CHM 230 Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:17 AM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
What is a model that uses electrostatics to explain electronics in complexes?
crystal field
2
New cards
What is a model that uses molecular orbital approach in the structure of complexes?
ligand field
3
New cards
What do colors in transition metal complexes come from
energy HOMO-LUMO gap
4
New cards
What kind of coloration is glowing or light?
emissive coloration
5
New cards
What kind of coloration is paint or clothes?
absorptive coloration
6
New cards
We see the _____color of wavelengths absorbed
complementary
7
New cards
In an octahedral field, what d orbitals are not point at the axis
dxy, dyz, dxz
8
New cards
In an octahedral field, what d orbitals are affected most by electrostatic interaction?
dz2, and dx2-y2
9
New cards
octahedral d1 through d 3 have all _______ electrons
unpaired
10
New cards
octahedral d __ __through d_______ have both high and low spin states
4-7
11
New cards
low spin means less _____ electrons
unpaired
12
New cards
If delta O is less than repulsion between paired electrons than electrons ______ want to pair
don’t
13
New cards
Ligands ____ the d-orbitals of transition metal complexes
split
14
New cards
Electrons fill into the orbitals based of the size of what
delta O
15
New cards
What influences the size of delta O
\-size of metal
\-charge of metal
\-nature of ligand
\-charge of metal
\-nature of ligand
16
New cards
big metals give a _____ delta O
larger
17
New cards
as the charge on the metal increases, delta O ____-
increases
18
New cards
Delta O increases as you go ___ __to__ _____ across a period
left to right
19
New cards
What is the order of ligands from small delta O to large delta O
halogens< oxygen compounds< nitrogen compounds< carbon compounds
20
New cards
What d orbitals are higher energy for tetrahedral complexes
dxy, dyz, dxz
21
New cards
What d orbitals are lower in energy for tetrahedral complexes
dz2, dx2-y2
22
New cards
Delta T is always ____- than delta O
less
23
New cards
All tetrahedral complexes are ____ spin
high
24
New cards
What square planar d orbitals have the lowest energy
dxz and dyz
25
New cards
What square planar d orbital has the largest energy
dx2-y2
26
New cards
What ions are mostly square planar
d8 (Ni2+, Pd 2+, Pt2+, Au3+, Rh +, Ir+)
27
New cards
The delta SP is very ____-
large
28
New cards
square planar are typically
diamagnetic
29
New cards
What is beers law
absorbance= molar absorptivity x path length x molar concentration
30
New cards
Molar absorptivity indicates how __ a species undergoes a ______
efficiently; transition
31
New cards
a high molar absorptivity means
more photons absorped
32
New cards
What impacts molar absorpitvity
selection rules and geometry
33
New cards
The laporte rule is d-to-d transitions forbidden in ____ complexes
octahedral
34
New cards
Transitions that require the spin of an electrion to change are
forbidden
35
New cards
Tetrahedral complexes tend to be strongly
colored
36
New cards
most transition metals show ___ main electronic transitions
3
37
New cards
What is the equation for energy of transition?
energy= (hc/wavelength)
38
New cards
When more energy is enetering a system than leaving or vise versa it is called a
dynamic system
39
New cards
Enthalpy is hear flow measured at constant
pressure
40
New cards
state functions are
\-size dependent
\-additive
\-value depends on the difference btwn 2 energentic states
\-additive
\-value depends on the difference btwn 2 energentic states
41
New cards
what is it called when gas goes to liquid
condensation
42
New cards
what is it called when liquid goes to gas
vaporization
43
New cards
What is it called when a solid goes to a gas
sublimation
44
New cards
what is it called when a gas goes to a soild
deposition
45
New cards
what is a solid going to a liquid
melting
46
New cards
what is a liquid going to a solid
freezing
47
New cards
What process of phase changes are endothermic
melting, vaporization, and sublimation
48
New cards
What processes of phase changes are exothermic
freezing, condensation, and deposition
49
New cards
what does combustion produce
co2 (g) and H20 (l)
50
New cards
What is hess’s law
the summation of enthalpies
51
New cards
What are the standard conditions
25 C, 1 atm pressure, 1 M solutions
52
New cards
In enthalpy you assume that all elements have an enthalpy of _____ in their standard state
0
53
New cards
for enthalpy of balanced thermochemcial reactions you can use the equation
h rxn= hf products - hf reactants
54
New cards
What is the equation for estimating delta H using bond enthalpies?
Hrxn= h broken -h formed
55
New cards
In bond enthalpies phases of matter _____ taken into account
are not
56
New cards
What are the qualities common to spontaneous reactions?
