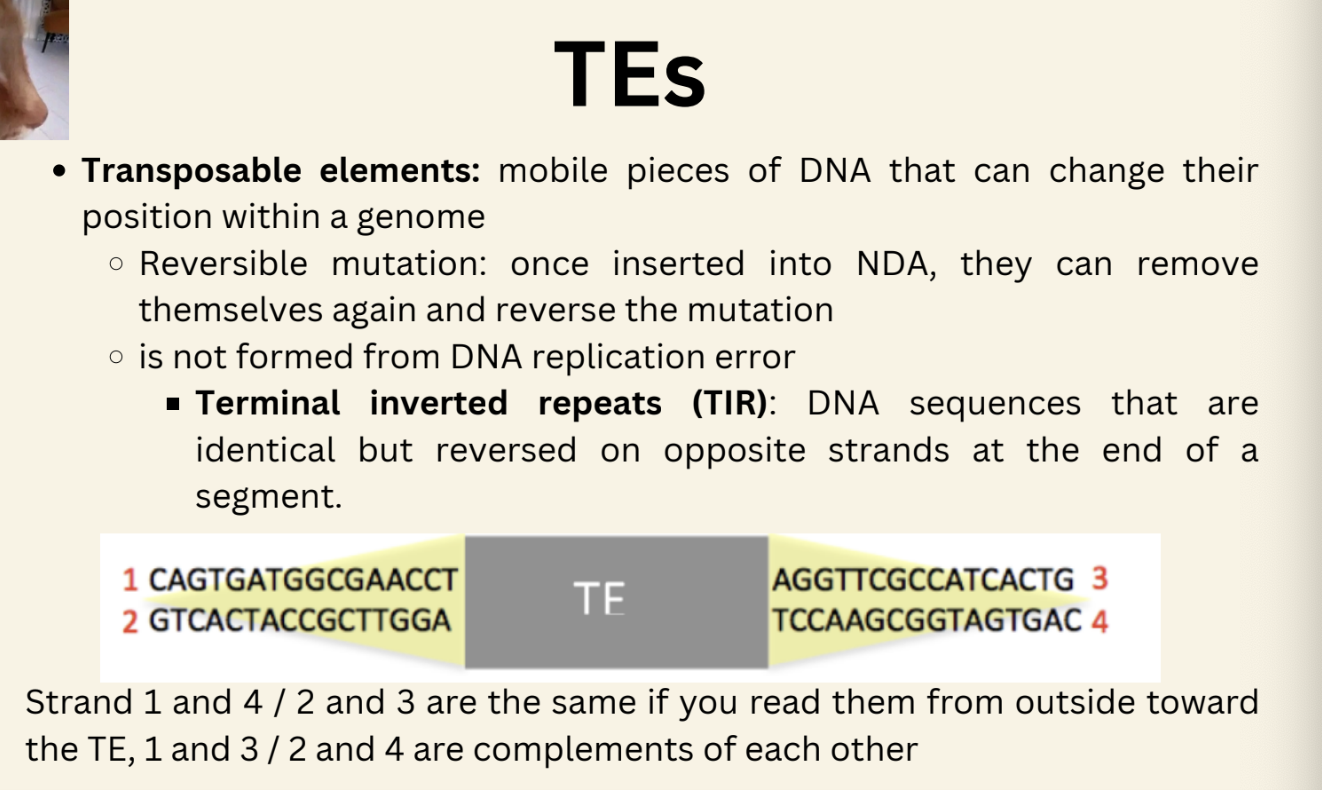
TEs
Compare the 3 polymorphisms
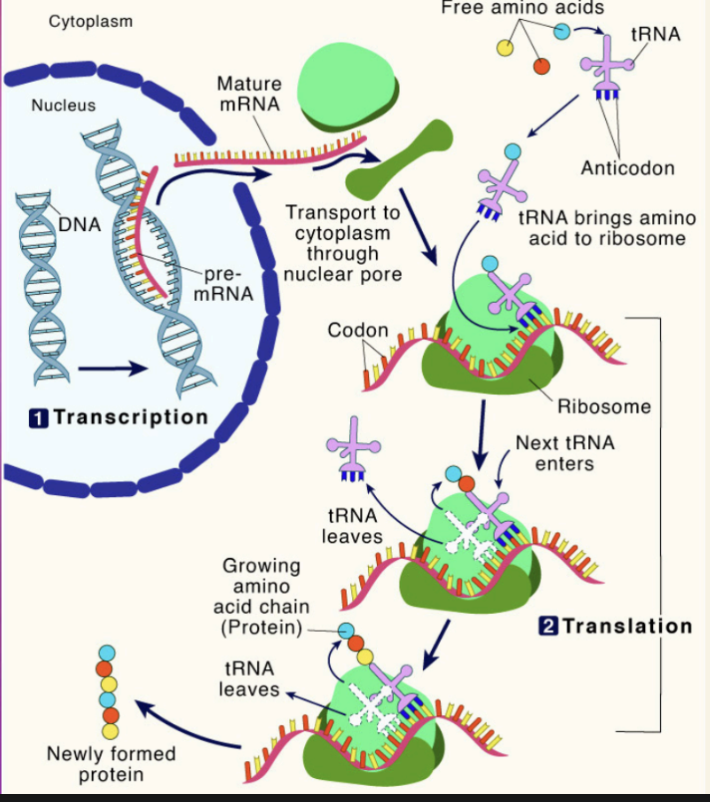
Gene Expression
process of transcribing and translating DNA→protein
transcription:
in the nucleus, DNA → pre-mRNA →mRNA
RNA polymerase, spliceosomes
Translation
in cytoplasm, mRNA → tRNA → amino acid chain
ribosome
transcription and translation steps
Reverse Transcription
allows synthesis of DNA (in cDNA form) from mRNA using reverse transcriptase
cDNA is intron-less version of gDNA since it is based on the spliced mRNA
allows us to determine what was spliced out of mRNA and the difference in sequence length
more stable than mRNA
