Simple and Facilitated Diffusion
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ib bio unit 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
passive and active transport
types of membrane transport
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
types of passive transport
pump proteins, bulk transport (exocytosis + endocytosis)
types of active transport
the movement of a substance down a concentration gradient
diffusion definition
concentration gradient, distance, temperature, size, polarity
factors impacting diffusion rate
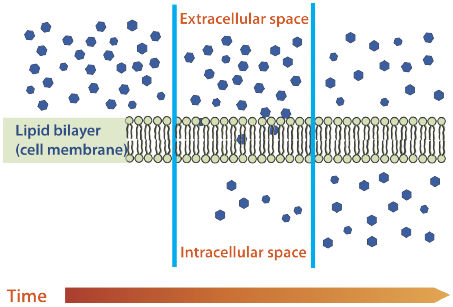
equal concentration of a substance on either side of a semi-permeable membrane, but with constant movement, and in equal amounts and opposite directions. No net movement!
dynamic equilibrium
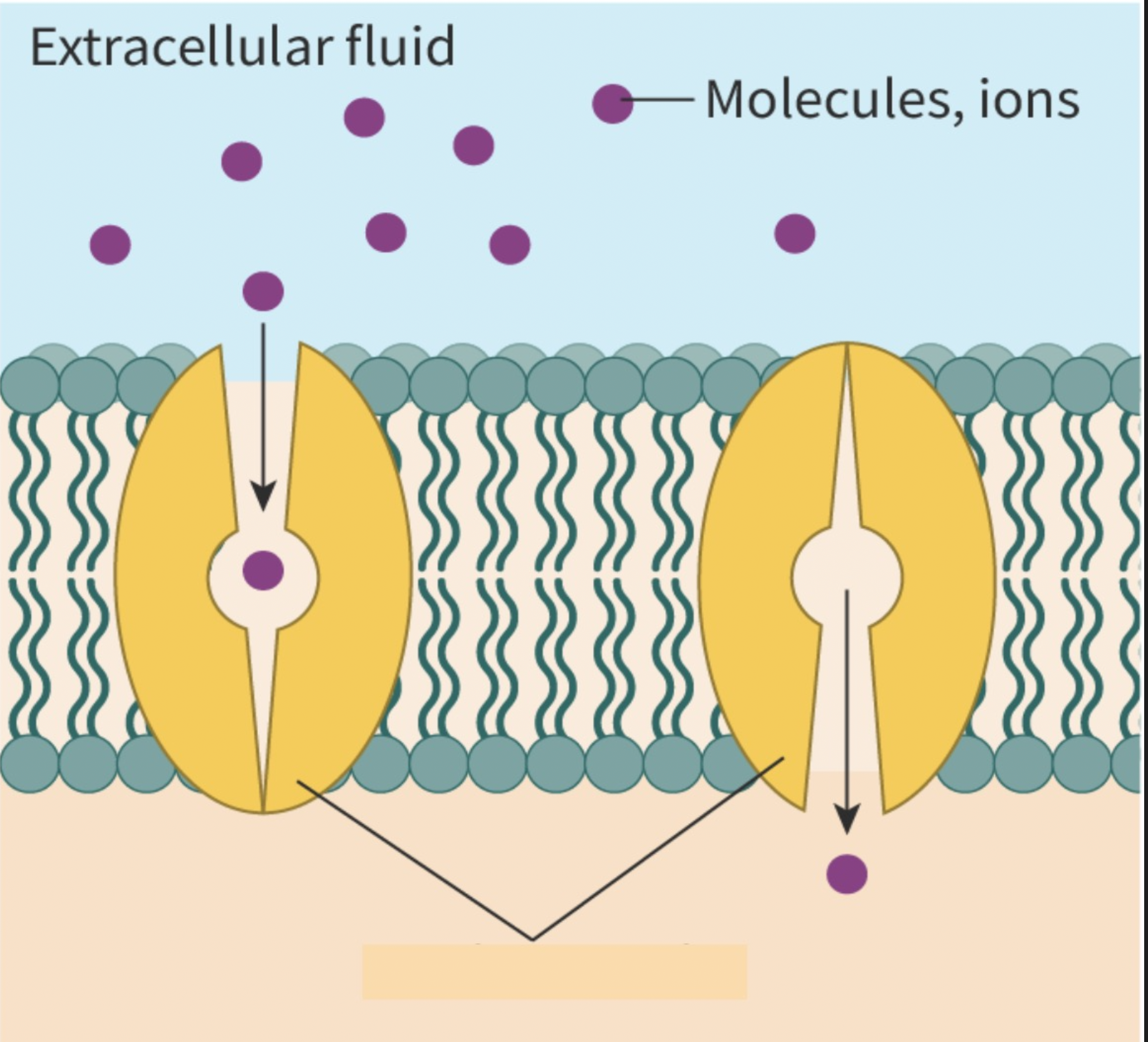
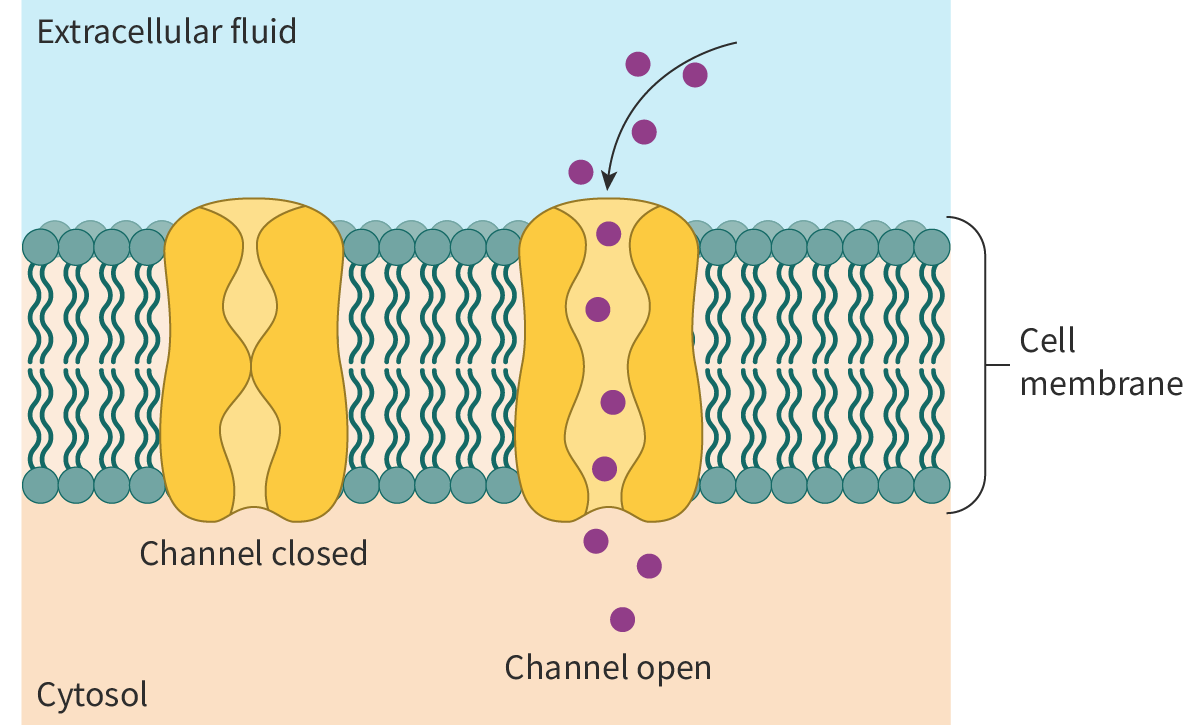
a type of passive transport where the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient is assisted by transmembrane transport proteins. ex: glucose or ions
facilitated diffusion definition
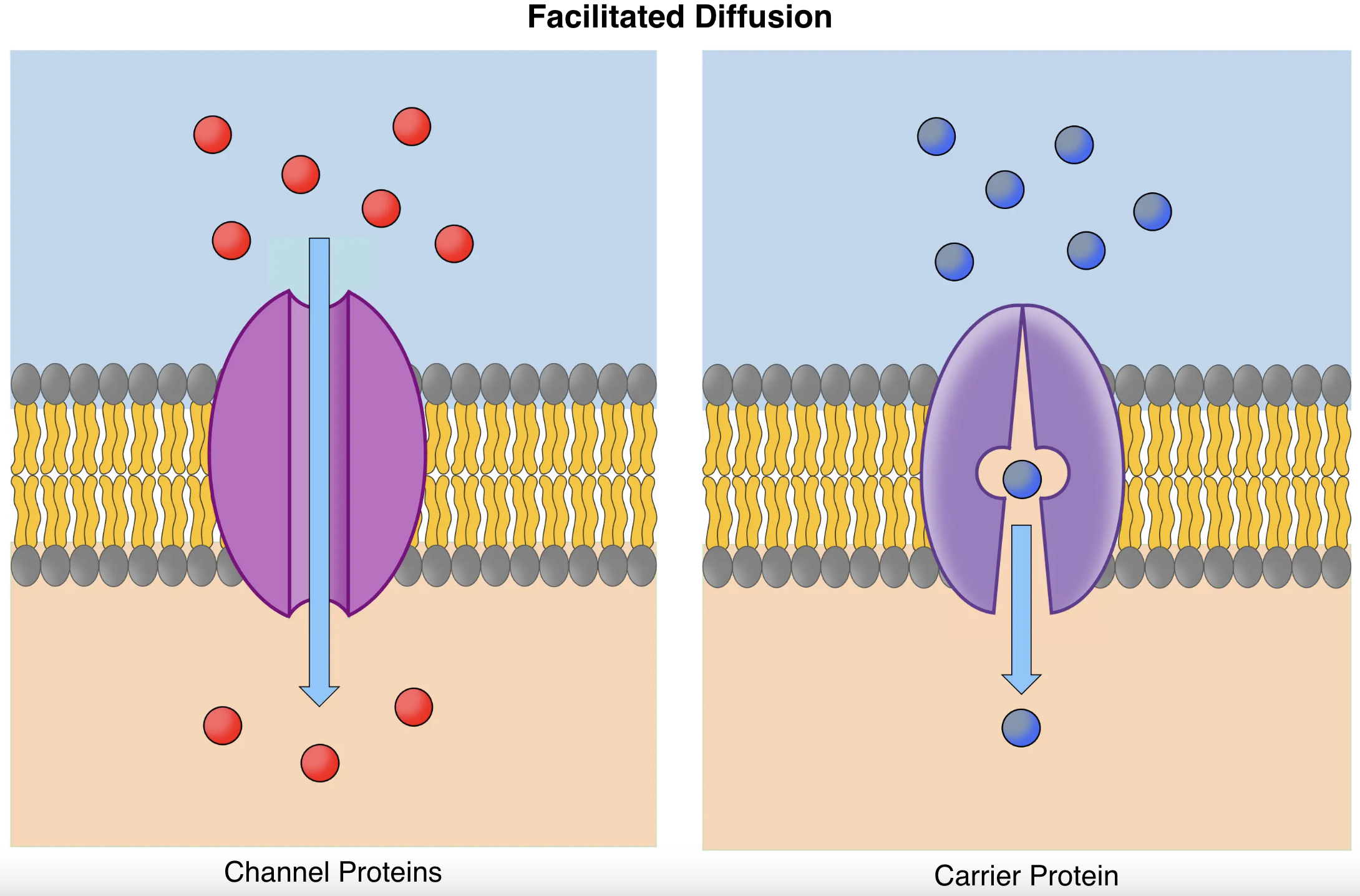
channel proteins and carrier proteins
types of transmembrane proteins in facilitated diffusion
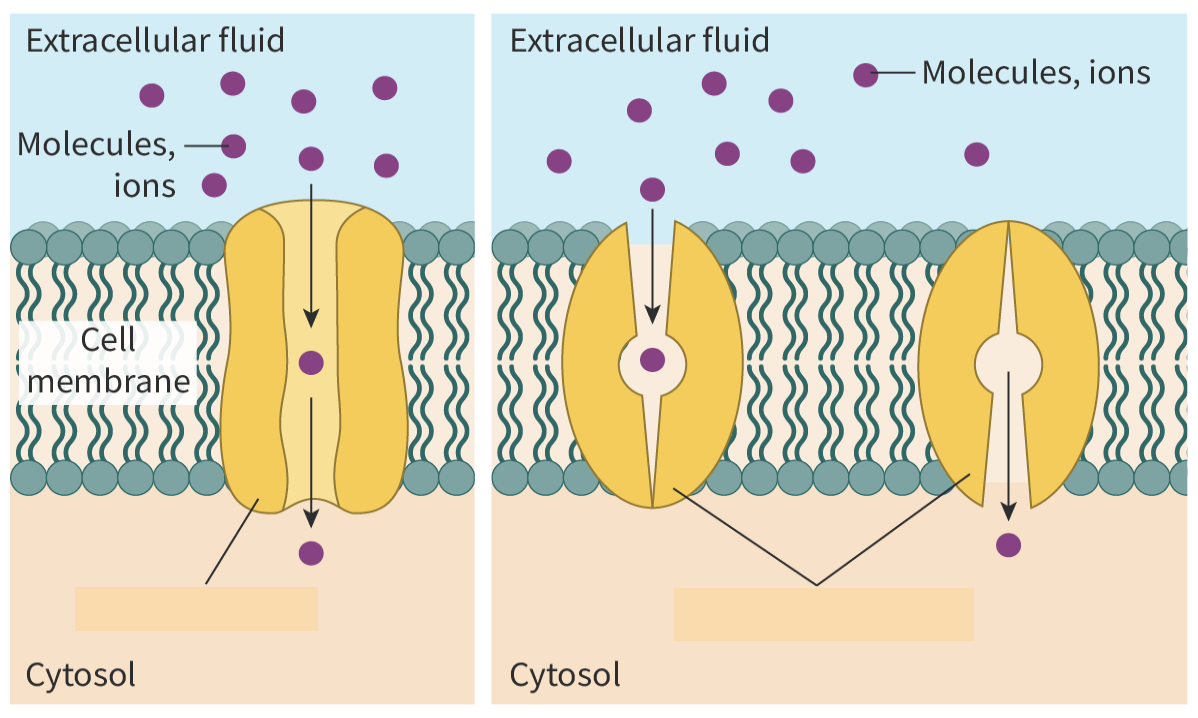
channel proteins are selective and can be opened and closed. carrier proteins are selective.
two ways to control the process of facilitated diffusion
maintained by hydrophilic/phobic side chains lining the channel and the size of the channel. Many channel proteins only allow 1 type of ion/molecule through.
selectivity of channel proteins
ligand (open/close in response to a ligand binding), and voltage (open/close in response to changes in charge along the membrane)
types of gates channels
When the molecule/ion binds to the carrier protein, the carrier protein undergoes a conformational change and transfers the molecules to the other side of the membrane
carrier protein