DAY 1 EXAMS
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
Themes in direct action
self determination - goes against the traditional masculine roles, determined to protect that fish he caught and now the river that harms the fish
environment - son protesting, river being pumped with chemicals
family - son wishes to make his father proud but fails to in his social justice attempt that ultimately get thwarted.
conflict - : ”Get a skill and you’ll always be in demand” and as soon as he stands up for what he believes in he’s fired even though he has a trade.
communication - father/sons differing opinions on social issues
Main idea in direct action
an unemployed welder, who takes part in protest activities against a local company that is pumping effluent into the nearby river
issues in direct action
Courage to stand up for what you believe in
Preservation of the environmet > employment/ financial security
Not critical of those who are doing their jobs
(policeman)
Wastefullnes of humans, scrqpping gary and his father of their jobs
Characters in direct action
Gary
Gary’s father
manager of barron papermills
literary devices in direct action
1st person narrative
flashbacks - creates sense of belonging
italics - characters thoughts
lots of humor - “welding your arse shut”
important quotes in direct action
“looked at me with what an eight-year-old boy could only take for respect”
“he’s the kind of bloke i’d buy a beer”
“installed dogs of a famously aggressive breed, but it has neglected to train them”
Changes in Gary throughout the text (start, changes, what caused change)
eco warrior
decided protesting wont do anything, chose to act
catching a fish for the first time caused him to realize how precious the environment is
Important quotes from Gary
“ecowarriors” finds himself cringey v
“watch out world, here comes mr activist”
“you get a fair bit of reading done when you’re unemployed”
“i am a qualified welder … who does not have a job”
Changes in greg’s father throughout the text (start, changes, what caused change)
had opposing views to Greg
realized greg had strong views and cared about morals, respect
once greg went to court, he realized how serious he was
Important quotes from Garys Father
“get a skill and you’ll always be in demand”
“they’re pouring human shit straight into the ocean, too … but i haven’t noticed you welding your arse shut”
Themes in the testosterone club
misogyny/the role of women
self determination
morality
What is the main idea of the testosterone club
wife who takes revenge on her egotistical husband and his sport-watching buddies by leaving them a batch of male-organ-wilting pickles, before driving away with all of their wedding crockery.
Characters in the testosterone club
monica
macca
chooka
barry/baazza
Issues in the testosterone club
male bonding,
the impact of traditional masculinity on relationships
consequences of prioritizing physical strength and aggression over emotional intelligence
Literary devices in the testosterone club
short sentences to amplify the humor
repetition to emphasize certain moments
dramatic pauses created through punctuation to create impact
Imagery, especially in describing mundane or even painful events, is also used to create a vivid and sometimes unnerving atmosphere
Important quotes in the testosterone club
“they were a club. A testosterone club”
“their complete confidence in their own majestic sexual magnetism”
“you won’t tell Barry about this, will ya?”
“rejection hadn’t occurred to him”
“the script was written and directed by testosterone”
“he brought home a box of chocolates and a much larger one of very small vegetables”
Changes in Monica throughout the text (start, changes, what caused change)
began at the end, then started at the beginning
realized how stupid men are
caused by chooka and macka coming onto monica
Important quotes from monica
“they entered a room pelvis-first”
“he’d even bought me a new book, the home preserver: everything you need to know”
“I hade the mistake of letting an incredulous laugh escape me”
“Snap and colour, Barry? … You shall have them”
“suddenly i realized i had no intention of being there”
“it was me against the testosterone club”
Changes in barry throughout the text (start, changes, what caused change)
sport loving guy
didnt care much for his wife
suddenly cared when macca and chooka blames monica
Important quotes from barry
“when a bloke cant trust his own wife”
“you propositioning them”
“are you trying to tell me my best mates propositioned you?”
“high note of disbelief in his tone”
Important quotes from macka
“if you ever need anything, you know who to call”
“i always knew you liked me”
“some other time, eh? you give me a ring”
Important quotes from chooka
“sweaty hand landed across my shoulders”
“you must get a bit lonely here by yourself of a day”
“you won’t tell barry about this, will ya?”