cDNA are often shorter →further downstream in gel electrophoresis
Sequence analysis (MUSCLE & BLAST)
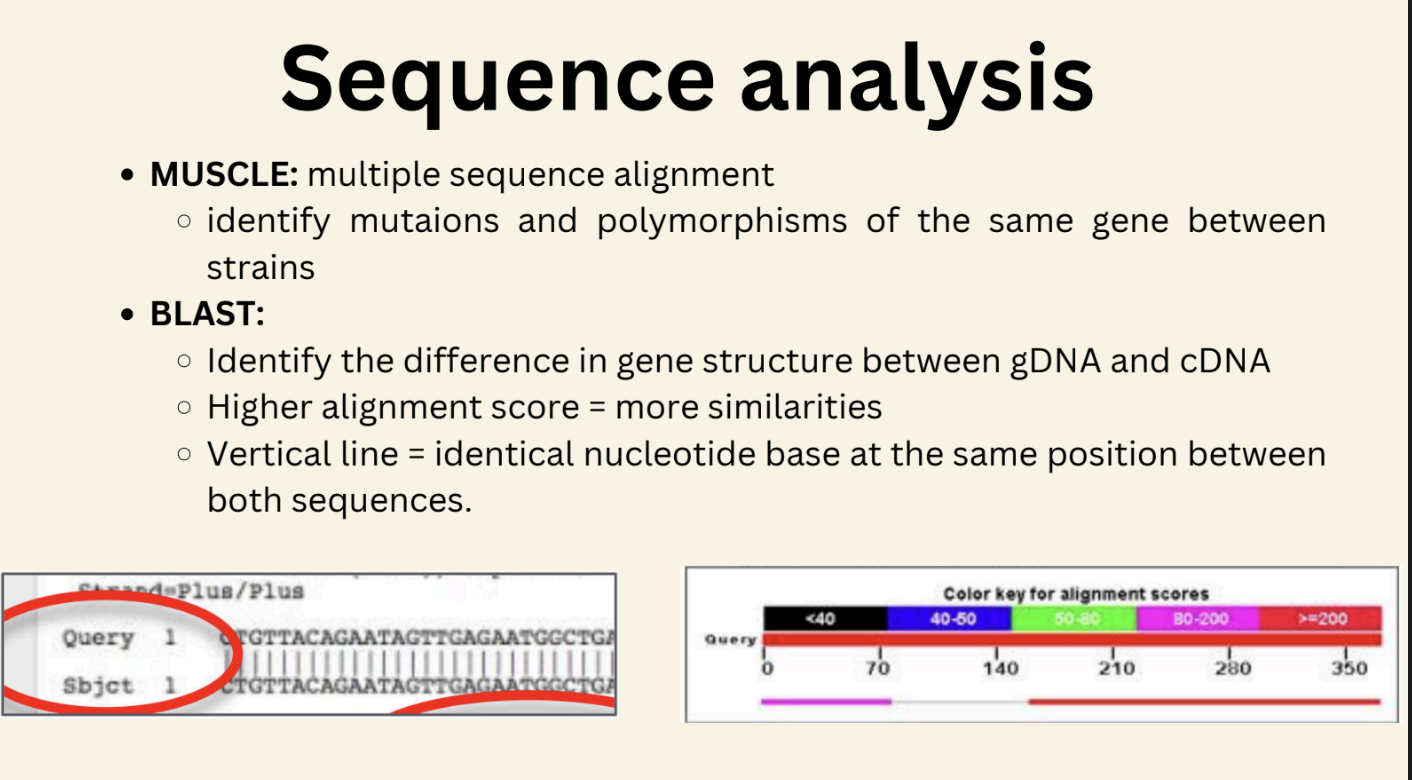
experiment 3

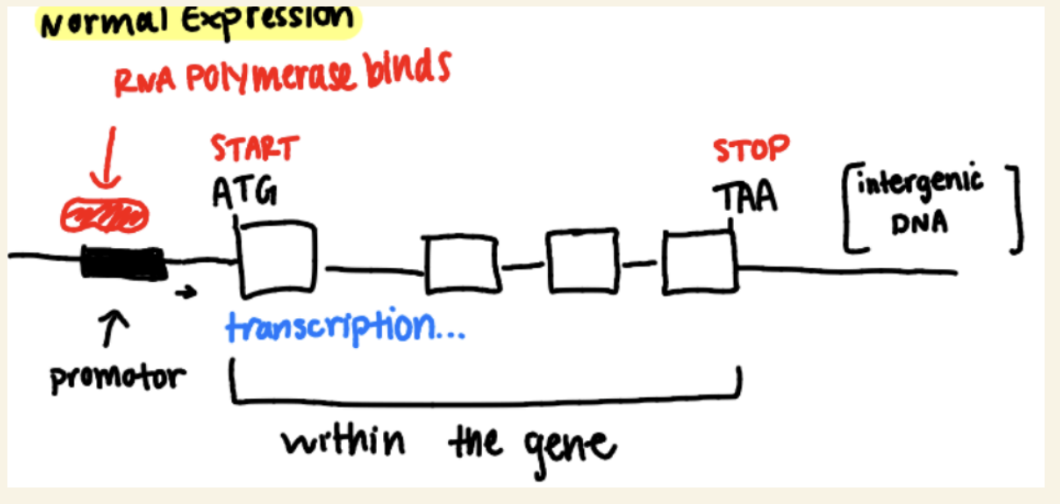
Regulation of gene expression
Constitutive: genes that are always on
conditional: genes that are conditionally on
Transformation
inserting DNA into living organism, the organism can take up the DNA DNA as its own and express into protein
Plasmid
A circular strand of DNA that can be taken up by the bacteria, bacteria can express the genes located in the plasmid as their own DNA
genes added to the plasmid must be cDNA/intron-less because bacteria cant slice out introns
reporter gene