\-release heat
\-form gases
\-form precipiates
\-form compounds with strong bonds
\-form gases
\-form precipiates
\-form compounds with strong bonds
57
New cards
What is the most convient and precise way to measure delta H
using Hf values
58
New cards
What property of spontaneous reactions is hard to measure with enthlapy
forming gases
59
New cards
A _____ is one of any possible configurations in a system
microstate
60
New cards
What is the measure of the number of microstates available to the system being studied?
entropy
61
New cards
entropy ___- with pressure
increases
62
New cards
The _____ of particles increases the entropy of a system
mobility
63
New cards
When a scoop of ice cream melts entropy ____
increases
64
New cards
When a solid is turned into aqueous ions entropy ____
increases
65
New cards
When a liquid and gas turn into a solid and gas entropy____
decreases
66
New cards
What are the units of entropy
J/K
67
New cards
Delta S =
n(S products)- n (S reactants)
68
New cards
reactions that are spontaneous tend to be ___ and have an _______ in entropy
exothermic; increase
69
New cards
What is the equation for delta G
delta G= delta H- (temp(K) x delta S)
70
New cards
for a spontaneous process delta G has to be _____ zero
less than
71
New cards
\-H and + S means the reaction is
spontaneous at all Temps
72
New cards
\-H and -S means the reaction is
spontaneous at low temp
73
New cards
\+H and +S means the reaction is
spontaneous at high temps
74
New cards
\+H and -S means the reaction is
never spontaneous
75
New cards
The best way to calculate delta G is using
free energies of formation
76
New cards
When should you use delta G= delta H- (T x delta S)
when you need to determine TEMPERATURE of spontaneity and when entropy and enthalpy values are available
