MET 201 Statics - Chapter 2
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Force
A force represents the action of one body on another. It is generally characterized by its point of application, its magnitude, and its direction. Force acting on a given particle, however, have the same point of application.
Magnitude of a force
characterized by a certain number of units
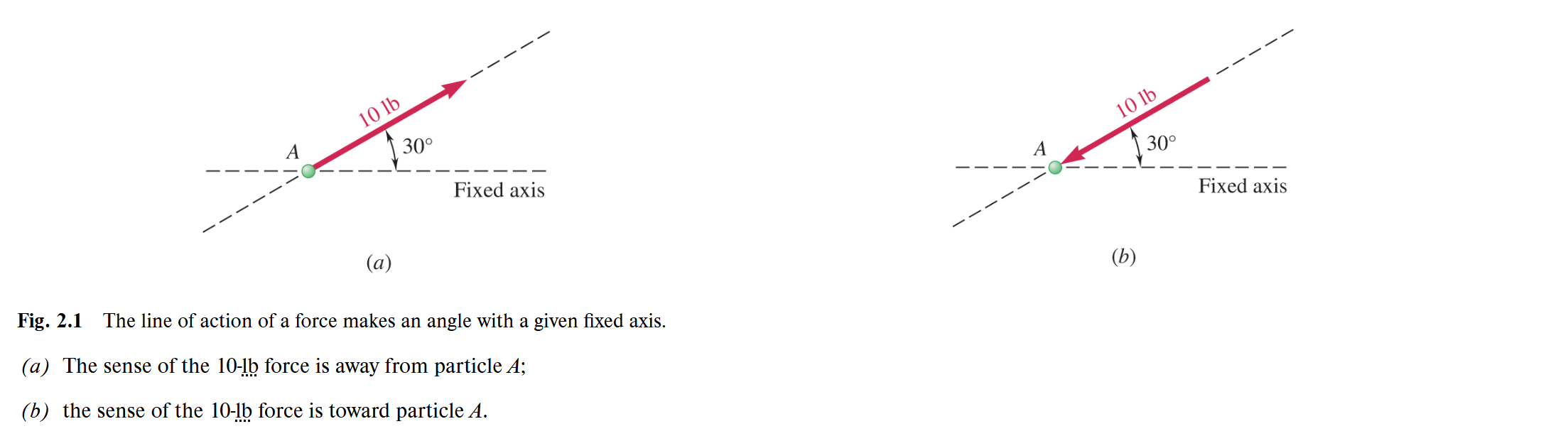
Line of action
The infinite straight line along which the force acts; it is characterized by the angle it forms with some fixed axis.
Resultant of the force P and Q
two forces P and Q acting on a particle A can be replaced by a single force R that has the same effect on the particle.
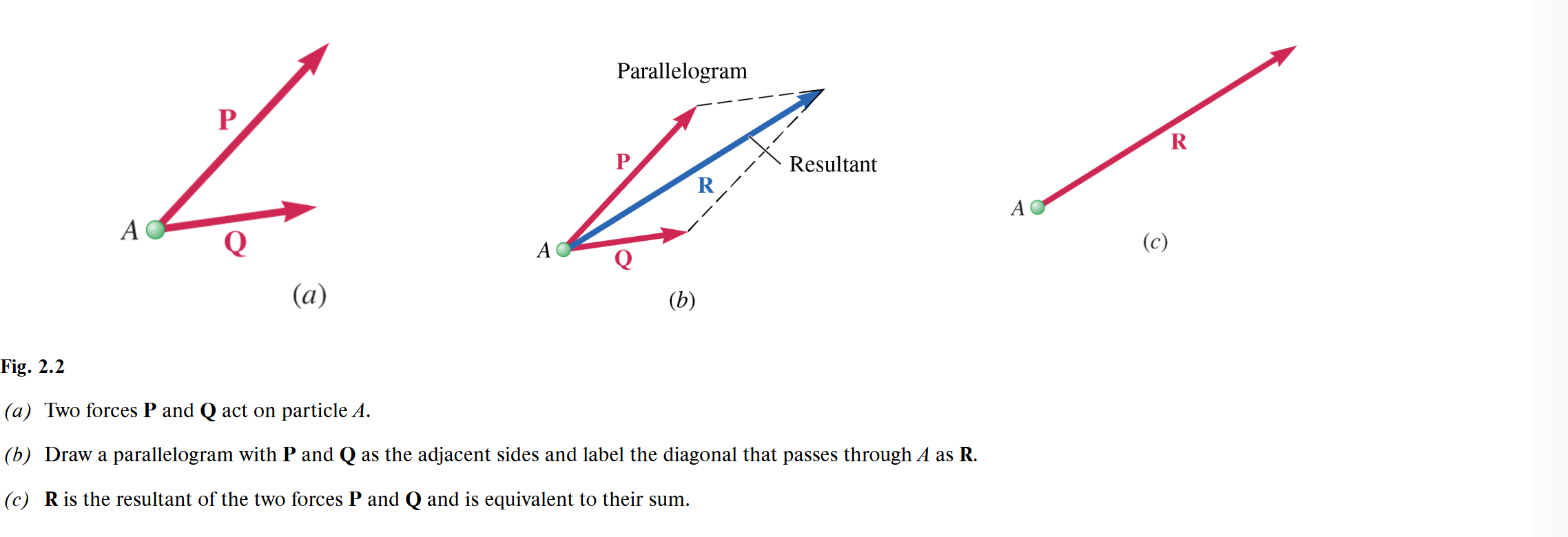
Parallelogram law
The method for finding the resultant. We can obtain R, by constructing a parallelogram, using P and Q as two adjacent sides. The diagonal that passes through A represents the resultant.
Scalars
Physical quantities that have magnitude but not direction, such as volume, mass, or energy, are represented by plain numbers.
Vectors
Mathematical expressions possessing magnitude and direction, which add according to the parallelogram law.