a gene that indicates gene expression is occuring (ex GFP)
Selective gene
gene that ensures only transformed bacteria are left alive (AmpR)
constitutive expression process
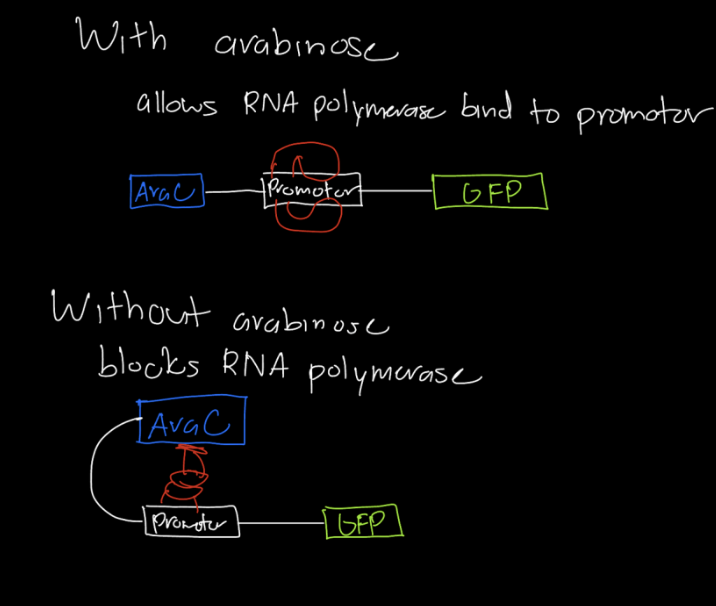
Conditional Expression process
RNA polymerase cannot bind to promoter because a transcription factor is already binded
sugar/hormones if it binds to TF then it comes off from the gene and the RNA polymeras can bind to the promoter
how to calculate DNA copies per PCR cycle
2 n (x)
n= # of cycles
x= # of starting cycles
Translation
in cytoplasam mRNA meats with ribosomes where it contains both proteins and rRNA
Which of the following is needed for DNA amplification to occur?
