Principles of Life, Chapter 9 Reading
9.1 DNA is the Molecule of Inheritance
- Virtually all nondividing somatic cells of a particular organism have the same amount of nuclear DNA. This amount varies from species to species.
- Cells resulting from meiosis have half the amount of nuclear DNA as somatic cells.
- Phage: Any of a group of viruses that infect bacteria; mad eof DNA and only a few types of protein.
- Total Purines = Total Pyrimidines
- Sugar-Phosphate Backbone: The repeating deoxyribose then phosphate groups that form a strand of a nucleic acid.
- Antiparallel: Pertaining to molecular orientation in which a molecule or parts of a molecule have opposing directions.
- The surfaces of the base pairs are chemically distinct from one another both in identity and spatial orientation, allowing other molecules, especially proteins, to recognize specific base-pair sequences
- Because of complementary base pairing, the information contained in a DNA molecule is fully contained in each of the two strands.
9.2 DNA Replication is Semiconservative
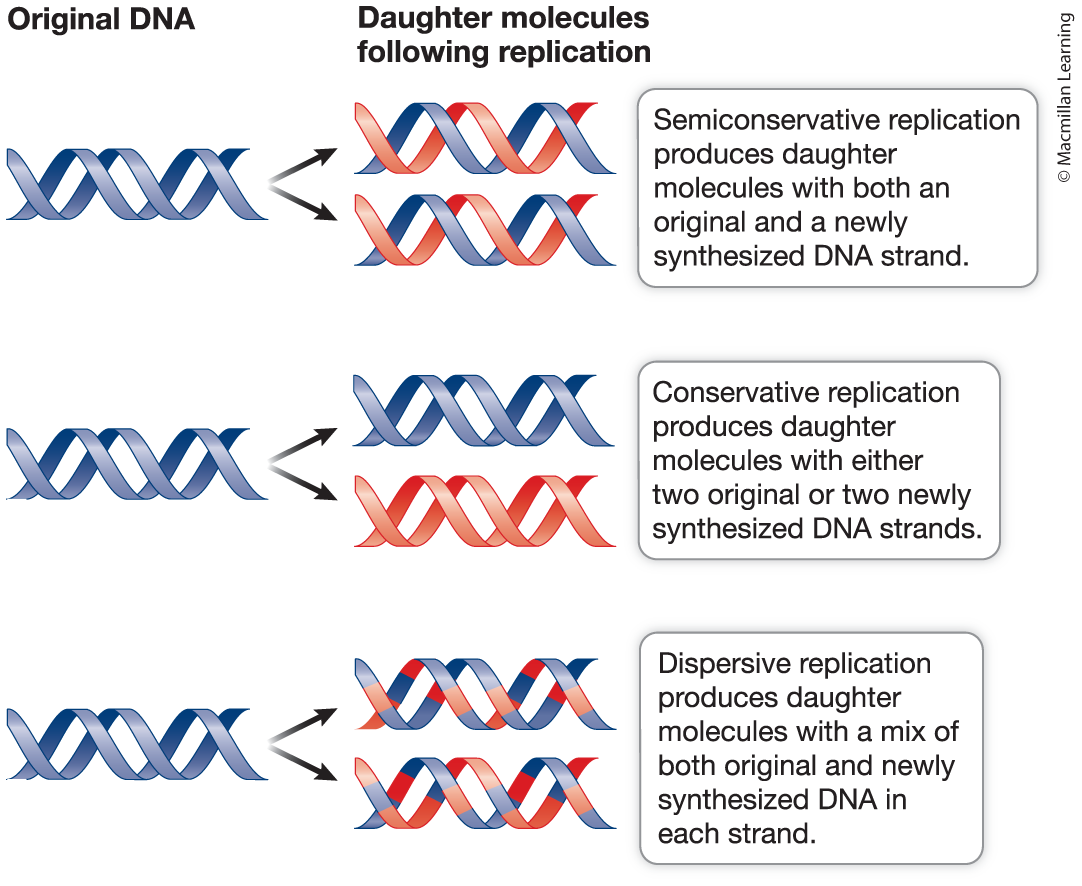
Semiconservative replication: Each strand of the parental molecule could be used as a template for the synthesis of a new strand in each daughter molecule.
Conservative replication: The two parental strands could remain together (that is, could be “conserved”) in one daughter molecule, while serving as a template for another daughter molecule consisting of two newly synthesized strands.
Dispersive replication: The parental molecule could end up dispersed among both strands in the two daughter molecules.
As we will see, DNA replication involves several different proteins. The overall process occurs in three steps:
- Initiation: The beginning of replication, transcription or translation; involves unwinding (denaturing) the DNA double helix to separate the two strands and synthesizing of RNA primers
- Elongation: the addition of monomers to make a longer DNA, RNA, or protein during replication, transcription or translation.
- Termination: the end of transcription or translation (after each region has been replicated)
DNA synthesis always proceeds in the 5′-to-3′ direction, but the DNA is read in the 3’-to5’
When added to the growing strand during DNA synthesis, the two outer phosphate groups are released together as pyrophosphate, and the resulting dAMP (or other base) is added to the growing nucleic acid chain
The pyrophosphate is then hydrolyzed into two inorganic phosphates, releasing additional energy, which makes the overall free energy change of DNA polymerization more negative
Origins of Replication: A DNA sequence at which helicase unwinds the DNA double helix and DNA polymerase binds to initiate DNA replication.