Different forms of Writing
opinion piece, speech, short story, podcast, letter, blog, recount
structure of opinion piece

structure of a letter
What’s a DV (dependent variable)
the variable that will (or may) change because you changed the independent variable
What’s a IV (independent variable)
The variable that your changing in order to test the effect
What’s the purpose of a CV (control variable)
to ensure that only the independent variable can be causing a change in the dependent variable
increases validity of the experiment
What is a controlled variable
factor in an experiment that is kept constant to ensure that the results are reliable and accurate
What’s precision
How close all the data is to each other
What’s accuracy
How close the data is to the true value
What’s validity
how well an experiment or investigation actually measures what it is supposed to measure
Difference between quantitative and qualitative data
‘Quali(ty)’tative- describing
‘Quan(tity)’titative- numbers, data
What information needs to be included in a hypothesis?
How you expect the IV to affect the DV
including the direction of change
Advantages of larger surface area to volume ratio (SA:V)
Faster diffusion rates
allows cells and organisms to exchange nutrients, gases, and waste products with their environment more efficiently
Does SA:V affect rate of diffusion or efficiency?
yes, lower SA:V means it will take longer for nutrients or waste to absorb therefore being less efficient
When a cell grows, does the SA:V increase?
no, it decreases because volume of the cell increases faster than its surface area
What is surface area to volume ration a measure of?
compares the surface area of an object to its volume
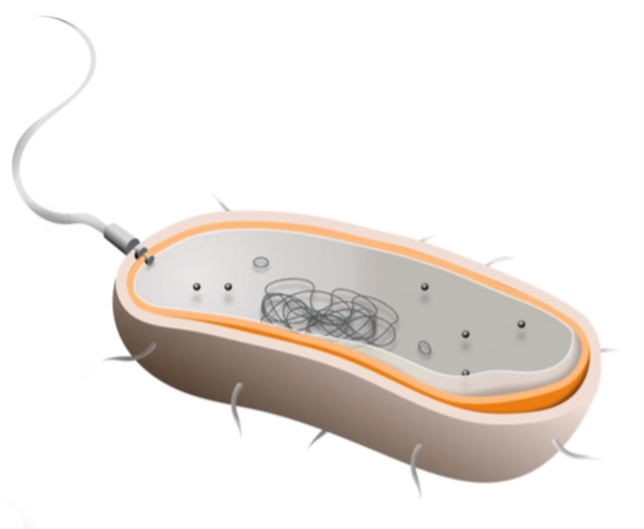
Prokaryote cell features
Lack membrane-bound organelles
has no nucleus
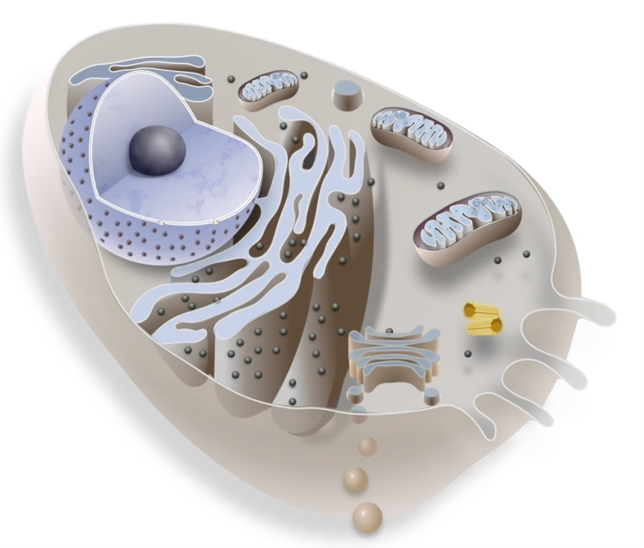
Eukaryote cell features
membrane-bound nucleus & organelles
bigger than prokaryotic cells
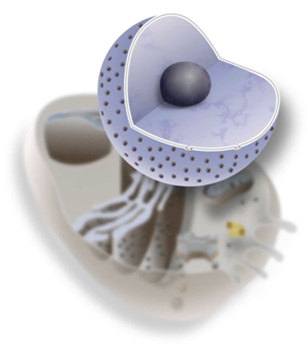
What’s the function of the Nucleus
To contain most of the genetic material (DNA) of the cell
regulates protein synthesis and cell division
What’s the function of the Endoplasmic reticulum
To transport materials such as proteins and lipids
What’s the function of the Golgi body
Modifies and packages proteins to be exported from the cell
What’s the function of ribosomes
read the genetic code from mRNA
What’s the function of chloroplast
site of photosynthesis in plant cells