A) Ribonucleotides
B) RNA primers
C) DNA polymerase
D) Both B and C
E) All of the above
cDNA polymerase
What does PCR stand
Polymerase Chain Reaction
What volume of a 75% stock solution is needed to make 10 µl of a 12% working solution, and how much water will need to be added to the stock?
1.6 µl of stock, and 8.4 µl of water
What volume of stock and water is required to make 725 µl of a solution with a concentration of 55 µg/µl when starting with a stock concentration of 275 µg/µl?
0.145 mL of stock and 0.580 mL of water
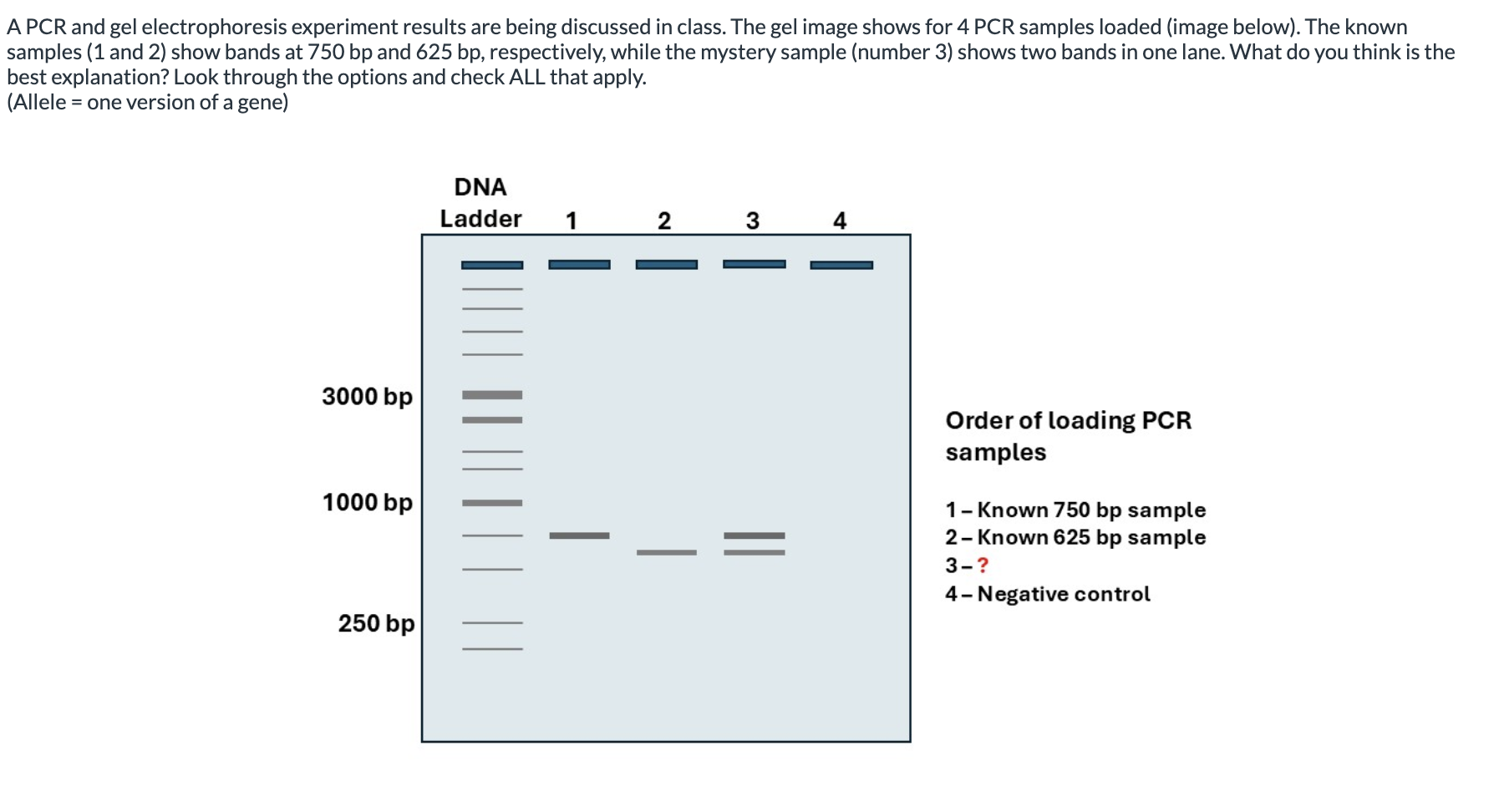
A. Two different alleles, one with a synonymous SNP compared to the other allele.
B. It has no significance.
Incorrect answer:
C. Two different alleles, one with an SNP compared to the other allele.
D. A heterozygous allele which appears as two distinct bands