Replication Fork: A point at which a DNA molecule is replicating; The _ forms by the unwinding of the parent molecule.
DNA Helicase: An enzyme that catalyzes the unwinding of a nucleic acid double helix.
- Additional twisting within each helix occurs because of topiosomerase
Eukaryotic chromosomes are much longer than those of prokaryotes, are linear, and have multiple oris
- Critical that initation from an ori occurs only once per round of replication
Following dentaturation at the ori, a primer is synthesized
- Primer: A strand of nucleic acid, usually RNA that is the necessary starting material for the synthesis of a new DNA strand, which is synthesized from the 3’ end of the primer.
- Primase: An enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of a primer for DNA replication.
Elongation
- Priming with a short RNA strand is required because DNA polymerases are unable to start polymerization using single-stranded DNA —they require a short region of double-stranded molecule to which they can add nucleotides.
Leading & Lagging
- Leading Strand: In DNA replication, the daughter strand that is synthesized continuously.
- Lagging Strand: In DNA replication, the daughter strand that is synthesized in discontinuous stretches.
- The leading template strand is oriented so that DNA polymerase can add nucleotides to the 3′ end of the new strand in the same direction as fork movement and so polymerization occurs continuously.
- The lagging template strand is oriented so that DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3′ end of the new strand in the direction away from the movement of the replication fork.
- Okazaki Fragmant: Newly formed DNA making up the lagging strand in DNA replication; DNA ligase links these together to give a continuous strand.

The termination of DNA replication occurs when replication forks that are moving toward one another meet.
There is no 3’ end to extend after replication, because the RNA primer is on the 5’ end. This means there is an overhang, and some of the double-strand DNA gets cut off. Thus, DNA gets shorter for every cell division
- Telomeres: Repeated sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes that do not encode proteins.
- Telomeres get cut off so important stuff doesn’t
Telomerase: An enzyme that catalyzes the addition of telomeric sequences lost from chromosomes during DNA replication.
9.3 DNA Mutations Alter DNA Sequence
- Incorcporation Error Rate: The probability that an incorrect base will be inserted into a new strand during replication.
- Mismatched DNA: A base pair in which the two bases are not complementary (e.g., AC or AG instead of AT).
- DNA Repair:
- Proofreading: During DNA replication, a mechanism that excises a base that is incorrectly inserted according to the template (AG) and inserts the correct base (CG).
- 99% perfect
- Mismatch Repair: A mechanism that scans DNA after it has been replicated and corrects any base-pairing mismatches; looks for abnromal H bonding that changes the helix width
- Types of Mutations
- Base-Pair Substitutions: A change of a single base pair in a nucleotide sequence (e.g., AT to GC).
- Point Mutation: A mutation that results from the gain, loss, or substitution of a single nucleotide.
- Mismatches lead to base-pair substitutions in one of two ways:
- when the mismatch repair complex removes the original instead of the new strand
- when the mismatch is not repaired before the next round of replication
- A base can exist as two different structural isomers, pairing with a different base
- Occasional removal of an amino group in cytosine (produces uracil instead and a A bonds when it isn’t supposed to)
- Spontaneous Mutations: A genetic change caused by internal cellular mechanisms, such as an error in DNA replication.
- Mutagens: Any agent (e.g., a chemical, radiation) that increases the mutation rate.
- Cigarette smoke contains a lot of this
- Induced Mutation: Changes in the sequence of DNA caused by a mutagen.
- The excision repair proteins recognize damaged and remove a fragment of the strand that includes the damaged nucleotide(s), and then DNA polymerase and ligase fill the gap.
- Silent Mutations: A change in a gene’s sequence that has no effect on the amino acid sequence of a protein because it occurs in noncoding DNA or because it does not change the amino acid specified by the corresponding codon.
- Loss of Function Mutations: A mutation that results in the loss of a functional protein.
- Loss of Function mutations almost always show recessive inheritance in a diploid organism
- Gain-of-Function Mutations: A mutation that results in a protein with a new/altered function.
- Conditional Mutations: A mutation that results in a characteristic phenotype only under certain environmental conditions (the wild-type phenotype is expressed under other conditions).
- Mutations that affect more than one nucleotide
- Deletions: A mutation resulting from the loss of a continuous segment of a gene or chromosome; Such mutations almost never revert to wild type.
- Duplications: A mutation in which a segment of a chromosome is duplicated, often by the attachment of a segment lost from its homolog (One of the two chromosomes produced by this mechanism will lack a segment of (it will have a deletion), and the other will have two tandem copies (a duplication)).
- Inversions: A rare 180° reversal of the order of genes within a segment of a chromosome; usually causes a loss of function.
- Translocations: In genetics, a rare mutational event that moves a portion of a chromosome to a new location, generally on a nonhomologous chromosome.
- Nonhomologous End Joining: A repair pathway that functions to join together (ligate) the two ends of a broken chromosome.