Exchange rates
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Show demand for the pound increasing on a diagram with correct labels
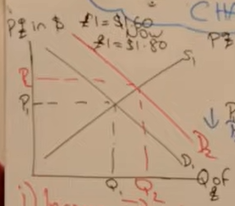
Show supply for the pound increasing on a diagram with correct labels
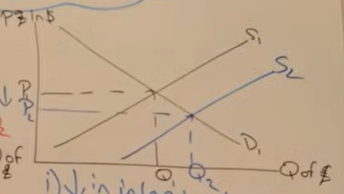
What will increase demand for the pound
Increase in relative interest rates - hot money - increased rate of return
Speculation - If there is anticipation that the pound is going to appreciate then people will convert their money to pound to try and make money
Increase in FDI - They have to pay for everything in pounds so they need to convert their money into pounds
Increase in incomes abroad - more UK exports demanded (Need to pay in pounds)
Increase in competitiveness - Higher demand for UK exports
What will increase the supply of the pound
Supply of the pound increases when economic agents swap the pound for another currency
Lower interest rates - Less hot money
Speculation that the pound will depreciate
Firms move away from Britain (Reverse FDI)
Increase in domestic incomes - more imports, exchanging pound to foreign currency to pay for these goods
What is a fixed exchange rate
What is floating exchange rate
The government or a central bank fixes the exchange rate in place - they do this by holding large amounts of currency reserves
Market forces determine how much a currency is worth
How does the government or central bank fix an exchange rate
They hold reserve currency and if the pound appreciates they will buy a foreign currency converting from pounds to increase the supply of the pound leading to the pound depreciating
To appreciate the pound they can buy the pound using foreign currency to increase demand for the pound reserves
Or they could lower or increase interest rates to use hot money but there is a conflict of objectives
How can an appreciation in the exchange rates be shown on a diagram other than the decrease in net exports decreasing AD
Due to cheap raw materials via importing
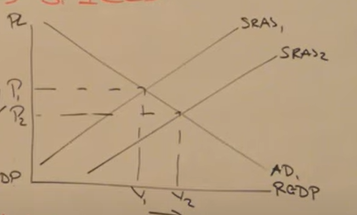
Cons of an exchange rate appreciating
Lower growth - AD falls (Current account deficit), real GDP falls
Higher unemployment - Higher unemployment in exporting industries - the relative price of our exports increases leading to demand for our exports falling so revenue falls and firms cut workforces to limit costs and because they are not needed to fulfil demand
