BIOL109.004-FALL23’ | Foundations in Biology I
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Evolution, Biodiversity, and Ecology. CHAPTER 1!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
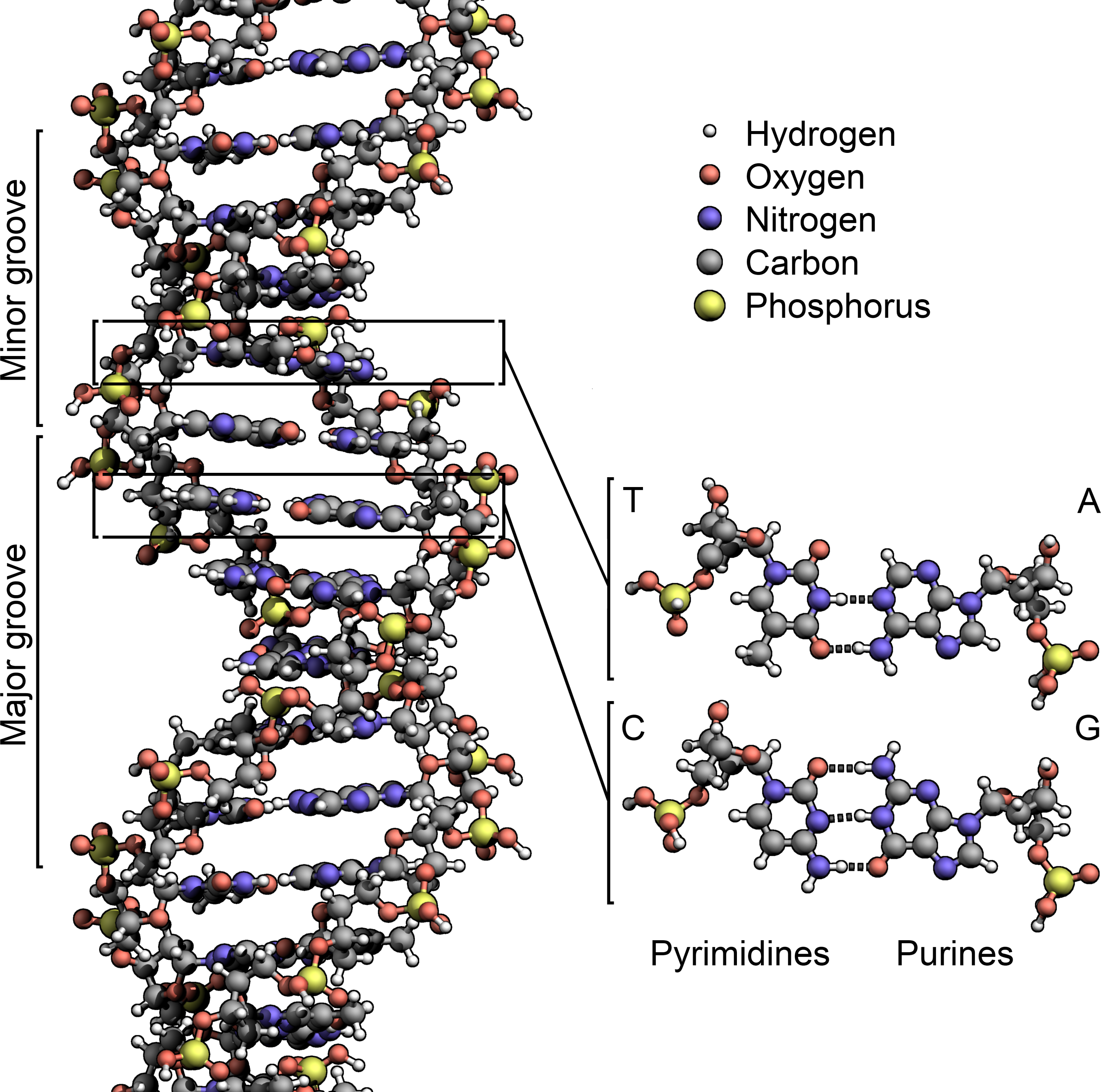
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid
The polymer carries geneticinstructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
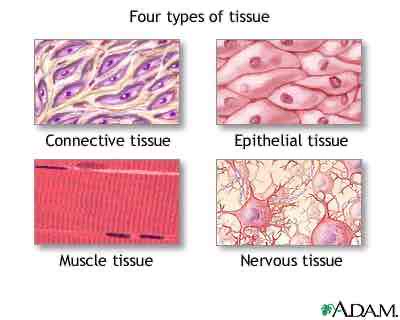
TISSUES
In biology, tissue is a historically derived biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ.
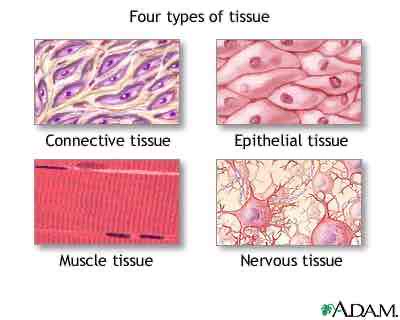
How do Tissues form?
Tissues are formed from the assemblage of cells and intercellular materials in various proportions in which one component predominates. In nervous tissue as an example, nerve cells predominate while in connective tissues such as Ligaments and Tendons, intercellular fibrous materials predominate.
Biological Organism Hierarchy
Biological organisms follow this hierarchy:
Cells < Tissue < Organ < Organ System < Organism
POPULATION
all the organisms of the same group or species that live in a specific area and are capable of breeding among themselves.
CELL
The smallest basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.
ATOM
An atom is the smallest component of an element.
ECOSYSTEM
a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life.
HOMEOSTASIS
the state of steady internal, physical, chemical, and social conditions maintained by living systems.
GENETIC MATERIAL
DNA
ORGANISM
a living thing that has an organized structure, can react to stimuli, reproduce, grow, adapt, and maintain homeostasis.
CELL THEORY
the cell is the basic unit of life, the components of a cell, organelles and molecules, are not living.
ENVIRONMENT
the external conditions, resources, stimuli, etcetera., with which an organism interacts.
REPRODUCTION
process by which organisms replicate themselves
BIOTIC
of, pertaining to, or produced by life or living organisms (of an ecosystem). e.g. secretions, wastes, and remains.
ABIOTIC
any component of the ecosystem that is devoid of life.