77
New cards
When should you use delta G- (products)- reactants
when only delta G values are avaible and you only need to determine spontaneity
78
New cards
What does Gibbs free energy have to be in order for a reaction to be spontaneous?
less than O (-)
79
New cards
What state functions do elements in their standard state = 0
enthalpy and Gibbs Free Energy
80
New cards
What are the units of delta G
kJ/mol
81
New cards
The equilibrium constant is ( ) over ( )
products; reactants
82
New cards
What drops out of the K expression
solids and liquids
83
New cards
the molarity of gas is what
mols gas/ Volume container
84
New cards
When reagents are added to a solution the equilibrium will shift
away from what was added
85
New cards
If an endothermic reaction is warmed where will the equilibrium shift
to the right towards the products
86
New cards
What are the top orbitals of an octahedral compound d orbital splitting diagram called?
eg
87
New cards
What are the bottom orbitals of an octahedral compound d orbital splitting diagram called?
t2g
88
New cards
What are the top orbitals of a tetrahedral compound d orbital splitting diagram called?
t2
89
New cards
What are the bottom orbitals of a tetrahedral compound d orbital splitting diagram called?
e
90
New cards
What is the order of square planar diagrams from bottom to top?
(dxz + dyz), dz^2, dxy, dx^2-y^2
91
New cards
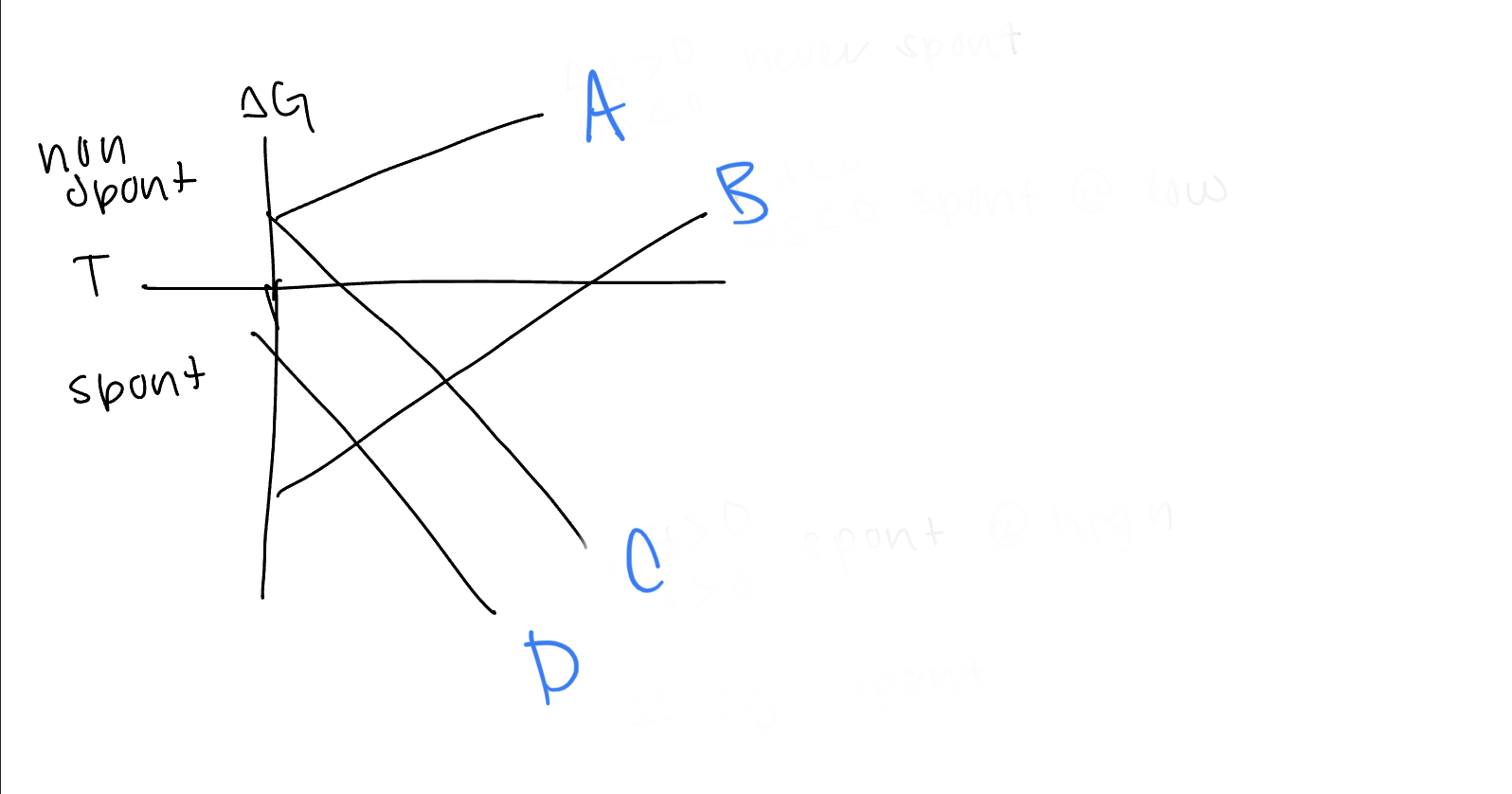
What are the values of h and s for line A
h>0, s
92
New cards
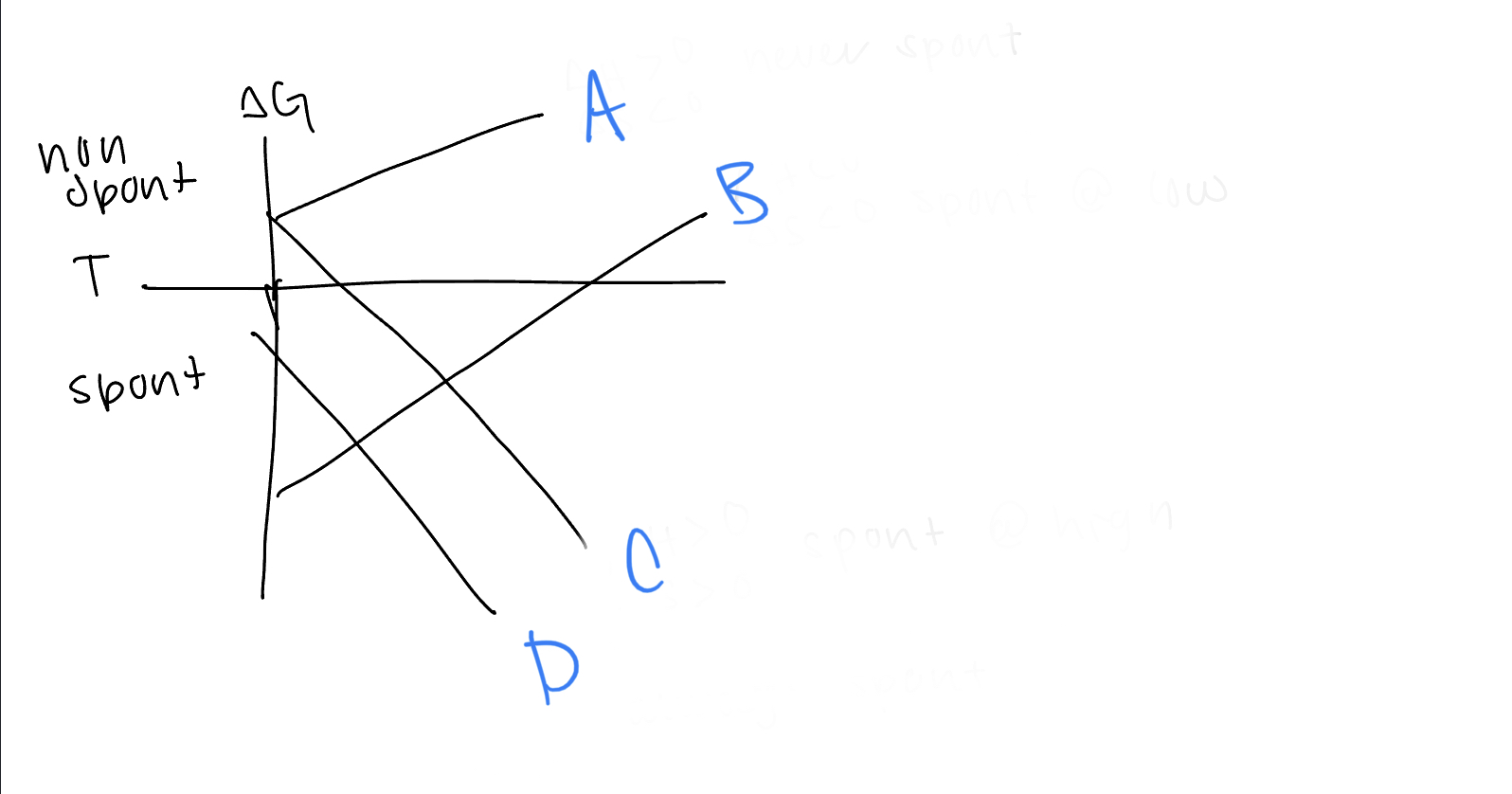
What are the values of h and s for line B
h
93
New cards
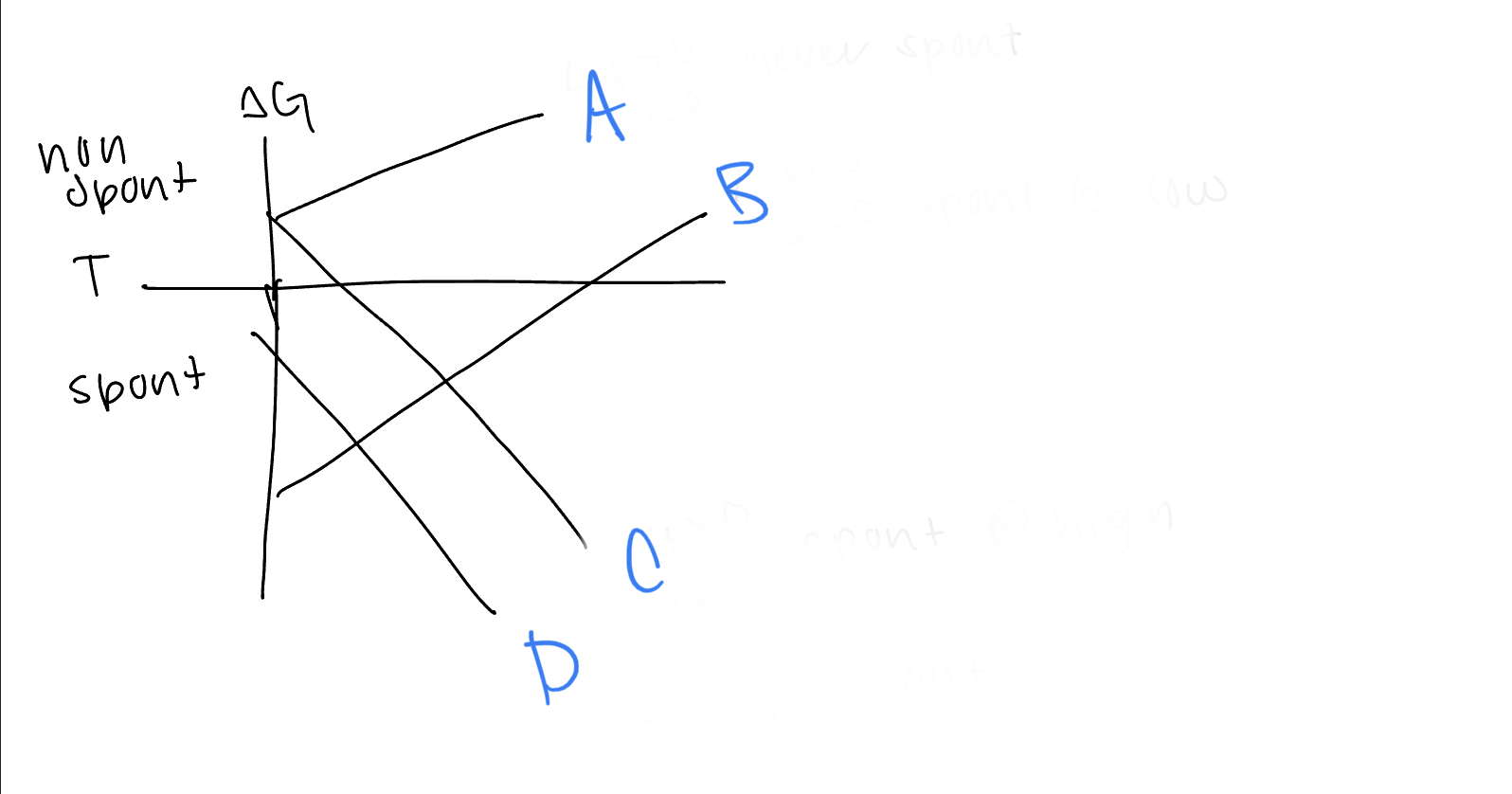
What are the values of h and s for line C
h>0, s>0
94
New cards