Higher unemployment in domestic industries - Relative price for imports falls potentially being below domestic alternatives so consumers switch to imports leading to domestic firms cutting workforces to limit costs and because they are not needed to fulfil demand
However growth may be increased due to raw materials being cheaper
And however regulations on hiring/ firing laws may prevent this from occurring
Consequences of exchange rates appreciation
Lower inflation due to increased competition and lower prices offered
Cheaper imports could mean increased material living standards
Domestic firms will also become more efficient due to the increased competitiveness
Evaluate if that appreciation will increase demand for imports
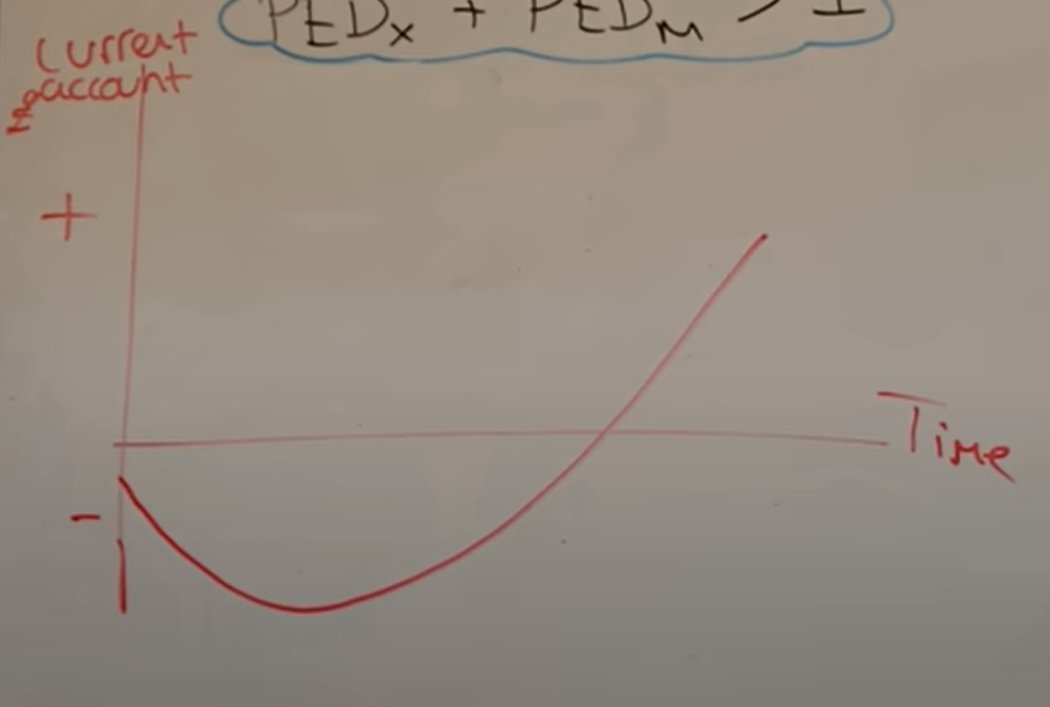
Marshall-Lerner condition = PED of imports + PED of exports > 1 it will increase demand for imports
How does an exchange rate/ current account automatically correct
In a current account deficit supply of the pound increases then exchange rate falls so exports are cheaper leading to higher demand for exports and lower demand for imports correcting the current account deficit
in the real world this won’t really occur - speculation will dominate the supply and demand of currency
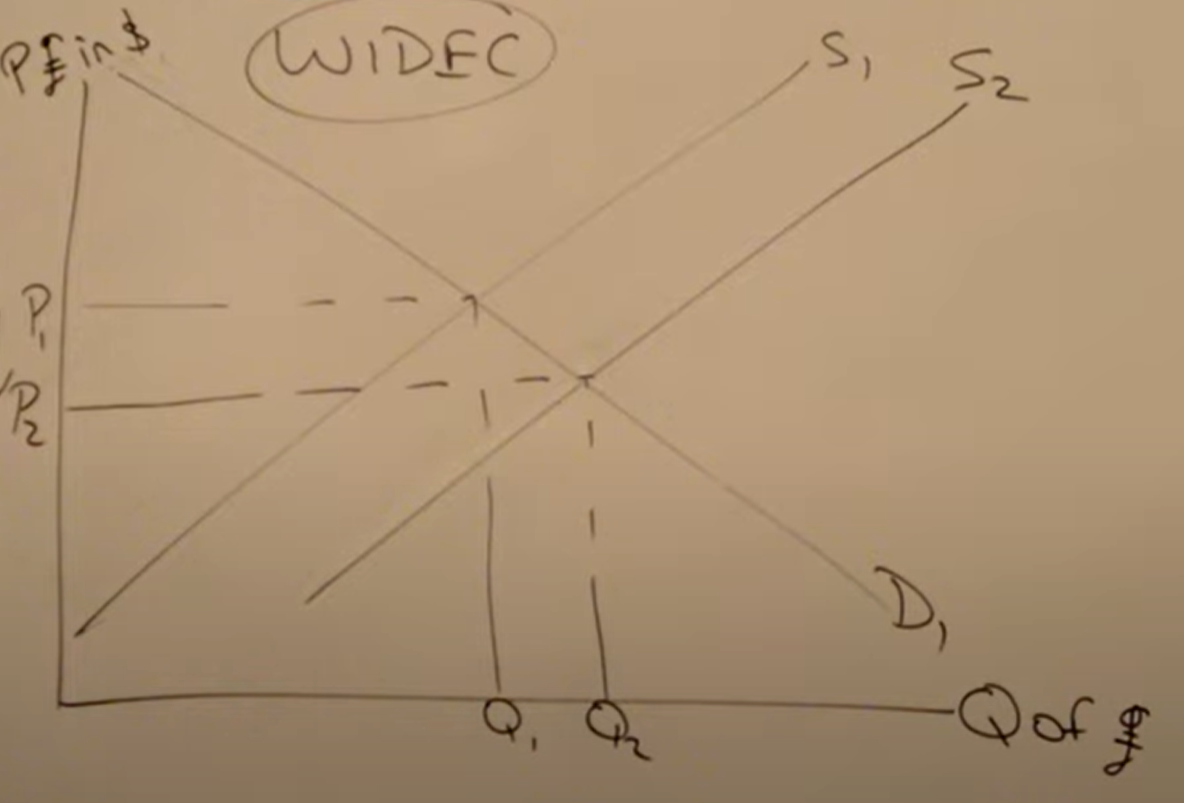
What is the Marshall-Lerner condition
Why will this be accurate
The Marshall-Lerner conditions states that a currency depreciation will only increase net exports if 1 < PED of imports + PED of exports
If PED of imports is inelastic and they become relatively more expensive - quantity demanded will fall a smaller amount but because of the price rise the actual value of imports increases
If PED of exports is inelastic and they become relatively less expensive - quantity demanded will rise a smaller amount but because of the price fall the actual value of imports increases
What is the J curve effect
That in the SR demand for imports will decrease a little and this will cause total value of imports to temporarily rise before consumers realise imports are more expensive and switch to domestic goods reducing the total value of imports improving the current account deficit
Vice versa for exports becoming cheaper
How does inflation affect exchange rates
If there is inflation in another country they can afford goods in another country at a lower price so they purchase more imports, supply of pound increases and demand for the other currency increases updating the exchange rates according to the inflation
Positives of a floating exchange rate
Evaluation
