PD E3- Study Guide
1/149
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
What is hegar’s sign?
Softening of isthmus of uterus
What is Chadwick’s sign?
Increased vascularity throughout pelvic region → bluish discoloration of vagina and cervix
What does melanocyte stimulating hormone cause during pregnancy?
Linea nigra, darkening of nipple & areola, facial chloasma, melasma, longlasting suntan
What skin changes does estrogen cause during pregnancy?
Spider nevi, palmar erythema
What skin changes do corticosteroids cause during pregnancy?
Striae on abdomen & breasts
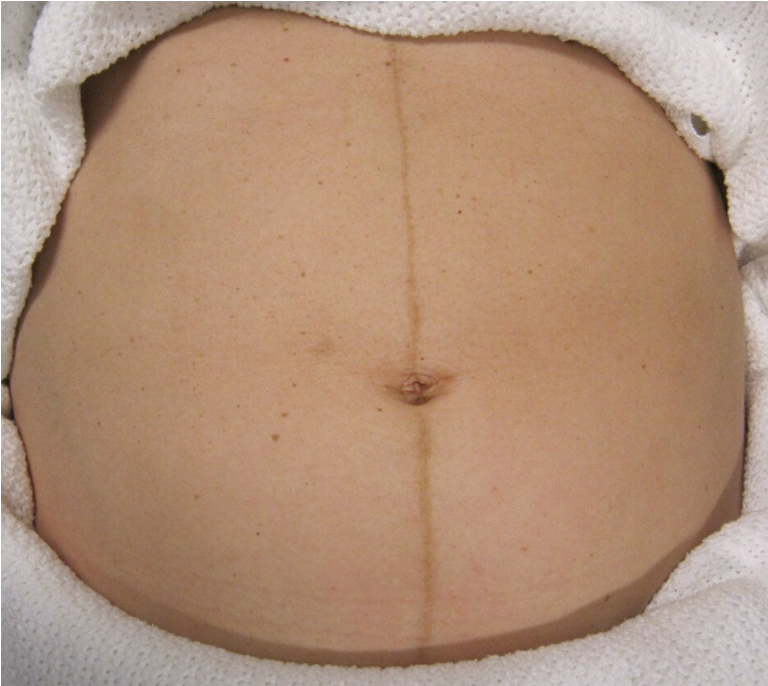
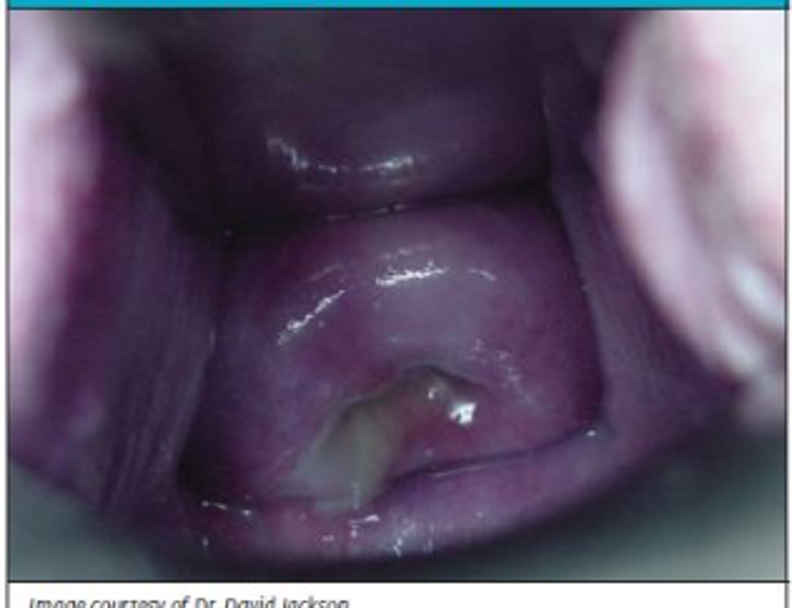
What is brownish-black pigment along the midline of the abdomen?
*d/t melanocyte stimulating hormone
Linea nigra
What is diastasis recti?
Rectus abdominis muscles separate at midline (noticeable in later trimesters)
How does the abdomen enlarge throughout pregnancy?
Uterus rises out of pelvis into abdomen by 12th week → inc in abdominal girth apparent by 15th week
*enlargement may appear earlier if multiparous female
What is the first trimester?
