3.5 - Labour market
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Factors that influence demand for labour
Productivity of labour
Productivity increases → output/worker increases → does not need that much worker → demand for labour decreases
Economic activity/state
If recession → demand for good decreases → demand for labour decreases
Price of g/s
Price increases & demand for good stay the same → profit increase → want to expand production → labour demand increases
Cost & availability of substitution (machineries)
Cheap capital → replace more worker → demand for labour decreases
Technology good → demand for labour decreases
Government regulation
Regulation increases → Cost for firm increases → demand for labour decreases
Demand for labour is a derived demand
Ie. If increased demand for cars → increased demand for auto workers
Factors that influence supply of labour to a particular occupation
Supply of labour shift out
Net inward migration ( of qualified workers)
Migration increases → labour pool increases → supply of labour increase
Decrease in relative pay in substitute occupation
People would want to come and work in another similar job as they have better pay → labour supply increase
Decrease in entry barriers
Demographic factors which causes an increase in the active labour supply
These factors are ie. Age, gender, race, education
Supply of labour shift in
opposite to the above
Decrease in non-monetary rewards advocated with jobs
Ie. Promotion
Brain Drain effect = lose skilled workers to oversea countries due to them searching for better opportunities / better working conditions
Market failure in labour markets (COMMON as 3 markers + mcq)
There are 2 forms of market failure
Geographical immobility of labour
(Question: Which one is most likely to increase the geographical mobility of labour - 1mcq+3marker)
Definition of geographical mobility of labour = the ability of labour to move from 1 region to another to take available work
A decrease in regional house price (common reason)= more people can afford to buy houses in different areas they move to
ie. workers from countryside can move to towns & cities
Definition of geographical mobility
One major obstacle of geo mobility is asymmetric info (hence the answer from above: increased government provision of info on job vacancies in different areas of the UK)
one way is to increase funding of job centres so can provide this info
(Question: Which one is most likely to decrease the geographical mobility of labour - 1mcq+3marker)
Definition of geographical mobility
a shortage of affordable housing = harder for labour to move into a region with higher average house prices
as it become more expensive to buy them
Occupational immobility of labour
(Question: Which one is most likely to increase the geographical mobility of labour - 1mcq+3marker)
Definition of occupational mobility of labour = the ability of labour to change occupations to take available work
Sometimes can add in a response, occupational mobility may be quite low, if there is a possibility of occupational immobility
some unemployed may lack skills to take available work
so training programmes can increase skills for unemployed to gain work in different occupations