contain chlorophyll
What’s the function of the mitochondria
to do aerobic respiration
What’s the function of large vacuoles
to help plant maintain its structure with turgor (swelling) pressure
stores metabolic wastes from the cell
What’s the structure of the Nucleus
surrounded by a nuclear envelope that has two layers of membrane
pierced with nuclear pores
What’s the structure of the Endoplasmic reticulum
network of membrane channels
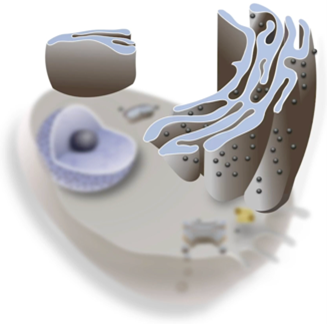
What’s the structure of the Golgi body
stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs

What’s the structure of ribosomes
not membrane bound
made of 60% rRNA and 40% protein
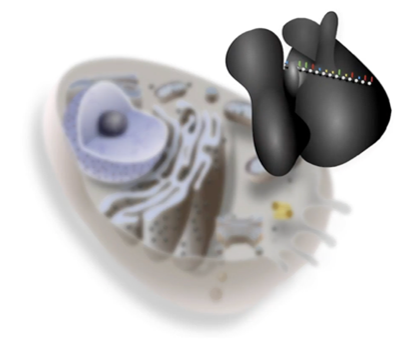
What’s the structure of chloroplast
bound by two layers of membrane
smaller structures called thylakoids, each membrane-bound
thylakoids stacked are grana

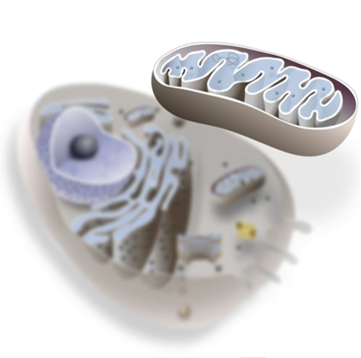
What’s the structure of the mitochondria
double membrane-bound
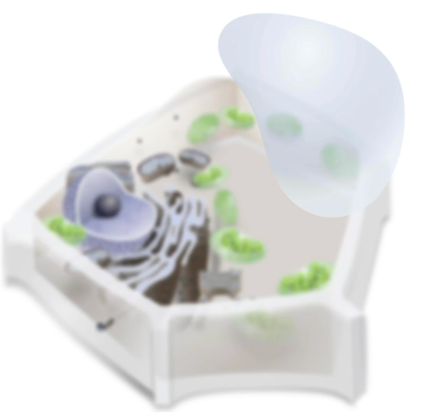
What’s the structure of large vacuoles
membrane bound sac
What’s anaerobic respiration
metabolic process that generates energy (ATP) in the absence of oxygen
What’s aerobic respiration
metabolic process that utilizes oxygen to convert glucose into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water
What’s the equation for anaerobic respiration
Glucose → Lactic Acid + Energy (ATP)
What’s the equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
What’s the purpose of aerobic respiration
produce energy in the form of ATP for cells to use
What’s the purpose of an anaerobic respiration
provide energy in the absence of oxygen, allows glycolysis to continue producing ATP
What are the limiting factors of aerobic respiration
oxygen concentration, glucose concentration, and temperature. influence the efficiency and speed of biochemical reactions in breaking down glucose to produce energy
What are the limiting factors of anaerobic respiration
oxygen deficiency
Examples of anaerobic respiration
alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation and in decomposition of organic matter
Examples of aerobic respiration
Krebs cycle
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
What do plant cells look like

What do animal cells look like
What’s diffusion
molecules dispersing between a membrane until they have reaches equilibrium
What’s osmosis
passive net movement of free water molecules through a semi permeable membrane