0-14 wks
What is the second trimester?
14-28 wks
What is the third trimester?
28 wks - birth
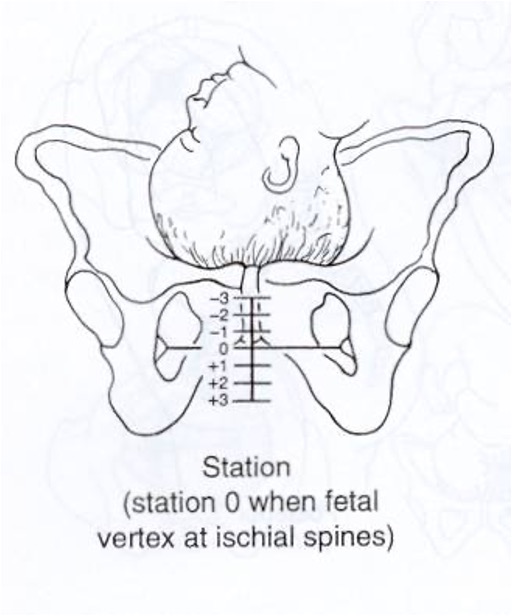
What characterizes the level of descent of the presenting part of the fetus?
0 = fetal occiput (vertex presentation) has reached level of maternal ischial spines (engagement)
-1 = 1 cm above
+1 = 1 cm below
Station
What is the degree to which the cervix has thinned, expressed as a number of cm in which cervix has changed?
also expressed as percentage
determined by digital exam
4 cm = is unchanged
Effacement
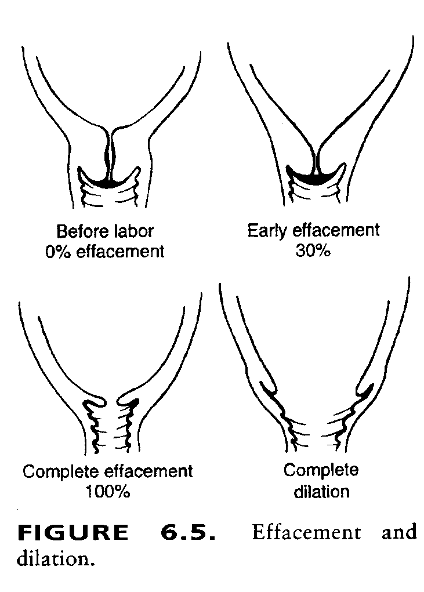
What is the number of cm of the opening of the internal os, determined on exam with 1-2 fingers?
Dilation
What rule is used to calculate estimated date of confinement (EDC)?
Naegele’s rule → first day of LMP - 3 months + 1 year & 7 days
What can compression of the descending aorta and IVC during the OB exam cause (patient should sit briefly before proceeding to pelvic exam; semi-sitting position with knees bent)?
Supine hypotensive syndrome
What is mammary soufflé?
Increased blood flow through dilated internal mammary artery → easily heard in 2nd & 3rd interspace in parasternal areas
Which murmurs, if heard in pregnancy, may accompany anemia & should be investigated?
Diastolic murmurs & dyspnea
What is the fundal height at 12 weeks?
Barely palpable above pubic symphysis
What is the fundal height at 15 weeks?
Midpoint between pubic symphysis and umbilicus
What is the fundal height at 20 weeks?
At the umbilicus
What is the fundal height at 28 weeks?
6 cm above umbilicus
What is the fundal height at 32 weeks?
6 cm below xyphoid process
What is the fundal height at 36 weeks?
2 cm below the xyphoid process
What is the fundal height at 40 weeks?
*d/t engagement & descent, fundal height at 40 weeks is less than at 36 weeks
4 cm below xyphyoid process
What maneuvers provide useful information to assess the lie and presentation of the fetus from the 28th week & on?
Leopold’s maneuvers
What are the 4 parts of Leopold’s maneuvers?
Determine what fetal part occupies fundus: buttocks feels firm but irregular, head feels hard & moveable
Determine what side is fetal back: one side rounded but firm, other is irregular, lumpy, & moves
Identify descent of presenting part: if lower pole not engage, moveable part will be felt
Identify cephalic prominence: confirm presentation part & locate side of cephalic prominence
What exercise is appropriate during pregnancy?
Moderate exercise for 30 min/day most days of week
*active before pregnancy → continue mild-moderate; non-active before pregnancy → join program
What exercise should patient avoid after first trimester?