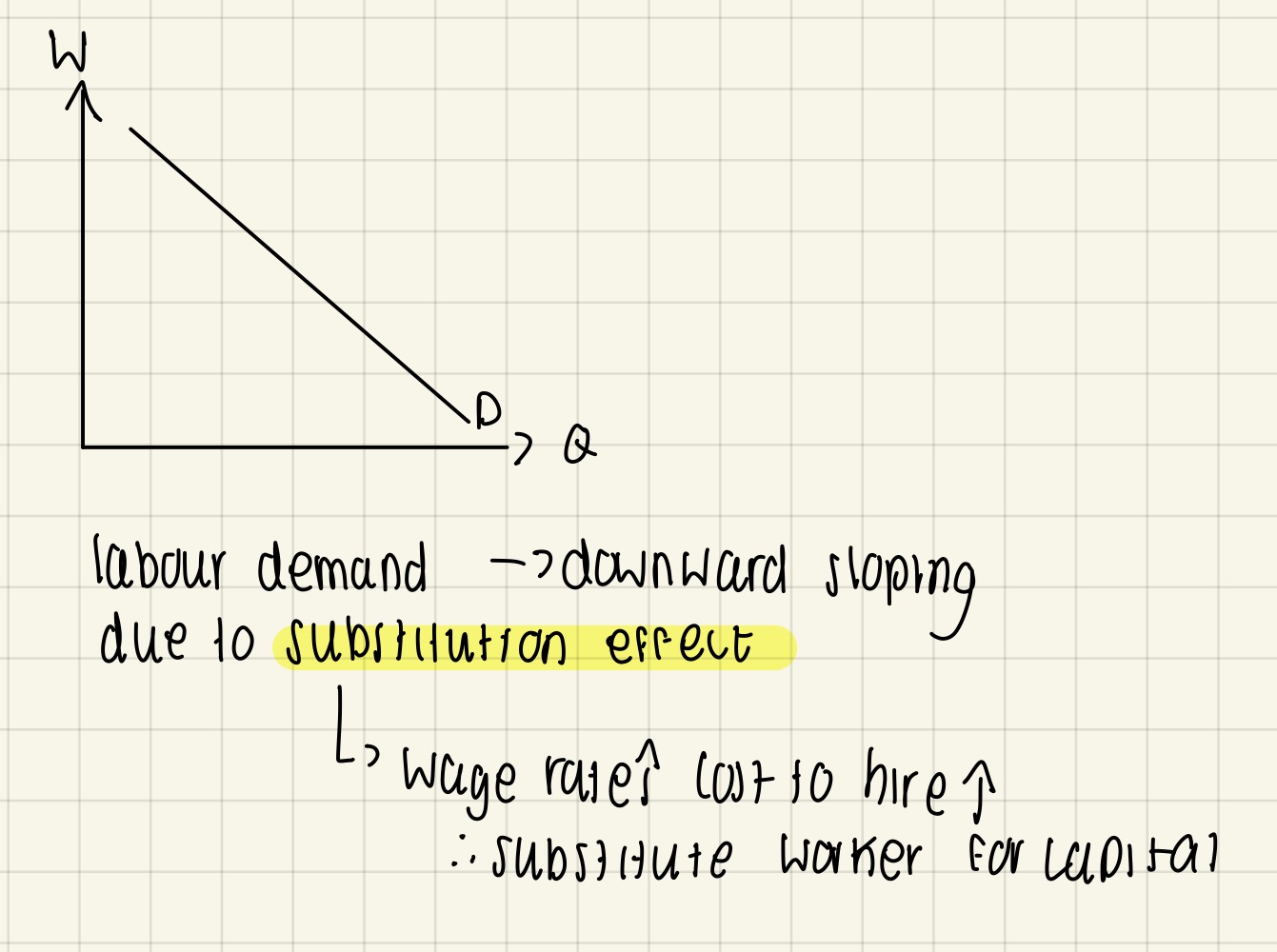
Diagrammatic analysis of labour market equilibrium (Demand)
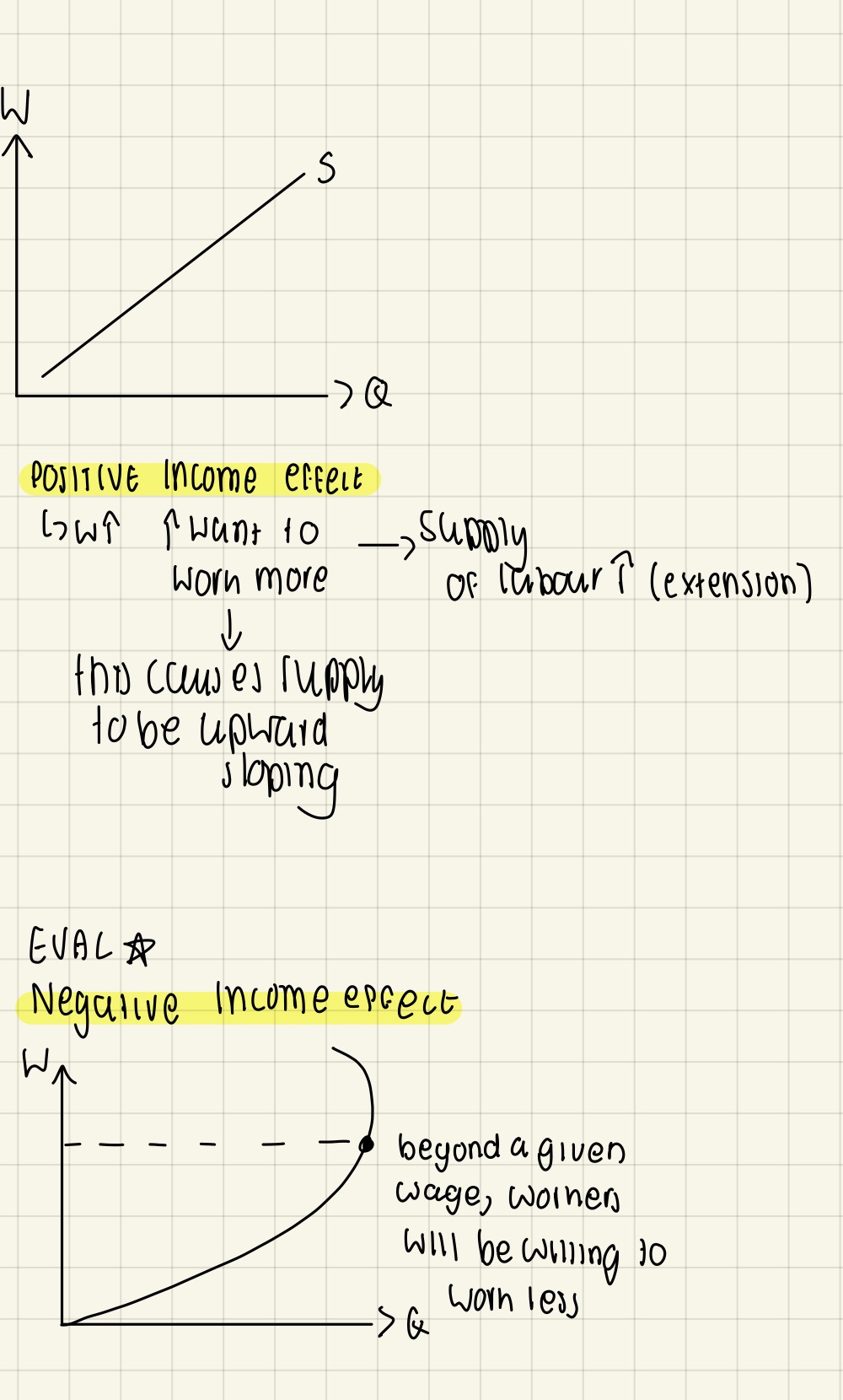
Diagrammatic analysis of labour market equilibrium (Supply)
Understanding of current labour market issues
COVID 19 causing unemployment
businesses going bankrupt after the pandemic → recovery takes time → unemployment
Zero-hour contracts
have permanent contracts but not guaranteed a set number of hours each week → no stable income
AI
causes unemployment
Government intervention in the labour market: minimum & maximum wages
minimum wage = lowest possible wage a firm is allowed to pay their workers
increase in minimum wage ➜ increase in excess supply ➜ decrease in quantity demand for labour ➜ decrease in employment
Reason for implementing national minimum wage:
reduce poverty
as it will help poor people who are in low paid job ➜ maintaining their incentive to work
How an increase in national minimum wage result in government failure:
Employers may pay below NMW due to immigrants / young unskilled works ➜ less tax revenue to the government
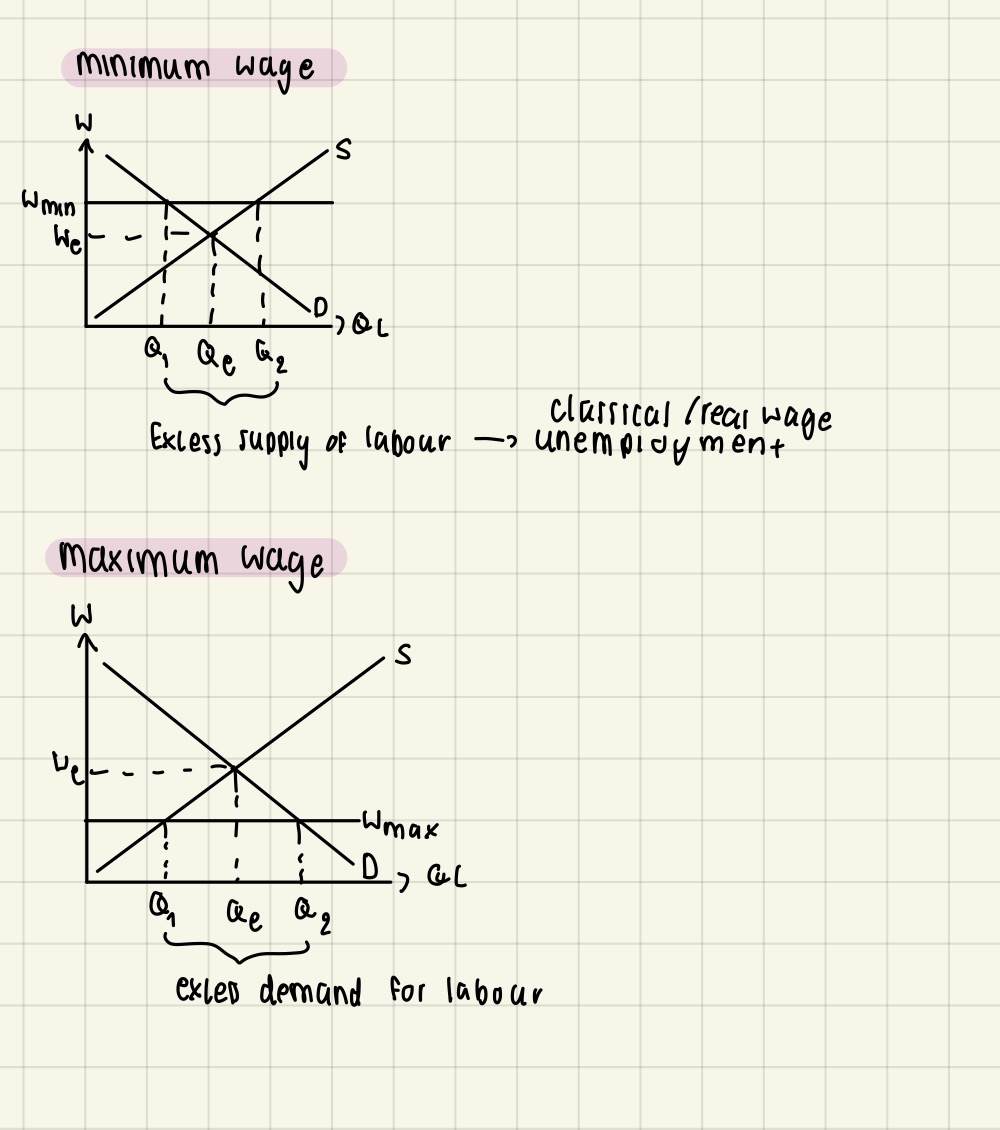
Government intervention in the labour market: public sector wage setting
sets the wages received by the workers in public sector
Government intervention in the labour market: policies to tackle labour market immobility
Measures to reduce geographical immobility of labour:
provision of affordable housing
subsidy
improvements in transport
Measures to reduce occupational immobility of labour:
Training schemes
Apprenticeships
Reduce educational requirements/regulations