D. A heterozygous allele which appears as two distinct bands
In a PCR reaction which of the following is required for DNA amplification to occur?
A. RNA primers
B. RNA primers and (Taq) DNA polymerase
C. Ribonucleotides
D. (Taq) DNA polymerase
D. (Taq) DNA polymerase
gDNA is a copy of ________, while cDNA is a copy of _________.
A. genomic DNA, mRNA
B. genomic DNA, tRNA
C. rRNA, genomic DNA
D. mRNA, genomic DNA
D. mRNA, genomic DNA
In a PCR reaction which of the following is required for DNA amplification to occur?
(Taq) DNA polymerase
tRNA
Has a complementary sequence of mRNA and carries an amino acids to the growing protein chain
RNA Polymerase
Has a complementary sequence of mRNA and carries an amino acids to the growing protein chain
The following question assumes the same transformation protocol that was used for the experiment you conducted in lab.
What would happen if you took some of the E. coli bacteria from the 'LB + ampicillin plate' and spread the bacteria on a new plate with 'LB + ampicillin + galactose'? (alive/dead & glow/no glow)
The bacteria will be dead.
The bacteria will be alive but won't glow under
The bacteria will be alive and will glow under UV light.
The bacteria will be alive but won't glow under UV light.

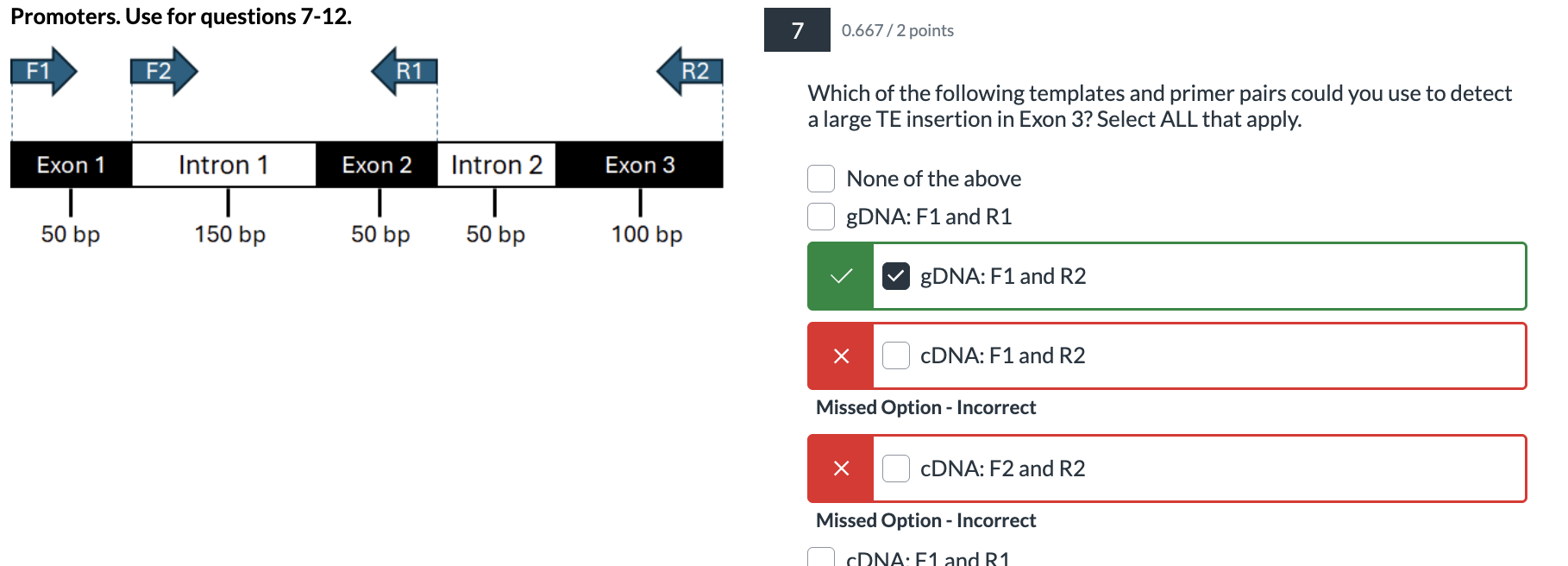
Which of the following templates and primer pairs could you use to detect a large TE insertion in Exon 3? Select ALL that apply.
gDNA: F1 and R1
gDNA: F1 and R2
cDNA: F1 and R2
cDNA: F2 and R2
cDNA: F1 and R1
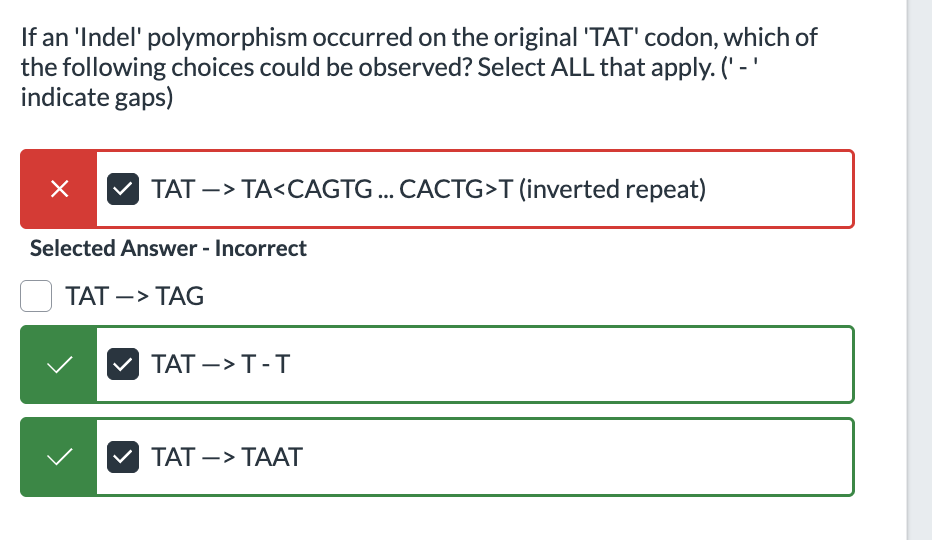
If an 'Indel' polymorphism occurred on the original 'TAT' codon, which of the following choices could be observed? Select ALL that apply. (' - ' indicate gaps)