Contact sports, anything in supine position → compresses IVC and decreases blood flow to placenta
What vaccines should be avoided in pregnancy?
Live vaccines (VZV, MMR)
What vaccines can be given in pregnancy?
Tetanus, influenza, pneumococcal, meningococcal, HBV
What is polythelia?
Extra nipples
What is polymastia?
Accessory breasts
In what positions should the breasts be inspected?
Sitting w/ arms over head or pressed on hips: dimpling & retraction
Sitting leaning forward: asymmetry, retraction of nipple / areola
Lying w/ arm behind head: allow breast tissue to spread over chest
What does retraction of the nipple or areola suggest?
Cancer
What are possible causes of peau d’orange?
Breast cancer, mastitis, & lymphedema
What would nipple inversion (if previously everted) along with signs of itching & pain be a sign of?
Inflammatory breast cancer
How should breast normally appear to palpation?
*use pads of middle 3 fingers held together w/ metacarpal-phalangeal joint slightly flexed
Firm w/o masses, tenderness or warmth, no nipple dc, & smooth axillae w/ non palpable nodes
What imaging do you do for a suspicious breast mass in an adolescent female?
US
How are geriatric breasts anatomically different?
Flatter, elongated, loosely suspended, granular feel, smaller flatter nipples, breasts cysts if on HRT
When should self breast exams be performed?
Monthly at the end of menses in all menstruating women
What is the most sensitive screening tool for breast cancer?
Mammogram
What is roentgenography of breasts without injection of contrast medium?
Mammogram
Screening or diagnostic mammogram?
look for breast disease in women who appear to have no breast problems
Screening
Screening or diagnostic mammogram?
Find breast disease in women who have sx or found a lump or abnormal radiological changes
Diagnostic
What should you do if an area of concern is found on mammogram?
Biopsy
What is the presence of a painless, firm, solitary, mobile, slowly growing lump in the breast of a woman of childbearing years?
*MC young women, 1-3 cm, no menstrual cycling; 2nd MCC of benign breast problems
FIbroadenoma
What breast condition?
long follicular or luteal phase of cycle
fluid filled cysts, BL, multiple, tender
MC 30-55 y/o
Fibrocystic disease
What condition?
benign breast condition → NOT a disease
exaggerated response to hormones (cyclic BL pain & engorgement)
diffuse, may radiate to shoulders or upper arms
changes most prominent just prior to menses
Fibrocystic changes
When are fibrocystic changes to the breast MC?
Premenstrual time frame, nulliparous women, non uses of hormonal contraceptives, mid 20s - early 30s, high caffeine or nicotine intake
What is the treatment for fibrocystic changes?
OCs, DMPA, NSAIDs, dietary changes- low fat, caffeine free, vits E & B, & stop smoking
What is the workup for fibroadenoma?
PE, mammo/ US, tissue sample w FNA or excision, cystic aspiration (therapeutic and diagnostic)
What does straw colored fluid on a breast cyst aspiration indicate?
Fibrocystic
Can a mammogram alone prove that an area of concern is breast cancer?
No
What does persistent redness, scaling, crusting on nipple or areola that is unilateral usually indicate?
Paget’s disease
What is the shape of the external os in nulliparous patients?
Round or oval
What is the shape of the external os after childbirth?
Slit like or stellate
What are periurethral glands that lie on either side of urethral meatus?
Skene’s glands
What is the extension of the peritoneum off the superior surface of the uterus and on the anterior face of the rectum that is reachable on rectal exam?
Pouch of Douglas / retrouterine pouch / cul-de-sac
What has in utero DES exposure been linked to?
Mother: breast CA
Females: vaginal adenosis, cervical hood, clear cell carcinoma
Males: cryptorchidism, hypospadias, testicular cancer
How should the female patient be positioned for GU exam?
Drape mid abdomen to knees & depress drape between knees so patient can see you, dont place arms overhead bc can tense abdominal muscles
What glands are responsible for vaginal lubrication, located at 5 & 7 o’clock at introitus?
*obstruction will lead to pain, enlargement, and discharge
Bartholin’s glands
What types of hernias are more common in women?