What’s a hypertonic solution
having a higher osmolality (concentration of solutes) than the extracellular fluid
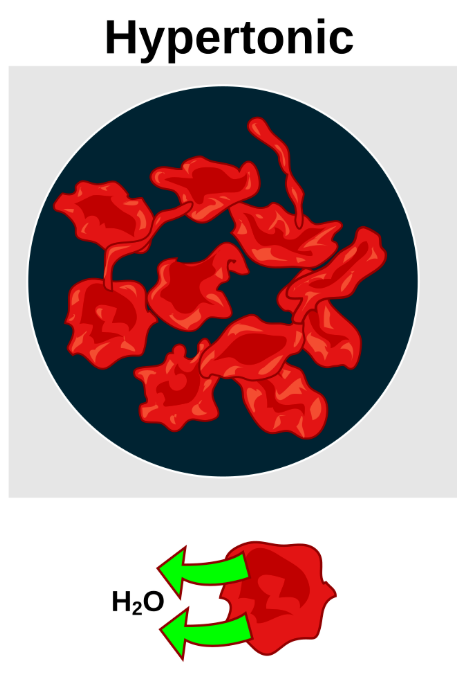
What’s a hypotonic solution
having a lower osmolality (concentration of solutes) than the extracellular fluid
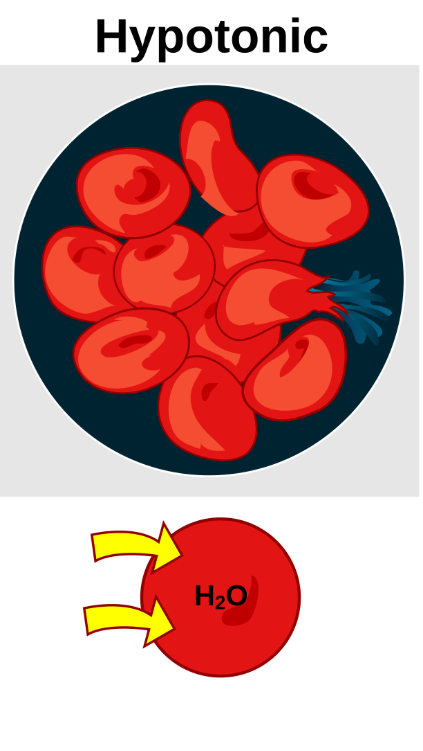
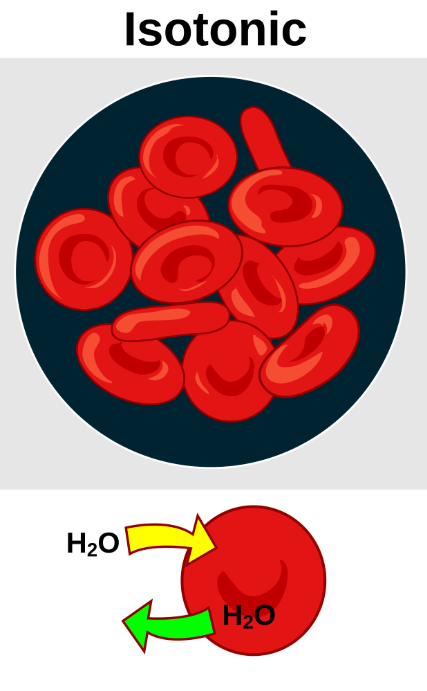
What’s an isotonic solution
having the same osmotic pressure as the extracellular fluid
What’s passive transport (Include examples)
transport though the membrane that doesn’t require energy
e.g oxygen, carbon dioxide, salts, ethanol
What’s facilitated diffusion (Include examples)
passive transport through the cells that does NOT require energy
e.g glucose, amino acids, and certain ions like sodium, potassium, and chloride
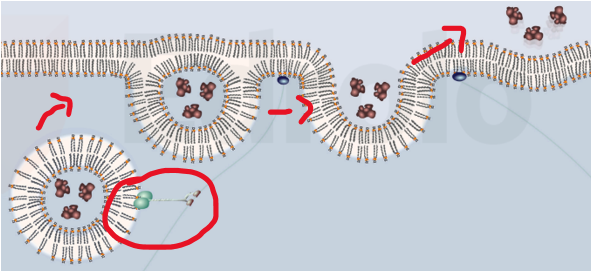
What’s endocytosis
cell takes in substances from its surrounding environment by forming a vesicle
essentially "eating" the external material
type of active transport that requires energy
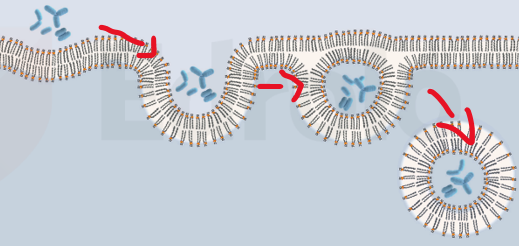
What’s exocytosis
substances are released from inside a cell to the external environment
What’s a hydrophobic molecule
repels or doesn't mix well with water
e.g flour
What’s a hydrophilic molecule
one that readily dissolves in water or other polar solvents
What are polar molecules
molecules that have a separation of electric charge
one end of molecule slightly positive and the other end slightly negative
water, ethanol, ammonia
What are non-polar molecules (Include example)
molecules that lack an overall electric charge
co2, methane, most molecules containing carbon
What’s the function of the plasma membrane
act as a barrier, separating the cell's internal environment from the external one
role in regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell
Diagram of the plasma membrane

Parts of the plasma membrane
phosphate head
fatty acid tails
carbohydrate chains
glycoprotein
transport proteins
Difference between simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and active transport
Simple diffusion involves small, nonpolar molecules moving directly through the lipid bilayer
Facilitated diffusion uses membrane proteins to aid the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient, doesn't require energy
Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy and specific membrane proteins
Difference between eukaryote and prokaryotic cells
presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