TAT —> TA<CAGTG ... CACTG>T (inverted repeat)
TAT —> TAG
TAT —> T - T
TAT —> TAAT

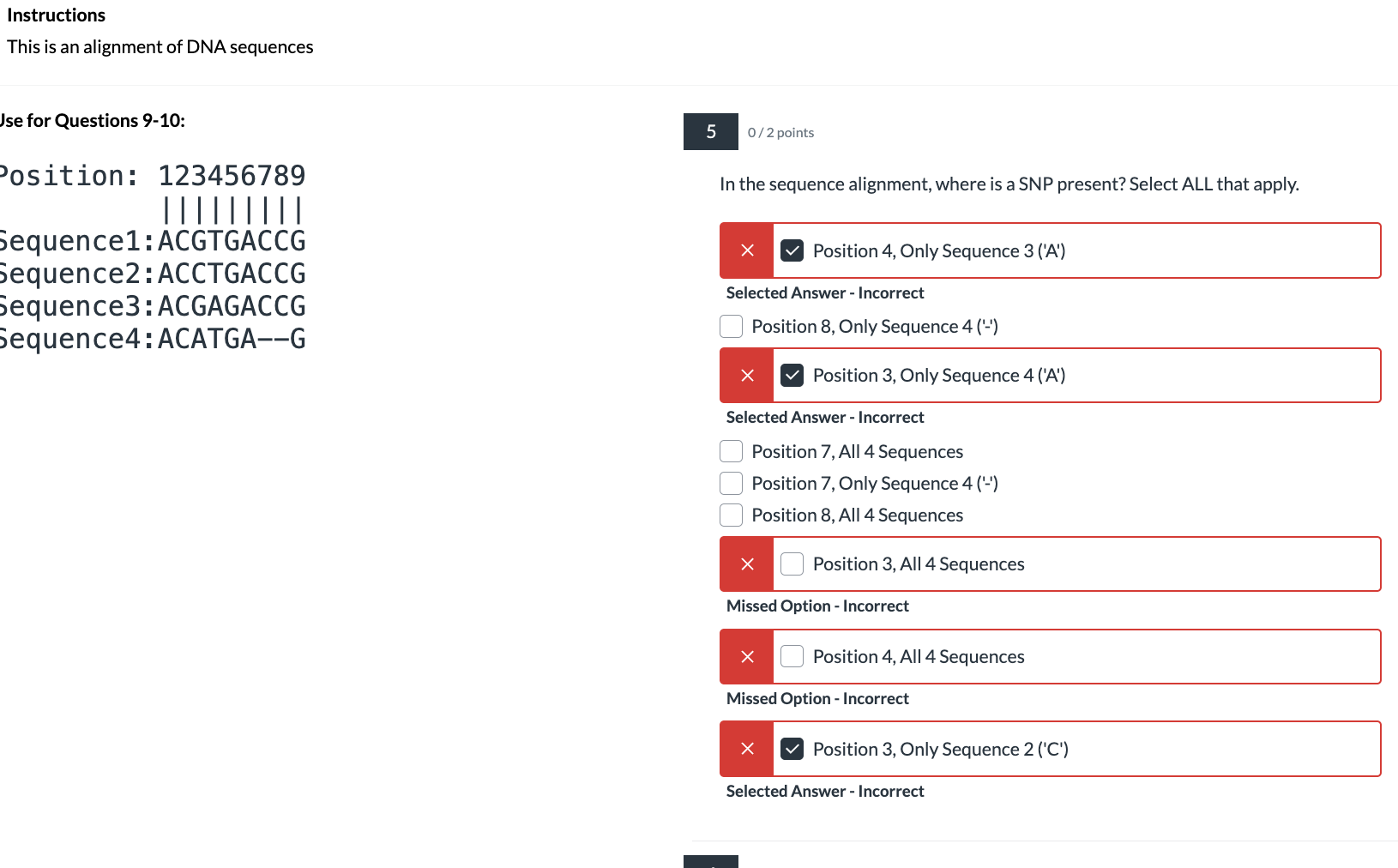
identify snps

where is indel

what is in mytaq
taq polymerase, nucleotides, buffer
t/f an indel can cause a frameshift
true
t/f indels are reversible
true
what is the order of gene expression
Transcription, splicing, translation
how do we get cDNA from gDNA
reverse transcription of mrna
What is the difference between MUSCLE and BLAST?
BLAST shows difference between gDNA and CDNA, MUSCLE shows polymorphisms
transformation efficiency formula
1.) calculate the mass of plasmid used
#ng of plasmid = (volume of DNA used)(concentration of DNA)
2.) calc the transformation efficiency
transformation efficiency (cfu/nzg)= (#colonies/#ng of plasmid) x ( total volume µl/ plated µl)
3.) change to cfu/µg
cfg/ng x 1000 ng/µg = cfu/µl