The significance of the elasticity of demand for labour
Definition: Change in QD/Change in W
the responsiveness of quantity of labour demanded to changes in wage rate
Factors of elasticity of labour demand
Labour costs as a percentage of total costs
If labour costs (wages) are a high percentage of total costs: wages increases → total production cost increases by a lot → demand for labour decreases by a lot → elastic
East & cost of factor substitution (ie. machineries)
If easy & cheap to replace labour with machinery → demand for labour decrease by a lot → elastic
PED for final output produced by a business
if PED for the final product is elastic → PED for labour elastic
Time period
Time period increases → more elastic
The significance of the elasticity of supply of labour
Definition: Change in QS/Change in W
the responsiveness of quantity of labour supplied to changes in wage rate
Factors of elasticity of labour supply
Level of skill/educational qualifications required for an occupation
low-skilled → elastic (lots of supply available)
high-skilled → inelastic (long period of training is required)
Ease of migration
easy → elastic
not easy → inelastic
Degree of mobility of labour
if both geographically & occupationally mobile → supply of labour elastic
Time period
short run → inelastic
long run → elastic
A question asking about demand (of anything) COMMON
include the fact that: demand for labour is a derived demand = its demand is derived from the demand for the product it makes
What is marginal revenue product of labour
An additional increase in revenue per one more unit of labour