What are unipotent cells
a specialized stem cell that can only differentiate into one type of cell
e.g Epidermal stem cells, Muscle stem cells
What are pluripotent cells
embryonic stem cell that can differentiate into any cell type found within the three primary germ layers of the body
ectoderm - skin, nervous system
mesoderm - muscle, bone, blood, urogenital
endoderm - lungs, gastrointestinal
What order to stem cells develop in
TPMOU Toti-pluri-multi-oli-uni
What are multipotent cells
The ability of a stem cell to differentiate into multiple, but limited, cell types within a specific lineage.
e.g blood stem cells, capable of giving rise to all blood cell types, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
What are totipotent cells
capable of developing into any cell type in a complete organism, including both embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues (like the placenta)
How do uni-, pluri-, multi-, toti- potent cells differ from each other
toti- can give rise to all cell types in the embryo and extra-embryonic tissue
pluri- can differentiate into all cell types within the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) but not extra-embryonic tissues.
multi-can differentiate into multiple cell types within their specific lineage
toti-can only differentiate into a single cell type
Difference between binary fission and mitosis
Binary fission is the primary method of cell division in prokaryotes, while mitosis is the primary method in eukaryotic cells
Phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle
mitosis (PMAT)
interphase (cytokenesis, G1, Synthesis, G2)
= 2 daughter cells
Where do checkpoints appear in mitosis
Metaphase - chromosome spindle attachment
G1 - Nutrients, growth factors, DNA damage
G2
What type of errors do checkpoints look for in mitosis and how do they fix the errors
DNA damage, incomplete DNA replication, or chromosomes not properly attached to the spindle.
fix errors by pausing the cell cycle to allow repair
if the problem can't be fixed, the cell will self-destruct through apoptosis
What is apoptosis?
programmed cell death
What is Necrosis?
uncontrolled cell death
How are living things organized?
Cell, tissue, organ, system, organism
What are the systems in the body?
skeletal
muscular
nervous
endocrine
respiratory
digestive
urinary
reproductive
What organs are in the digestive system
mouth
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
rectum
liver
gallbladder
pancreas