*palpate in labia majora, go upward just lateral of pubic tubercles
Indirect inguinal / femoral
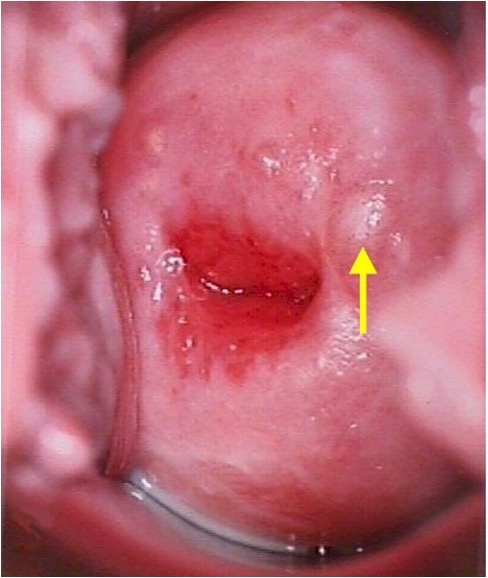
What are endocervical glands on the cervix that become filled with secretions that accumulate as pimple-like elevations (benign)?
Nabothian cysts
PAP smear guidelines
start at age 21 x every 3 years, start HPV testing at 25 ? (idk what he wants since he put 3 different guidelines)

What checks for abnormal cells (dysplasia) and cancerous cells on the cervix & checks the endocervical canal?
*checks for cervical cancer only, not uterine
Pap smear (Papanicolaou)
What area of the cervix should you obtain the specimen when performing a Pap smear?
Transformation zone
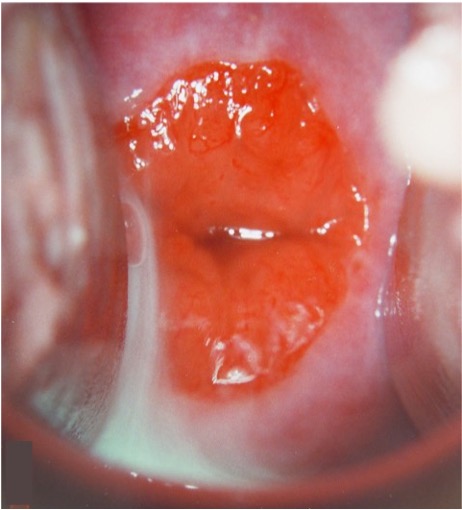
What does cervical ectropion (eversion) indicate in menstruating women?
Normal
What do cultures taken from the cervix test for?
Gonorrhea & chlamydia
What do cultures taken from the vagina test for?
*pH, wet mount, KOH on vaginal discharge
Trich, BV, candidiasis
What does cervical ectropion (eversion) in postmenopausal women indicate?
Ominous finding, requires consideration of cervical CA
What will you feel on a bimanual exam if an infection is deposited along the vaginal wall or a tubo-ovarian abscess is present?
*d/t fallopian tubes opening into abdominal cavity
Enlarged tender mass on lateral vaginal wall
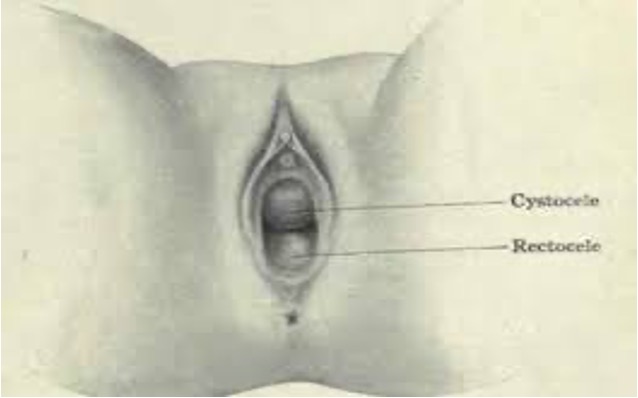
What defects are you inspecting for with female internal pelvic exam?
Anterior wall defect → cystocele
Posterior wall defect → rectocele
apical → prolapse
*present if protruding mass seen
What exam would you perform to palpate a retroverted uterus?
Rectovaginal exam
When is a rectovaginal exam performed?
Colon cancer, incontinence, rectocele, cul-de-sac tumors, infx suspected
Which cancer does the Pap smear rule out?
Cervical cancer
What does an ovary > 1-3 cm suggest?
Cysts or cancer
What are the borders of Hesselbach’s triangle?