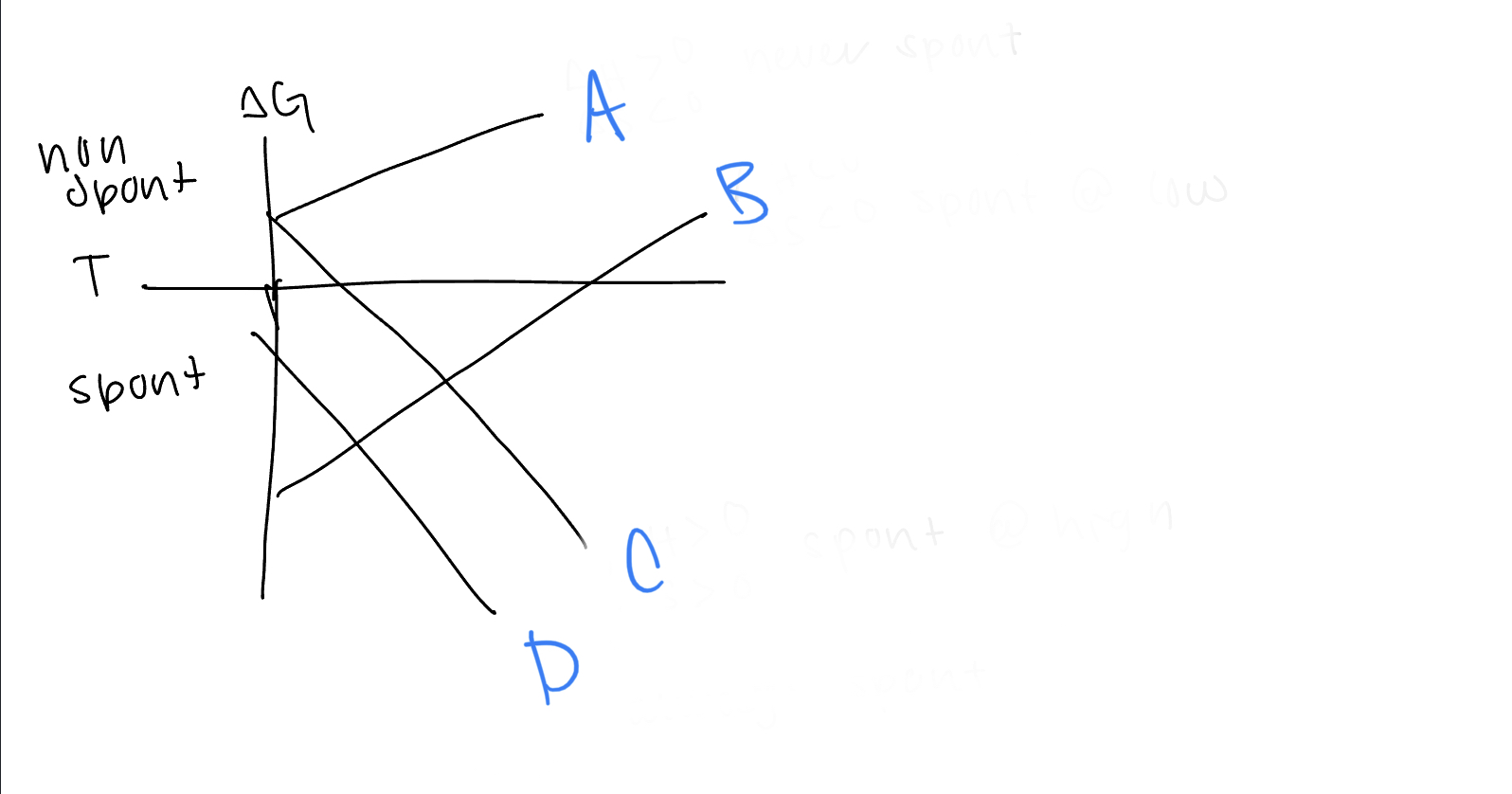
What are the values of h and s for line ~~D~~
h
95
New cards
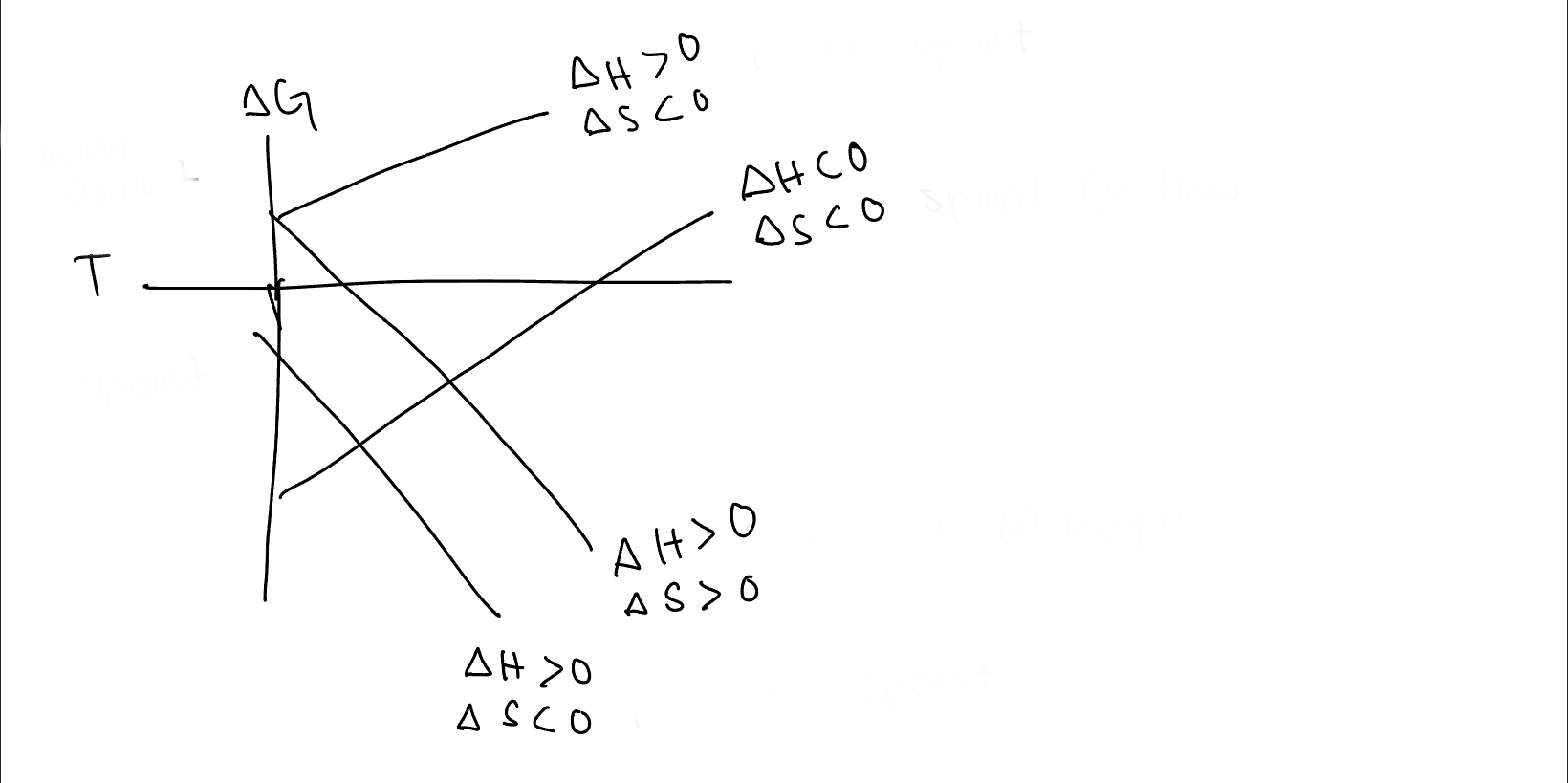
under what conditions is the top line spontaneous
never spontaneous
96
New cards
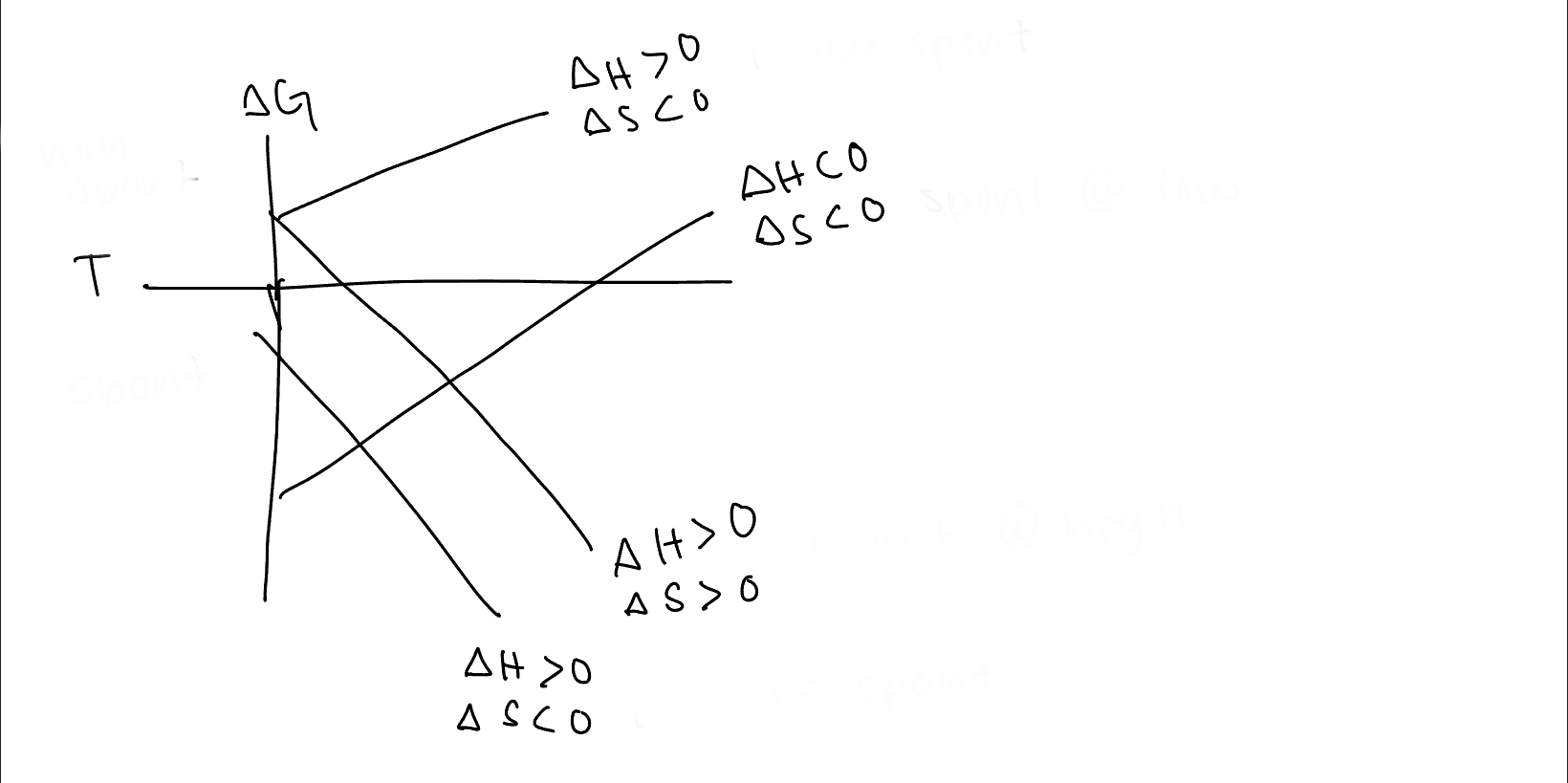
under what conditions is the 2 line spontaneous
spontaneous at low temps
97
New cards
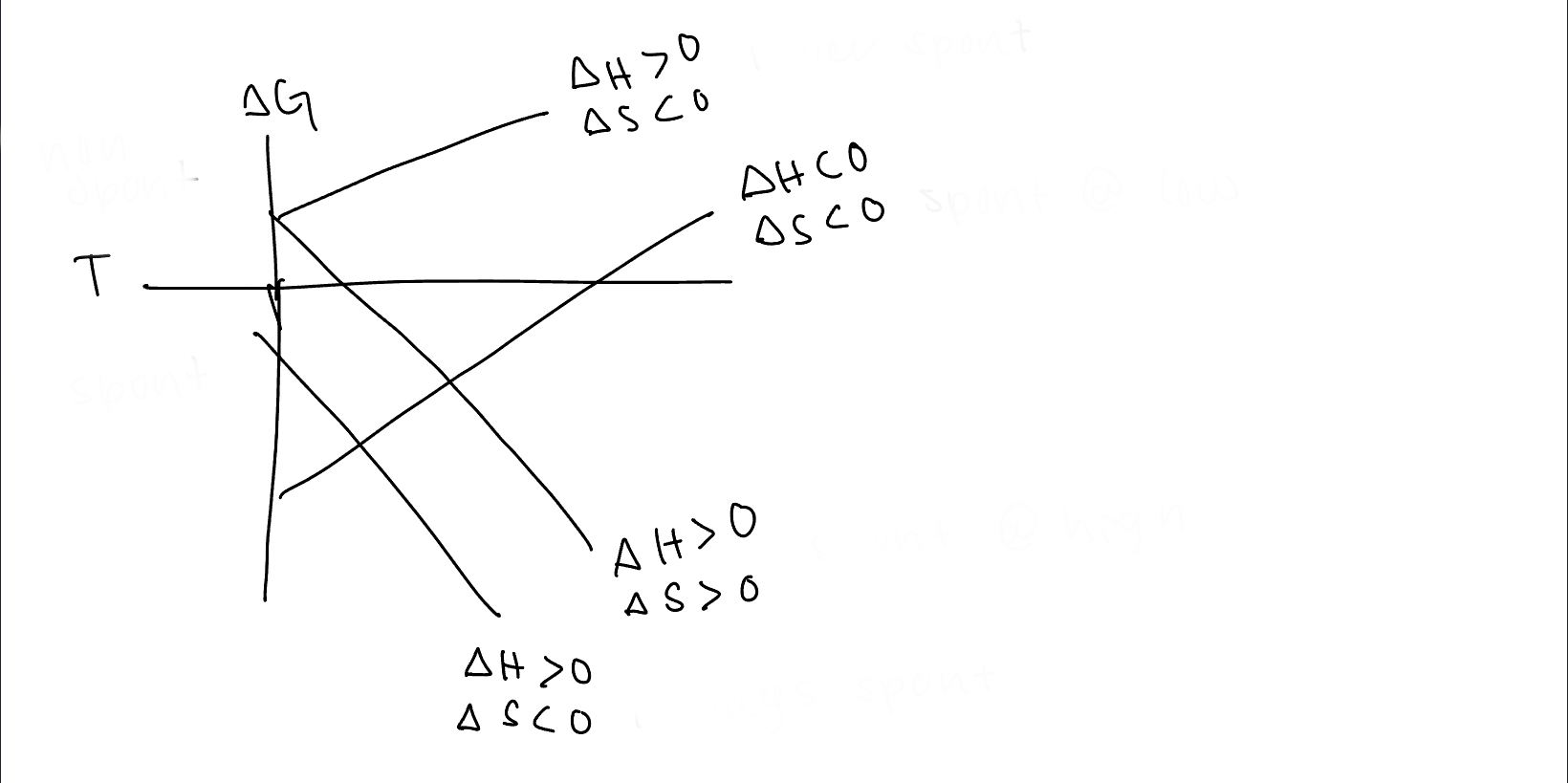
under what conditions is the 3rd line spontaneous
spontaneous at high temps
98
New cards
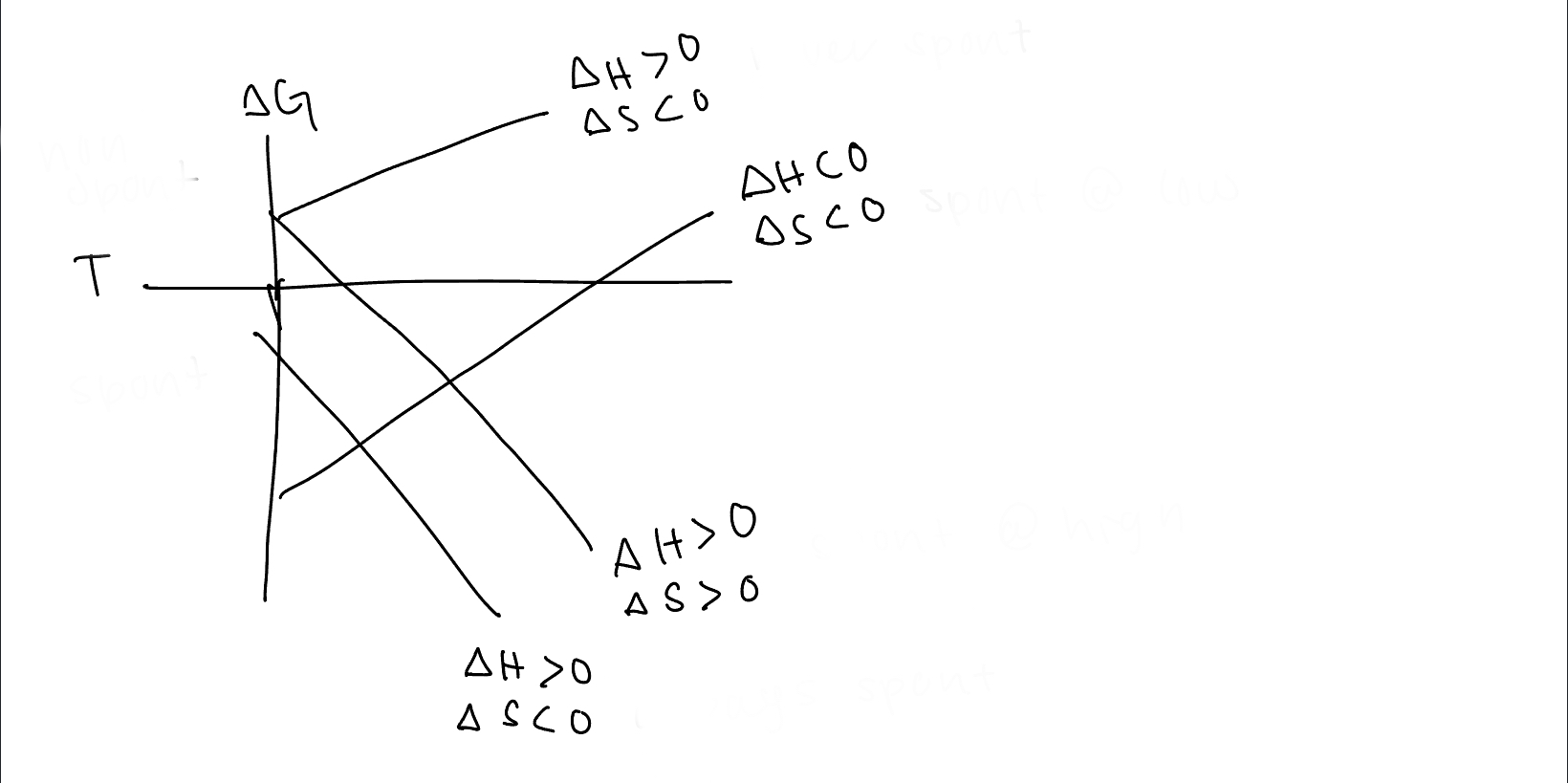
under what conditions is the bottom line spontaneous
always spontaneous