Biology ✿ organisation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
order these from biggest to smallest
cells, organs, system, tissue
system, organ, tissue, cells
cell
basic building blocks of all living organisms
tissue
a group of cells with similar structure or function
organs
group of tissues which do specific jobs
systems
groups of organs which work together to form organisms
enzymes
biological catalysts and proteins which increases rate of chemical reaction without being used up
what is the role of the digestive system?
to digest and absorb food
Metabolism
the sum of all the reactions in an organism
Enzymes
biological catalysts made of proteins to speed up chemical reactions without being used up themselves
Explain the “lock and key theory” of enzyme action [3]
enzymes bind a specific substrate that fits it’s active site
substrate is broken down
products are realised
what and where is amylase broken down into?
simple sugars
salivary glands, pancreases and small intestine
what and where is protease broken down into?
amino acids
pancreas, small intestine and stomach
what and where is lipases broken down into?
fatty acids and glycerol
pancreas and small intestine
what is the role of the digestive enzymes?
to breakdown food into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream
where is bile made?
liver
where is bile stored?
gall bladder
what is the role of bile?
to emulsify fats to make them into small droplets which increases the surface area
give 2 adaptations of Bile
alkaline to neutralise stomach acid and provides optimum pH for enzymes
emulsifies fat making them into small droplets to increase surface area
what is the food test and positive result for starch?
iodine solution
black-blue colour
what is the food test and positive result for sugars?
benedict’s solution
green, yellow or brick-red
what is the food test and positive result for proteins?
biuret solution
purple/ lilac
what is the food test and positive result for lipids?
ethanol
milky-white
double circulatory system
when the blood passes through the heart twice during one complete circuit of the body
![<p>Describe how <strong><u>both</u></strong> the <strong>alveoli and villi</strong> are adapted to <strong><em><u>increase absorption</u></em></strong> [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7a49a3fc-79fe-4d00-8dec-201f3e08d005.png)
Describe how both the alveoli and villi are adapted to increase absorption [3]
large surface area to maximise diffusion
one cell thick walls to reduce diffusion distance
good blood supply to maintain concentration gradient
give two adaptions of the villi
contain microvilli to further increase surface area
contain many mitochondria for active transport
describe the pathway of the blood through the heart [4]
deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava
blood flows into the right ventricle which pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery
oxygenated blood enters the left atrium via the pulmonary vein
blood flows into the left ventricle which pumps blood to the rest of the body via aorta
what is the role of the vena cava?
returns deoxygenated blood into the heart from the body
what is the role of the pulmonary artery?
moves deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs
what is the role of the pulmonary vein?
returns oxygenated blood into the heart from the lungs
what is the role of the aorta?
moves oxygenated blood away from the heart to body
pacemaker
a group of cells located in the right atrium which controls the resting heart rate
Artificial pacemakers
an electrical device used to send regular electrical impulses to control resting heart rate
equation for rate of blood flow
volume of blood / time
![<p>explain the <em>structure and functions</em> of the <strong><u>artery</u></strong> [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/501f5bbb-e192-4243-8ee2-45c815bff303.png)
explain the structure and functions of the artery [3]
thick walls to withstand high pressure of blood flow
small lumen to maintain high pressure
carries blood AWAY from the heart
![<p>explain the <em>structure and functions</em> of the <strong><u>vein</u></strong> [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9804f131-2bbb-4595-ae6e-9a1574a6bc64.png)
explain the structure and functions of the vein [3]
thin walls due to low pressure of blood flow
large lumen to allow blood to easily flow
carries blood INTO the heart
![<p>explain the <em>structure and functions</em> of the <strong><u>capillary</u></strong> [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/79f8c8ab-47aa-4450-b810-f34f9354091f.png)
explain the structure and functions of the capillary [3]
one cell thick walls to reduce diffusion distance
narrow lumen to reduce diffusion distance and slows blood flow for more exchange time
connects the arteries to veins
what 4 components is the blood made up of?
plasma
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets

give the function and 2 adaptations of the red blood cell
carries oxygen from the lungs to the body’s cells
no nucleus for more space for haemoglobin
small and flexible to squeeze through narrow capillaries
give the function and 2 adaptations of the white blood cell
defends the body against pathogens
produce antitoxins/ antibodies to fight pathogens
change shape to engulf pathogens
give the function and 2 adaptations of platelets
causes blood to clot at wounds to stop bleed and microbes from entering
no nucleus
releases chemicals to help blood to clot
give the function and an adaptation of plasma
to carry the blood components around the body
liquid to allow easy flow through blood vessels
coronary heart disease
a disease which causes fatty material to build up inside the coronary arteries
explain the effect of a partly blocked coronary artery on the body [4]
reduced blood flow causing a lack of oxygen and glucose in blood cells
heart muscles will start anaerobically respiring, producing lesser energy and more lactic acid
muscle contraction is less so less blood is pumped around the body
this leads to muscles to become tired quickly, causing them to breath in more oxygen
![<p>Explain how the <strong>human lungs</strong> are adapted for <em>efficient exchange of gases by diffusion.</em> [4]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fb7e3b30-6b8b-418a-8f18-39e1deb914a7.png)
Explain how the human lungs are adapted for efficient exchange of gases by diffusion. [4]
many alveoli provide more surface area
one cell thick walls to shorten diffusion distance
lungs are ventilated to bring in fresh oxygen
good blood supply to maintain concentration gradient
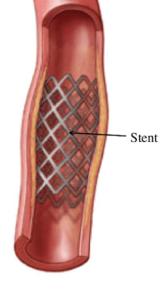
Stents
a metal mesh which keeps the coronary arteries open
statins
a drug used to lower blood cholesterol levels by lowering the rate of fatty material deposit
explain the effects on a person if a valve develops a leak [4]
causes backflow of the blood, causing less blood to leave the heart
there is less oxygenated blood around the body so cells get less oxygen for respiration
so they anaerobically respire and less energy is released
lactic acid is produced, causing the person to become tired easily
explain why veins have valves but arteries do not [2]
veins carry blood at lower pressure
so they need valves to prevent backflow of the blood
valves
“gates” which control the direction of blood flow in the veins
leaky valve
when the valve cannot close tightly, causing the backflow of the blood
give 2 advantages + disadvantages of a mechanical valve
lasts for at least 20-30 years
doesn’t wear out easily
must take blood thinning medication everyday
risk of blood clotting at the valve
give 2 advantages + disadvantages of a biological valve
no need for blood thinning medication
lower risk of blood clots
doesn’t last as long, only 10-15 years
can wear out easily
health
the state of physical and mental well-being
diseases
major causes of ill health
give 4 ways diseases may interact
weakens the immune system so they’re more likely to catch diseases
viruses living in cells can cause cancers
immune reactions caused by a pathogen can cause allergies
severe physical health can lead to depression and other mental illness