Lateral (upper L to center): inferior epigastric vessels
Inferior (upper R to bottom L): Inguinal ligament
Medial (upper L to bottom L): rectus abdominis muscle
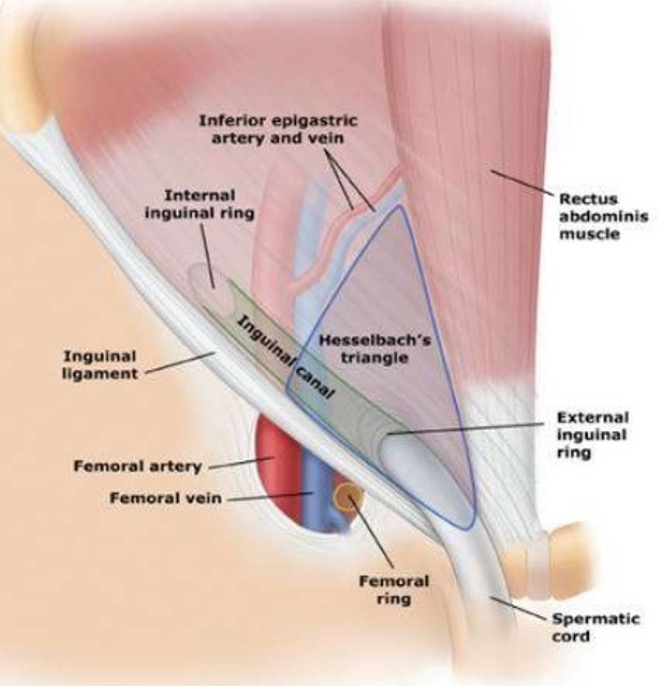
What is the region of potential weakness where a direct inguinal hernia can occur?
Hesselbach’s triangle
Direct or indirect inguinal hernia?
protrudes through both deep inguinal ring & superficial inguinal ring
can protrude into scrotum
due to incomplete closure of deep inguinal ring
possibly congenital
MC in males - infancy or old age
Indirect inguinal hernia
Direct or indirect inguinal hernia?
protrude through hesselbach triangle into inguinal canal
exit inguinal canal through superficial inguinal ring
lump in groin
caused by weakness in abdominal wall due to age
Direct inguinal herna
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none
Location: testes > 4cm inferior to pubic tubercle
Association: smooth with epididymis
Normal testes
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none
Association: risk of testicular cancer
Cryptorchidism
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: yes
Tenderness: none
Location: anterior to testes
Association: fluid in tunica vaginalis
Hydrocele
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: yes
Tenderness: none
Location: head of epididymis posterior to testes
Association: benign
Spermatocele
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless infarction or torsion
Location: contiguous with testes anterior & posterior
Association: irregular nodule or mass
Neoplasm
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none to mild
Location: posterior to tests - left side
Association: increase with valsalva, decrease with scrotal elevation; “bag of worms”
Varicocele
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: yes
Location: posterior to testes
Association: swelling or discrete nodule or mass
Epididymitis
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: yes
Location: swelling and mass tender around testes
Association: exquisite pain and tenderness, associated with testicular cancer
Torsion
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: no
Location: epididymitis anterior to testes
Association: normal variant
Anteverted epididymitis
What are hydroceles commonly associated with?
Indirect inguinal hernia
Where is an indirect inguinal hernia?
Out of hesselbachs triangle → enters inguinal canal lateral to inferior epigastric vessels & exits inferior to inguinal ligament
Where is a direct inguinal hernia?
Within hesselbach’s triangle → breaches posterior inguinal wall & passes medial to inferior epigastric vessels
What kind of hernia?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless incarcerated or strangulated
Location: base of mass from hesselbach’s triangle floor → may extend into scrotum
Etiology: reducible or incarcerated or strangulated
Direct inguinal hernia
What kind of hernia?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless incarcerated or strangulated
Location:scrotal hernia; congenital; through the internal and external rings
Etiology: reducible or incarcerated or strangulated
Indirect inguinal hernia
What kind of hernia?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless incarcerated or strangulated
Location: thigh hernia under the medial inguinal ligament
Etiology: reducible or incarcerated or strangulated
Femoral hernia
What is edematous foreskin that becomes trapped behind the head of the penis?
Paraphimosis
What is foreskin that is unable to be retracted from the head of the penis?
Phimosis
What condition?
inflammation of glans → redness, pain & swelling
urinary discharge, dysuria, dribbling of urine
Balantitis
What are causes of balantitis?
Candida albicans, reiter’s syndrome, AI disorder