No need for currency reserves - opportunity cost when a country has a currency reserve
Freedom for domestic monetary policy - to pursue macro-economic objectives
Automatically corrects current account deficit
Reduced risk of currency speculation
Evaluation: Volatile exchange rate will discourage FDI
Self-correction of CA very unlikely as speculation will usually cause exchange rate changes
Positives of a fixed exchange rate
Decreases uncertainty of exchange rates - increasing FDI and trade
Some flexibility is permitted (Managed exchange rate) and can realistically revalue an exchange rate
Reductions in cost of trade (Reduced hedging)
Discipline on domestic producers - Through cannot rely on exchange rates and must become more competitive through efficiency
What is ‘hedging’
Where an importer who will need to exchange their money for another currency does so they set a fixed rate before they make the deal because they think this currency will appreciate (Or vice versa) this exchange rate will be higher than the current but possibly smaller than the future - risk mitigating
What is a managed exchange rate
Where a country has a permitted band where they keep their exchange rate for example £1 = between $2.10 and $2.30 and so the government/ central bank keeps it between those values by intervening
Drawbacks of a fixed exchange rate
If interest rates are used then it could conflict macro-economic objectives
Large level of foreign reserves needed - expensive - Huge opportunity cost
Speculative attacks if exchange rate is set inaccurately
What is quantitative easing
Used when traditional policies of monetary policy have failed (Low credit, low confidence, low willingness to lend)
Central bank creates money electronically
That money is used to buy financial assets (Especially government bonds) from financial institutions (Banks, building societies)
Increases price of government bonds and decreases yield/ interest rates
This supplies these financial institutions with lots of cash from the selling their assets (loanable funds increases in supply) which they either loan out or use to purchase corporate bonds (riskier)
Corporate bonds rise in price and fall in yield/ interest rates reducing the cost of borrowing
Access to credit is easy for banks, general interest rates have fallen so they can raise finance cheaper increasing the willingness to lend at lower interest rates (Matching central bank IR)
Stimulates borrowing - spending and investment - AD, Growth